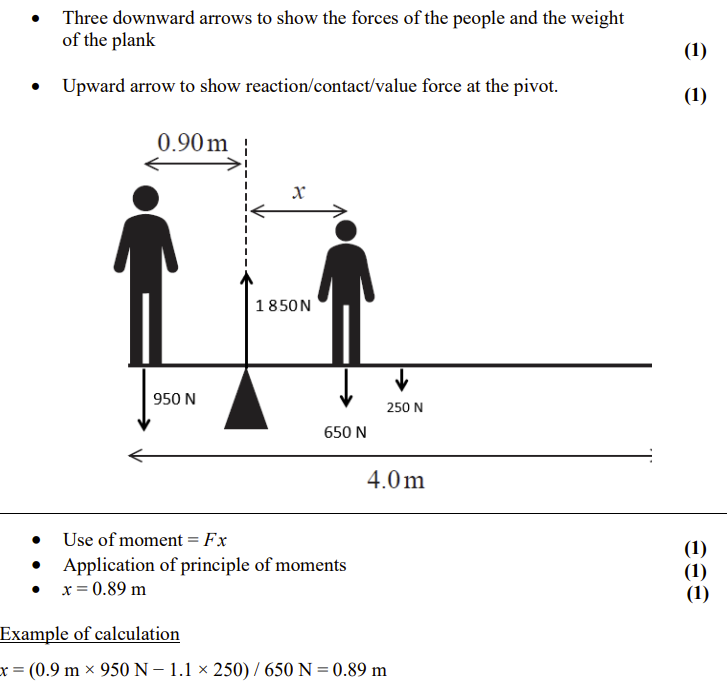
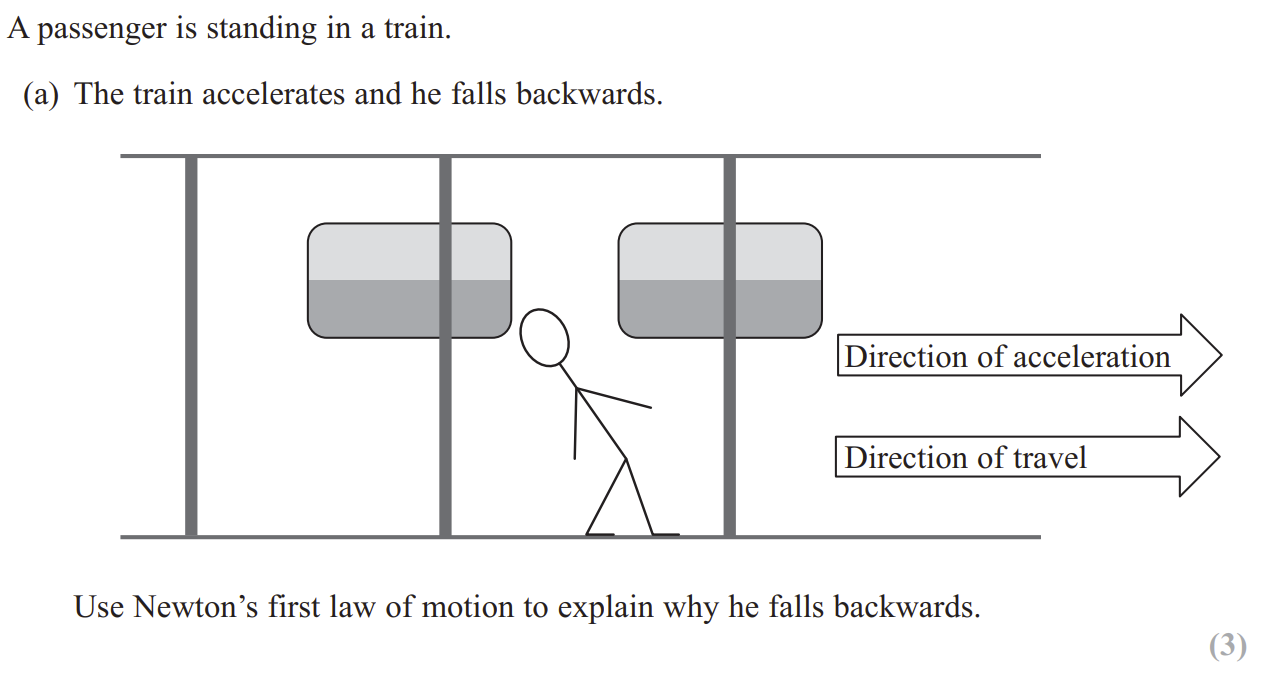
Physics Mechanics
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A - Level Edexcel Physics Revision
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms

A

key word ‘vacuum’ D

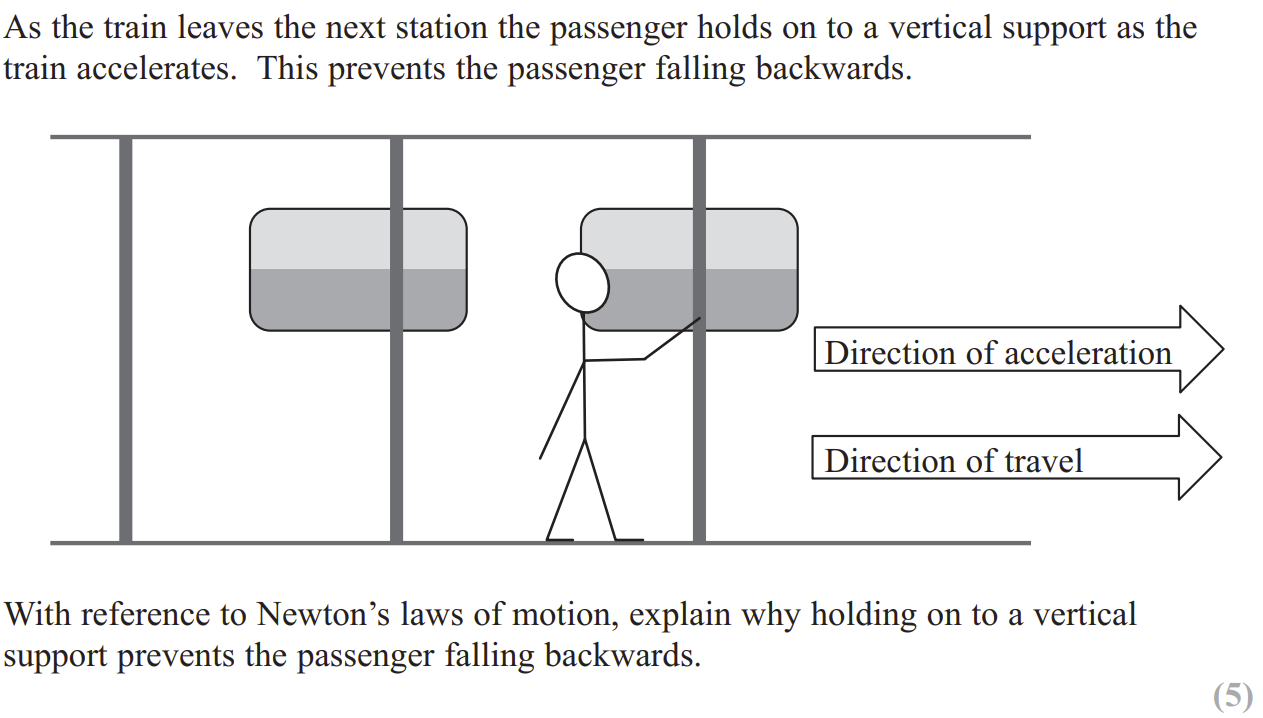

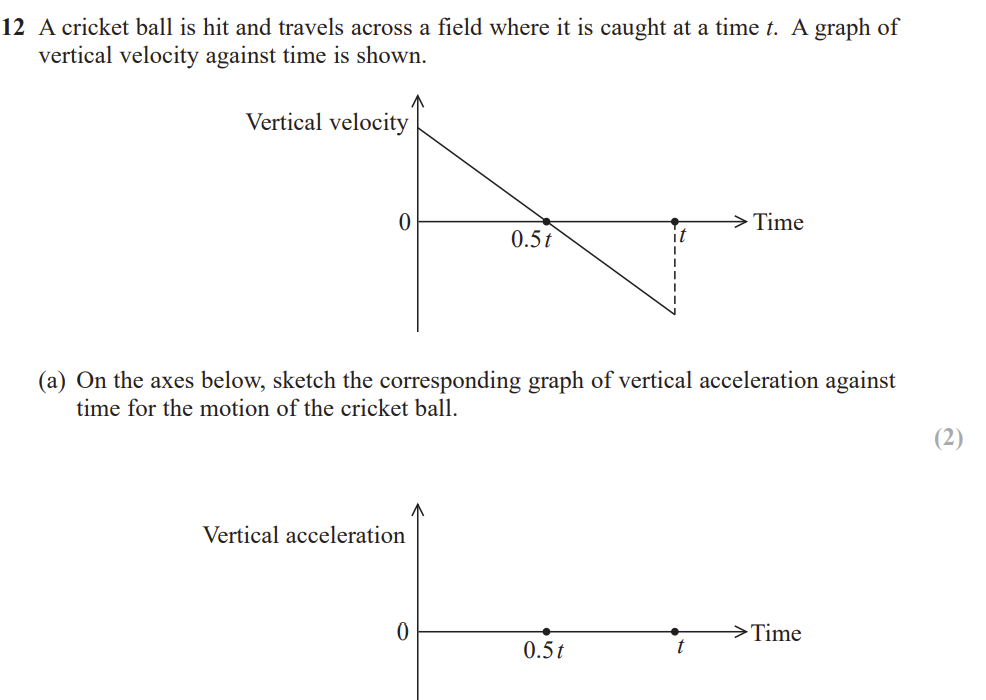
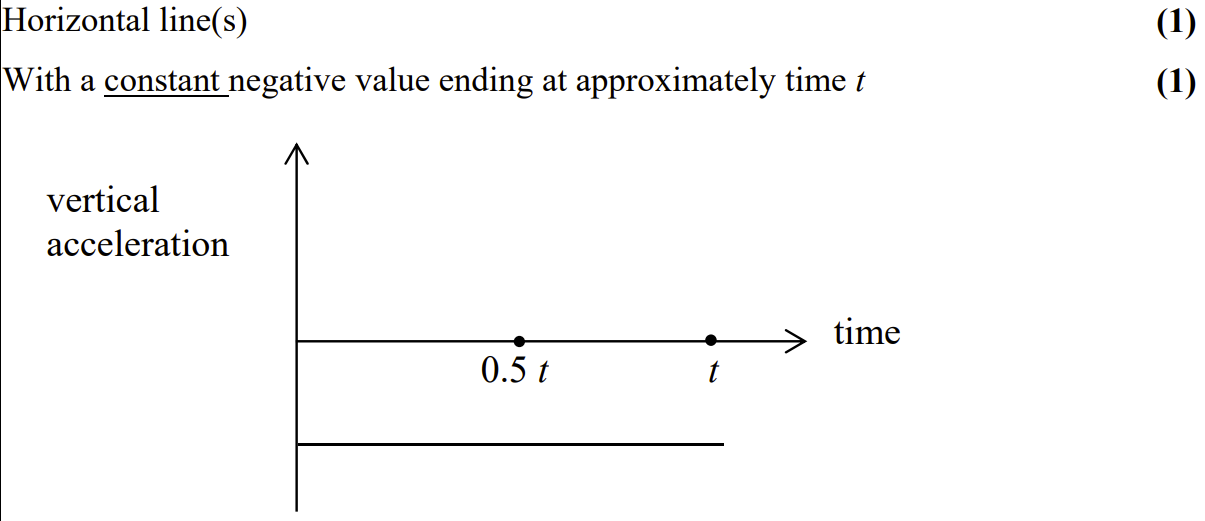
sketch the corresponding acceleration- time graph
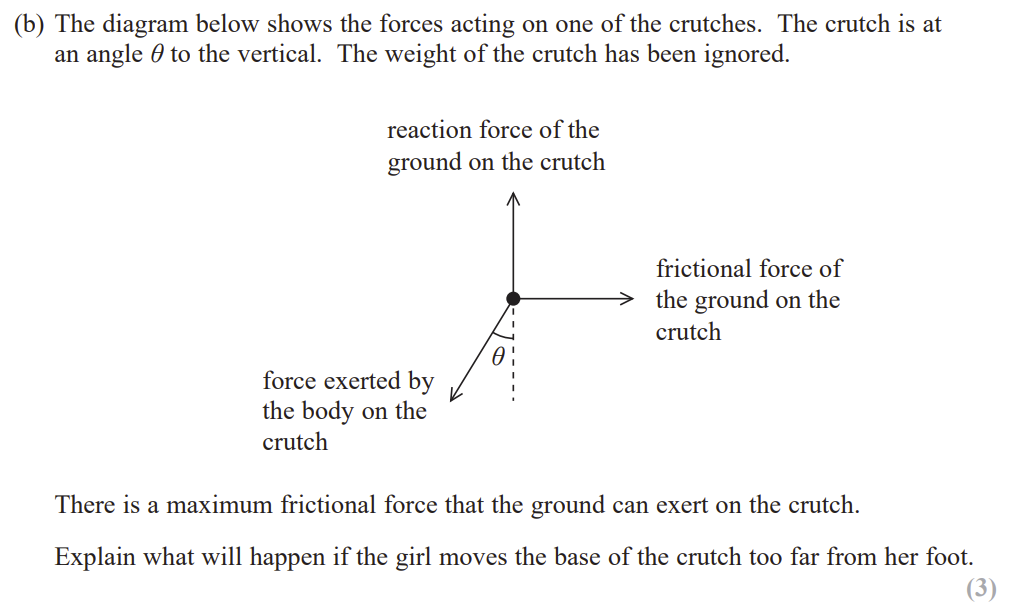
Explain why assumptions about calculated accelerations could be incorrect [2]
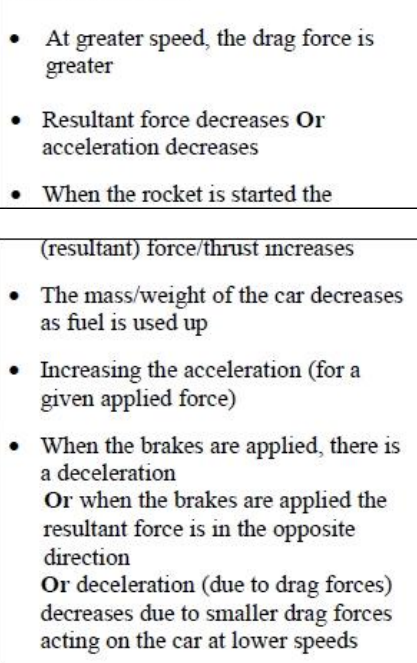
