CSC 230 (3) - Searching & Sorting
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
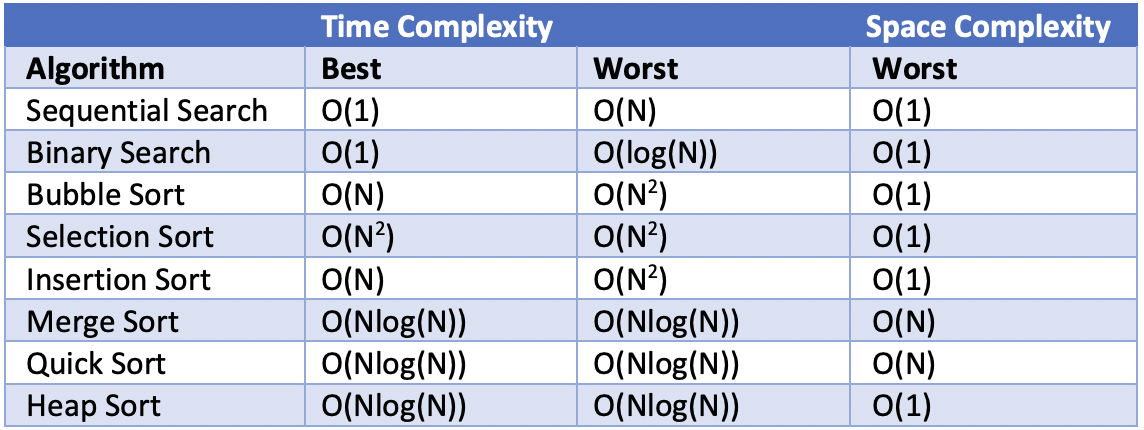
Time and Space Complexity of Seach and Sort Algorithms
What is linear (sequential) search?
A search method where you check each element of a list or array one by one until you find the target or reach the end.
Does linear search require a sorted array?
No, it works on both sorted and unsorted arrays.
Steps to perform linear search:
Start at the first element.
Compare it to the target.
If it matches → found.
If not → move to the next element.
Repeat until the target is found or end of array is reached.
Example: Perform linear search for target = 4 in array [3, 8, 4, 1, 9].
Check 3 → not 4
Check 8 → not 4
Check 4 → found at index 2
Time complexity of linear search?
O(N) in worst case, O(1) in best case (if target is first element).
What is binary search?
A search method for sorted arrays where the search space is repeatedly divided in half until the target is found or no elements remain.
Steps to perform binary search:
Find the middle element of the array.
Compare it to the target.
If equal → found.
If target < middle → search left half.
If target > middle → search right half.
Repeat steps 1–2 on the selected half until found or no elements remain.
Example: Perform binary search for target = 4 in array [1, 3, 4, 8, 9].
Step 1: Middle = 4 → found at index 2
Example: Perform binary search for target = 8 in array [1, 3, 4, 8, 9].
Step 1: Middle = 4 → target > 4 → search right half
[8, 9]Step 2: Middle = 8 → found at index 3
Does binary search work on unsorted arrays?
No, the array must be sorted.
Time complexity of binary search?
O(log N) in worst case, O(1) in best case.
When performing linear or binary search on an array, what should you report as the answer?
The index of the target element in the array (or “not found” if it doesn’t exist).
Sort the following sequence using the Bubble Sort Algorithm
Sweep | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
1 | |||||
2 | |||||
3 | |||||
4 |
Sweep | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 5 |
2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Sort the following sequence using the Selection Sort Algorithm
Sweep | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
1 | |||||
2 | |||||
3 | |||||
4 |
Sweep | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Sort the following sequence using the Insertion Sort Algorithm
Sweep | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
1 | |||||
2 | |||||
3 | |||||
4 | |||||
5 |
Sweep | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
3 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
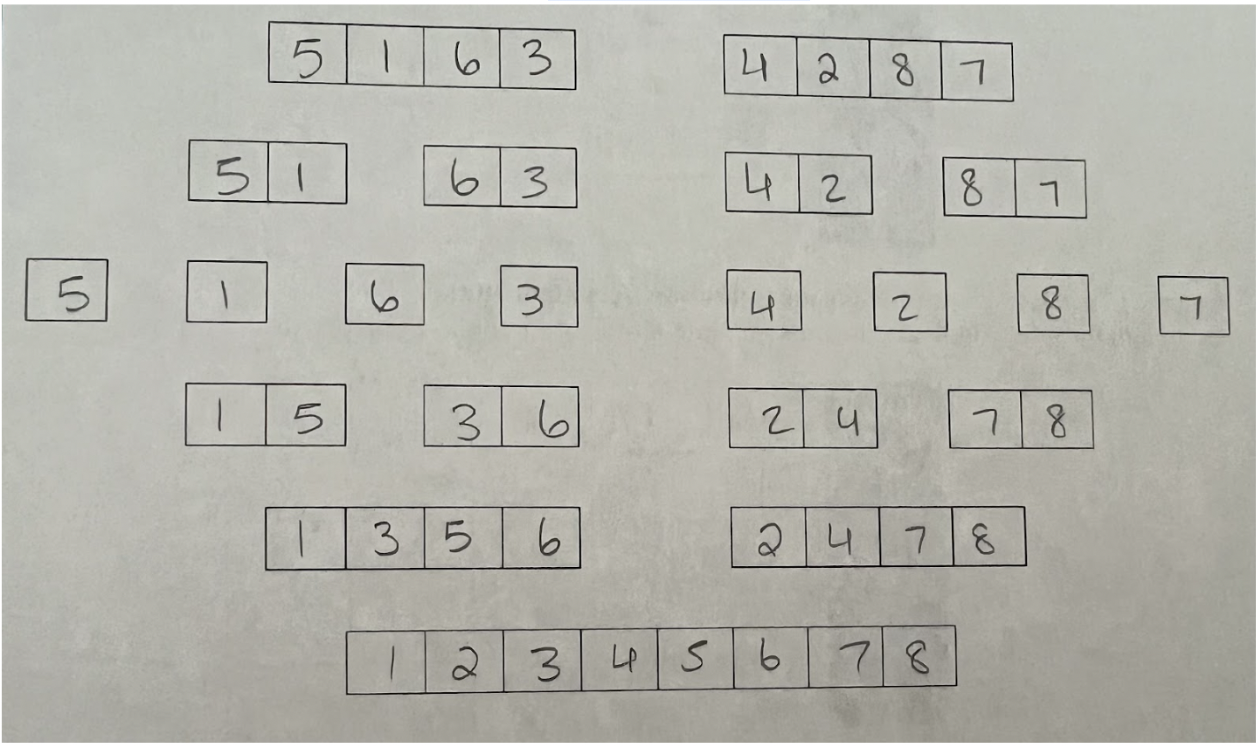
Sort the following sequence using the Merge Sort Algorithm
[5, 1, 6, 3, 4, 2, 8, 7]
DO PROBLEM SET 7 NOW AND CHECK WITH ANSWER KEY