Midterm Exam Review for BSC1010L
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Steps of the Scientific Method
Observations, Testable Questions, Formulate hypothesis (null hypothesis vs alternative hypothesis), Test hypothesis (Experiment-where measurements collected), Collect/Analyze Data, Make conclusions (reject or accept hypotheses)
Independent Variable
Controlled (we can control this variable, the cause)
Dependent Variable
Response (changes in function of the independent variable, the effect)
Calculations: Mean
Average of a number set (addition of all data and divide by 'n')
Calculations: Standard deviation
Calculate by subtracting the mean from the data set, square the deviation, and then add the sum
Metric system-conversions
K H D b d c m
Example of Independent Variable
Type of food being given to yeast
Example of Dependent Variable
The CO2 production
Length
measured in base unit 'm' meters (know how to use a measure with a ruler)
Volume
measured in base unit 'L' liters (know how to use and measure with a pipette, graduated cylinder (meniscus) and by water displacement)
Mass
measured in base unit 'g' grams (know how to use a triple beam balance and digital scale-taring)
Temperature
measured in 'C' Celsius (know how to read a thermometer)
pH
measure of the concentration of H+ ions (H+)
Acid
more H+ ions than OH- ions (i.e. the lower the pH, the more H+ ions present)
Base (alkaline)
more OH- ions than H+ ions
