unit one geography !
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
some of these flashcards are trash just warning
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
Magnitude of WOOROLOO
Fire burned through over 10,500 hectares, causing significant damage.
86 properties destroyed, more than 100 damaged
Declared level 3 incident
2 fire trucks
8 non-fatal injuries
Duration WOOROLOO
Fire active from February 1st to 7th, 2021.
Frequency WOOROLOO
Bushfires occur seasonally in this region.
90% of WA is bushfire prone, can happen anytime and anywhere.
Probability WOOROLOO
Rainfall patterns- high rainfall in November 2021 increased vegetation growth. Weather persistent hot and dry, low humidity and strong winds. Fuel loads- Dry cured vegetation and high fuel loads
spring to autumn experiences high probability of bushfires occurring
Scale of Spatial Impact WOOROLOO
it burned an area of more than 10,500 hectares inside a perimeter of 154km. started in Wooroloo in shire of Mundaring then spread to shires of chittering and Northam and the city of swam. Local impact because it impacts two shires
Hight Of Flames WOOROLOO
Flame heights exceeded 20 meters during the fire.
Insurance Claims WOOROLOO
Fire resulted in 92 million dollars in claims.
Recovery Package WOOROLOO
18.1 million dollar package for rebuilding efforts.
Level 3 Incident WOOROLOO
Declared on February 2nd, indicating severity.
Fire Ban Violation WOOROLOO
Fire allegedly started by angle grinder use.
Daniel Gunter WOOROLOO
Individual linked to the fire's ignition.
Fuel Loads WOOROLOO
Increased due to high rainfall in November 2020.
Humidity Conditions WOOROLOO
Low humidity worsened fire suppression efforts.
Wind Conditions WOOROLOO
Strong winds accelerated the fire's spread.
Terrain Challenges WOOROLOO
Steep terrain made fire suppression difficult. spread faster
Fire Rate WOOROLOO
Recorded moving as fast as 5 km/h.
Total Fire Ban WOOROLOO
Legal restriction against starting fires during high risk.
Spot Fires WOOROLOO
Fires ignited by embers landing on dry fuel.
Terrain Elevation Impact WOOROLOO
10-degree increase doubles fire speed.
Wind Speed on Feb 1 WOOROLOO
Ranged from 15 to 31 km/h.
Temperature Range WOOROLOO
Highs between 30 to 36 degrees Celsius.
Habitat Loss WOOROLOO
10,500 hectares burnt, affecting biodiversity.
Soil Fertility Reduction WOOROLOO
Vegetation loss increased erosion risk.
Aquatic Ecosystem Impact WOOROLOO
Ash and debris harmed local waterway animals.
Veterinary Assessments WOOROLOO
Over 750 assessments conducted for affected animals.
Economic Cost WOOROLOO
Combined recovery costs totaled $125 million.
Homes Destroyed WOOROLOO
86 homes lost, costing millions to rebuild.
Government Recovery Funding WOOROLOO
$18.1 million allocated for rebuilding efforts.
Social Displacement WOOROLOO
Families evacuated, causing trauma and anxiety.
Community Donations WOOROLOO
Over $16.7 million raised for recovery support.
COVID Lockdown Impact WOOROLOO
Delayed evacuations due to uncertainty during fire.
Indigenous Site Damage WOOROLOO
Fire harmed culturally significant Aboriginal sites.
Land Management Failures WOOROLOO
Lack of controlled burns led to fuel buildup.
Urban Expansion Risks WOOROLOO
Homes built in high-risk, wooded areas.
Fire Break Maintenance WOOROLOO
Poorly maintained fire breaks hindered containment.
Emergency Response Challenges WOOROLOO
Difficulties faced in evacuating affected communities.
Evacuation Hesitation WOOROLOO
Residents delaying departure increased risk of entrapment.
Lack of Preparedness WOOROLOO
Insufficient emergency plans among households.
Firefighter Strain WOOROLOO
Intense firefighting caused physical and mental exhaustion.
Rising Temperatures WOOROLOO
Human actions increased summer heat, worsening fire risk.
Drought Conditions WOOROLOO
Dry vegetation made fires harder to control.
Ignition Risks WOOROLOO
Human activities raised chances of fire ignition.
Land Clearing Practices WOOROLOO
Altered water cycles, reducing soil moisture retention.
Steep Terrain WOOROLOO
Increased fire spread speed up to 5 km/h.
Slope Elevation Effect WOOROLOO
10-degree slope increase doubles fire speed.
DBCA WOOROLOO
Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions.
Community Programs WOOROLOO
Educate on evacuation plans and fire safety.
