Urinalysis: Cerebrospinal Fluid
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
plasma-like clear fluid circulating in and around the brain and spinal cord
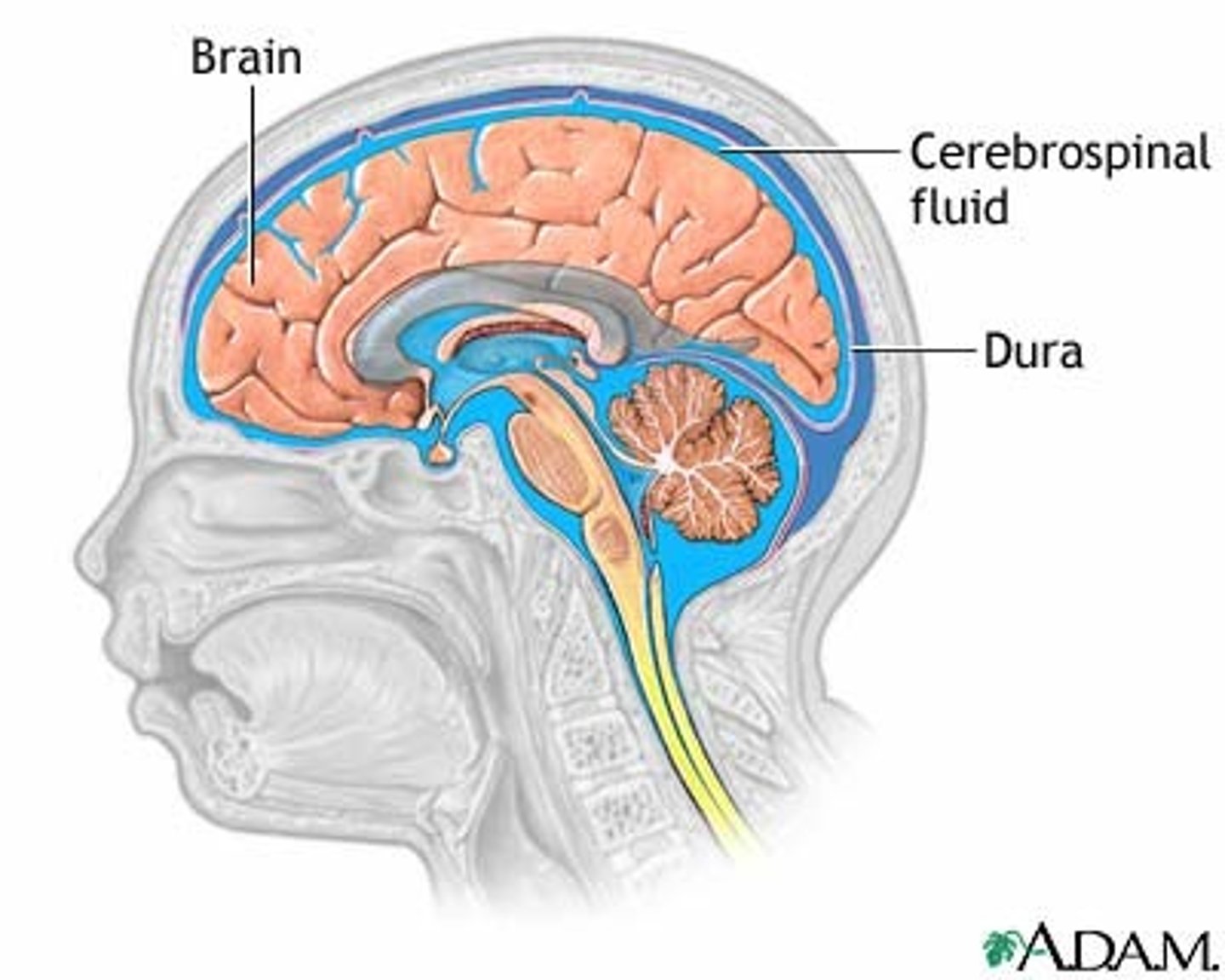
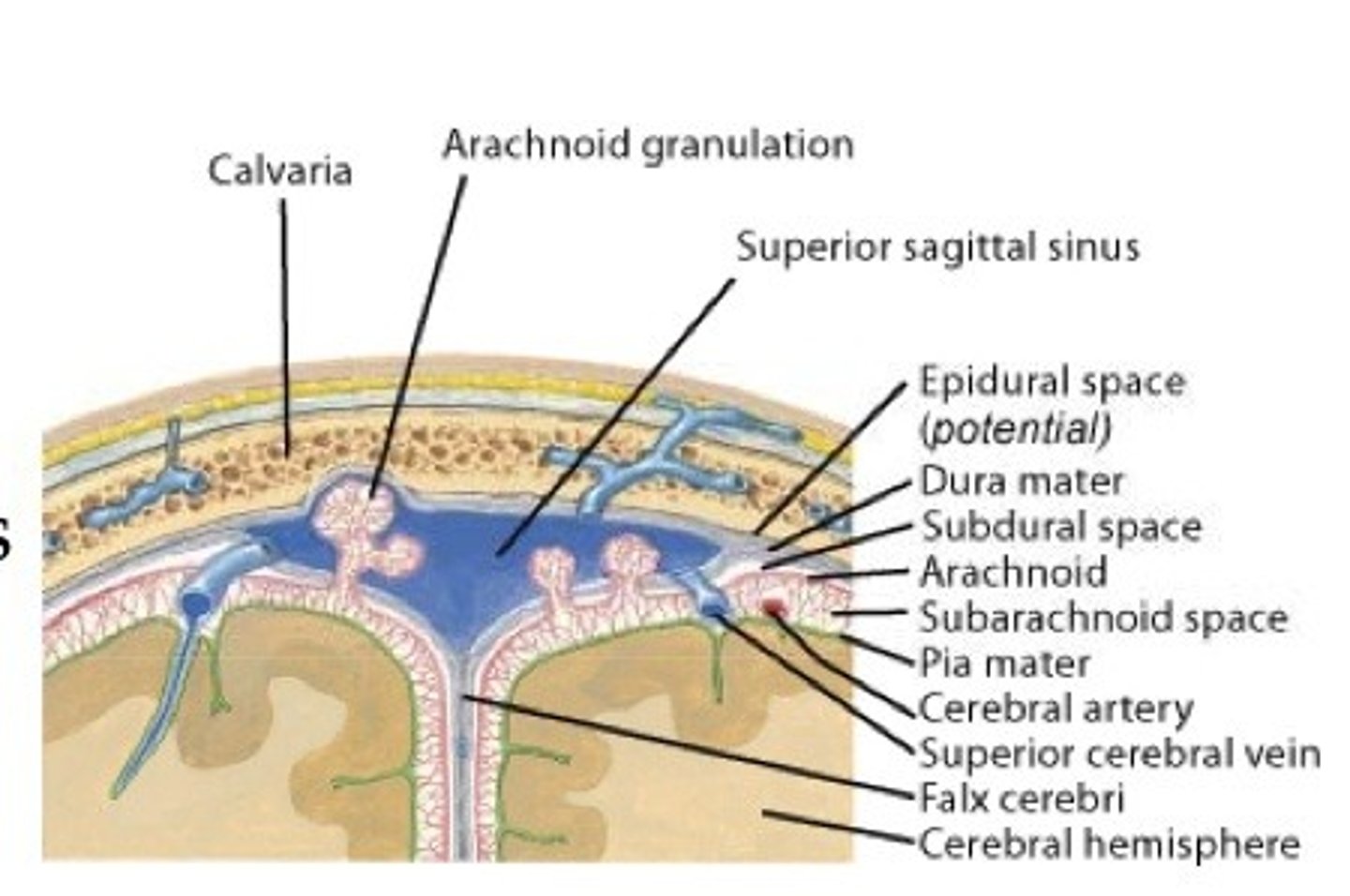
Meninges
three layers of connective tissue (the dura mater 'hard mother', the arachnoid 'spiderweb-like', and pia mater 'gentle mother') in which the brain and spinal cord are wrapped

dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
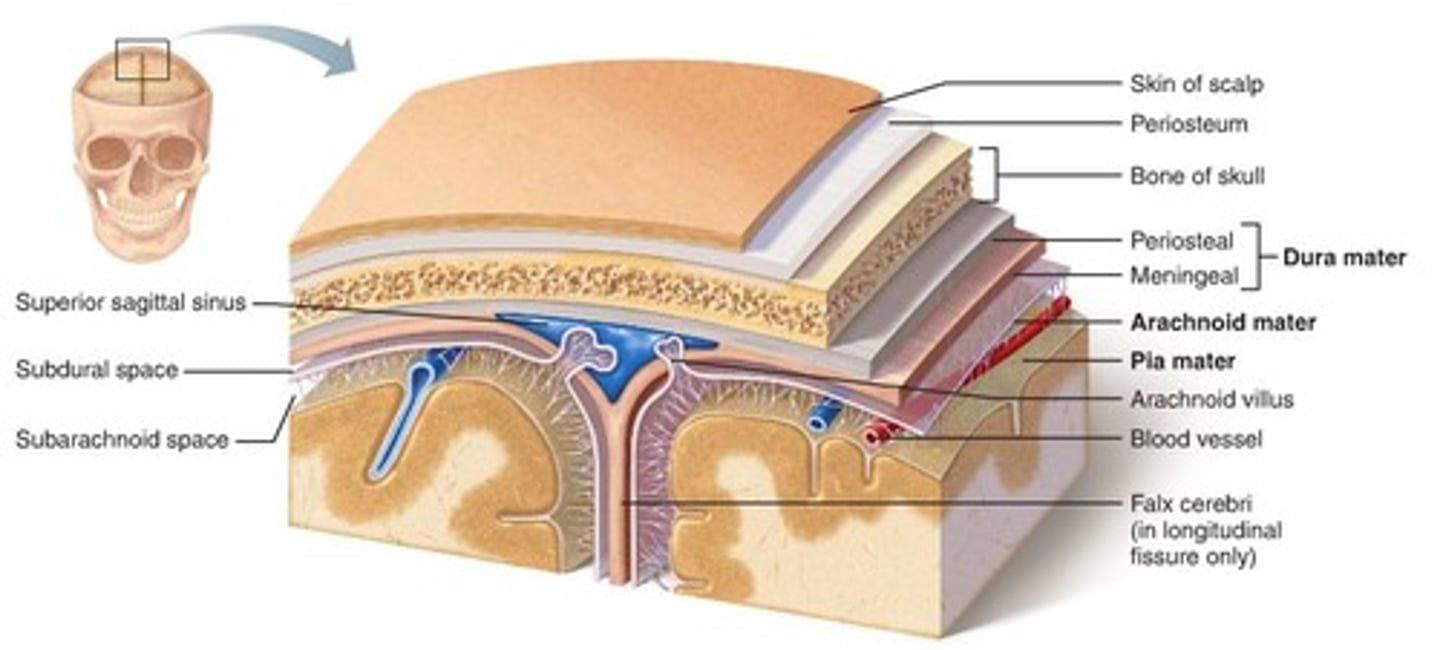
arachnoid mater
weblike middle layer of the three meninges
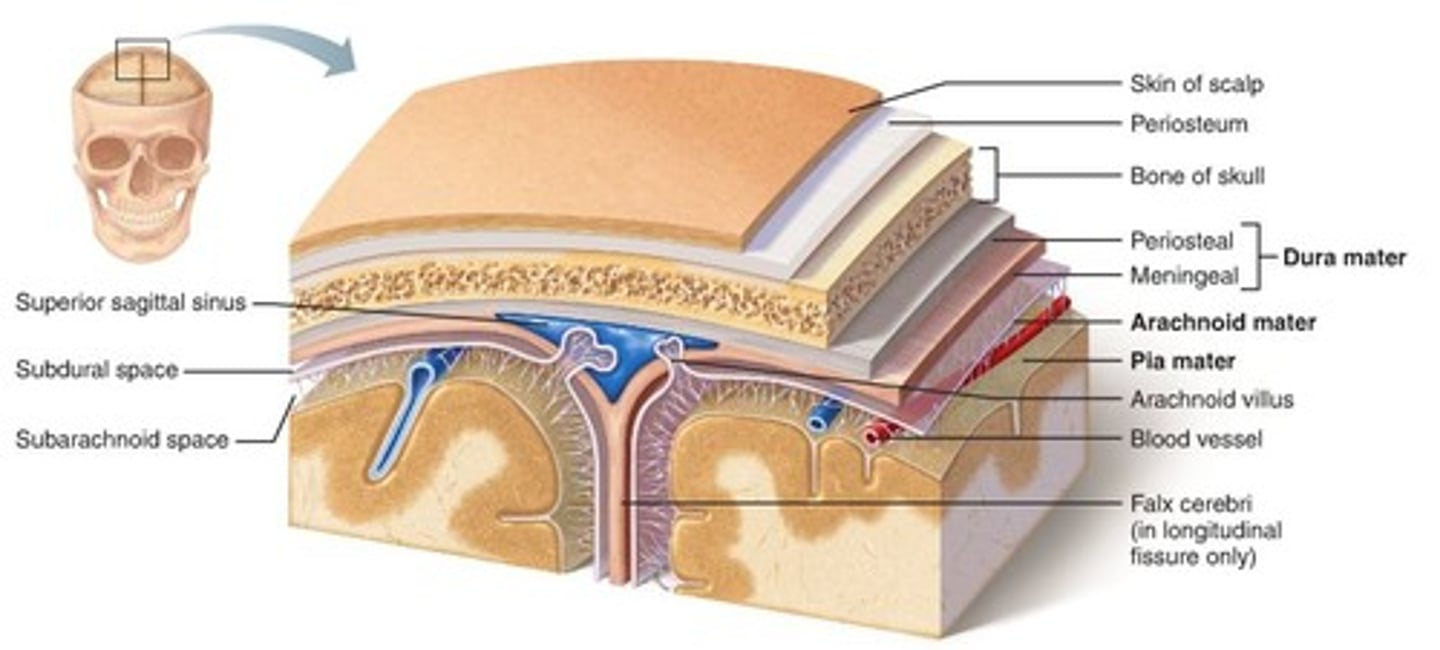
pia mater
the delicate innermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord.