Air resistance/ friction increases at greater speeds, so acceleration decreases
Car could brake at a greater force than the previous one

D

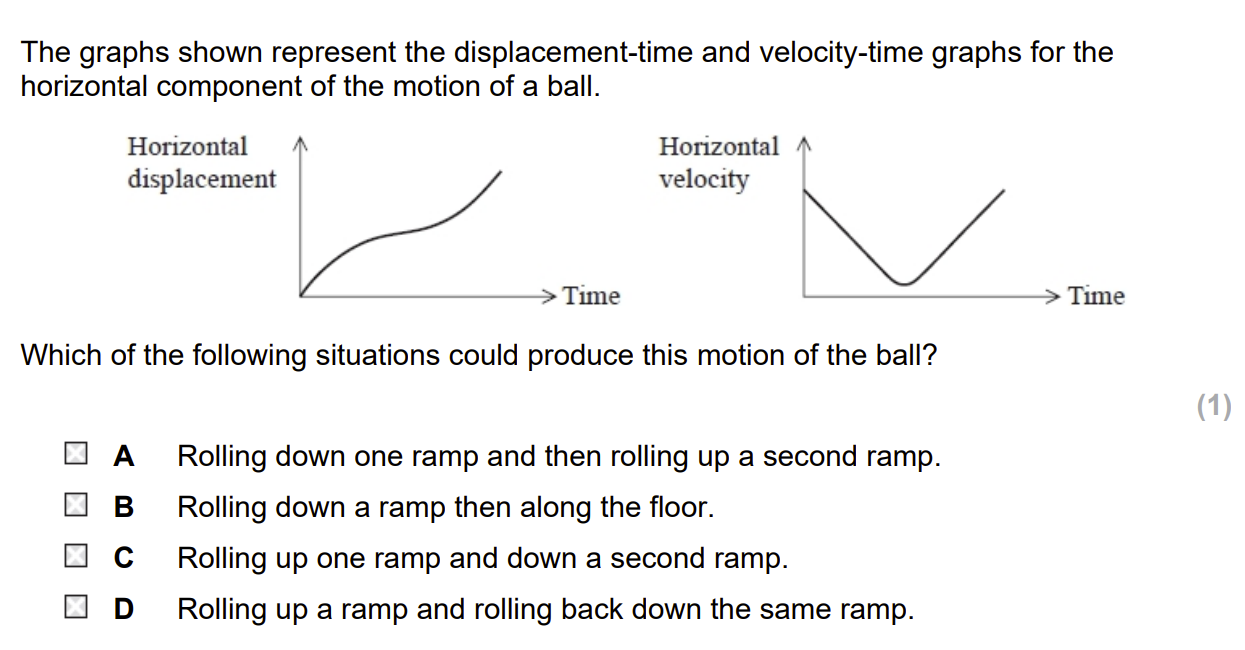
C
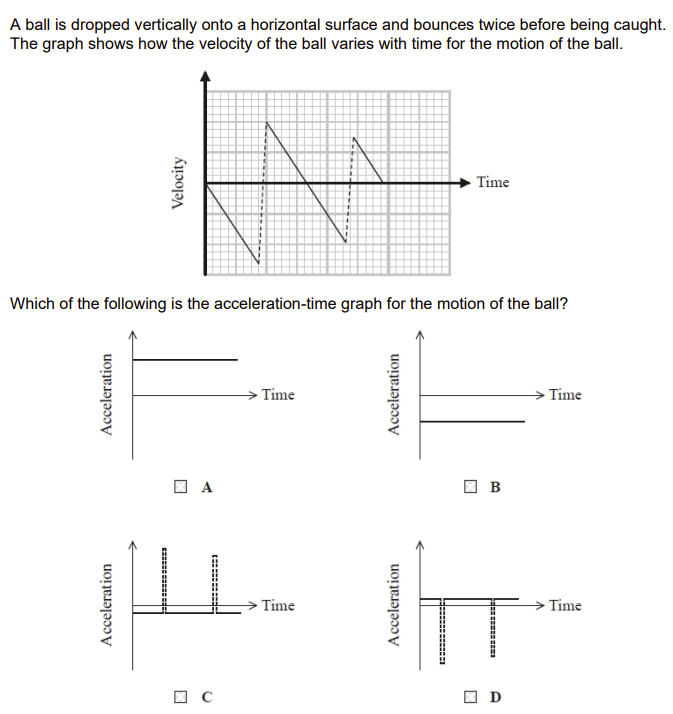
C
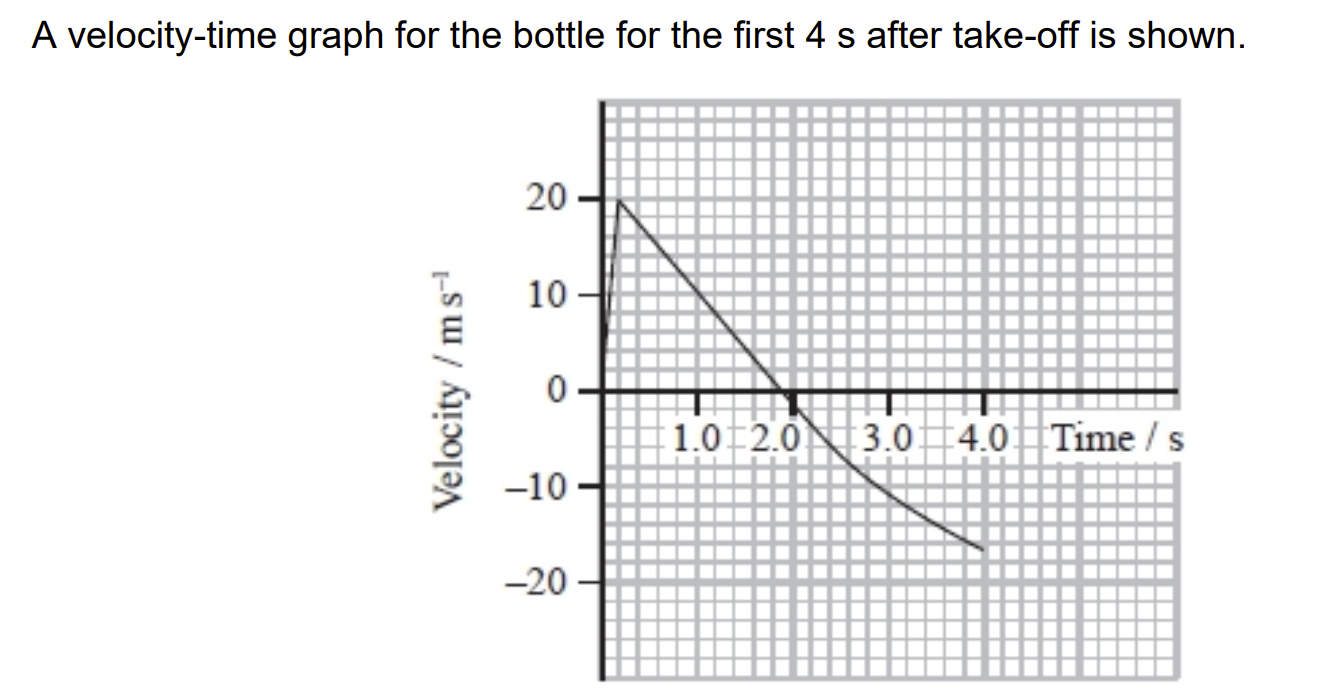
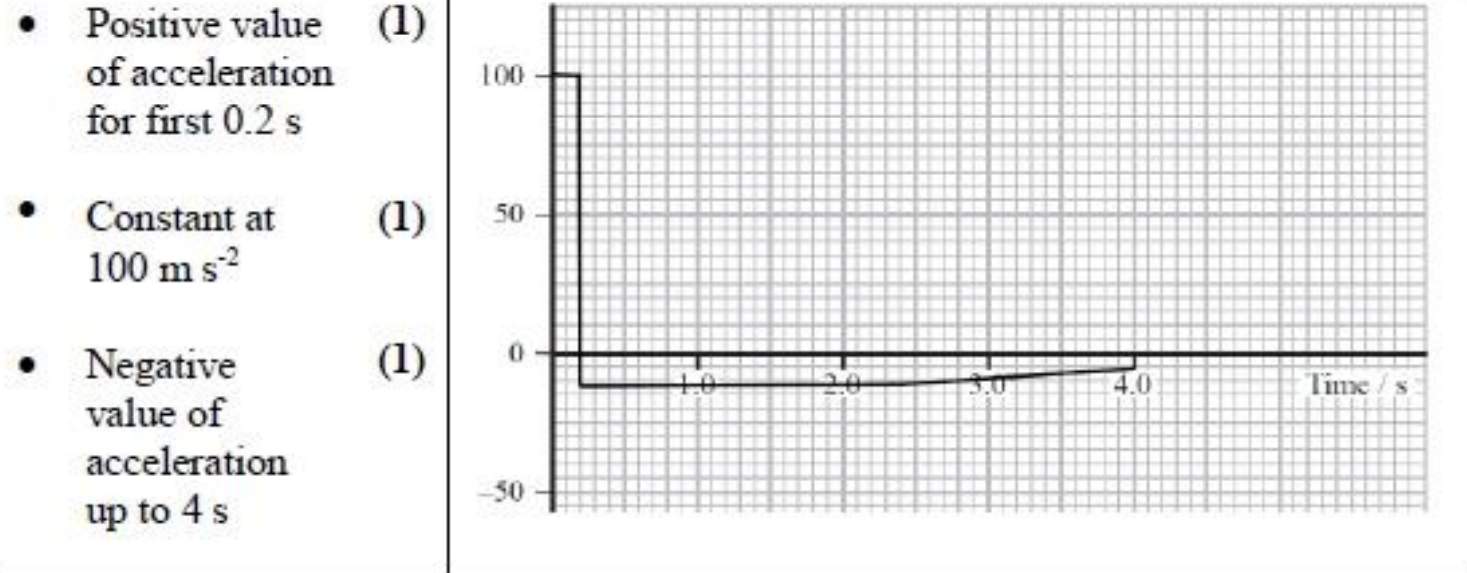
![<p>AKA discuss why the shape of the graph is that [6]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b5e59ab1-7515-4464-b9e1-897f9faab421.png)
AKA discuss why the shape of the graph is that [6]
![<ul><li><p>Explain how the velocities have been calculated from the successive vertical positions