Metabolic States
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
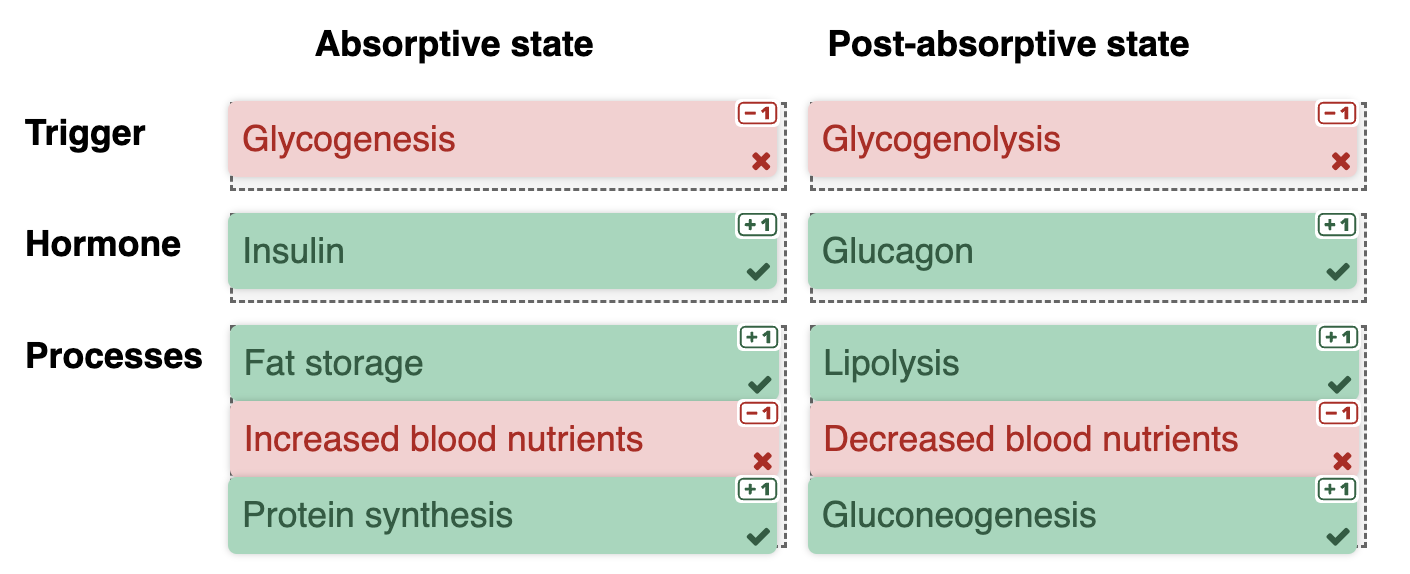
Absorptive State
‘Fed’ state.
Occurs after eating when digesting food. Lasts ~4 hrs.
Amino acids & glucose go to the bloodstream. Fats go to lymphatic system.
Effects:
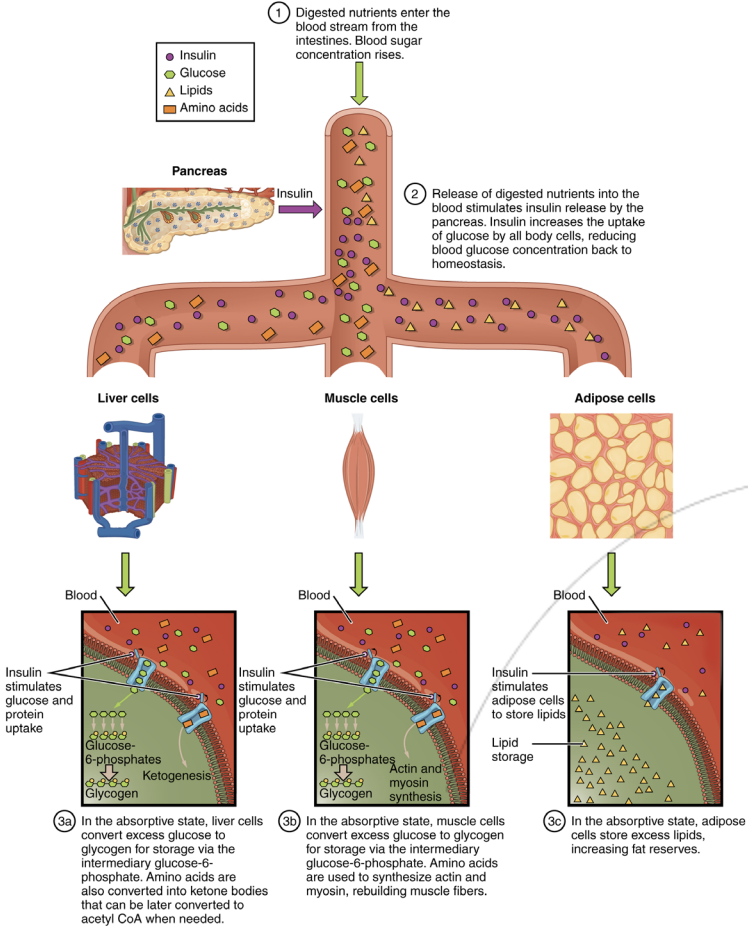
Food digestion results in a rise in blood glucose
Absorption of glucose (breakdown product of carbohydrates) into the bloodstream
Presence of elevated blood glucose & parasympathetic activity triggers insulin release
β cells (beta) from pancreas release insulin
Stress can inhibit parasympathetic activity, and in turn inhibit insulin release. This is how conditions such as diabetes can develop.