choroid plexus
produces CSF

In adults, approximately __mL of fluid is produced every hour.
20mL
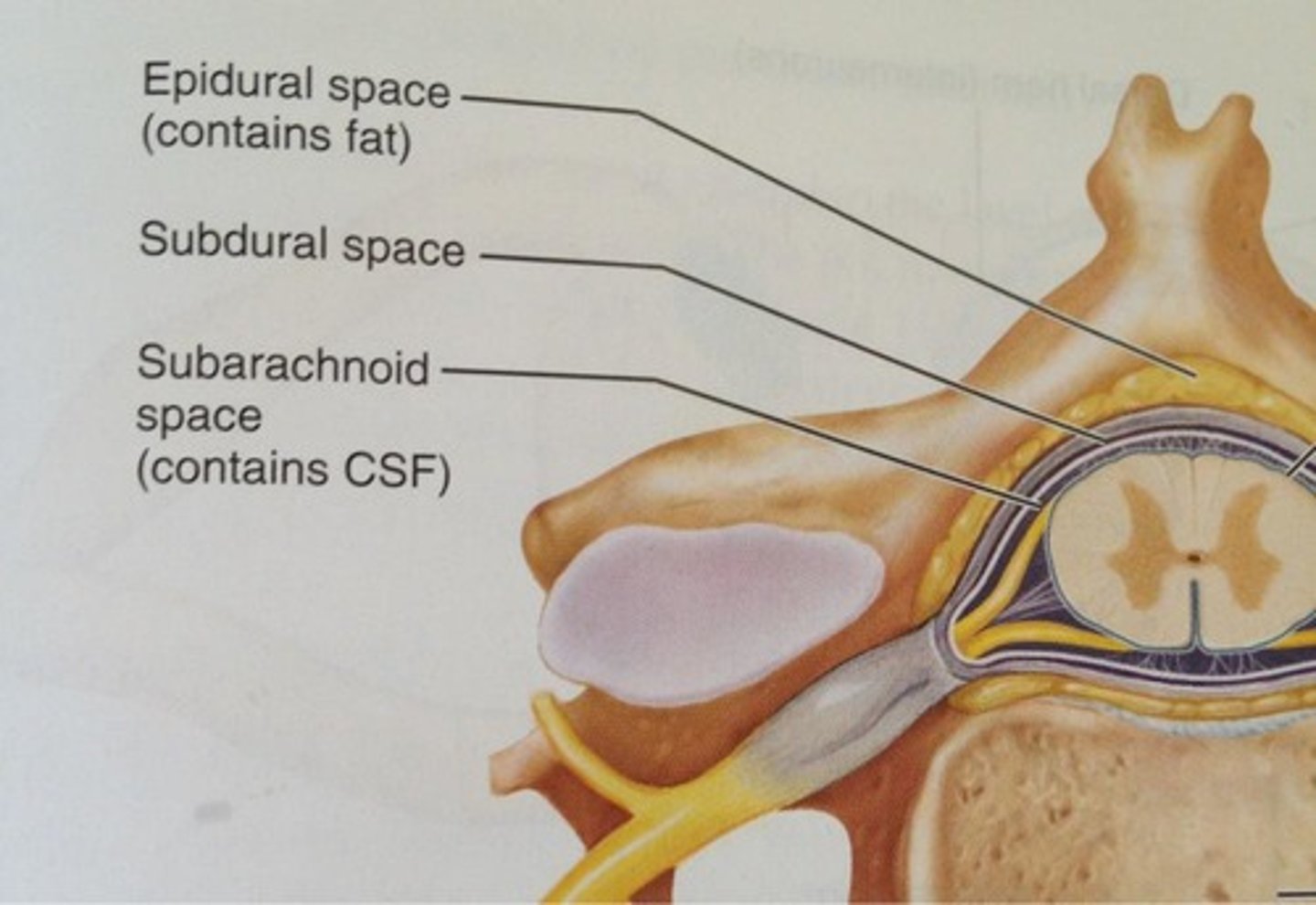
subarachoid space
located between the arachnoid mater and pia mater; filled with CSF and contains blood vessels
arachnoid granulations (villi)
projections that act as one-way valves to control passage of CSF into sinuses and prevent reflux of fluid
blood-brain barrier
A mechanism that prevents certain molecule from entering the brain but allows others to cross

Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges (layers of the brain)

lumbar puncture
CSF is withdrawn from between the 3rd and 4th or the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae for analysis

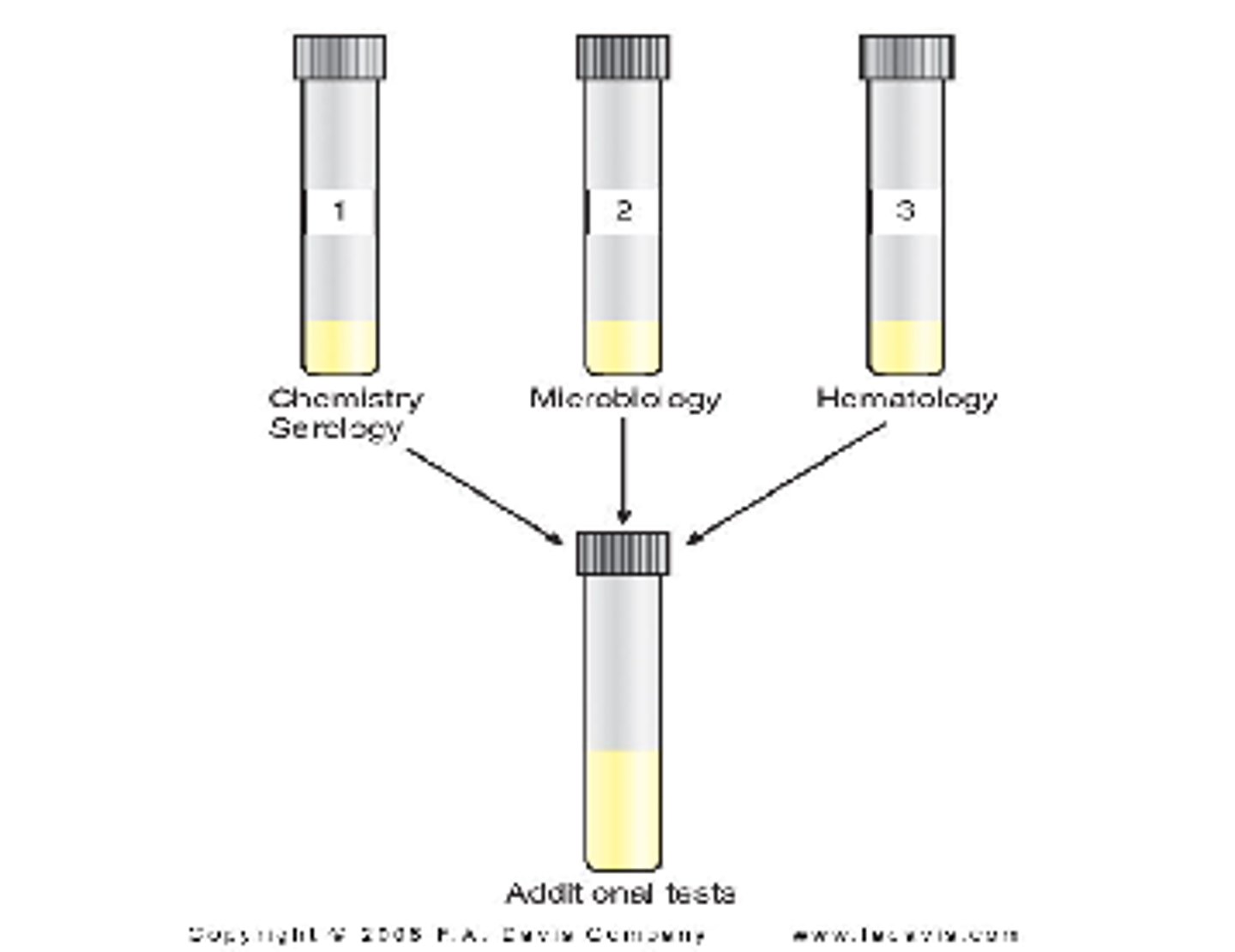
CSF collection:
-specimens are collected in 3 sterile tubes (labeled 1, 2, 3 in the order they are withdrawn)
-Tube 1: used for chemical and serologic tests because they are least affected by blood or bacteria introduced as result of the tap procedure
-Tube 2: usually designated for the microbiology laboratory
-Tube 3: used for the cell count, because it is the least likely to contain cells introduced by the spinal tap procedure.
*4th tube may be drawn for the microbiology lab to better exclude skin contamination
*excess fluid should not be discarded and should be FROZEN