of the shuttlecock. [2]</p></li><li><p>State why these velocities have been plotted at the mid-range of the time interval [1]</p></li><li><p>State, with a reason, two pieces of evidence from the graphs that show that the shuttlecock does not follow the motion of a projectile moving freely under gravity. [3]</p></li><li><p>Show, using the velocity-time graph, that the maximum height gained by the shuttlecock is about 3 m.[3]</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/373e56fd-ba3b-41c4-ae01-897228575f80.png)
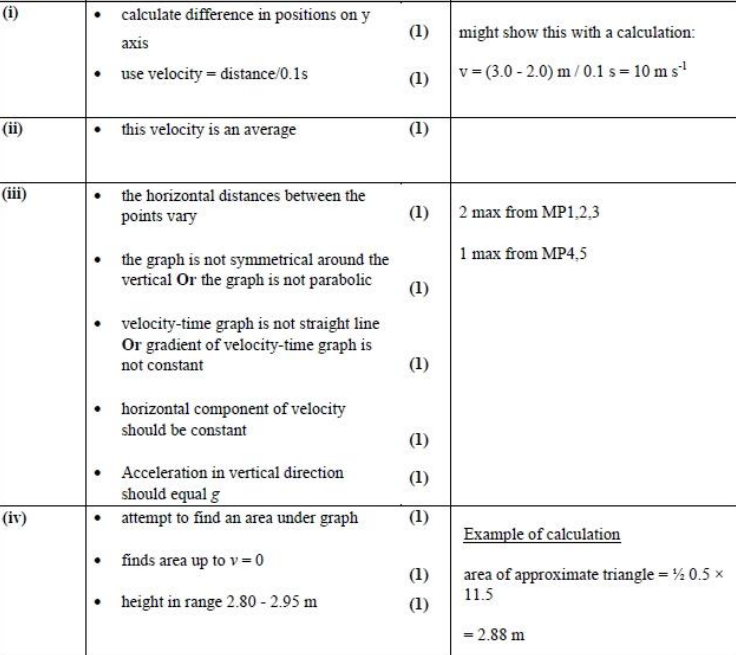