DFES WOOROLOO
Department of Fire and Emergency Services.
Burned Area Map WOOROLOO
Highlights regions affected by the bushfire.
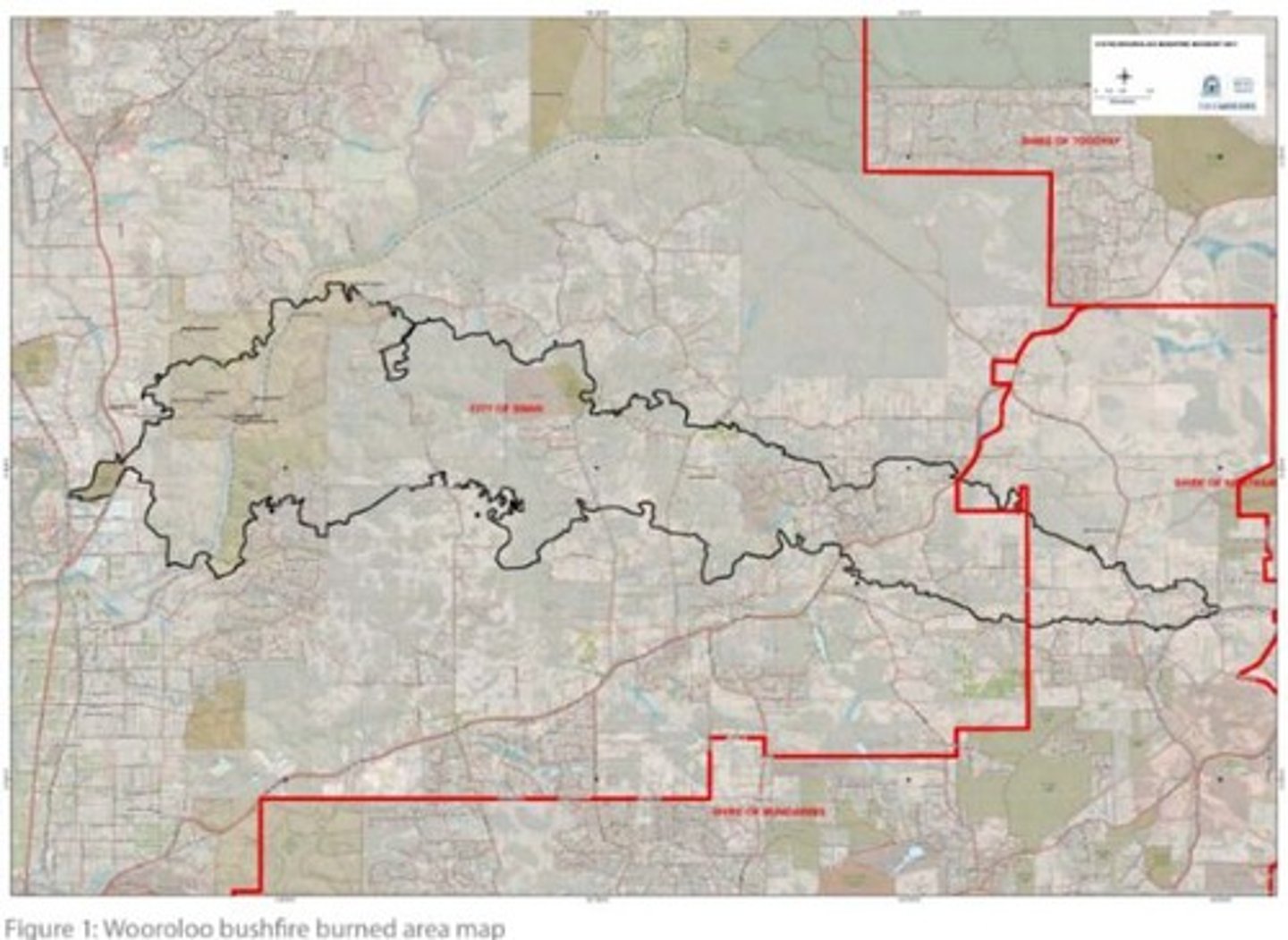
Escape Routes WOOROLOO
Roads for evacuation often blocked by fire.
Infrastructure Damage WOOROLOO
Fire melted non-stone or metal materials.