CSF Handling
Ideally CSF tests are performed STAT, if not possible-
*Hematology Tubes are refrigerated
*Microbiology Tubes remain at Room Temp
*Chemistry and Serology tubes are Frozen
Major terminology used to describe CSF appearance includes:
crystal-clear, cloudy/turbid, milky, xanthochromic, and hemolyzed/ bloody

If only one tube of CSF can be collected, it must be tested first by:
microbiology
Clinical significance of CSF appearance: Crystal clear
Normal
Clinical significance of CSF appearance: Hazy, turbid, milky, cloudy
-Cause: WBCs/ Meningitis
-Cause: Microorganisms/ Meningitis
-Cause: Protein/ disorders affecting blood-brain barrier, production of IgG within the CNS

Clinical significance of CSF appearance: Oily
Cause: radiographic contrast media

Clinical significance of CSF appearance: Bloody
cause: RBCs/ Hemorrhage, traumatic tap

Clinical significance of CSF appearance: Xanthochromic
-cause: hemoglobin/ old hemorrhage, lysed cells from traumatic tap
-cause: Bilirubin/ RBC degradation, Elevated serum bilirubin
-cause: carotene/ increased serum levels
-cause: protein/ disorders affecting blood-brain barrier
-cause: melanin/ meningeal melanosarcoma

Clinical significance of CSF appearance: Clotted
-cause: protein/ disorders affecting blood-brain barrier
-cause: clotting factors/ introduced by traumatic tap

Why does normal spinal fluid not clot
It does not contain fibrinogen
Clinical significance of CSF appearance: Pellicle
-cause: protein/ disorders affecting blood-brain barrier
-cause: clotting factors/ tubercular meningitis

Pellicle
a thin skin, cuticle, membrane, or film.
Traumatic Collection (Tap)
Grossly bloody CSF can be an indication of intracranial hemorrhage, but it may also be due to the puncture of a blood vessel during the spinal tap procedure. (blood concentration gradually decreases in traumatic tap)

Clot formation
fluid collected from a traumatic tap may form clots due to the introduction of plasma fibrinogen into the specimen
RBCs usually remain in the CSF for approximately __ hours before noticeable hemolysis begins. (therefore, a xanthochromic supernatant would be the result of blood that had been present longer than that introduced by the traumatic tap)
2 hours
Cell count
number of cells of one type in 1 microliter
(cell count that is usually performed on CSF specimens is the leukocyte count)
(RBC counts are usually done only when a traumatic tap has occurred)
Any cell count should be preformed:
immediately
WBCs and RBCs begin to lyse within __ hour, and 40% of leukocytes disintegrate after __ hours.
1 hour, 2 hours
Normal adult CSF leukocytes:
0-5 WBCs/uL
(this would be higher in children)
Neubauer counting chamber
Routinely used for performing CSF cell counts
-nine large square counting areas

Calculating CSF cell counts
Standard Neubauer calculation formula used for blood cell counts is also applied to CSF cell counts to determine the number of cells per microliter.
(# cells counted x dilution/ #cells counted x volume of 1 square= cells/uL)
-purpose is to convert the # of cells counted to the # that would be present in 1uL of the fluid

Counting 4 large corner squares (0.4uL) and the large center square (0.1uL) on each side of the counting chamber.
-eliminates the need to correct for the volume counted
# of cells counted x dilution x 1uL/1uL (0.1x10)(volume counted)= cells/uL

hemocytometer
Instrument used in counting blood cells
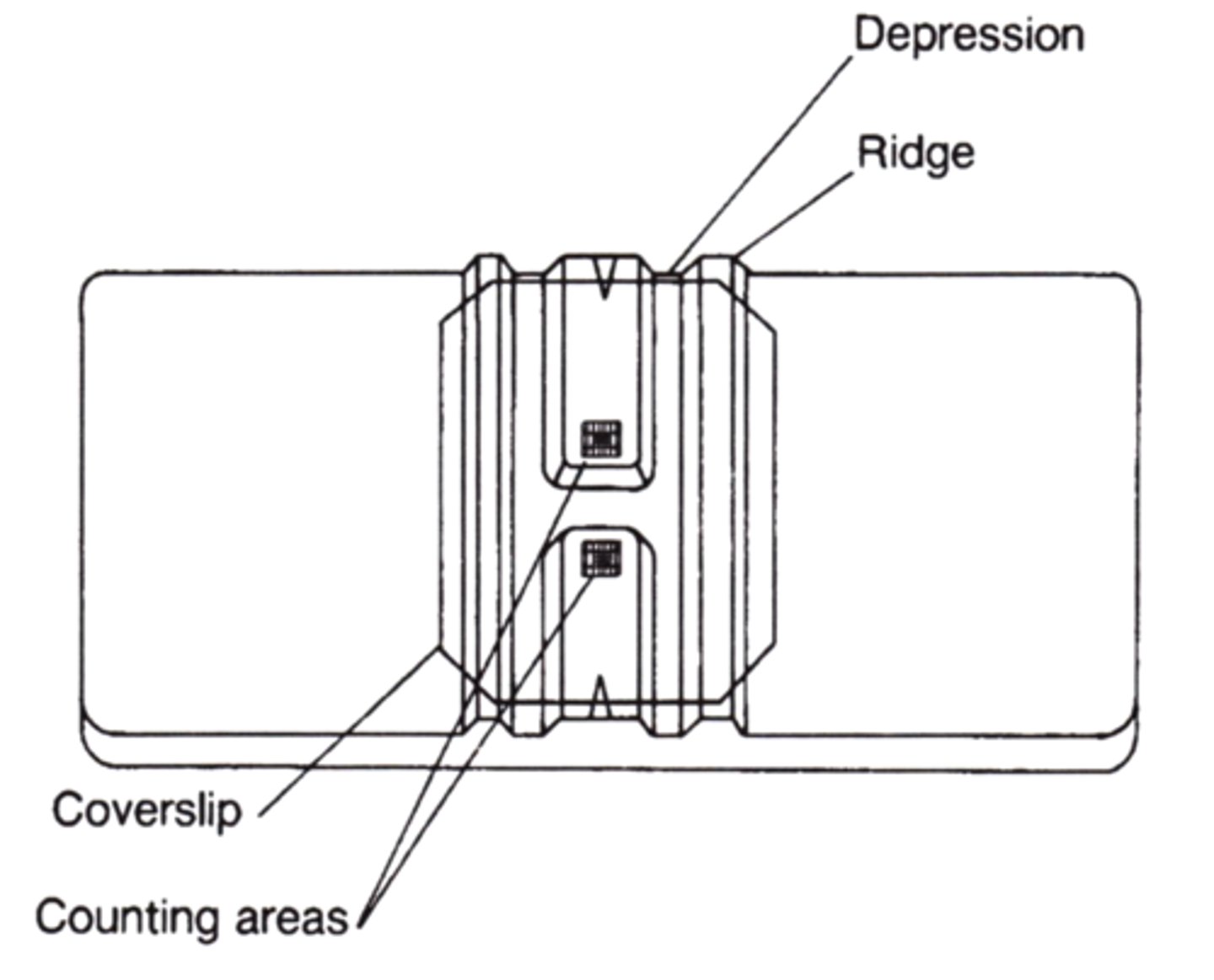
total cell count
Total number of cells in a culture including viable (live) cells and dead cells
-if dilutions are required- they are made with NS, mixed by inversion, and loaded into they hemocytometer w/ a pasteur pipette.

Pasteur pipette
A long, skinny tube with a bulb at one end. These pipettes are like eye droppers and do not provide accurate measurements.

WBC count
-Place 4 drops of mixed specimen in a clean tube.
-Rinse pasteur pipette with 3% glacial acetic acid, draining thoroughly, and draw 4 drops of CSF into rinsed pipette.
-Allow pipette to sit for 1min, mix the solution in the pipette, discard the first drop, and load hemocytometer.

Differential count on a CSF specimen
-should be done on a stained smear and not from the cells in the counting chamber
-specimen should be concentrated before preparing the smear which include: sedimentation, filtration, centrifugation, and cytocentrifugation
-specimen centrifuged for 5-10mins.
-supernatant fluid is removed and saved for additional test
-slides are made from sediment
-100 cells should be counted, classified, and reported in terms of percentage
*if cell count is low and finding 100 cells is not possible, report only the #s of the cell types seen.
cytocentrifugation
Mechanical process in which centrifugal force is used in a machine to deposit cells on a glass slide for staining and viewing
-fluid is added to conical chamber, and centrifuged, cells present in the fluid are forced into a monolayer within a 6-mm diameter circle on the slide

Represents a cytocentrifuge recovery chart for comparison with chamber counts. The chamber count should be repeated if too many cells are seen on the slide, and a new slide should be prepared if not enough cells are seen on the slide.
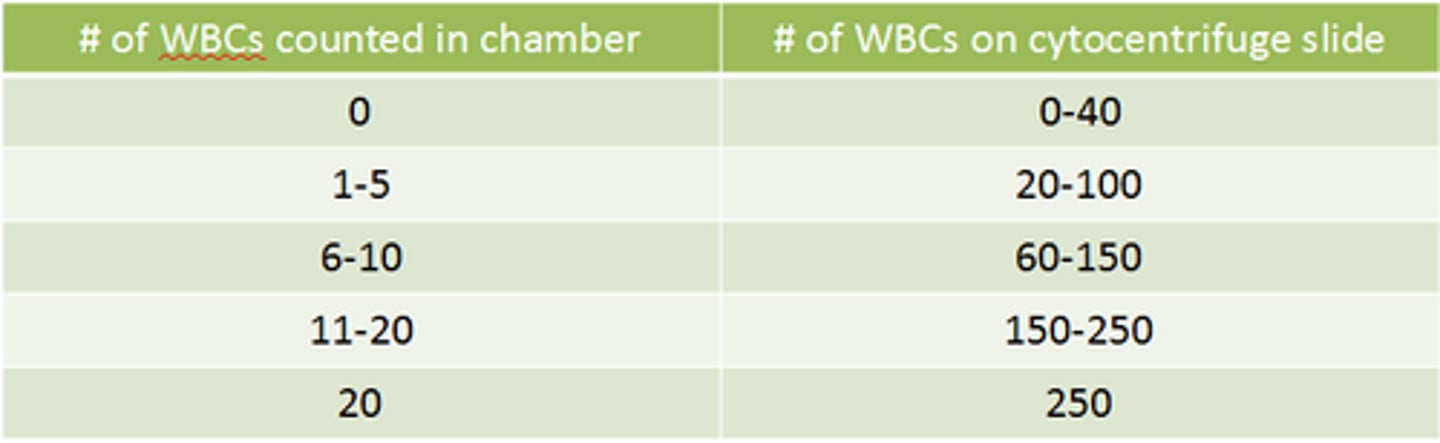
Cells seen in CSF: Lymphocytes
-Major clinical significance: Normal/ viral, tubercular, and fungal meningitis/ multiple sclerosis
-microscopic findings: all stage of development may be found