Explain how the velocities have been calculated from the successive vertical positions of the shuttlecock. [2]
State why these velocities have been plotted at the mid-range of the time interval [1]
State, with a reason, two pieces of evidence from the graphs that show that the shuttlecock does not follow the motion of a projectile moving freely under gravity. [3]
Show, using the velocity-time graph, that the maximum height gained by the shuttlecock is about 3 m.[3]
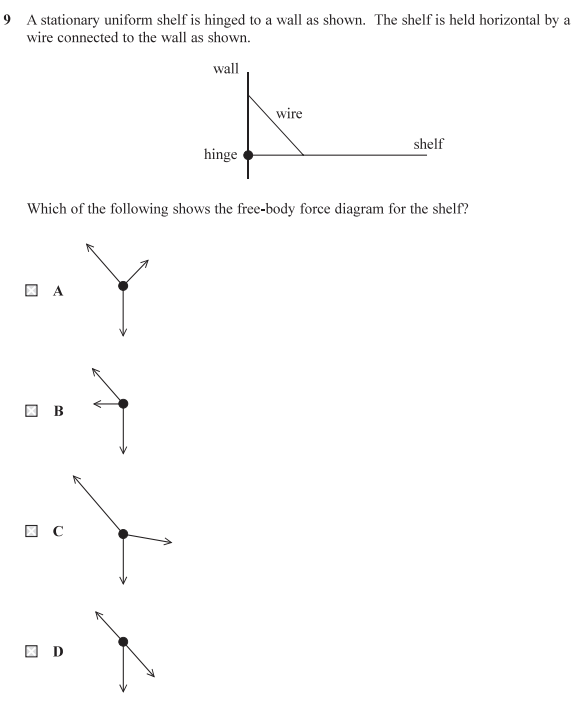
C - tip: look at the horizontal and vertical components instead of eyeing. make sure the cancel out
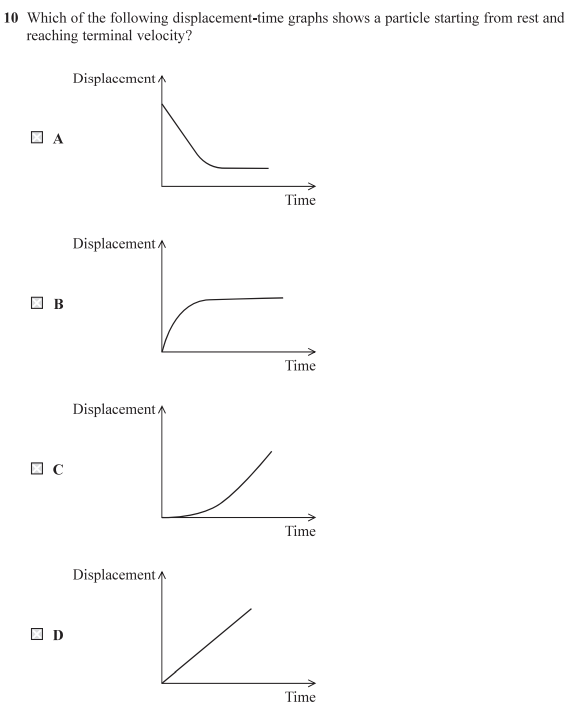
