Cornell Mechanical Ventilation Video
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Trigger Variable
What starts inspiration
Limit Variable
What determines the max volume or pressure
Cycle Variable
What switches the ventilator from inspiration to expiration
Mandatory Breath
Vent does all the WOB
Triggered, limited, and cycled by the ventilator
Assisted Breath
Vent does most of the WOB
Triggered by the patient, limited and cycled by the ventilator
Supported Breath
Supports breath with positive pressure
Triggered by the patient, limited by the ventilator, and cycled by the patient
Spontaneous Breath
Patient does all the WOB
Triggered, limited, and cycled by the patient
Volume Control
Delivered breath has a constant volume
Set tidal volume
Continuous Mandatory Ventilation
Preset breaths/minute of a preset TV
Ventilator performs all WOB
Volume Assist/Control Mode
Preset breaths/min of TV
Spontaneous respirations allowed
Vent detects, assists with breath
WOB: negative pressure to start breath
Downside of volume assist/control is that the vent helps with all of the breaths so can get hyperventilation
Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation and Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation
Set number of breaths of a set TV
Patient allowed to breathe spontaneously, not assisted so variable TV
IMV: mandatory breaths delivered at a set time
SIMV: synchronized to spontaneous breath
Pressure Control
Pressure is constant for every breath
Volume Control vs Pressure Control
With volume control, ventilator will use whatever pressure is necessary to get that volume in
Good for still diseased lungs because it will get the volume in
Downside is that we can cause barotrauma
Upside to pressure control is that the ventilator will never give excessive pressure
Downside is that there are variable tidal volumes so may not be giving enough volume
Good when we are ventilating a patient who has normal lungs, neuromuscular disease
Difference Between PEEP and CPAP
Difference between PEEP and CPAP is that CPAP is on a patient that is spontaneously breathing
CPAP - Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
Positive pressure applied throughout the respiratory cycle in a spontaneously breathing patient
Pressure Support
Patient’s spontaneous respirations are augmented by preset inspiratory positive pressure
“Helps” breath on inspiration by applying a small amount of positive pressure, decreasing WOB
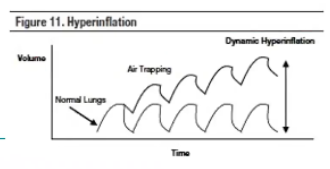
Auto-PEEP
Incomplete expiration prior to the initiation of the next breath causes progressive air trapping (hyperinflation)
This accumulation of air increases alveolar pressure at the end of expiration, which is referred to as auto-PEEP
Usually because we haven't given the patient enough time to expire
RR too high
Patient spontaneously breathing on their own and overriding the ventilator breaths
On a waveform will see baseline pressure continue to go up
High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV)
A typpe of mechanical ventilation that uses a constant distending pressure (mean airway pressure [MAP]) with pressure variations oscillating around the MAP at very high rates (up to 900 cycles per minute
This creates small tidal volumes, with constant PEEP/positive airway pressure
Decreased ventilator-induced lung injury
![<p>A typpe of mechanical ventilation that uses a constant distending pressure (mean airway pressure [MAP]) with pressure variations oscillating around the MAP at very high rates (up to 900 cycles per minute</p><p>This creates small tidal volumes, with constant PEEP/positive airway pressure</p><p>Decreased ventilator-induced lung injury</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/592a57d3-e464-49f7-9d5d-c6f11f5007ec.png)