JFK Muhlenberg: Abdomen Final exam A
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Decreased hematocrit is associated with which on the following?
A) adrenal hemorrhage
B) living an high altitude
C) dehydration
D)polycythemia
A) adrenal hemorrhage
Why?
Increased hematocrit means the percentage of red blood cells is above the upper limits on normal. Causes include dehydration, living at a high altitude, COPD, and polycythemia vera. A low hematocrit means the percentage of red blood cells is below the lower limits if normal. Causes include internal bleeding (varies), red blood cell destruction (anemia), kidney failure, and malnutrition.
Increasing the imaging depth will:
A) reduce beam intensity
B) reduce the frame rate
C) increase the pulse repetition frequency
D) improve temporal resolution
B) reduce the frame rate
Why?
The deeper the structure you are imaging the longer the time the pulse needs to reach it and return. The pulses are emitted an a slower rate (lower PRF) because they need to travel a longer distance. If the pulses are transmitted and received at a slower rate, the rate that the image is produced (frame rate) will also be reduced. Lower frame rates lead to degraded temporal resolution. Changes in imaging depth do not affect beam intensity.
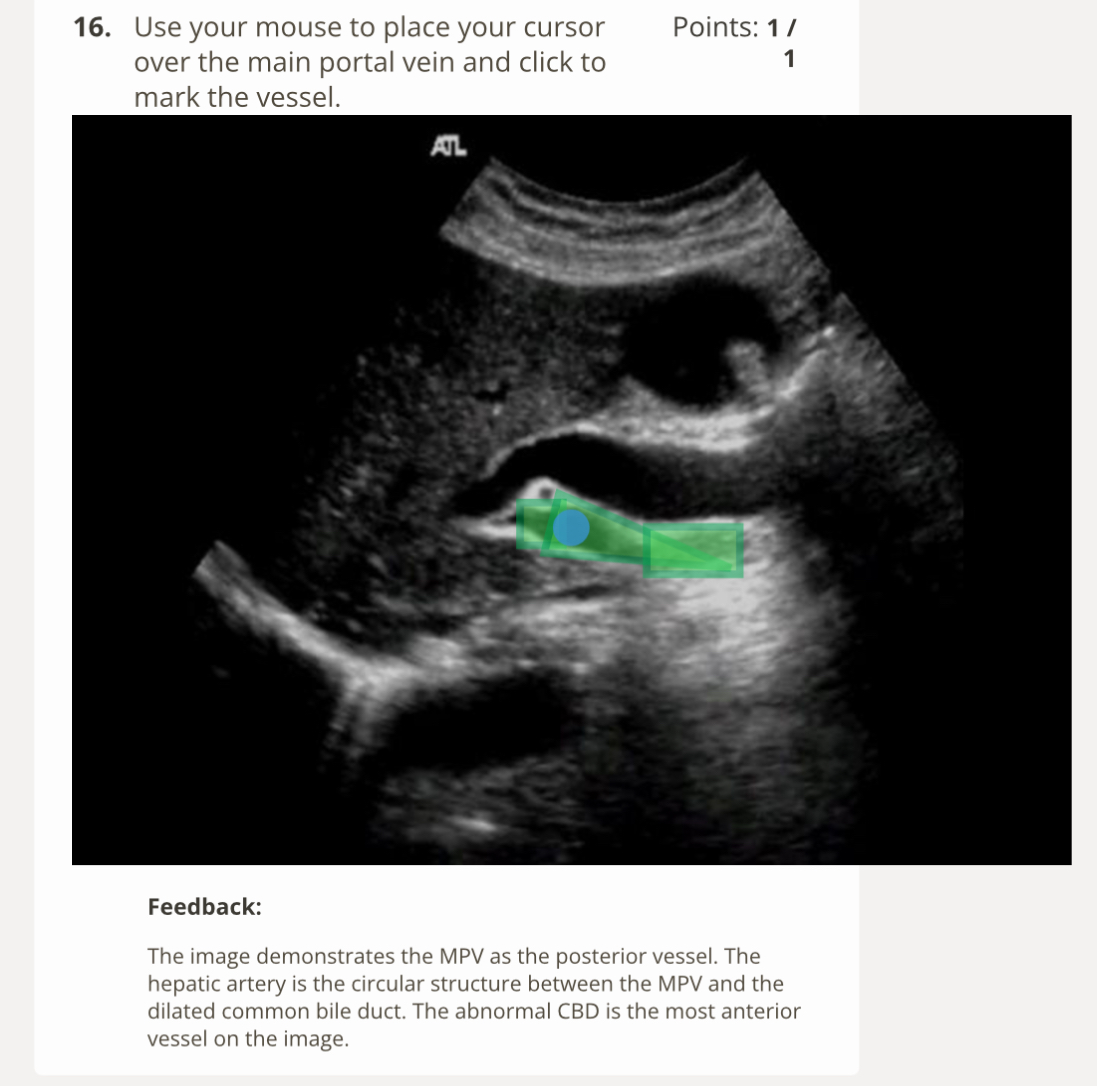
The findings on the image are common complication of:
A)Marfan syndrome
B) Lupus
C) Leriche syndrome
D) Irritable bowel syndrome
A) Marfan syndrome
Why?
The image demostrate a critical finding of an aortic dissection. Note the aorta is separated into two channels by a flap of tissue. Aortic dissection is a common complication of Marfan syndrome
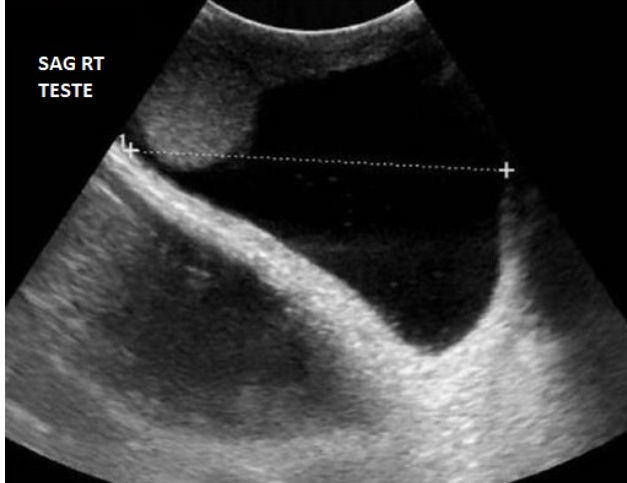
Which measurement on the hydrocele is being assessed on the image?
A) length
B) AP
C) width
A) length
Why?
The image is a Sagittal view which means the calipers are measuring the superior to inferior dimension AKA length.
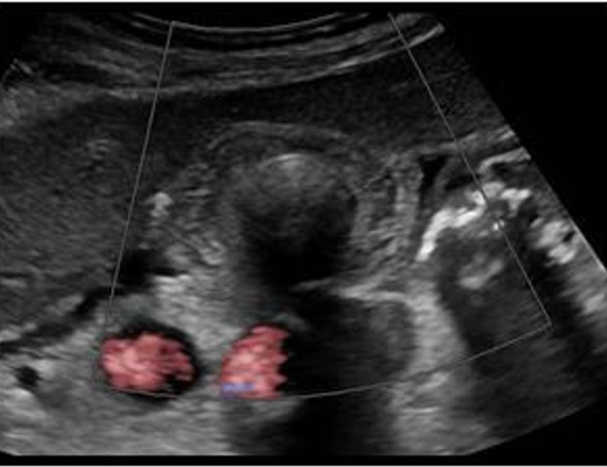
The diaphragm sign, displaced crus sign, and bare area sign are indicative on what abnormality?
A) pneumonia
B) diaphragmatic hernia
C) ascites
D) pleural effusion
D) pleural effusion
why?
Diaphragm sign- when using an abdominal approach to view the fluid, fluid below the diaphragm and more centrally located = ascites; fluid above the diaphragm and more peripherally located= pleural effusion.
