HSM 110 Midterm
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the primary motivation of development in Managed Care?
Managed Care seeks to achieve efficiency by integrating the basic functions of health care delivery, and it employs mechanisms to control (manage) utilization and cost of medical services. As the dominant health care delivery system in the U.S., it covers most Americans in both private and public health insurance programs through contracts with a managed care organization (MCO), such as an HMO or a PPO.
What is the mission of the public health system?
The mission of the public health system is to improve and protect community health. The Institute of Medicine's Future of Public Health in the 21st Century has outlines the need for a more robust public health infrastructure and a population-based health approach for a healthier America.
Public health focuses on improving the health and well-being of the total population. In evaluating the effectiveness of public health, indicators are developed along with a national surveillance system to consistently track the health indicators. Determinants of population health play a major role in evaluating a public health system.
10 essential public health services that a system needs to deliver:
1. Monitoring health status to identify and solve community health problems
2. Diagnosing and investigating health problems and hazards
3. Informing, educating, and empowering people about health problems and hazards
4. Mobilizing the community to identify and solve health problems
5. Developing policies and plans to support individual and community health efforts
6. Enforcing laws and regulations to protect health and safety
7. Providing people with access to necessary care
8. Assuring competent and professional health workforce
9. Evaluating the effectiveness, accessibility, and quality of personal and population-based health services
10. Performing research to discover innovative solutions to health problems
Main characteristics of the U.S Health Care System
- No central governing agency and little integration and coordination
- Technologically-driven delivery system focusing on acute care
- High in cost, unequal in access, and average in outcome
- Delivery of health care under imperfect market conditions
- Government as subsidiary to the private sector
- Quest for integration and accountability
- Fusion of market justice and and social justice
- Multiple players and balance of power
- Access to health care services selectively based on insurance coverage
- Legal risks influence practice behaviors
How is the Health Care System of a nation influenced?
Political climate, level of economic development, technological progress, social and cultural values, the physical environment, and population characteristics such as demographic and health trends.
What are reasons for current rising health care costs?
Although some medical technology may reduce costs, as a whole technology has contributed to health care cost escalation. For both the consumer and the provider, the excessive treatment has generally been of little concern as long as a third party--either an insurance plan or the government--pays for it.
People are living longer, People have unhealthy habits, Medical malpractice lawsuits, Misuse of healthcare, Subsidizing federal programs, Other regulatory requirements(HIPAA), Drug trials, etc...
Indicators of health are;
Self-reported health status, life expectancy, morbidity(disease), mental well-being, social functioning, functional limitations, disability, spiritual well-being
List cost-containment measures enacted by employers, government and/or private insurers.
In 1983, the U.S. government decided it needed to contain the exploding cost of hospital care, mostly because of its impact on the rising cost of Medicare. This goal of cost containment was achieved through the enactment of the Social Security Amendments of 1983. The law required Medicare to stop paying hospitals per diem rates established on the basis of their costs of operation (retrospective reimbursement). Instead, a prospective payment system (PPS) was established to reimburse hospitals on the basis of diagnosis-related groups (DRGs) Under this method, hospitals received a pre-established fixed rate per admission. To ensure that they would not lose money, hospitals has to cut their costs of operation. They also had to discharge patients more quickly than before because keeping patients in the hospital longer than necessary cut into the hospitals profits.
During the 1990s, managed care emphasized cost containment and efficient delivery of care through early discharge from hospitals, and, if necessary, continuity of care through home health agencies and skilled-care nursing homes.
Also refer to the Affordable Care Act.