C- to reach constant velocity, velocity must first increase


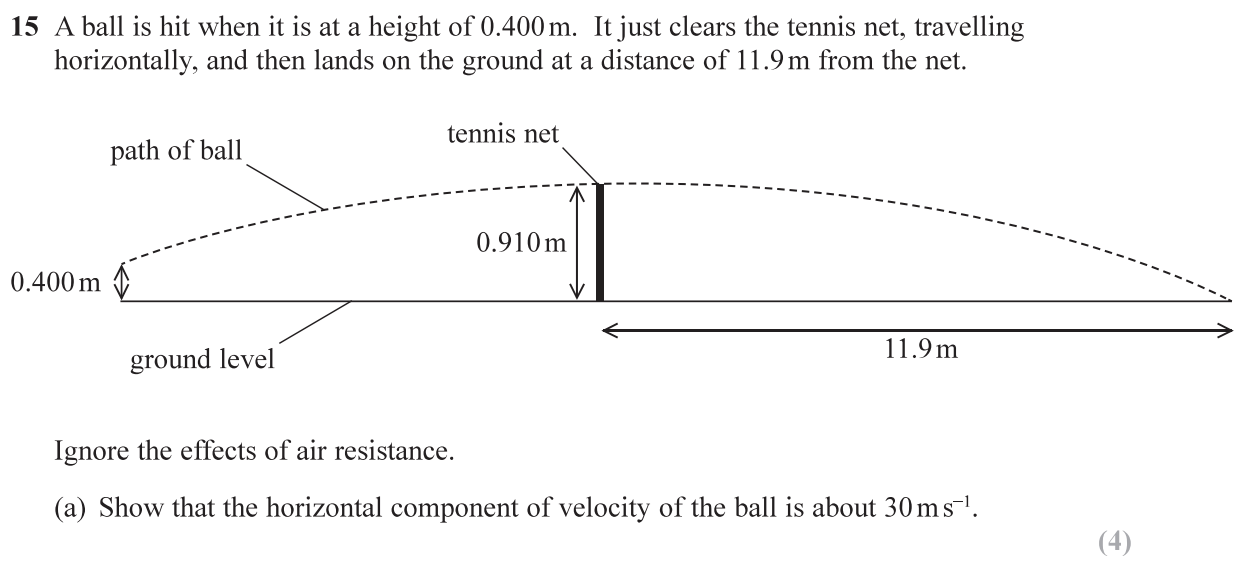

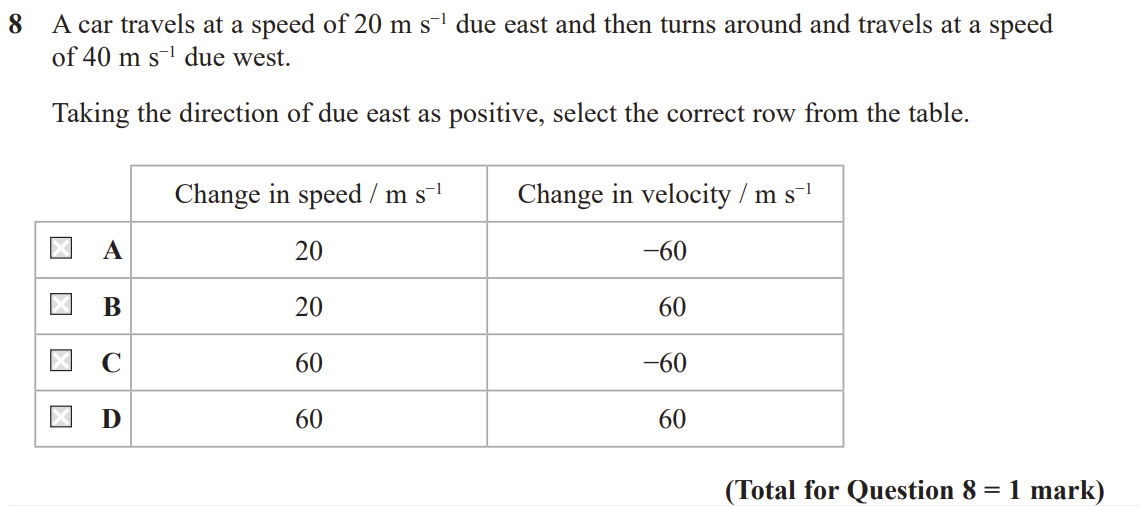
A

D
![<p>The force of the supporting ropes could cause the poles to fall inwards. By considering the vertical and horizontal components of the tension in one of the supporting ropes, explain why a larger value of θ creates a smaller force on the poles supporting the hammock. [5]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/73837bec-f406-476c-89b6-a717bf704523.png)