Displaced crus sign- if the fluid is displacing the crus a way from the spine, it is located on the chest cavity
Bare area sign- pleural fluid will extend behind the liver at the level of the bare are a, ascites cannot reach this area
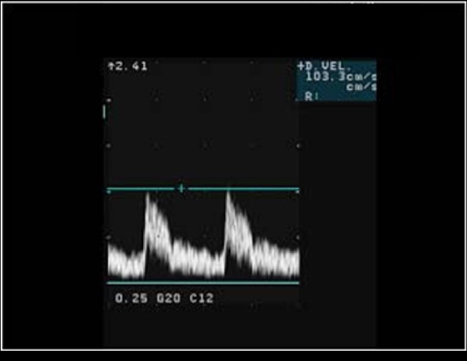
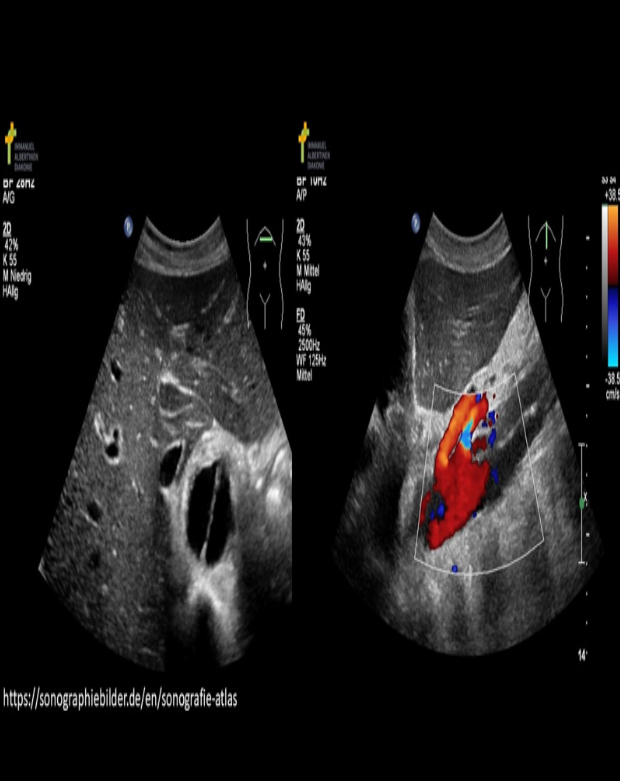
Note the Doppler measurement on the image. What other Doppler measurement should be taken to calculate the resistive index?
A) end diastolic velocity
B) peak systolic velocity
C) end systolic velocity
D) peak diastolic velocity
A) end diastolic velocity B
Why?
The velocities used to calculate the RI are measured by placing the cursor a the true peak systolic velocity and the end diastolic velocity.
RI= PSV-EDV/PSV
Acoustic Radiation Forced Impulse (AFRI) is typically used to assess the _____ for signs on ____.
A) aorta, stenosis
B) kidneys, obstructive calculi
C) liver, chronic disease
D) abdominal wall, hernia formation
C) liver, chronic disease
why?
Acoustic Radiation Forced Impulse is typically used to assess the liver for signs on chronic disease. It is similar to shear wave elastography because it provides a quantitative assessment on tissue stiffness. Cirrhosis, fibrosis, and chronic hepatitis are examples on chronic conditions that would benefit from a AFRI evaluation. Other applications in renal, Thyriod and breast tissue a are being explored
Which on the following frequently occurs a late complication of pharyngitis (throat infection)?