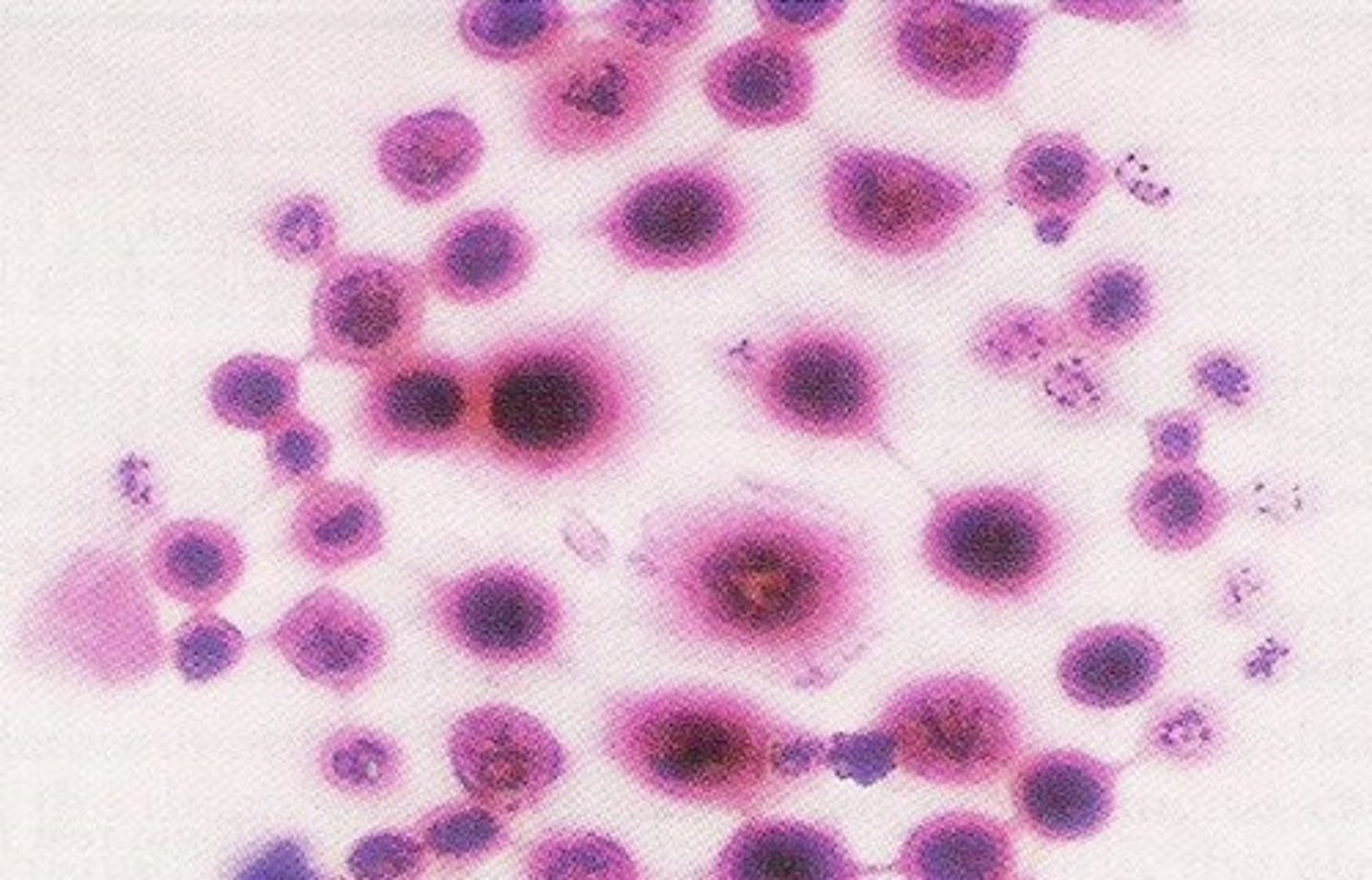
Cells seen in CSF: Neutrophils
-major clinical significance: Bacterial meningitis/ early cases of viral, tubercular, and fungal meningitis/ cerebral hemorrhage
-microscopic finding: granules may be less prominent than in blood/ cells disintegrate rapidly
(image: x500: neutrophils with cytoplasmic vacuoles resulting from cytocentrifugation)
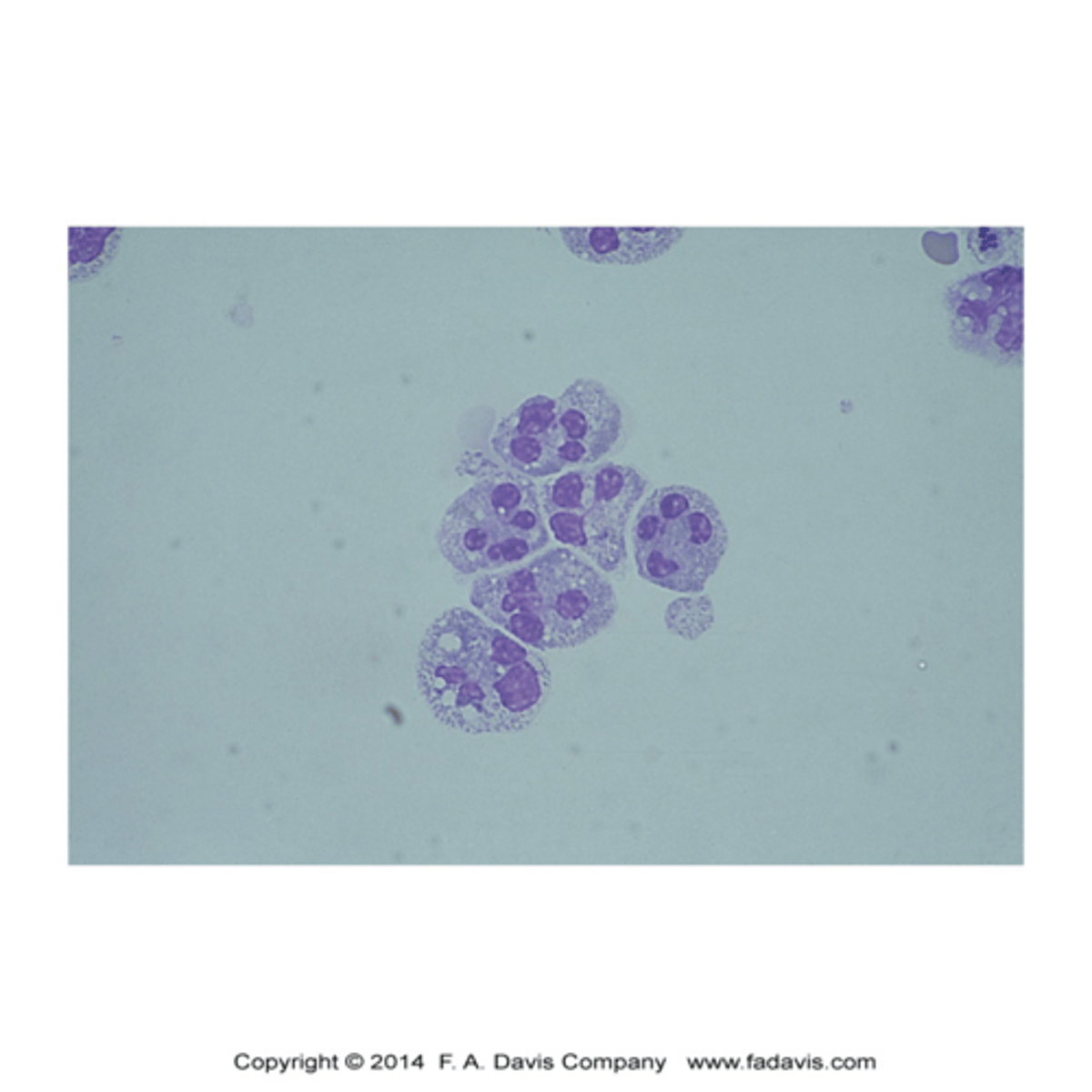
Neutrophils with intracellular and extracellular bacteria (x1000)
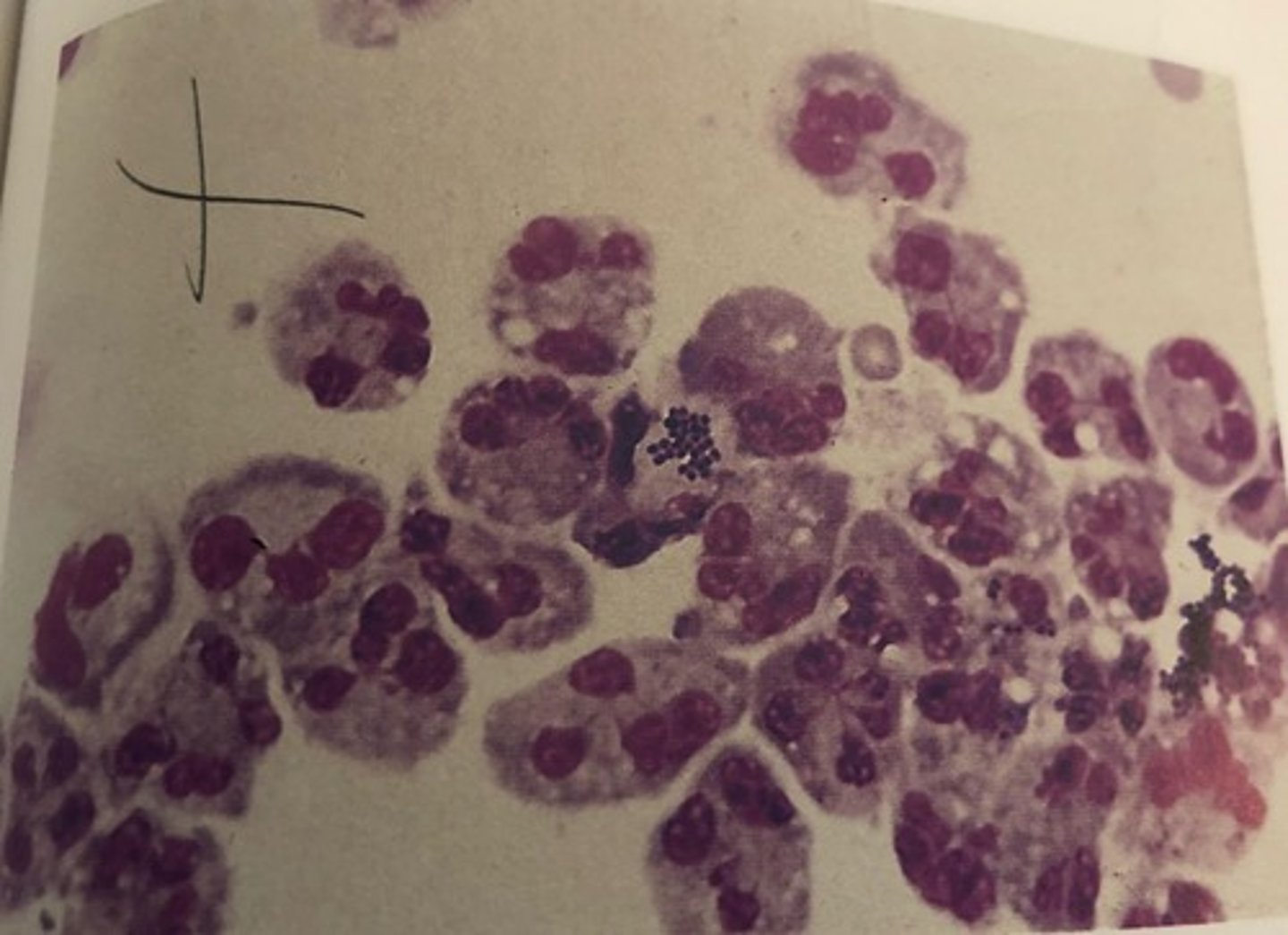
Neutrophils with intracellular bacteria
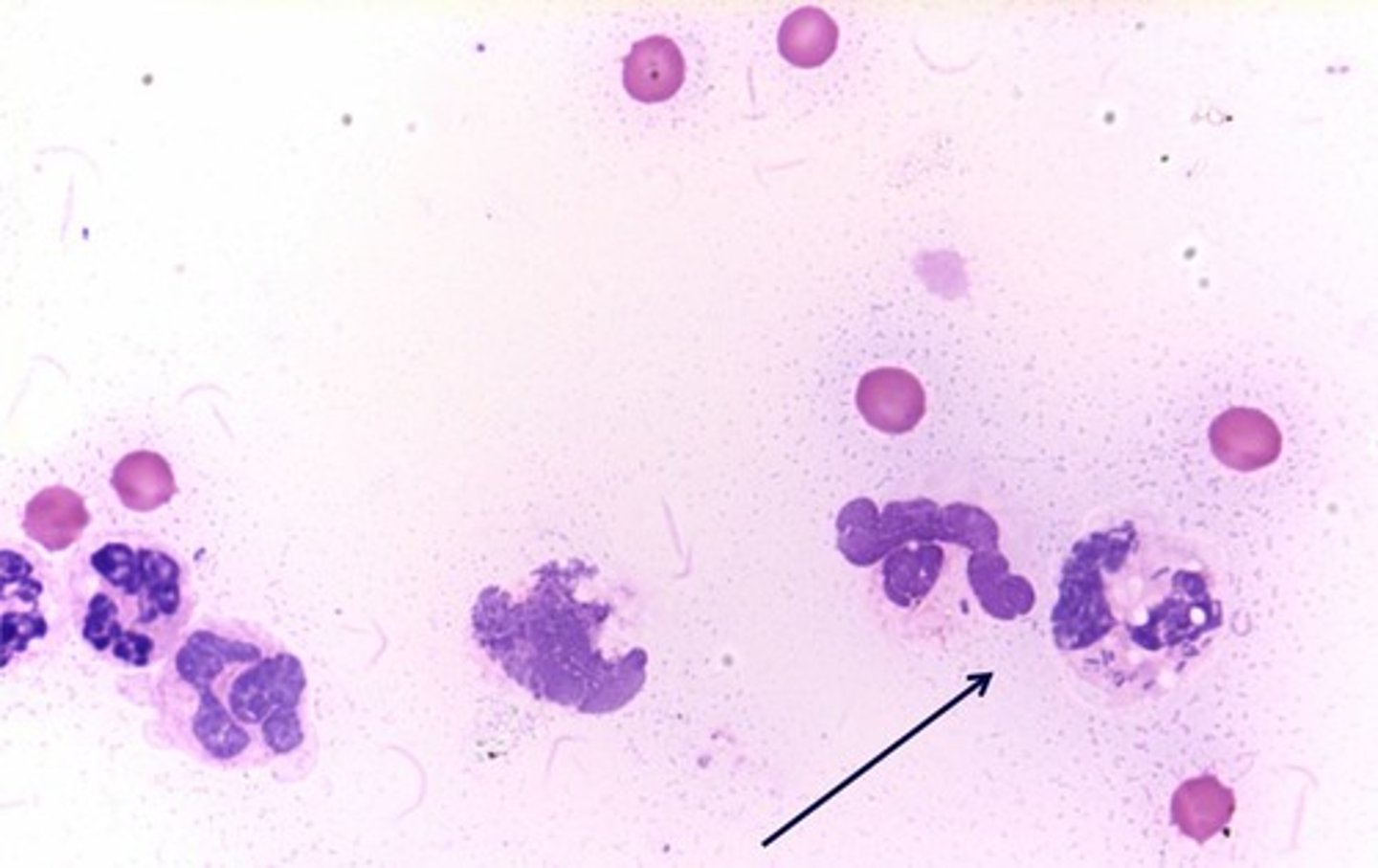
pyknotic
condensed
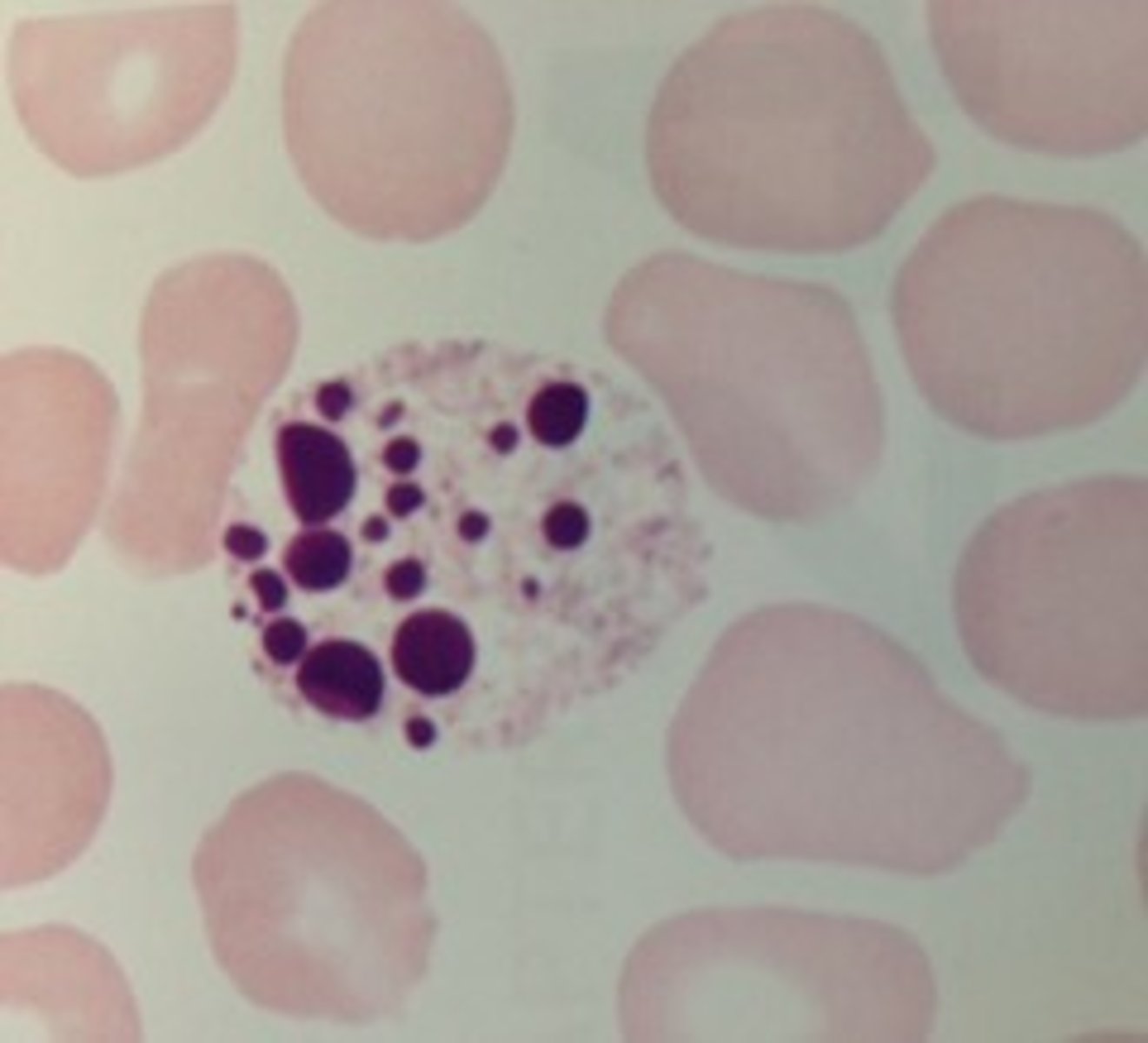