pH scale
scale from 1 to 14 with 1 being the most acidic and 7 being neutral
pH indicators
cabbage juice and pH alkacid test paper
Buffer
solution that resists change, made by mixing weak acid with its salt
Carbohydrates
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides (starch)
Reagent: Benedict's
tests for presence of reducing sugars (blue is negative, green to reddish orange is positive) Includes hot plate for boiling water bath
Reagent: Iodine
tests for presence of polysaccharides-starch (bluish-black is positive, brown is negative) Drops of iodine in test tube
Proteins
made up of amino acids bound together by peptide bond
Reagent: Biuret
tests for presence of peptide bond in proteins (violet is positive). Adds drops of Biuret
Lipids
dissolve in non polar solvents but not in polar solvents such as water (insoluble in water)
Reagent: Sudan IV
tests for presence of lipids (red droplets/clumping is positive for lipids)
Grease spot test
test brown paper for presence of lipids (translucent is positive for lipids)
Compound Microscope
know the parts of the compound microscope and functions (ocular lens, objective lens, condenser, iris diaphragm, course and fine adjustment knob)
Ocular lens
lens that you look through, magnification 10x
Objective lens
magnify the image and improve resolution (4x, 10x, 40x, 100x)
Total Magnification (TM)
ocular lens x objective lens
Field of view