A) renal artery stenosis
B) acute glomerulonephritis
C) cholecystitis
D) adrenal hemorrhage
B) acute glomerulonephritis
Why?
acute glomerulonephritis refers to inflammation of glomeruli. It frequently occurs a late complication on pharyngitis ( throat infection, autoimmune response, medications, toxins. Symptoms include the sudden onset hematuria, azotemia, proteinuria; foggy urine, fever, sore throat, joint pain, peripheral edema, Liguria, anemia,HTN
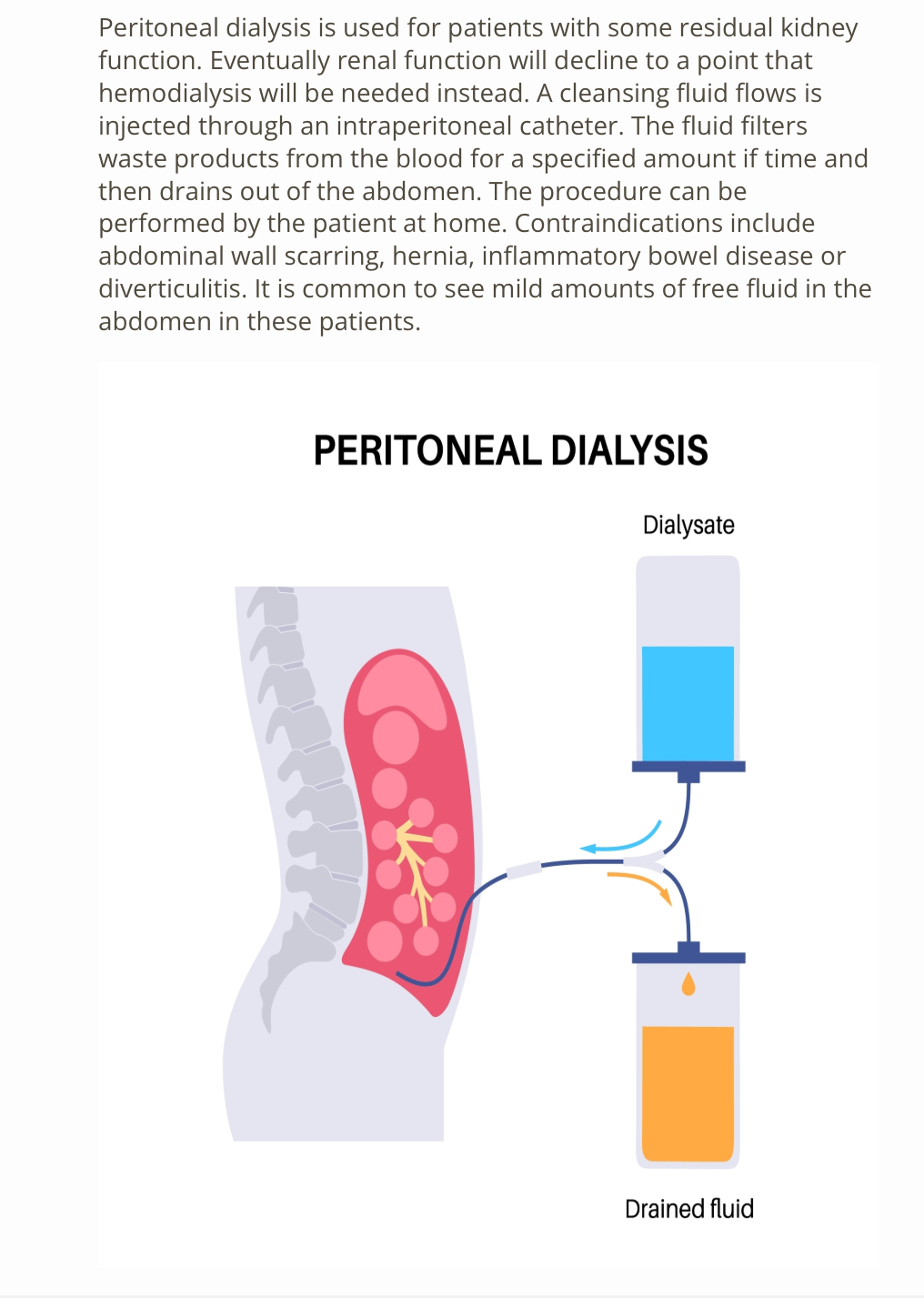
Which of the following correctly describes peritoneal dialysis?
