unit 2 - input output
1/79
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
magnetic stripe reader
device used to read the — of a card, which contains data
RFID
uses radio waves to identify and track special tags attached to objects
OCR
recognises typewritten or printed document and tanslates the images of the characters into digital text
OMR
recognising marks to select options to be captured for processing by a computer
CRT monitor ‘cathode ray tube’
allow users to instantly see outputs from the computer, also used with light pens to allow drawings to be created on screen
TFT/LCD monitor (‘thin film resistor’)
these are thin flat screened, monitors that are commonly seen today. They are used as screens in laptops and mobile phones
IPS/LCD monitor (liquid crystal display)
used for modern monitors and television sets. These are simply a development of the TFT monitors.
multimedia projector
Can be used for training presentations to allow the whole audience to see images from a single computer
laser printer
These produce high quality hard copy, use toner pressed on a page to produce printed documents. They can print large amounts of pages at a very quick rate.
inkjet printer
These are used to produce high quality hard copies. Although the quality of printouts is not as good as laser printers, it is far better than Dot Matrix printers
dot matrix printer
very robust and can be used in noisy and dirty environments. Can make ‘carbon copies’ of document using special ‘carbon paper’ underneath normal printer paper.
wide format printer
They are able to produce large scale projects which save time and money. They are often used for posters and banners.
actuator
a device that causes another machine or device to operate
differences and similarities between RFID and magnetic stripe
Data cannot be read by eye so more secure, Data can be re-written, RFID is contactless therefore has less wear and tear whereas magnetic is placed in reader RFID reads the data faster More data on RFID card
keyboard
used to input text, numbers and instructions into the computer, allows the user to type in command to the computer
keyboard advantages
fast entry if new data, easy use for most people
keyboard disadvantages
slow method of the data entry compared to direct entry deivces e.g. OMR, keyboards are quite large and takes up a lot of desk space
numeric keypad
used for ATMs and for chip and pin deivces when paying by credit/debit
numeric keypad advantages
faster than standard keyboards when entering numbers, they are portable
numeric keypad disadvantages
small keys can be difficult to use, sometimes the order of the keys isn’t intuitive
pointing devices
used to open, close, minimise software programs, can be used to group, move and delete files, edit images to change the size and position of an object
pointing deivces advantages
faster method of choosing options, quick to navigate through programs and the internet, doesnt take up a lot of desk space
pointing device disadvantages
needs flat surface, dirt can obstruct the sensor
remote control
used to control multimedia devices, used to remotely turn on/off devices, change the volume etc.
remote control advantages
can be used to operate from a distance, without a wire, can be safer to operate machinery from a distance
remote control disadvantages
signal can be blocked
joystick/wheel
used for computer games and simulators
joystick/wheel advantages
more realistic than a mouse for certain situations, easier than keyboard for navigating menus
joystick/wheel disadvantages
more difficult than a mouse to control a pointer
touch screen
used for self service tills, ATMs, interactive classrooms, public information systems
touch screen advantages
faster when choosing options than keyboard/mouse, easy to operate, user friendly and usually intuitive
touch screen disadvantages
options usually limited as user can’t do commands, can cause strain if used often, screen can become dirty, which reduces responsiveness
scanners advantages
faster and more accurate than typing documents again, recover damaged photographs by scanning and then using software
scanners disadvantages
quality can be limited, scanning is often slow, scanning multiple pages can be difficult
digital camera advantages
Easier to produce better photographs than traditional cameras, Faster to process and upload, rather than scanning , No need to develop or print film, Memory cards store many photographs
digital camera disadvantages
Need to know how to operate , Images often need to be compressed - reducing image quality, Can be bulky to carry, compared to a smartphone for example
microphone advantages
Faster to read than type text, with voice recognition software, Software can manipulate sound, Voice activated commands can improve safety, for example in cars
microphone disadvantages
Sound files can take up alot of storage, Voice recognition isn’t always accurate
sensors
can be used to measure temperature, light, pressure, sound, moisture and pH
sensors advantages
More accurate readings compared to humans, Readings are continuous, Systems can be automatic - no need for human interaction
sensors disadvantages
Faulty sensors give in inaccurate results, for example if they become dirty
light pen advantages
more accurate than touch screen to write/draw, portable, easy to use
light pen disadvantages
can lag when drawing quickly, doesnt work with all screens
magnetic stripe reader advantages
faster entry than typing, error free
magnetic stripe reader disadvantages
if the stripe gets damaged, the data is lost, needs close contact
chip and pin reader advantages
it is more secure than contactless cards as the PIN acts as a second security reader, it has a more robust system than magnetic stripe cards
chip and pin reader disadvantages
the PIN may be seen by someone whilst it is typed in
Radio frequency identification (RFID) reader advantages
no line of sight contact is needed, very robust and reliable technology, very fast read rate
Radio frequency identification (RFID) reader disadvantages
tag collision may occur, as they use radio waves, they are easy to jam/interrupt, easy to hack into the signal, rfid is more expensive than a comparable barcode system.