area that you can see through the ocular and objective lens
Dissecting Microscope
for specimen that are too large to view with a compound microscope (ex: external structures of organisms)
Eukaryotic cells
contain nuclei and membrane bound organelles
Plant cells
contain chloroplasts (chlorophyll) for photosynthesis, cell wall, central vacuole
Amyloplasts
for storing starch (dark round structures stained with iodine)
Diffusion
passive, directional movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
Osmosis
diffusion of water across permeable membrane (when molecules cannot cross membrane) to areas of high concentration of molecules
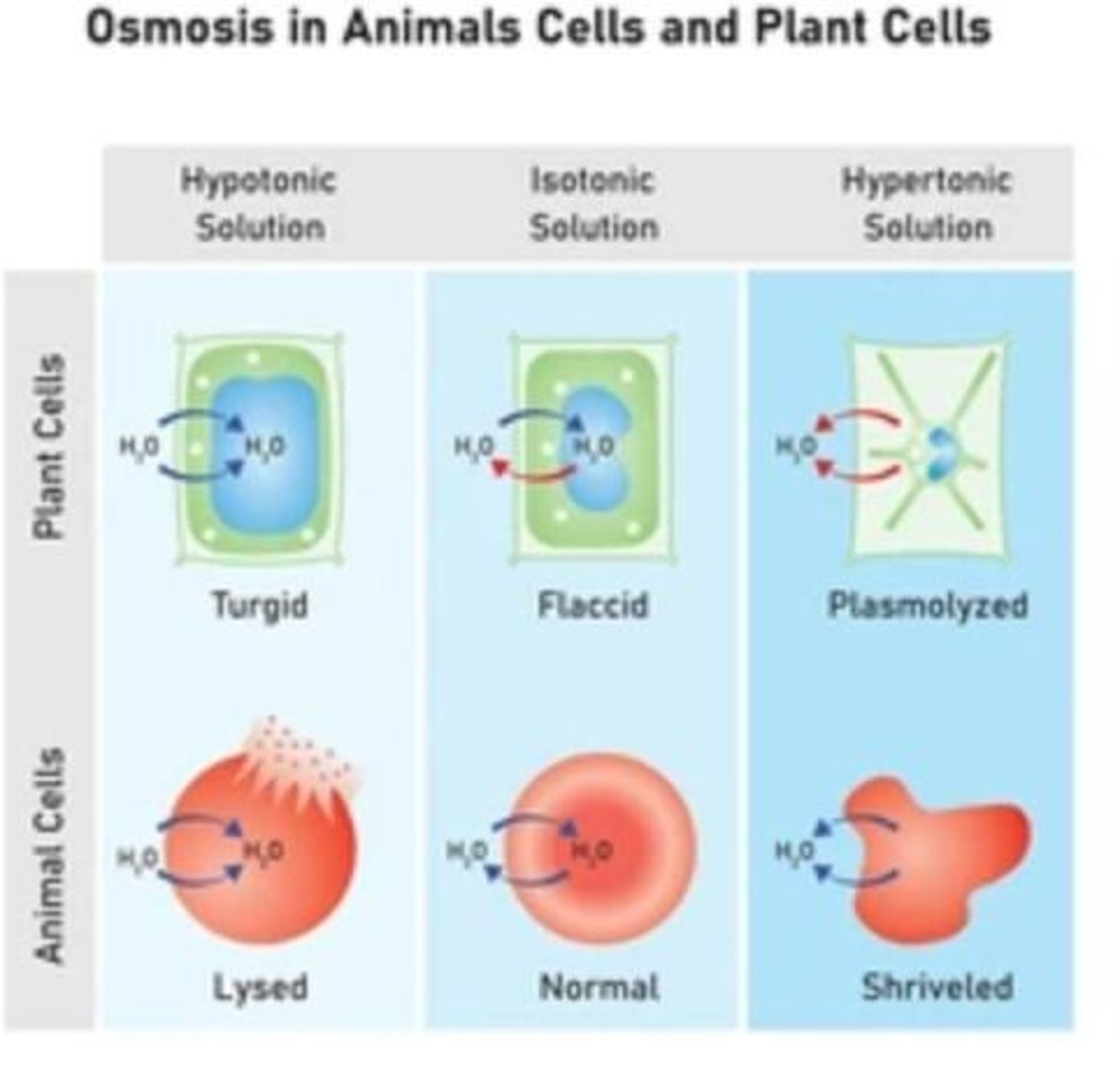
Hypotonic
lower concentration of solutes
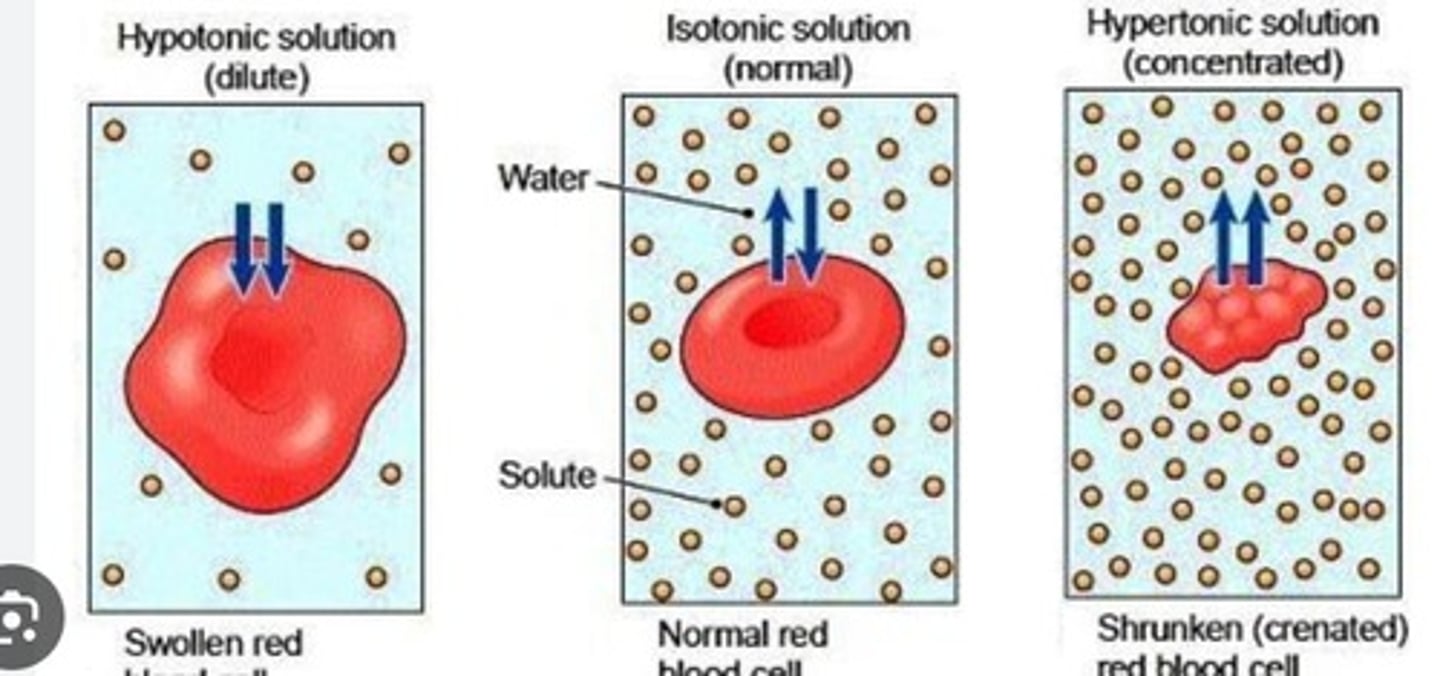
Hypertonic
high concentration of solute
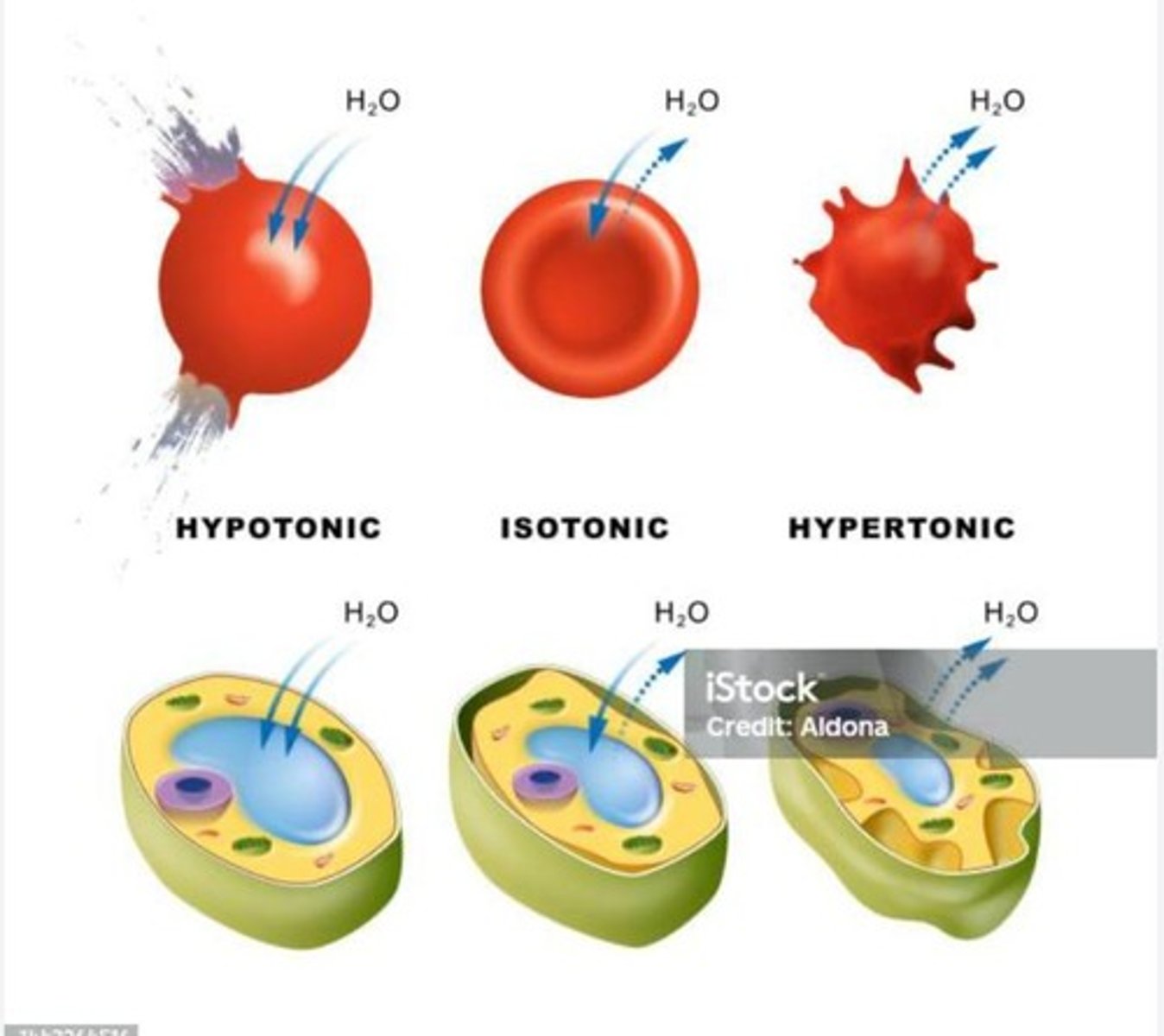
Isotonic
two solutions have equal concentrations of solutes
Water Potential
in animal cells, if water flows into the cell by osmosis, the cell can hemolyze (burst). While plant cells can swell without bursting due to their cell walls
Condenser
focuses light on specimen
iris diaphragm
Adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen.
fine adjustment knob
Moves the stage slightly to sharpen the image
course adjustment knob
Moves the stage up and down for focusing
null hypothesis
no significant difference between two groups
alternative hypothesis
proposes specific relationship between two groups