The force of the supporting ropes could cause the poles to fall inwards. By considering the vertical and horizontal components of the tension in one of the supporting ropes, explain why a larger value of θ creates a smaller force on the poles supporting the hammock. [5]
The idea that the horizontal force is the significant force. [1]
TH = T cos θ [1]
T = TV / sin θ [1]
TV does not change Or TV = (½) weight [1]
The horizontal component of tension/force decreases (as θ increases) Or Tension decreases (as θ increases) [1]
![<p>The idea that the horizontal force is the significant force. [1]</p><p>TH = T cos θ [1]</p><p>T = TV / sin θ [1]</p><p>TV does not change Or TV = (½) weight [1]</p><p>The horizontal component of tension/force decreases (as θ increases) Or Tension decreases (as θ increases) [1]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e2b3da8f-c054-4d85-b5fc-bb444159ebf7.png)

C
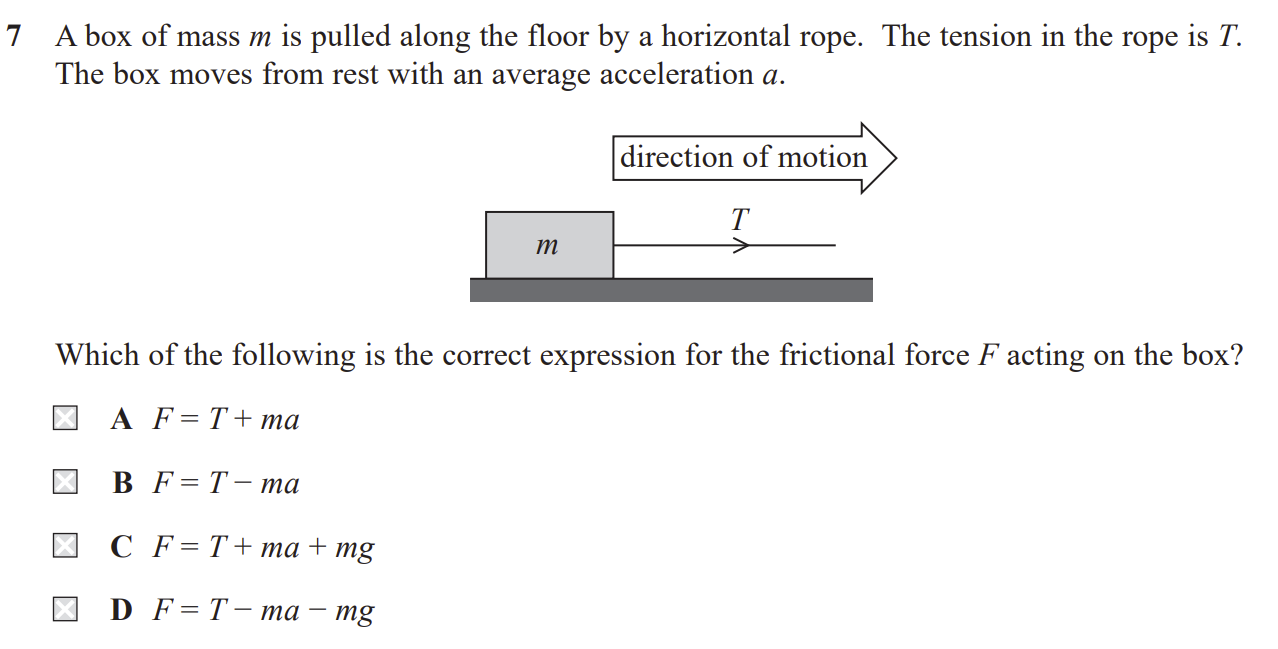
B
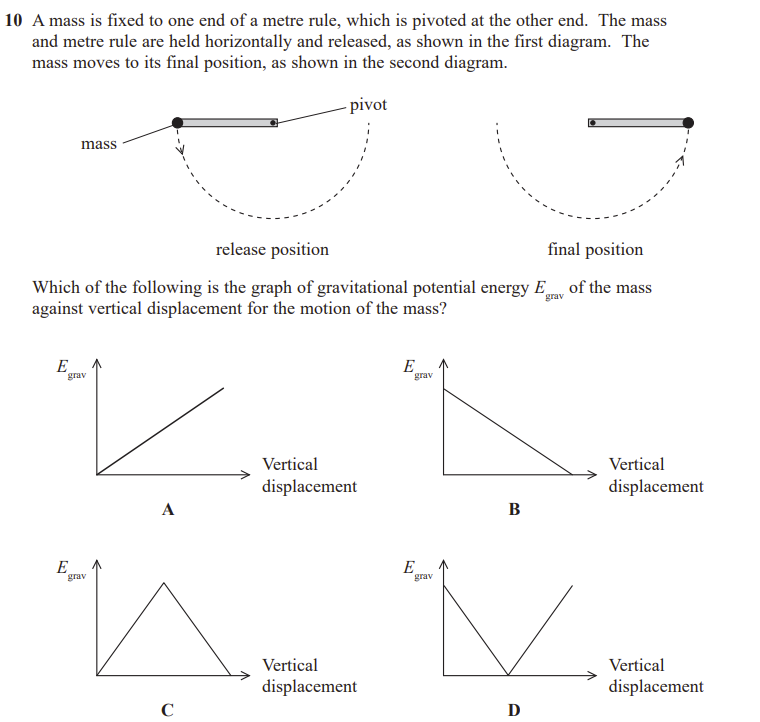
B









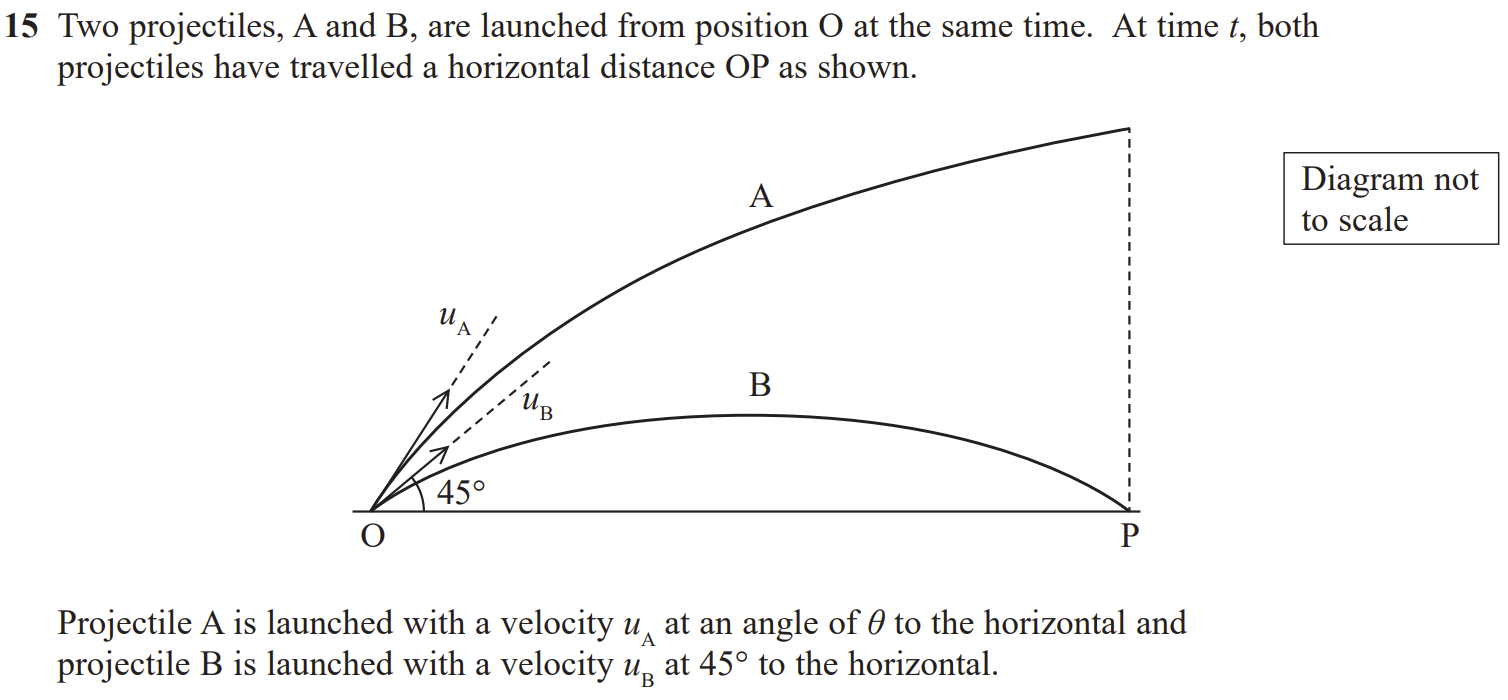
Explain why, for the paths of the two projectiles to be as shown, uA > uB.

![<p>On the axes below sketch labelled graphs for the vertical component of velocity against time for the motion of projectile A and projectile B between O and P. You may ignore