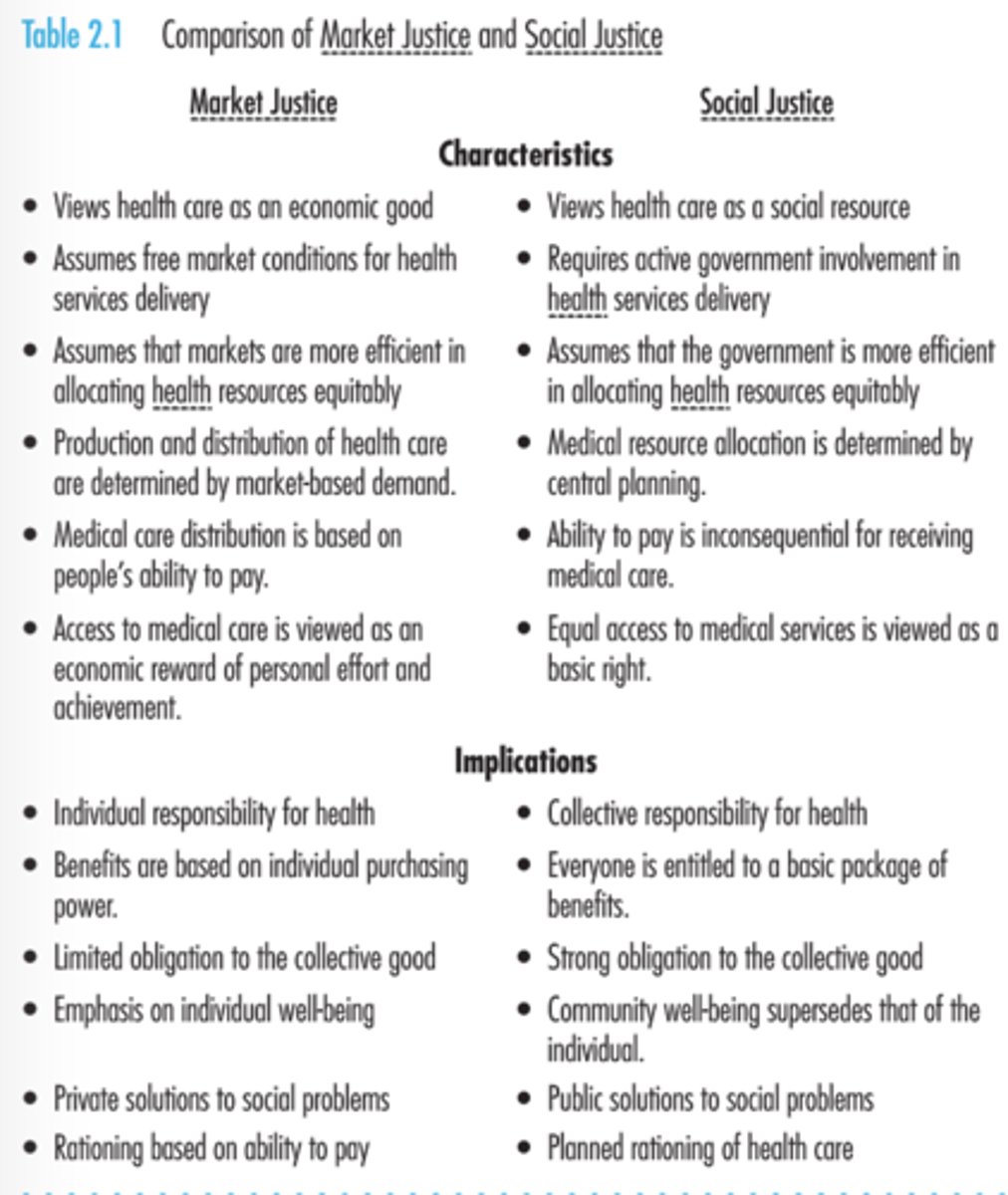
Market justice and social justice and how the two are at odds with each other in the U.S. health care system.
pg. 39 of textbook for reference
What is hot-spotting? In what ways can "hot-spotting" improve the delivery of care in the U.S.? What are the barriers to enacting hot-spotting in the U.S.?
Healthcare hotspotting is a data-driven process for the timely identification of extreme patterns in a defined region of the healthcare system. It is used to guide targeted intervention and follow-up to better address patient needs, improve care quality, and reduce cost.
The idea that drives this initiative is simple: every hospital has patients with complex care needs who struggle to navigate the equally complex system. These patients, often referred to as high-utilizers or "super-utilizers," typically have medical and social barriers that keep them from getting the quality care they need.Through accompaniment and observation, students will learn about the barriers that medically and socially complex patients face to obtaining high-quality care and maintaining their health.
What are the initiatives of Healthy People 2020?
Identifying nationwide health improvement priorities, increasing public awareness and understanding the determinants of health, disability, and disease; providing measurable objectives and goals that are applicable at all levels; engaging multiple sectors to take action to strengthen policies and improve practices that are driven by the best scientific evidence and knowledge; and identifying critical research, evaluation, and data collection methods. Healthy People 2020 will assess progress through measures of general health status, health-related quality of life and well-being, determinants of health, and disparities.
Overacting goals of Healthy People 2020;
- Attaining high-quality, longer lives free of preventable disease, injury and premature death
- Achieving health equity, eliminating disparities, and improving the health of all groups
- Creating social and physical environments that promote good health for all
- Promoting quality of life, healthy development, and health behaviors across all life stages
The 4 foundational health measures are;
General health status, health-related quality of life and well-being, determinants of health, and disparities among the population.