Aboriginal damage WOOROLOO
18 heritage sites impacted
economic impacts WOOROLOO
insurance claims related to the bushfire totaled approximately $91 million, encompassing over 1,000 claims for destroyed or damaged homes, vehicles, and other property .
social impacts WOOROLOO
3 evacuation centres were set up by department of communities with up to 900 people in attendance. The decision to open three evacuation centres was based on the number and geographical location of impacted residents, as well as COVID-19 considerations including social distancing requirements.
bushfire mitigation WOOROLOO
controlled burning was used to reduce fuel loads in high-risk areas prior to the bushfire season.
bushfire mitigation effectiveness WOOROLOO
Areas with recent prescribed burns saw significantly less damage, suggesting reduced fire intensity.
bushfire mitigation limitations WOOROLOO
In the case of Wooroloo, the rapid fire spread and extreme weather conditions overwhelmed some mitigated areas, showing that controlled burning alone isn’t always enough.
Fuel loads were still too high in some places due to wet conditions in the previous year encouraging regrowth, and not all areas had undergone prescribed burns in time.
bushfire preparedness WOOROLOO
The Emergency WA website and text alerts were used to issue real-time warnings and evacuation advice.
DFES and local councils promoted bushfire survival plans and community education prior to fire season.
Community hubs were set up post-fire to support displaced people.
bushfire preparedness effectiveness WOOROLOO
The Emergency WA system helped inform thousands of residents to evacuate early — likely saving lives.
DFES reported that over 1,000 residents safely evacuated, minimizing injury or death despite the scale of the fire.
bushfire preparedness limitations WOOROLOO
Not all residents had bushfire survival plans, and some didn’t evacuate despite warnings.
Internet or mobile outages in some areas impacted communication, leading to delayed responses.
mitigation definition
strategies used to reduce the impact and risk of a hazard
preparedness definition
the measures taken to prepare for, respond to, and recover from emergencies and disasters
Scale of spatial impact
The geographic extent or area over which a hazard or phenomenon occurs.
Mitigation
Strategies and actions taken to reduce or eliminate the severity and impacts of hazards or environmental issues.
Preparedness
The level of readiness of people, communities, and governments to anticipate, respond to, and recover from natural or human-induced hazards.
Wooroloo Bushfire
A catastrophic natural event that occurred in the Perth Hills in 2021, burning over 10,500 hectares of land.
Fire Triangle
The three components needed to start a fire: fuel, heat, and oxygen.
Duration
Refers to the length of time that a hazard event lasts.
Mitigation
Strategies and actions taken to reduce or eliminate the severity and impacts of hazards or environmental issues.
Preparedness
The level of readiness of people, communities, and governments to anticipate, respond to, and recover from natural or human-induced hazards.
Wooroloo Bushfire
A catastrophic natural event that occurred in the Perth Hills in 2021, burning over 10,500 hectares of land.
Hazards
Occur when the forces of nature combine to become destructive and a potential to damage the environment or infrastructure
Ecological Hazards
Are biological (diseases) or chemical hazard that has the impact adversely on the wellbeing of people or the environment
Natural hazards
Are atmospheric, hydrological and geomorphic processes and events in our environment that have potential to affect people adversely
Atmospheric hazards
Are created from weather processes
Geomorphic hazards
Are created by the movement of the earth's surface or crust
Hydrological hazards
Are those that involve the movement and distribution of water
Spatial distribution
The arrangement of geographical phenomena or activities across the earth's surface
Temporal distribution
The distribution (spread or pattern) of geographical phenomena over time
Magnitude
The strength of a hazard or how large and important a natural hazard event is
Duration
Refers to the length of time that a hazard event lasts
Frequency
Refers to how often a hazard event occurs in a particular area/country
Probability
Is the prediction that a hazard event will occur based on scientific observations or relevant factors to the hazard
Hazard preparedness
Involves planning the interventions required to prevent the effects of the hazard
Hazard mitigation
Involves the implementation of the strategies to eliminate or minimize the severity of a hazard
Hazard Risk management
The process of identifying and controlling hazards that could cause harm to people through measures before, during and after the hazard
Spatial technologies
Are any software or hardware that interacts with real world locations
Zoonotic disease
Infectious diseases that can pass from animals to humans
bushfires
Uncontrolled fires located in natural vegetation occurring in rural and semi-rural areas
topography
The physical features of an area
Fuel
Any material that burns in a fire
Fuel load
Quantity of fuel available
Less developed country
a low-income country with low levels of human and economic development.
More developed country
a high-income country with high levels of human and economic development.
Socioeconomic
Relating the interaction of social and economic factors
infectious diseases definition
Describe diseases that can spread from one person to another either directly or indirectly
infectious disease example
HIV – infectious disease, a virus that targets the immune system, which weakens the Bodys ability to fight infections and some cancers
Most common in east and southern Africa region
animal transmitted disease definition
Can also be referred to as vector borne diseases, these diseases are transferred to humans from animals