Insulin
Released into the bloodstream
Stimulates liver hepatocytes, muscle cells & adipose cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
Once glucose is absorbed, glycolysis occurs immediately to ensure a concentration gradient is maintained.
Higher glucose concentration in bloodstream
Lower concentration inside cells
Hepatocytes & muscle cells convert glucose to glycogen (glycogen synthesis)
Inhibits liver gluconeogenesis
Prevents creation of more glucose
Stimulates adipose cells to store excess lipids as blood glucose can provide adequate energy to the body
Absorptive State
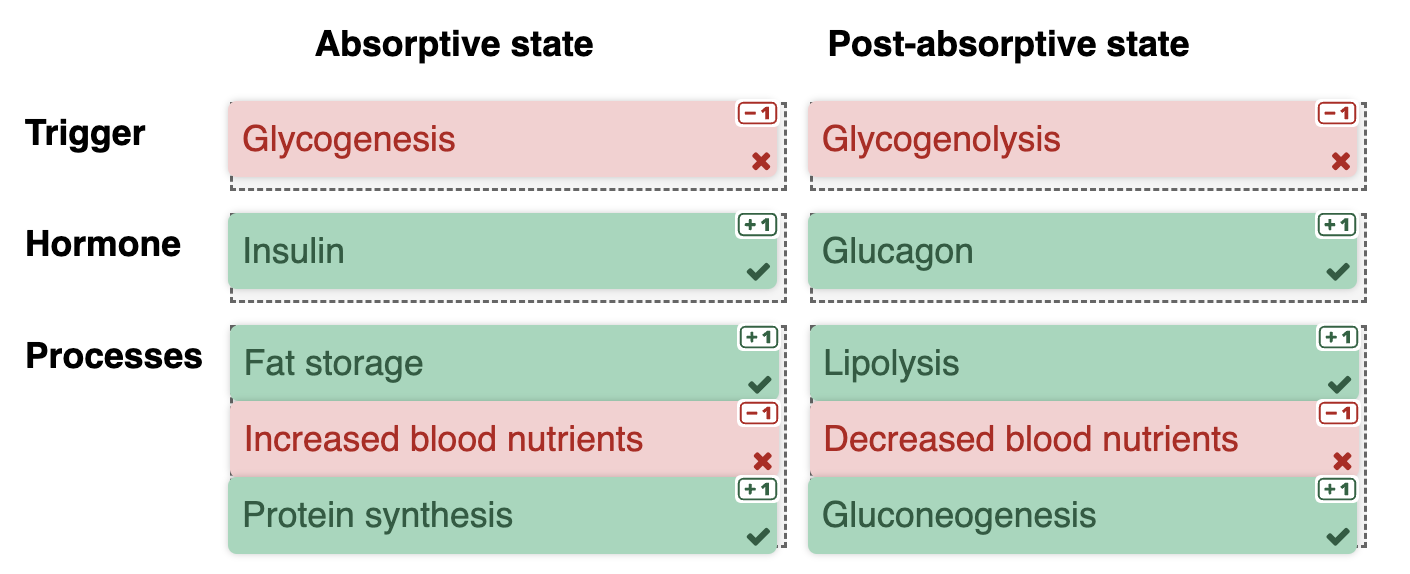
Post-absorptive State
‘Fasting’ State
After digestion, absorption & storage of nutrients has occured.