How does the U.S. compare to other developed countries in terms of health care and health care systems?
The United States has a unique system of health care delivery, but this system lacks universal access; therefore, continuos and comprehensive health care is not enjoyed by all Americans. Health care delivery in the United States is characterized by a patchwork of subsystems developed either through market forces or the need to take care of certain population segments.
Among seven other developed nations, (United Kingdom, Germany, Sweden, Canada, France, Australia, Japan), U.S. health status ranks 8th on important health status indicators:
Life expectancy at birth
Infant mortality rate
Probability of dying between ages 15 and 60
U.S. health expenses are triple those of Japan and more than double of the other nations.
What is the purpose of the DRG (Diagnosis-Related Groups)? How do they work? How does the reimbursement of the DRG work?
The diagnosis-related group method is used to pay for hospital inpatient services. The predetermined rate is set according to DRGs. Instead of a per diem rate, the reimbursement method based on DRGs prospectively sets a bundled price according to the principal diagnosis at the time of admission. The hospital receives the predetermined fixed rate for that particular DRG classification.
The primary factor governing the amount of reimbursement is the main clinical diagnosis, but additional factors can create differences in reimbursement for the same DRG. Such factors include differences in wage levels between geographic areas, an urban versus a rural hospital location, whether the institution is a teaching hospital, and an adjustment in the reimbursement related to treating a disproportionately large share of low-income patients.
The DRG-based prospective reimbursement has forced hospitals to control their costs. To keep the cost of services below the fixed reimbursement amount, this reimbursement method has also forced hospitals to minimize the length of inpatient stay. If the total cost of services is less than the DRG-based reimbursement amount, a hospital gets to keep the difference as profit.
What is Tricare? How does it work?
TriCare is an insurance program financed by the U.S Department of defense to permit the beneficiaries to receive care from both private and military medical care facilities. Families and dependents of the active-duty or retired military personnel are either treated at the hospitals or dispensaries, or they are covered by TriCare.
Why has managed care met with resistance from patient and from providers?
Patients, providers and payers are each experiencing pressure during the current social movement in American medicine. Patients and providers feel threatened for a variety of reasons, including the loss of freedom of choice and professional autonomy, while payers are challenged with identifying a method to finance health care for all working Americans. Throughout this debate, a variety of ethical concerns have emerged.
In what ways did the enactment of Medicare and Medicaid change the U.S. Health Care Delivery System?
The creation of Medicare and Medicaid had a drastic impact on both federal and state budgets, but the federal government bore the brunt of this burden. The programs did more than cover millions of Americans. They removed the racial segregation practiced by hospitals and other health care facilities, and in many ways they helped deliver better health care. By ensuring access to care, Medicare has contributed to a life expectancy that is five years higher than it was when the law went into effect. And children who are on Medicaid develop into healthier teenagers and adults.
What are the determinants of health?
Physical activity, overweight/obesity, tobacco use, substance abuse, responsible sexual behavior, mental health, injury and violence, environmental quality, immunization, access to health care.
Can be classified into four main categories: environment, behavior and lifestyle, heredity, and medical care.
Failure of adoption of national health care in the U.S.
- Unlike in Europe, national health care failed to get an early footing because of labor and political stability in the United States
- A decentralized American system gave the U.S. federal government little direct control over social policy
- The German social insurance system was denounced during World War I. Since ten, the term socialized medicine has been used as a synonym for nation health insurance
- The AMA(American Medical Association) opposed national care initiatives
- Middle-class Americans have traditionally espoused beliefs and values that are consistent with capitalism, self-determination, and distrust of big government
- Middle-class Americans have been averse to higher taxes to pay for the increased cost of a national care program
How has technology impacted physicians, quality of care, and the cost of health care?
Americans generally equate high-technology medicine to high-quality care, but such an association is not always accurate. Quality is enhanced only when new procedures can prevent or delay the onset of serious disease, provide better diagnosis, make quicker and more complete cures possible, increase safety of medical treatment, minimize undesirable side effects, promote faster recovery from surgery, increase life expectancy, and add to quality of life. Improvements in diagnostic capabilities increase the likelihood that timely and more appropriate treatments will be provided. Technology can provide new remedies that never existed before. It also offers improved remedies that are more effective, less invasive, or safer. Thus, physicians may enjoy the impact of technology only if it has proven to be efficacious.