nucleated red blood cell (NRBC)
an immature red blood cell that has not yet lost its nucleus
-seen as a result of contamination from bone marrow during the spinal tap
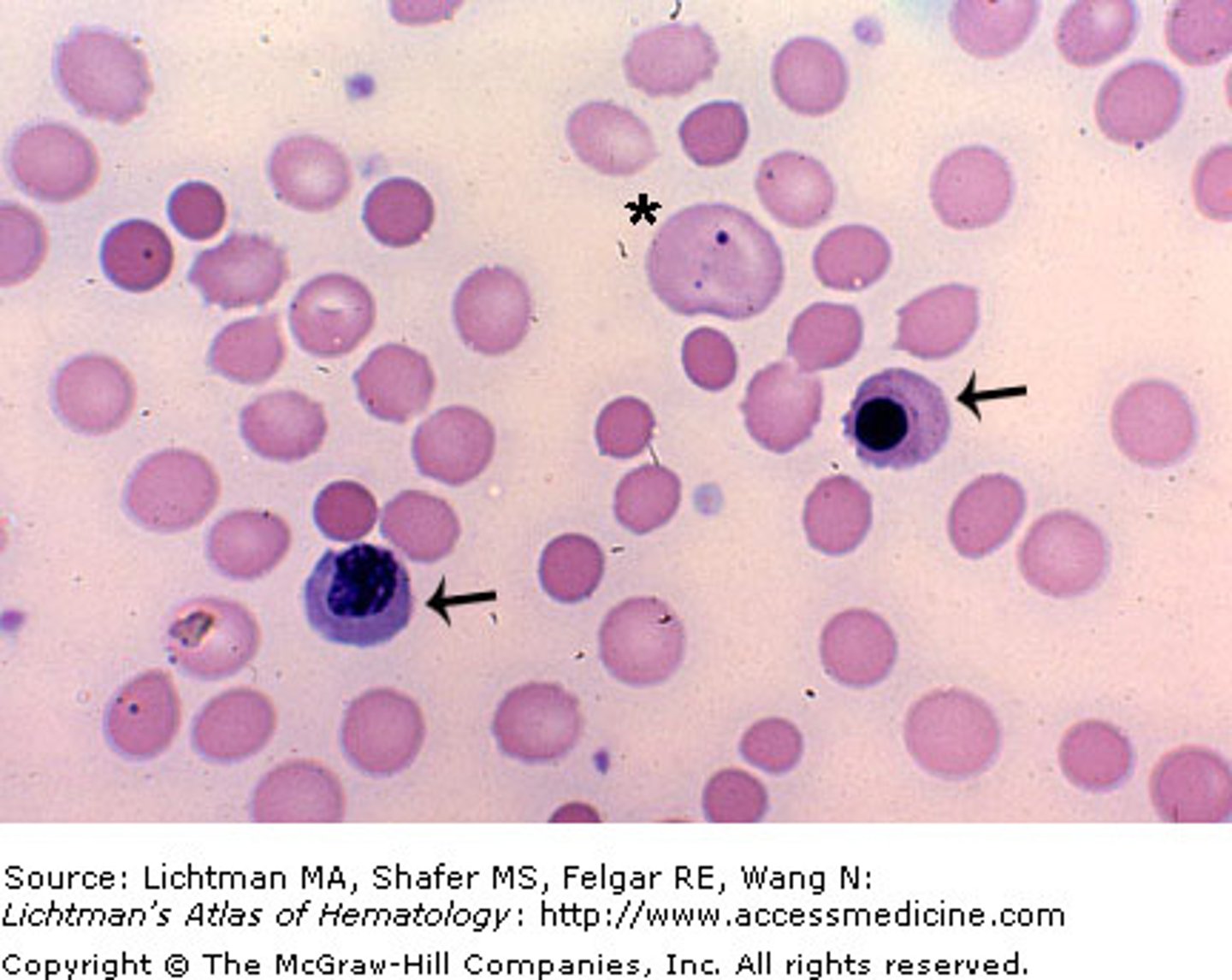
Cells seen in CSF: Monocytes
-major clinical significance: normal/ viral, tubercular, and fungal meningitis/ multiple sclerosis
-microscopic findings: found mixed with lymphocytes
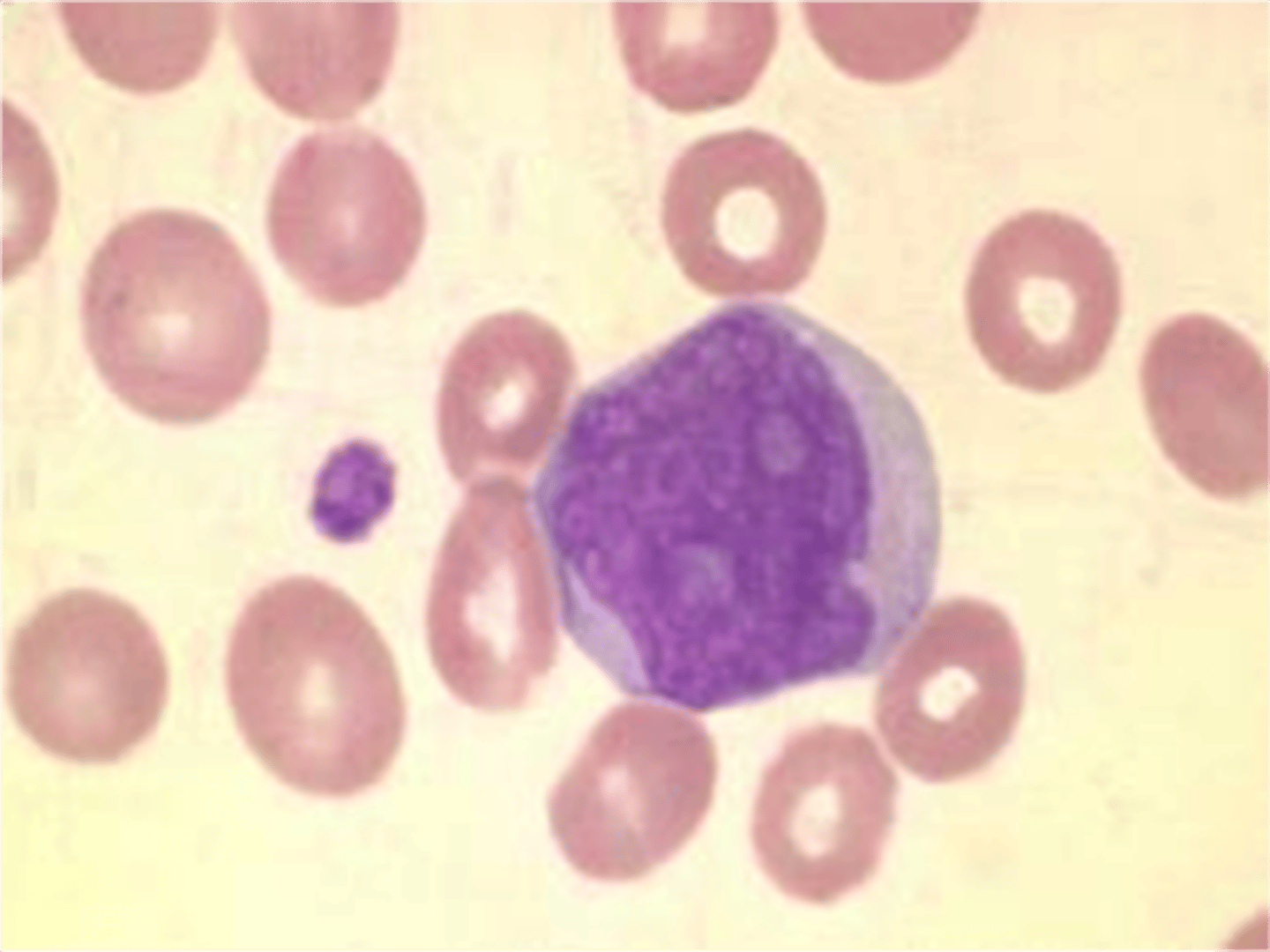
Cells seen in CSF: Macrophages
-major clinical significance: RBCs in spinal fluid
-microscopic findings: may contain phagocytized RBCs appearing as empty vacuoles or ghost cells, hemosiderin granules, and hematoidin crystals (image: large amount of cytoplasm and vacuoles)