Occurs often overnight when sleeping or skipping meals (>8 hrs)
Effects:
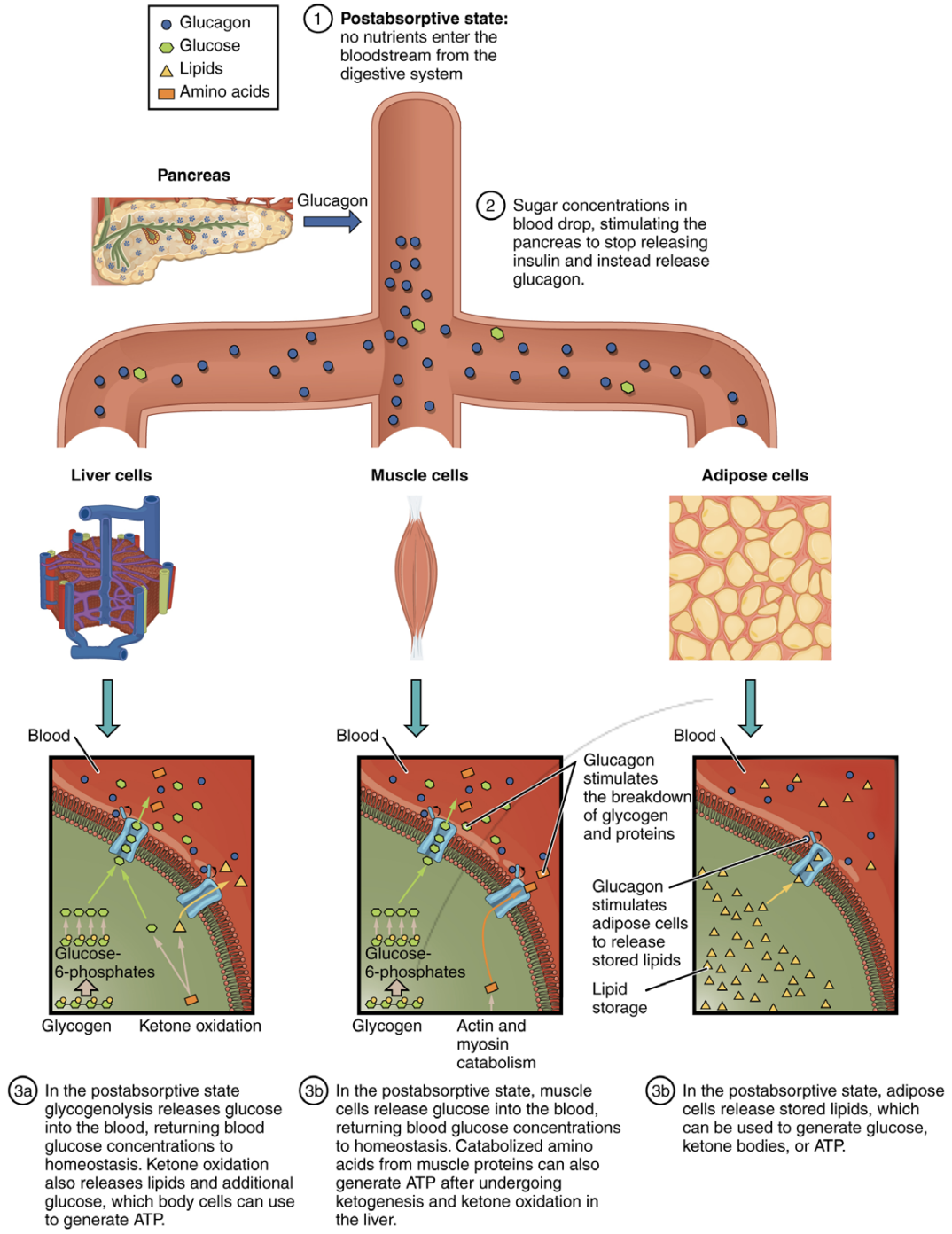
Blood glucose levels drop
Breakdown of glycogen polymer to release glucose monomers into the bloodstream
Presence of decreased blood glucose triggers glucagon release
α cells (alpha) from pancreas release glucagon
Glucagon
Inhibits the synthesis of glycogen
Stimulates breakdown of glycogen to glucose which is released into the bloodstream to be used by tissues, such as in the brain
Inhibits glycolysis to flip the concentration gradient
Higher glucose concentration inside cells
Lower concentration in bloodstream
ensures glucose is always flowing into the blood, to prevent blood glucose levels reaching 0.
Ensures fuel is available for cells at all times.
Stimulates gluconeogenesis to create even more glucose in the bloodstream
Triggers release of lipids by adipose cells
Lipids can be used to create glucose, ketone bodies & ATP
Post-absorptive State
Metabolism states
Switch between absorptive & post-absorptive states
Absorptive summary
After feeding, blood glucose levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin to stimulate the uptake of glucose by liver, muscle cells, and fat cells, to promote its conversion to glycogen.
Post-absorptive summary
As the post-absorptive state begins, falling glucose levels trigger the pancreas to release glucagon to turn off glycogen synthesis in the liver and stimulate its breakdown into glucose. The glucose is released into the bloodstream to serve as a fuel source for cells throughout the body.