A) A cleansing fluid flows, and injected through intro peritoneal catheter
B) requires the creation of arteriovenous fistula
C) requires regular visits to a dialysis center for treatment
D) blood is removed from the body cleaned and returned
A) A cleansing fluid flows, and injected through intro peritoneal catheter
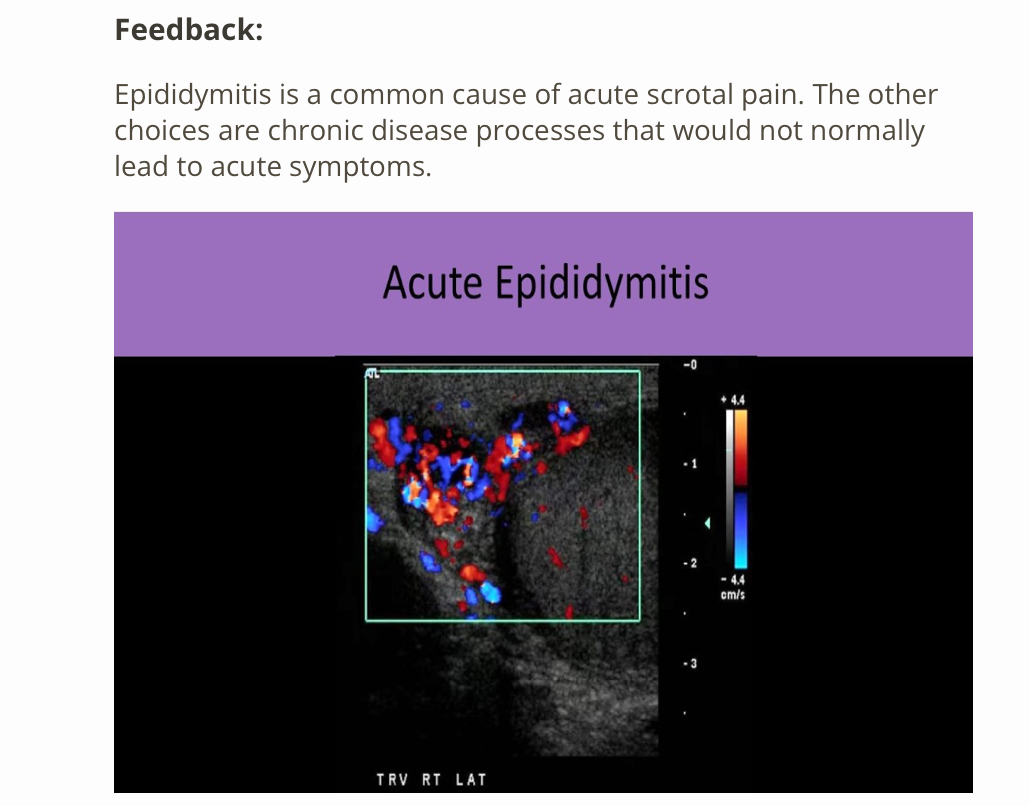
Which of the following commonly leads to acute scrotal pain?