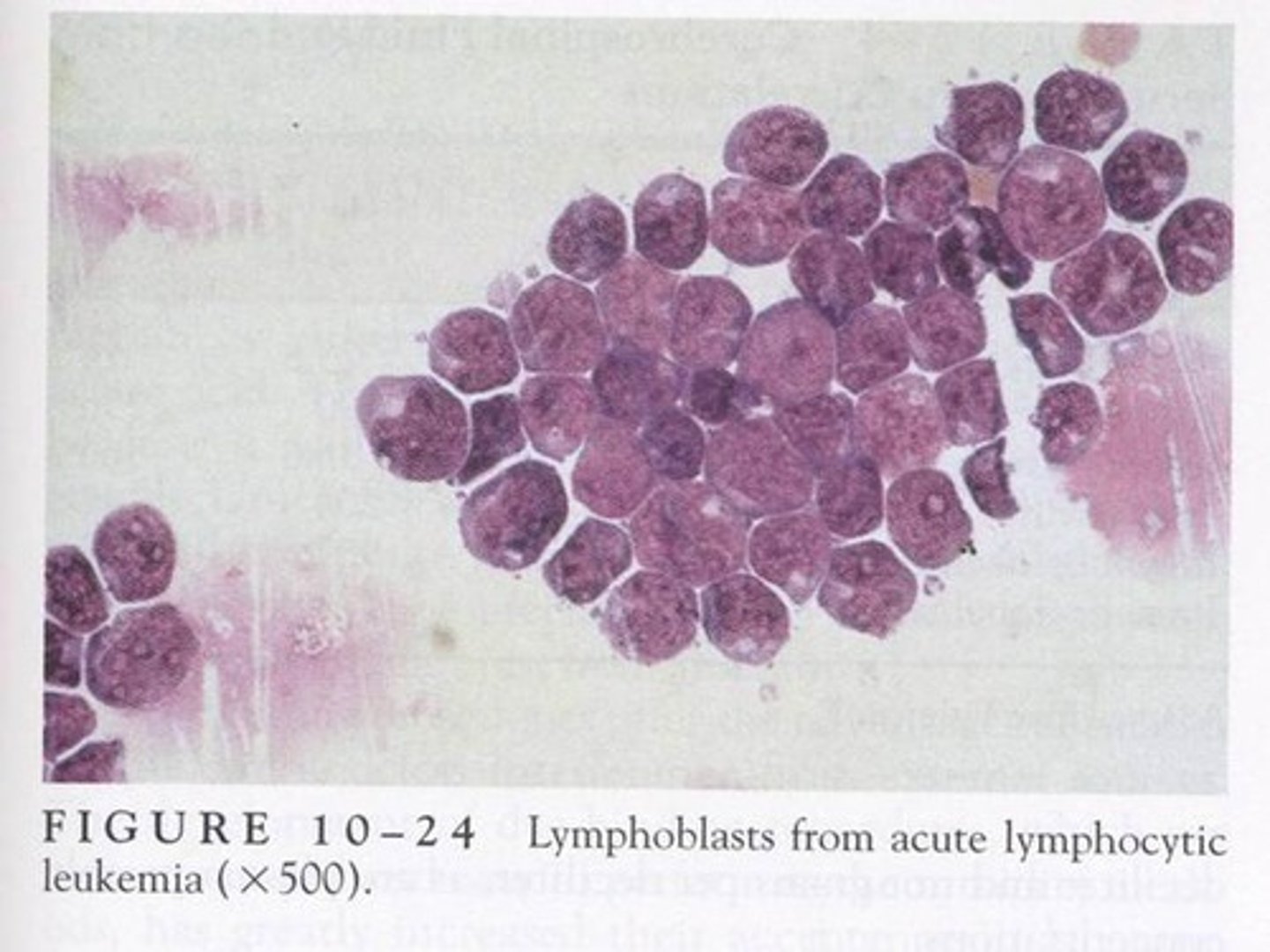
Cells seen in CSF: Blast forms
-major clinical significance: acute leukemia
-microscopic findings: Lymphoblasts, myeloblasts, or monoblasts