Technological innovations have been the single most important factor in medical cost inflation. In fact, they may have accounted for as much as half of the total rise in health care spending in recent years. The addition of new technology in health care usually increases both labor and capital costs. Acquisition costs are often high because of R&D and precision manufacturing, training or hiring of technicians with special skills, facilities may require refurbishing or expansion to accommodate the new technology, and utilization when covered by insurance.
Technology has the potential to not only enhance health benefits but also reduce costs.
What is HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability)? Why was it enacted? What purpose does it serve?
To alleviate concerns about the confidentiality of patient information, the Helath Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 restricted the legal use of personal medical information for three main purposes: health care delivery to the patient, operation of the health care organization, and reimbursement.
The HIPPA legislation mandated strict controls on the transfer of personally identifiable health data between two entities, provisions for disclosure of protected information, and criminal penalties for violation. It also established certain patient rights, such as the right of patients to inspect and have copies of their protected health information, to request corrections to the records, and to restrict the use of information.
The HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act of 2009) law strengthened the civil and criminal enforcement of HIPAA by including increased penalties for violations.
What are the levels of prevention?
Primary Prevention, Secondary Prevention, Tertiary Prevention
Primary Prevention - Health promotion: Health education, nutrition, safe housing, counseling on lifestyles and behaviors, periodic exams
Specific protections: Immunizations, personal hygiene, environmental sanitation, protection from occupational hazards, protection from carcinogens
(Viewed as a set of basic and routine services that include prevention, diagnostic and therapeutic services, health education and counseling, and minor surgery.)
Secondary Prevention - Early diagnosis and prompt treatment: Case-finding measures (individual and mass); screening surveys; selective examinations
To cure or prevent disease progression and complications
To prevent spread of communicable diseases
To shorten the period of disability
(Usually short term in nature, involving sporadic consultation from a specialist to provide expert opinions and/or surgical or other advanced interventions that primary care physicians are not equipped to perform.)
Tertiary Prevention - Disability limitation: Treatment to arrest disease process and prevent further complications; facilities (interventions) to limit disability and prevent death
Rehabilitation: Hospitals/other facilities for retraining to maximize use of remaining capacities; employer education about disabled; selective placement in group facilities
(The most complex level of care and is required for conditions that are relatively uncommon. Typically, tertiary care is institution based, highly specialized, and technologically driven.)
What are the levels of care? (i.e. long term care, skilled facilities, rehab, hospice care, and palliative care)
Private Practice, Hospital Outpatient Clinics, Freestanding Facilities, Mobile Facilities for Medical, Diagnostic, and Screening Services; Telephone Triage, Home Care, Hospice Care, Outpatient Long-Term Services, Public Health Services, Community Health Centers, Free Clinics, Alternative Medicine Clinics. (pp. 173-176)
What are the differences between D.O. (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine) and M.D. (Doctor of Medicine)
Both MDs and DOs use traditionally accepted methods of treatment, including drugs and surgery. The two differ daily in their philosophies and approaches to medical treatment.
Osteopathic medicine, practiced by DOs, emphasizes the musculoskeletal system of the body (e.g., the correction of joint or tissues). In their treatment plans, DOs stress preventive medicine such as diet and the environment as factors that might influence natural resistance. They take a holistic approach to patient care.
In contrast, MDs are trained in allopathic medicine, which views medical treatment as an active intervention to produce a counteracting reaction in an attempt to neutralize the effects of disease. Mods, particularly generalists, may also use preventive medicine along with allopathic treatments. Approximately one-third of MDs and more than one-half of DOs are generalists.
Common medical specialties;
Anesthesiology, cardiology, dermatology, specialized internal medicine, neurology, obstetrics and gynecology, ophthalmology, pathology, pediatrics, psychiatry, radiology, and surgery.
What are the differences between Medicare and Medicaid?
Although adopted together, Medicare and Medicaid reflected sharply different traditions. Medicare enjoyed broad grassroots support and, being attached to social security, had no class distinction. Medicaid, in contrast, carried the stigma of public welfare. As a federal program, Medicare had uniform national standards for eligibility and benefits. State-administered Medicaid programs varied across states in terms of eligibility and benefits. Medicare covered anyone age 65 or older, whereas Medicaid became a means-tested program, which confined people below a pre-determined income level. Consequently, many of the poor did not qualify because their incomes exceeded the means-test limits.
What is meant by "entitlement" in terms of health care insurance?
In other words, people are entitled to purchase a share of the available goods and services they value. They must purchase these valued goods and services by using the financial resources acquired through their own legitimate efforts.
What are the differences between palliative care and hospice care?