A) epididymitis
B) seminoma
C) microlithiasis
D) tubular estasia
A) epididymitis
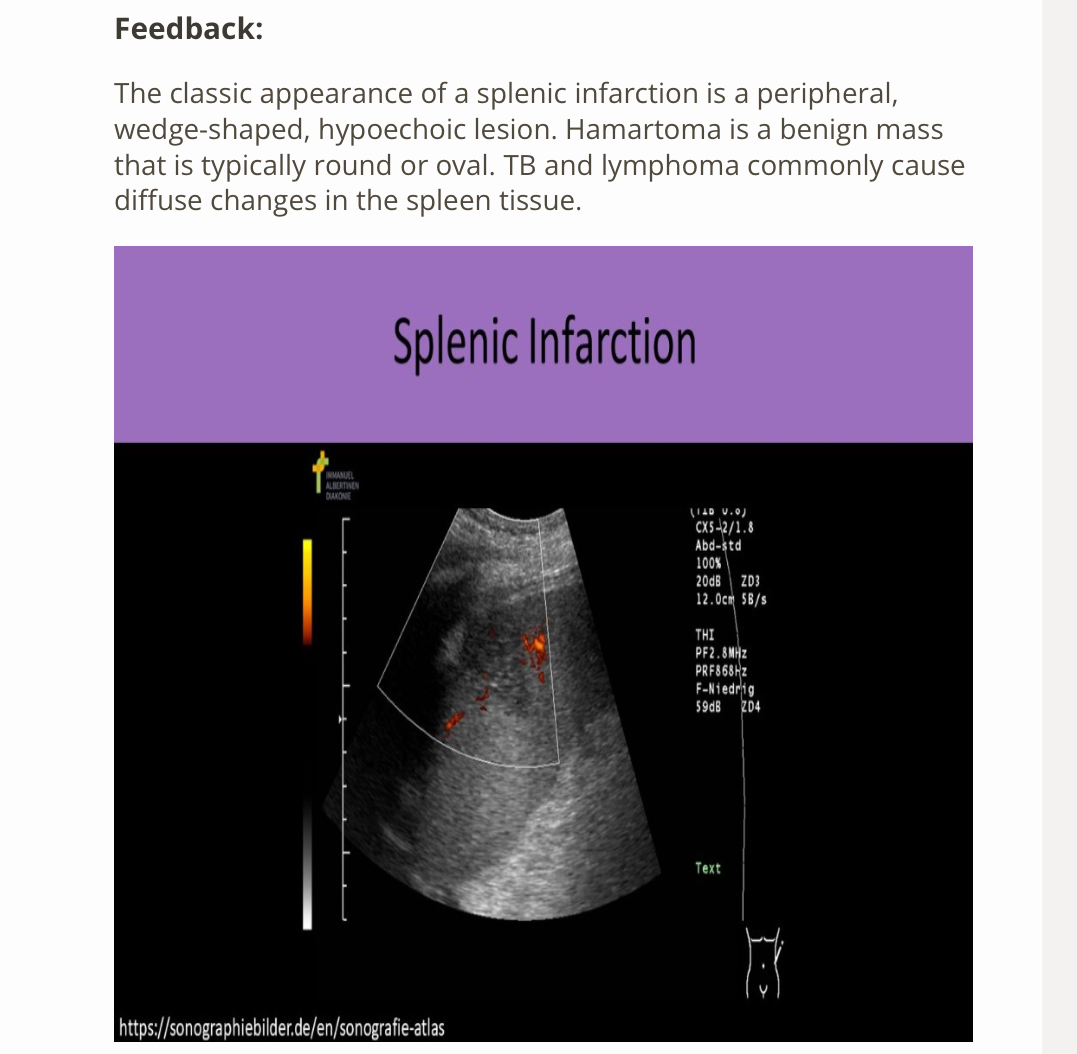
If a peripheral, wedge shap hypoechoic lesions is identified in the spleen, what should be the first diagnosis considered?
A) infarction
B) hamartoma
C) tuberculosis
D) Hodgkin lymphoma
A) infarction
The length measurements on adult kidneys should be within ___ of each other.
A) 1cm
B) 2cm
C) 3cm
D) 4cm
B) 2cm
The ____________________________ gland is located anterior to the ear and is drained by the __________________________.
A: submandibular, Stensen duct
B: sublingual, Wharton duct
C: submandibular, Wharton duct
D: parotid, Stensen duct
D: parotid, Stensen duct
Why?
Parotid gland - located anterior to the ear, drained by Stensen duct
Submandibular gland - located under the mandible, drained by Wharton duct
Sublingual glands - located under the tongue
The most common benign liver tumor is:
A: Cavernous hemangioma
B: Polycystic liver disease
C: Klatskin tumor
D: Hepatitis
A cavernous hemangioma
Why?
A hemangioma is malformation of an over-accumulation of vascular tissues within an area of the liver. It appears as a well-defined, hyperechoic area with posterior enhancement