Cells seen in CSF: Lymphoma cells
-major clinical significance: disseminated lymphomas
-microscopic findings: resemble lymphocytes with cleft nuclei
Cells seen in CSF: Plasma cells
-major clinical significance: multiple sclerosis/ lymphocyte reactions
-microscopic findings: traditional and classic forms seen/ reactive lymphs

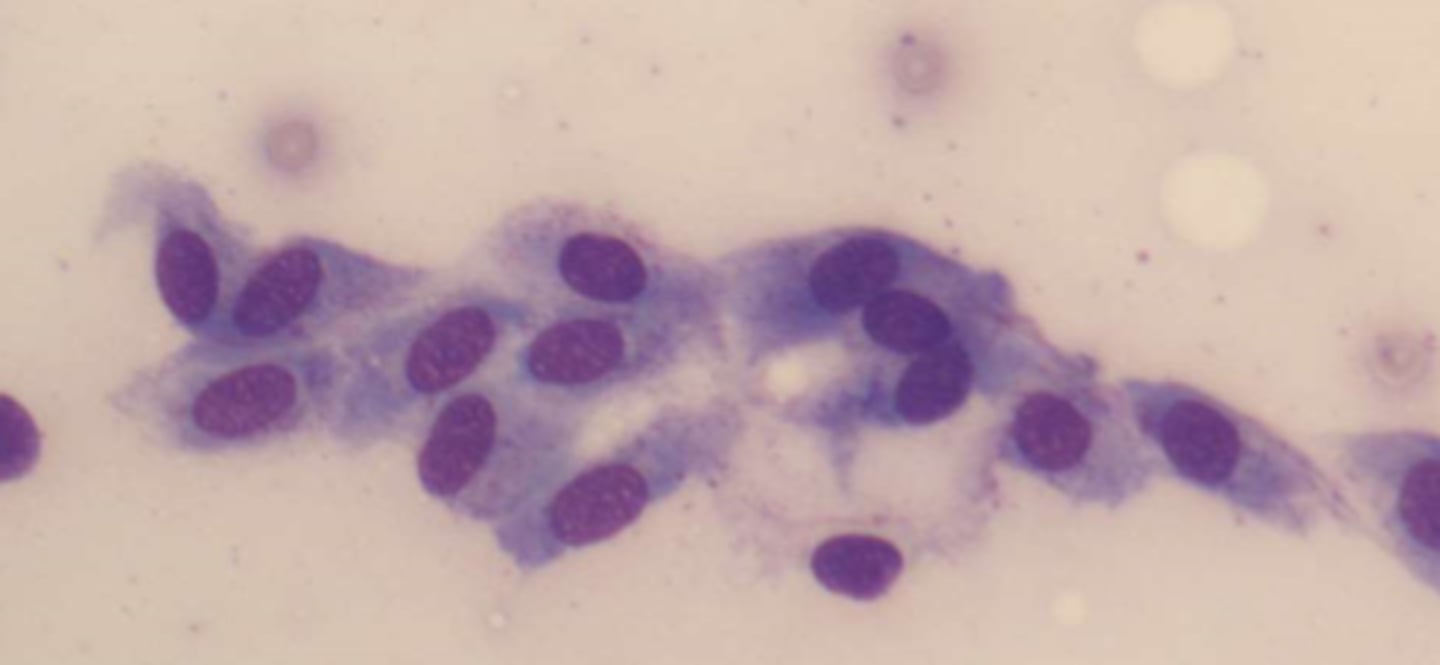
Cells seen in CSF: Ependymal, chorodial, and spindle-shaped cells
-major clinical significance: diagnostic procedures
-microscopic findings: seen in clusters with distinct nuclei and distinct cell
ependymal cells
line cavities of the brain and spinal cord, circulate cerebrospinal fluid

Choroidal cells
Cells that line the choroid plexus
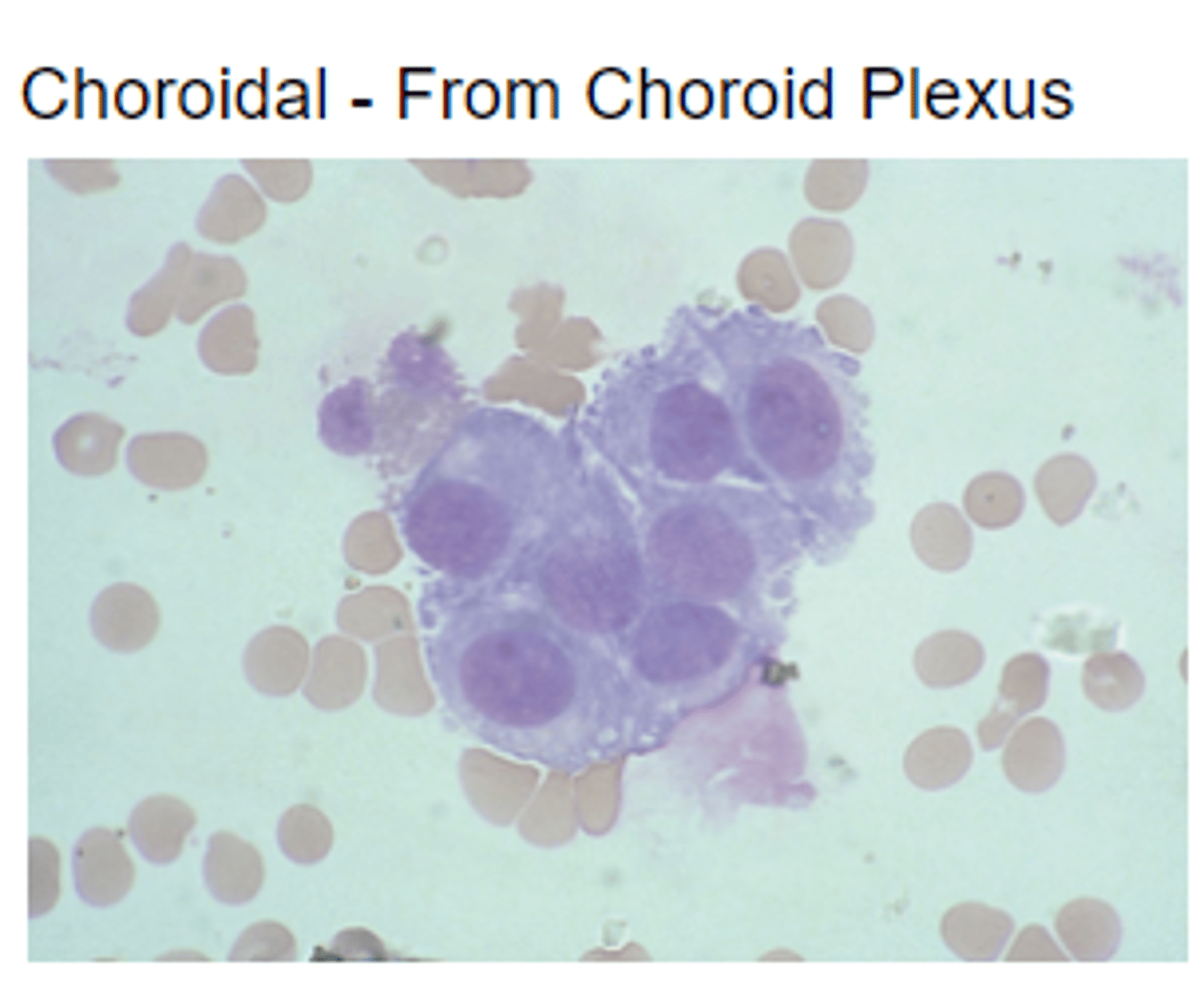
spindle shaped cells
lining cells from the arachnoid
Cells seen in CSF: Malignant cells
-major clinical significance: Metastatic carcinomas/ primary CNS carcinoma
-microscopic findings: seen in clusters with fusing of cell borders and nuclei

CSF - Lymphocytes and Monocytes
-common in cases of viral, tubercular, and fungal meningitis
- increased lymphocytes are seen in cases of both asymptomatic HIV infection and AIDS
CSF - Eosinophils
-seen in parasitic and fungal infections( primarily C. immitis) , and introduction of foreign materials, including medications and shunts into the CNS

CSF- Macrophages
-purpose is to remove cellular and other debris.
-enter CSF within 2 hours of hemorrhage to phagocyte RBCs
-seen in repeated taps
-more cytoplasm than monocytes
-Finding of macrophages indicates a previous hemorrhage
-degradation of the phagocytized RBCs results in appearance of dark blue/black iron containing hemosiderin granules
-yellow hematoidin crystals represent further degeneration (iron-free, consisting of hemoglobin and unconjugated bilirubin

CSF non-clinically significant cells:
-choroidal cells
-ependymal cells
-spindle shaped cells
A macrophage containing hemosiderin and hematoidin crystals

macrophage with aggregated hemosiderin granules

CSF - malignant cells of hematologic origin
-lymphoblasts
-myeloblasts
-monoblasts
*seen as serious complication of acute leukemias
Lymphoblasts
-have small amount of cytoplasm
-develop into lymphocytes

myeloblast
immature bone marrow that gives rise to granulocytes

monoblast
Immature white blood cell (monocyte).
-prominent nucleoli
CSF - malignant cells of non-hematologic origin
-metastatic carcinoma cells: primarily from lung, breast, renal, and GI
-cells from primary CNS tumors include: astrocytomas, retinoblastomas, and medulloblastomas
-usually appear in clusters
Cerebrospinal Protein
-most performed chemical test on CSF is protein determination
-normal CSF contains small amounts of protein
-usually 15-45mg/dL
-higher values found in infants and people >40.
-albumin makes up most of CSF protein, and second is prealbumin
-tau is found in CSF but not serum
-CSF gamma globulin is primarily IgG, w/ small amounts of IgA
-IgM, fibrinogen and beta lipoprotein is not normally found in CSF
clinical significance of Elevated protein values:
-elevated protein values are seen in pathologic conditions
-abnormally low values are present when fluid is leaking from the CNS
-The causes of Elevated CSF protein: blood-brain barrier, immunoglobulin production within the CNS, decrease normal protein clearance from the fluid, and neural tissue degeneration.
-Meningitits and hemorrhagin condition that damage the blood-brain barrer are the most common causes of ^CSF protein.
Methodology
-a system of methods used in a particular area of study or activity
-two most used techniques for measuring total CSF protein use the principles of turbidity production or dye-binding ability
-
protein fractions
-Proteins can be separated from the plasma
-for diagnosis of neurologic disorders assoc. w/ abnormal CSF protein
CSF/serum albumin index
Is used to determine whether IgG is increased because of being produced within the CNS or is elevated as the result of a defect in the blood-brain barrier
-comparisons between serum and CSF levels of albumin are made
-Methods:
*CSF/serum albumin index to evaluate integrity of the blood-brain barrier and
*CSF IgG index to measure IgG synthesis within the CNS
CSF/serum albumin index calculation:
CSF/serum albumin index is calculated after determining the concentration of CSF albumin in mg/dL and the serum concentration in g/dL.
{The FORMULA:
CSF/serum albumin index= CSF albumin (mg/dL) / Serum albumin (g/dL)}
-index values <9 represents an intact blood-brain barrier.
-index increases relative to the amount of damage
-calculation of IgG index:
{IgG index= CSF IgG(mg/dL)/ serum IgG(g/dL)// CSF albumin(mg/dL)/serum albumin(g/dL)}
*IgG index values >0.70 indicate IgG production with the CNS

Electrophoresis and Immunophoretic Techniques:
-primary purpose for performing CSF protein electrophoresis is to detect oligoclonal bands, which represent inflammation within the CNS
-the bands indicate immunoglobulin production
oligoclonal bands
the "bands" refer to groups of similar proteins. Normally, there are
lots of different groups of protein in CSF, but MS patients have fewer varieties. Oligo meaning
"few"; clonal meaning "identical." These identical proteins are IgG molecules directed against
antigens in myelin.

multiple sclerosis
myelin sheath destruction. disruptions in nerve impulse conduction
2 or more oligoclonal bands that are not found in serum
moderately elevated white count
increase in lymphs
plasma cells

Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS)
temporary paralysis caused by an autoimmune attack on peripheral myelin, causing weakness and usually ascending paralysis of the limbs, face and diaphragm

Myelin basic protein (MBP)
Major structural proteins of CNS and PNS myelin
-MBP in the CSF indicates recent destruction of the myelin sheath that protects axons and neurons (demyelination)
-the course of ms can be monitored by measuring the amount of MBP in the CSF
CSF glucose
-60-70% of plasma glucose
(if plasma glucose is 100mg/dL, then a reference CSF glucose would be approx. 65mg/dL)
-a blood glucose test must be run for comparison (blood glucose should be run 2 hours before the spinal tap to allow time for equilibration between the blood and fluid.
-specimens should be tested immediately because glycolysis occurs rapidly in CSF.
CSF Lactate
-can be a valuable aid in diagnosing and managing meningitis cases.
-levels >35mg/dL are seen w/ bacterial meningitis
-levels <25mg/dL are seen in viral meningitits