the air resistance. [4]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6bdd78a1-f36e-4fcf-a0da-f0169a7fe4d3.png)
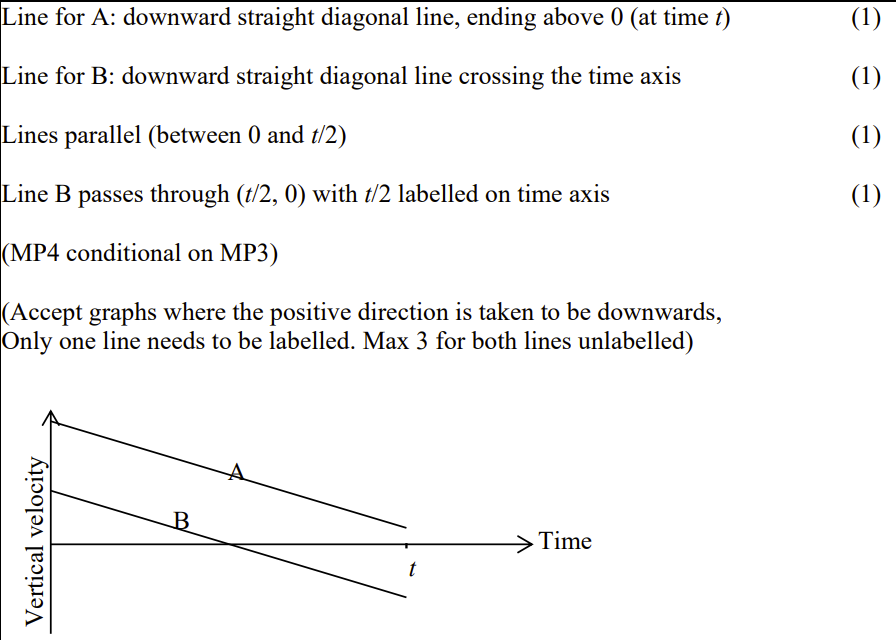
On the axes below sketch labelled graphs for the vertical component of velocity against time for the motion of projectile A and projectile B between O and P. You may ignore the air resistance. [4]


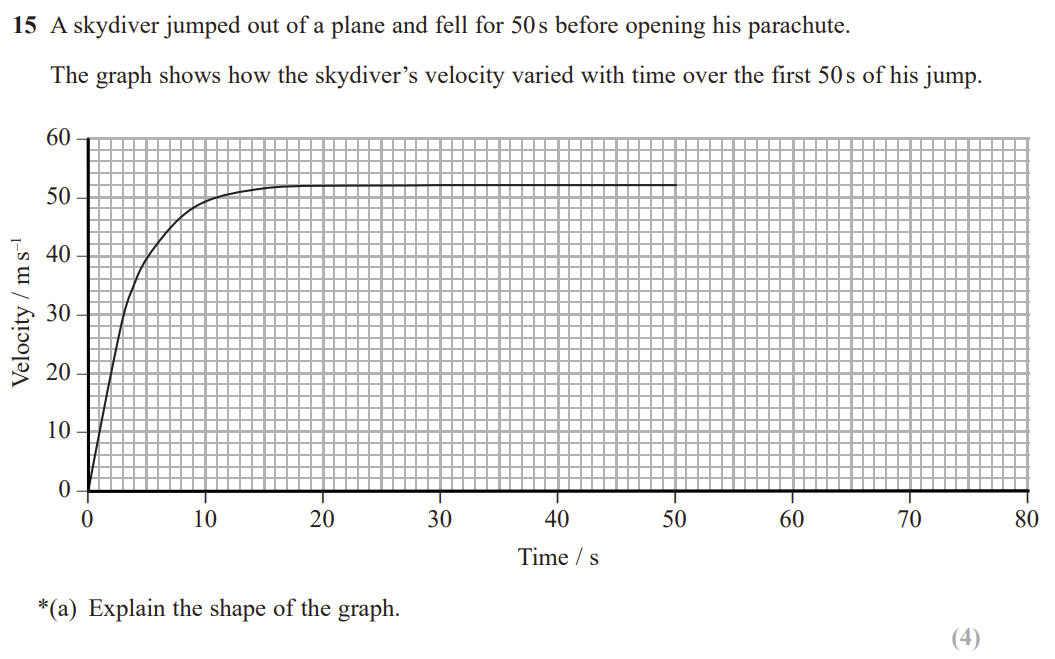

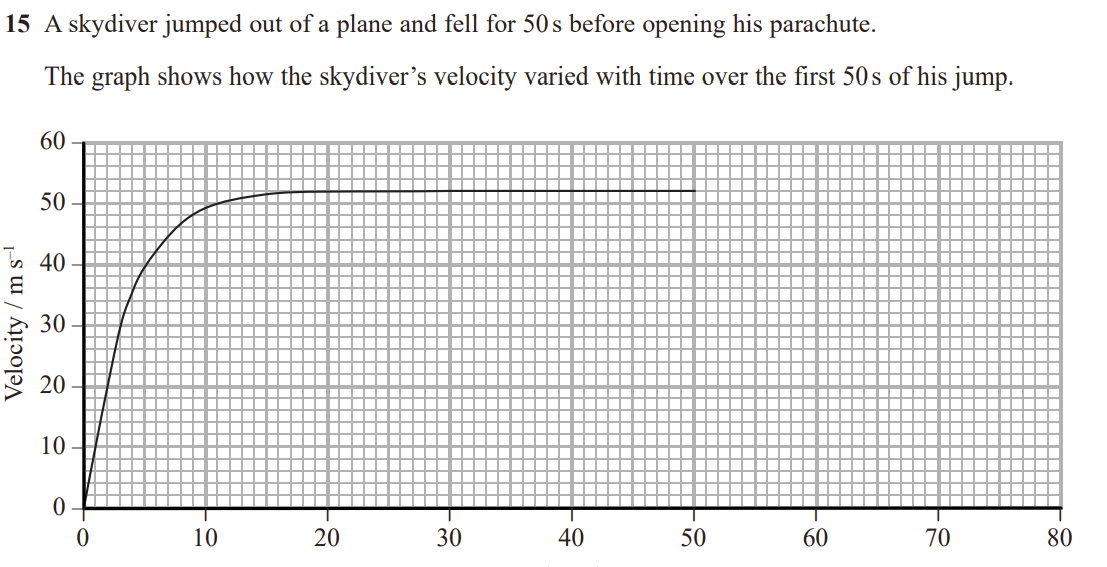
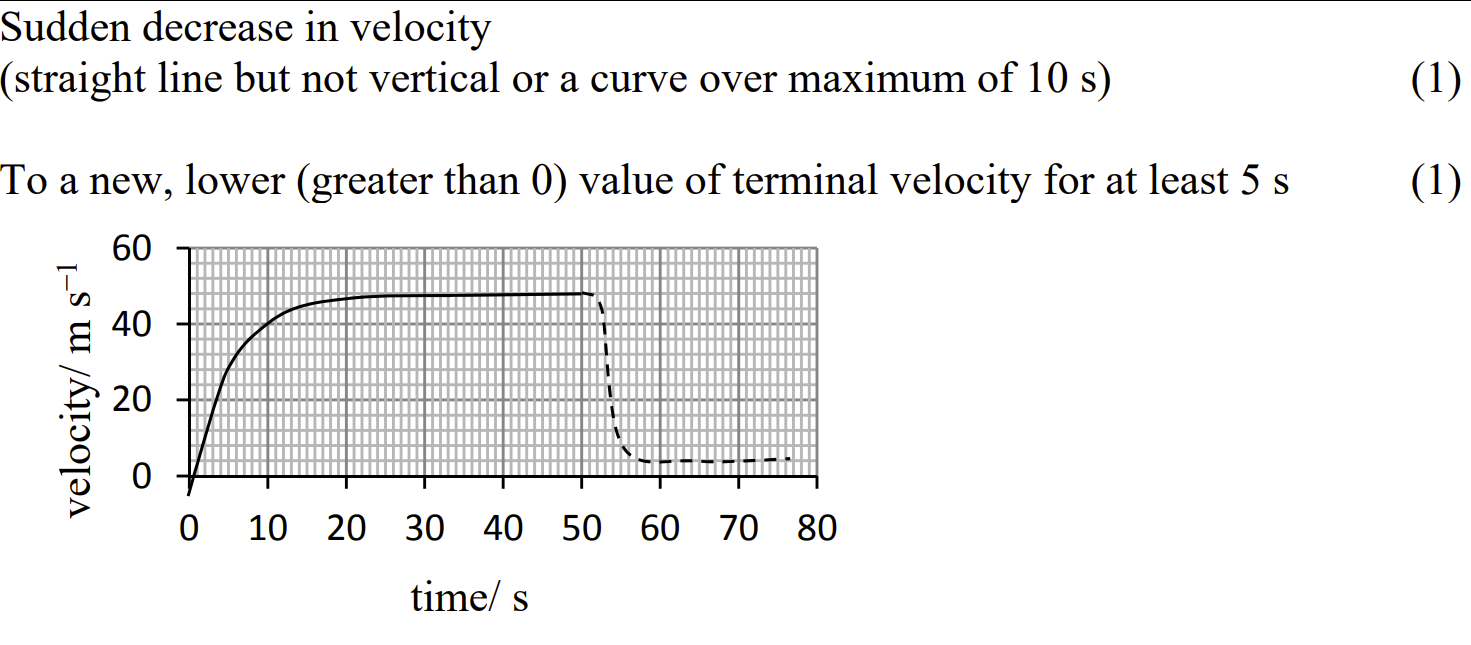
Sketch, on the graph above, the motion of the skydiver after he opens his parachute
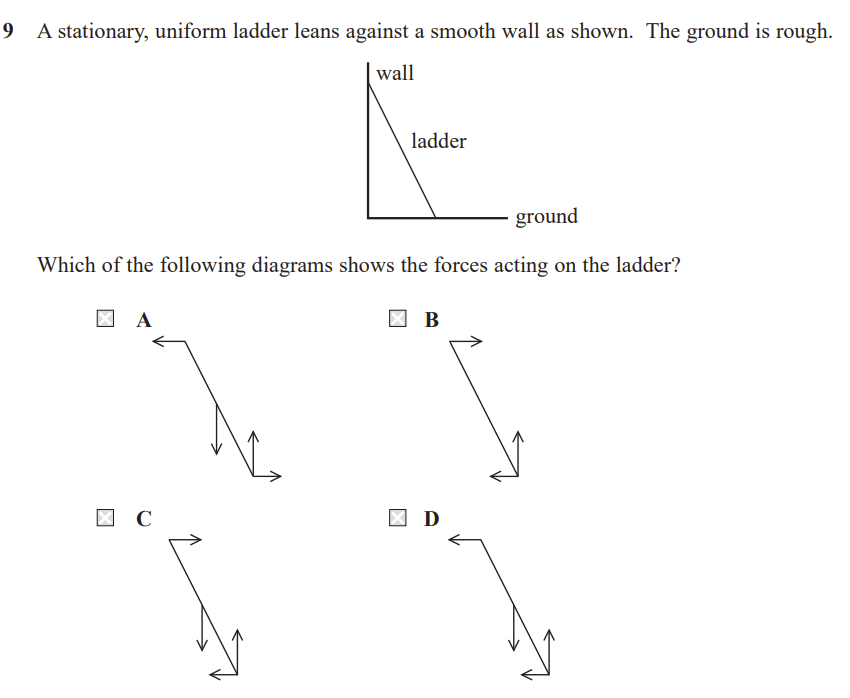
C