OMR advantages
very fast way of inputting survey results, it is more accurate because there is no human intervention, more accurate than OCR methods
OMR disadvantages
designing the forms can be complicated to ensure the marks are correctly positioned, if there are problems, they need to be manually checked, which can be time consuming
OCR advantages
it is much faster data entry system than manual typing, no human intervention so its error free
OCR disadvantages
system has difficulty in reading different handwriting, not a very accurate technique
barcode reader advantages
much faster than manually keying in data, allow automatic stock control, they are a tried and trusted technology
barcode reader disadvantages
relatively expensive system to administer, barcodes may be swapped between items, can be more easily damage than rfid tags or magnetic stripes
QR code scanner advantages
hold much more information than normal barcode, fewer errors than with barcodes, QR codes are easier to read, It is possible to encrypt QR codes.
QR code reader disadvantages
more then one QR format is available. QR codes can be used to transmit malicious data
Cathode ray tube (CRT) monitors advantages
unlike LCDs it can be seen at a wider range of angles, allow the use of light pens
Cathode ray tube (CRT) monitors disadvantages
they are very heavy and bulky, they run very hot and can cause fires if left unattended, they use a lot more power than LCDs. their flickering can lead to headaches, image burn in is a common issue
LCD advantages
very efficient and have low power consumption, lightweight devices, screens can be made in various sizes, no flickering images, very sharp image resolution
LCD disadvantages
color contrast from different angles are inconsistent, motion blur is a common issue, has lower contrast than CRT monitors
touch screens advantages
they don’t need additional input devices, they are very interactive and have many functions, they add a high tech feel to devices and interfaces
touch screen disadvantages
they tend to get dirty with frequent use, frequent use results in straining of arm muscles etc, if large amounts of data are input/output, they aren’t very accurate and the interface isn’t very fast