CSF glutamine
-glutamine is produced from ammonia and a-ketoglutarate by the brain cells
-removes toxic metabolic waste product ammonia from the CNS
-normal concentration of glutamine in CSF: 8-18 mg/dL
-elevated levels are assoc. with liver disorders
-excess ammonia in the CNS ^glutamine synthesis
-as concentration of ammonia in CSF increases, the supply of a-ketoglutarate becomes depleted; glutamine can no longer be produced to remove the toxic ammonia, and coma ensues.
Reye Syndrome (RS)
rare but serious condition that causes swelling in the liver and brain
-common in children

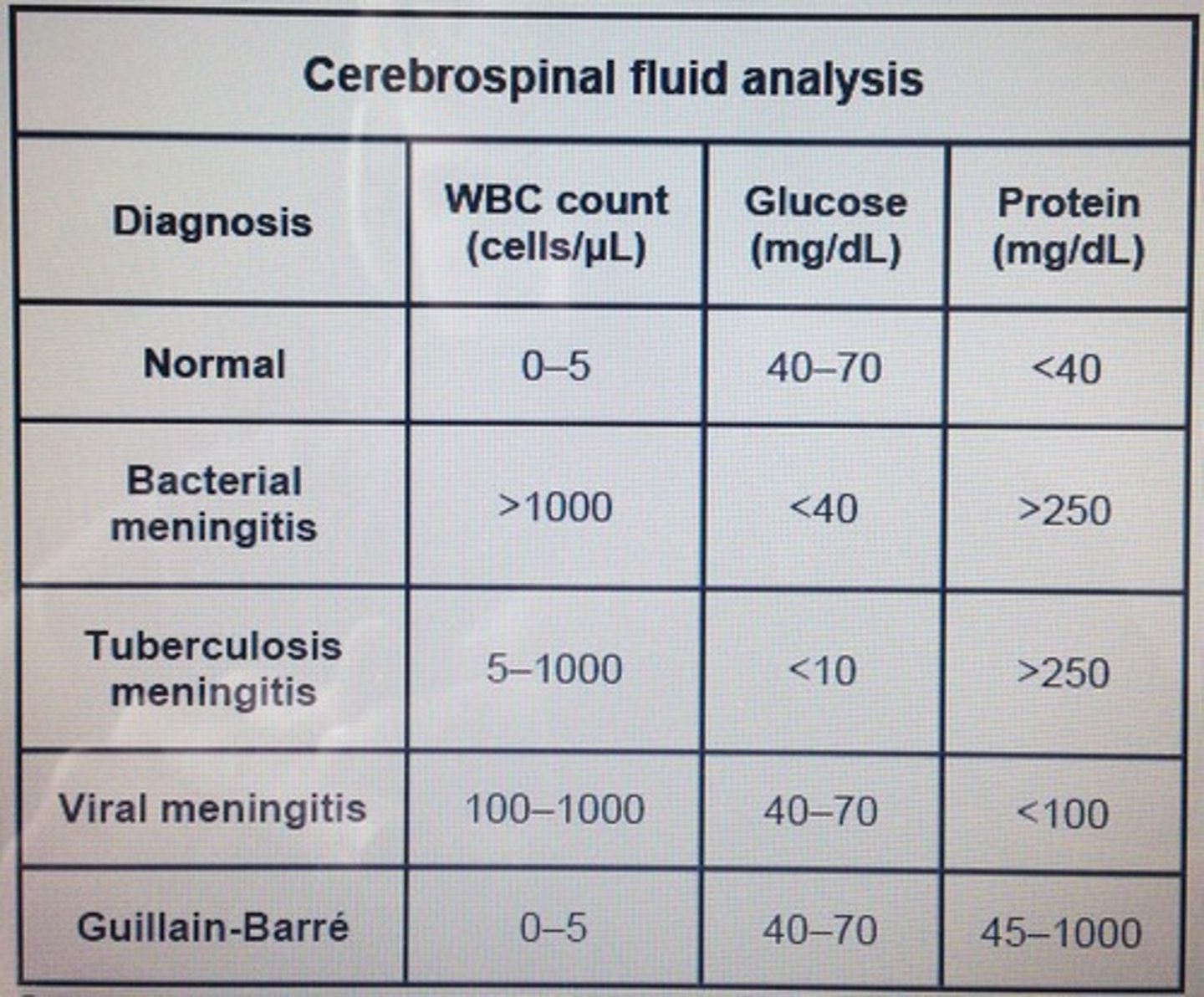
CSF chemistry tests

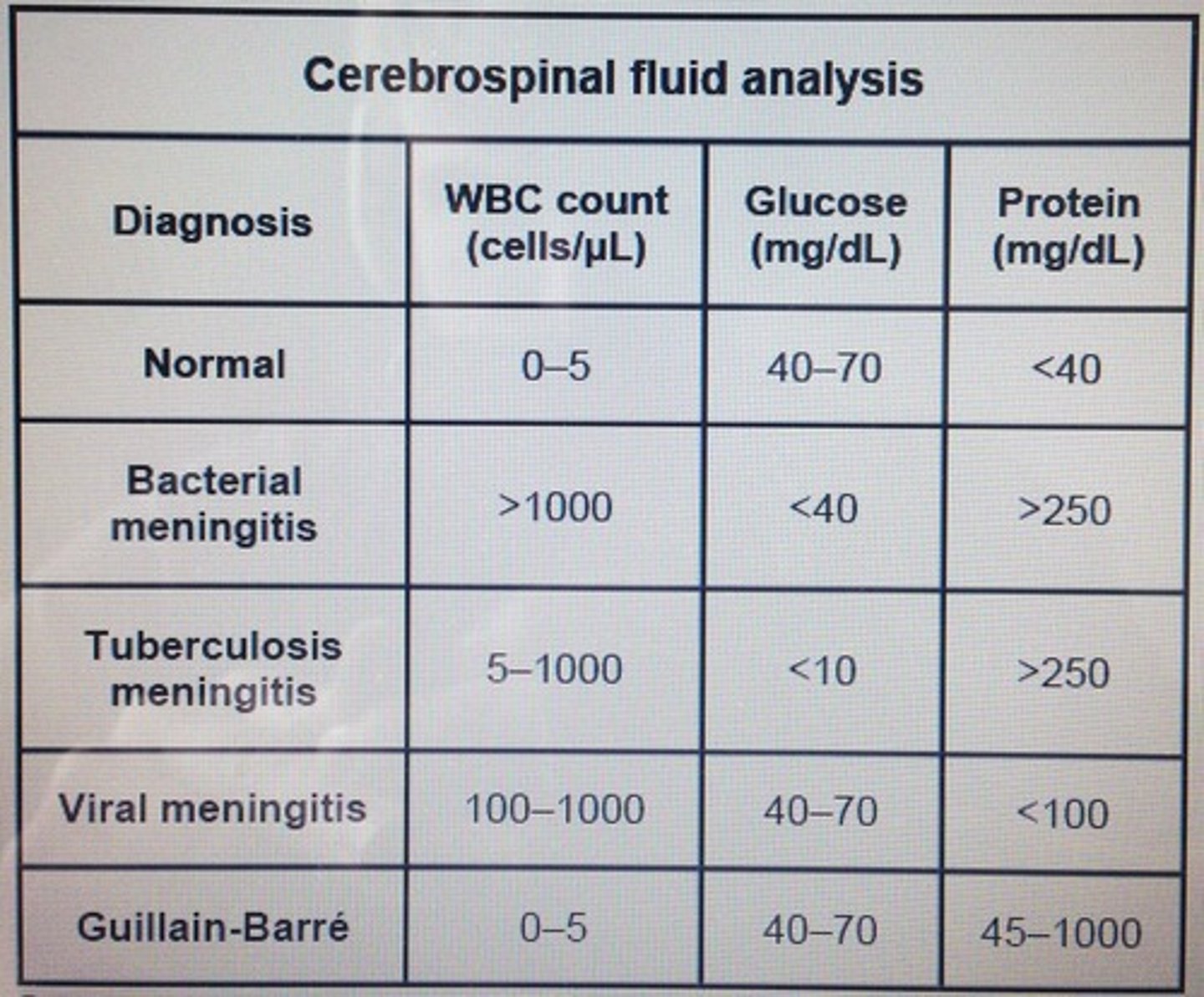
Major Laboratory results for differential diagnosis of meningitis: Bacterial
-elevated WBC count
-Neutrophils present
-marked protein elevation
-markedly decreased glucose level
-lactate level >35 mg/dL
-positive gram stain and bacterial antigen tests

Major Laboratory results for differential diagnosis of meningitis: Viral
-Elevated WBC count
-lymphocytes present
-moderate protein elevation
-normal glucose level
-normal lactate level

Major Laboratory results for differential diagnosis of meningitis: Tubercular
-elevated WBC count
-Lymphocytes and monocytes present
-moderate to marked protein elevation
-decreased glucose level
-lactate level >25 mg/dL
-pellicle formation

Major Laboratory results for differential diagnosis of meningitis: Fungal
-elevated WBC count
-lymphocytes and monocytes present
-moderate to marked protein elevation
-normal to decreased glucose level
-lactate level >25 mg/dL
-positive india ink with Cryptococcus neoformans
-positive immunologic test for C. neoformans
CSF Gram Stain
-performed on CSF from all suspected cases of meningitis.
-performed on concentrated specimens because often only a few organisms are present at the onset of the disease.
-CSF should be CENTRIFUGED at 1500 g for 15 minutes, and slides/cultures should be prepared from the sediment.
-a CSF gram stain is one of the most difficult slides to interpret bc the number of organisms present is usually small

Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
proteins produced by your immune system that can attack healthy tissue in your body
Gram stain of C. neoformans showing starburst pattern (x1000)
The functions of the CSF include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. removing metabolic wastes
b. producing an ultrafiltrate of plasma
c. supplying nutrients to the CNS
d. protecting the brain and spinal cord
B. producing an ultrafiltrate of plasma
The CSF flows through the:
a. choroid plexus
b. pia mater
c. arachnoid space
d. dura mater
C. arachnoid space
Substances present in the CSF are controlled by the:
a. arachnoid granulations
b. blood-brain barrer
c. presence of one-way valves
d. blood-CSF barrier
B. blood-brain barrier
What department is the CSF tube labeled 3 routinely sent to?
a. hematology
b. chemistry
c. microbiology
d. serology
A. hematology
The CSF tube that should be kept at room temperature is:
a. tube 1
b. tube 2
c. tube 3
d. tube 4
B. tube 2
Place the appropriate letter in front of the statement that best describes CSF specimens in these two conditions:
A. traumatic tap
B. Intracranial hemorrhage
___Even distribution of blood in all tubes (1)
___Xanthochromic supernatant (2)
___Concentration of blood in tube 1 is greater than in tube 3 (3)
___specimen contains clots (4)
1. B
2. B
3. A
4. A
The presence of xanthochromia can be caused by all of the following EXCEPT:
a. immature liver function
b. RBC degradation
c. a recent hemorrhage
d. elevated CSF protein
C. a recent hemorrhage
A web-like pellicle in a refrigerated CSF specimen indicates:
a. tubercular meningitis
b. multiple sclerosis
c. primary CNS malignancy
d. viral meningitis
A. tubercular meningitis