The term hospice refers t a cluster of comprehensive services for terminally ill patients who have a life expectancy of 6 months or less. Hospice programs provide services that address the special needs of dying persons and their families. Hospice is method of care, not a location, and services are taken to patients and their families wherever they are located. Hospice services include medical, psychological, and social services provided in a holistic context.
The two primary areas of emphasis in hospice care are pain and symptom management, which are referred to as Palliative Care, and psychological and spiritual support.
What are the differences between allopathic and osteopathic medicine?
Allopathic Medicine is primarily practiced by MDs (Doctors of Medicine), which views medical treatment as an active intervention to produce a counteracting reaction in an attempt to neutralize the effects of disease.
Osteopathic Medicine is primarily practiced by DOs (Doctors of Osteopathy), as it emphasizes the musculoskeletal system of the body. In their treatment plans, DOs stress preventive medicine such as diet and the environment as factors that might influence natural resistance. They take a holistic approach to patient care.
Whereas most DOs are generalists, most MDs are specialists.
Criteria for Quality of Care
1. Prevent or delay disease onset
2. Provide a more accurate diagnosis than is possible with currently available options
3. Provide a quicker cure
4. Provide a more complete cure
5. Increase safety of treatment
6. Minimize side effects
7. Provide for faster recovery from surgery
8. Increase life expectancy
9. Add to quality of life
Prevention - Levels of prevention and example; take a clinical situation and apply levels of prevention (e.g. stroke, spinal cord injury, amputation, cancer, diabetes)
Primary Prevention - (Viewed as a set of basic and routine services that include prevention, diagnostic and therapeutic services, health education and counseling, and minor surgery.)
An approach to providing health care services rather than a set of specific services.
Secondary Prevention - (Usually short term in nature, involving sporadic consultation from a specialist to provide expert opinions and/or surgical or other advanced interventions that primary care physicians are not equipped to perform.)
Includes hospitalization, routine surgery, speciality consultation, and rehabilitation.
Tertiary Prevention - (The most complex level of care and is required for conditions that are relatively uncommon. Typically, tertiary care is institution based, highly specialized, and technologically driven.)
Examples include trauma care, burn treatment, neonatal intensive care, tissue transplants, and open-heart surgery.
Primary Care - Describe primary care characteristics, distinct challenges, and solutions to the challenges.
According to WHO (World Health Organization), primary health is essential health care that is based on practical, scientifically sound, and socially acceptable methods of technology. Primary health care serves as the foundation of ambulatory services, characterized by the first level of contact between individuals, the family, and the community on one hand and the health care delivery system on the other hand, bringing health care as close as possible to where people live and work.
Domains of Primary Care
1. Point of entry
2. Community based
3. Coordination of care
4. Essential care
5. Integrated care
6. Accountability
Distinct Challenges
- As the supply and use of specialist services increase, specialist physicians have become more integrated the the primary care system; however, much improvement is still needed for coordination of care between specialists and primary care providers. Primary care must evolve and adapt to recent changes in the health care system; this is particularly important in light of research predicting a shortage of more than 44,000 primary care physicians by 2035.
Solutions to Challenges
- A medical-home model has been advocated to deliver primary care based on the principles of patient-centered care and team-based chronic disease management approaches. Several acts and models have been proposed and implemented in order to alleviate the underlying pressures that are imposed on primary care, however primary care delivery still faces mounting challenges in the wake of workforce shortages and financial constraints.
Medicare and Home Health - Understand and explain the advantages and the problems with fraud and abuse.
Home Health refers to health care provided in the home of the patient by health care professionals. the organizational setup commonly requires a hospital-based or freestanding home health agency that sends health are professionals and paraprofessionals to patients' homes to deliver services approved by a physician.
Home health services typically include nursing care, such as changing dressings, monitoring medications, and providing help with bathing; short-term rehabilitation, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy; homemaker services, such as meal preparation, shopping, transportation, and some specific household chores; and certain medical supplies and equipment, such as ostomy supplies, hospital beds, oxygen tanks, etc.
As the largest single payer for home health services, Medicare paid for 43% of home health expenditures in the United States in 2013.
Advantages
- Medicare covers all elderly persons, non-elderly disabled persons on Social Security, and non-elderly persons with end-stage renal disease. There are no income-test means, or class distinctions.
Problems with Fraud and Abuse
- Health care fraud has been identified as a major problem in the Medicare and Medicaid programs. It may also occur when more services are provided than necessary or when services not provided are billed to third-party payers. The latter practice may include billion for a higher-priced service when a lower-priced service is actually delivered.