multimedia projector advantages
more people can watch, avoids the need for several networked computers
multimedia projector disadvantages
images can be fuzzy, expensive to buy, set up can be complicated
laser printer advantages
printing is fast, they can handle very large print jobs, quality is consistently high, toner cartridges last for a long time
laser printer disadvantages
they are only considerably fast if several copies are being made, colored — printers are expensive to run
inkjet printer advantages
high quality output, cheaper than laser printes, very lightweight,
laser printer disadvantages
slow output if many copies are needed, cant do large print jobs, printing can smudge if user isnt careful, can be expensive if used a lot
dot matrix printers advantages
can be used in varying environments unlike laser/inkjet printers, very cheap to run and maintain, good for continuous printing
dot matrix printer disadvantages
very noisy, initial cost is more than an inkjet printer, very slow and poor quality printing
plotter advantages
very high quality output, can produce large drawings very accurately, can print on a variety of materials
plotter disadvantages
very slow printing, expensive equipmet to purchase initially, takes up a lot of space compared to a printer
3d printer advantages
manufacturing objects has become much easier, even though the initial cost is high it is still cheaper, customisable designs
3d printer disadvantages
potential to make counterfeit items, could lead to manufacture of dangerous items, job loss potential, very expensive
speaker advantages
can be heard by alot of people at a time, ranges of sizes and power output, immersive audio, helps people with disabilities
speaker disadvantages
speaker output can disturb other people in the area, varying sound quality, expenisve for higher quality output
actuators advantages
precise movement, programmable, allow automatic control of many devices, allow remote operation of many devices, they are relatively inexpensive devices
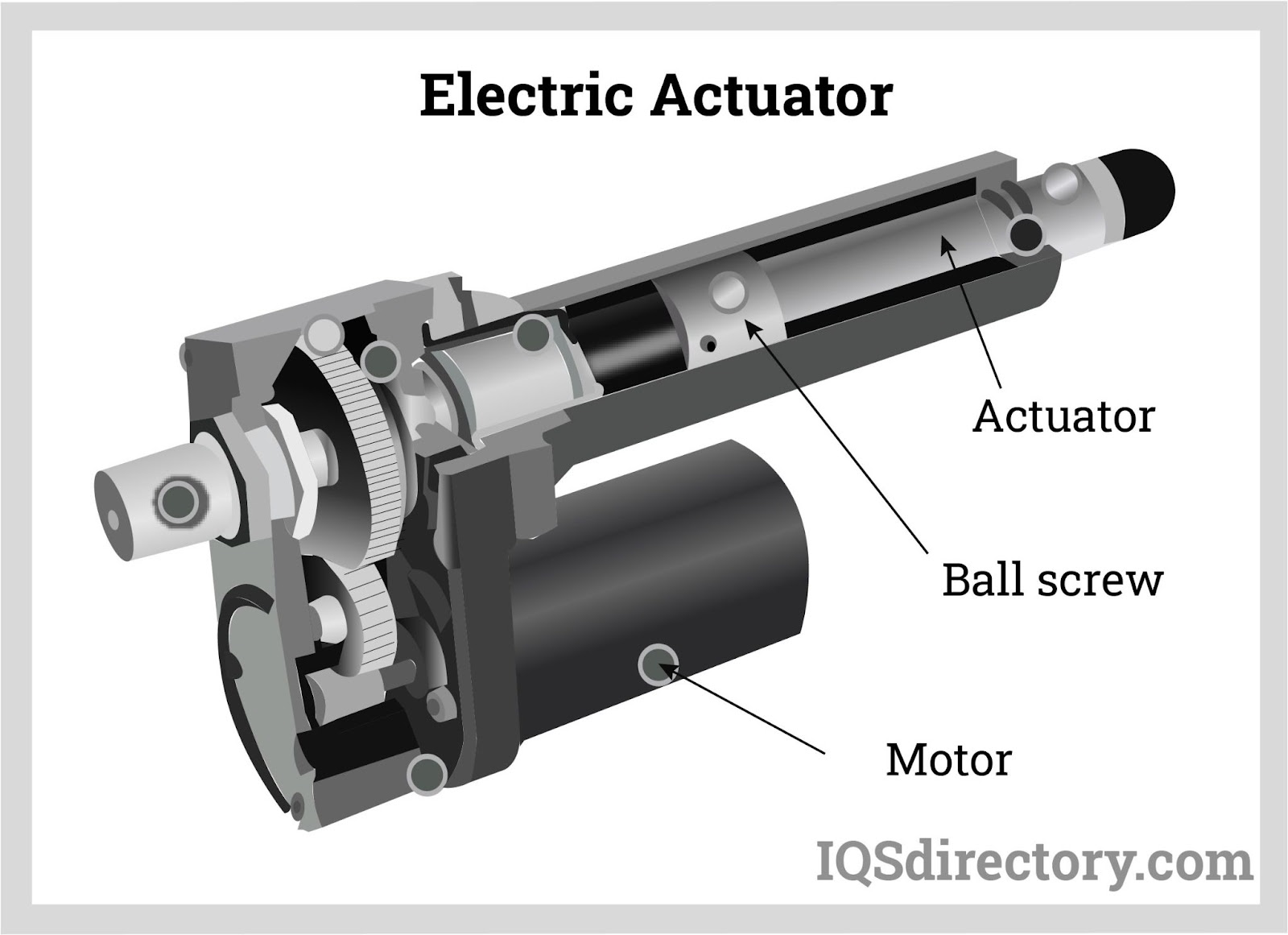
actuators
controls motors, pumps, switches etc
actuator disadvantages
requires power, potential mechanical wear, requires DAC (digital data to analogue data)