W3, Diabetes
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
What kind of disorder is diabetes?
Carbohydrate metabolism disorder
What is problem in diabetes?
Body is unable to produce or use insulin (secreted in pancreas by beta cells)
Where is insulin produced?
In pancreas by beta cells
True/False: In diabetes, patient has too much insulin
False; in diabetes, body is unable to produce or use insulin
Why is insulin needed in our bodies?
Insulin attaches to receptors which allows glucose to go into cells (could think of it like transporter protein allowing glucose into cells then), which provides us with energy and regulates our blood sugar levels
True/False: Insulin is needed in humans because it attaches to receptors which allows glucose to go into cells, which provides us with energy and regulates our blood sugar levels
True!
What happens in our bodies without insulin?
Sugars back up in bloodstream, which leads to hyperglycemia
What are 3 types of diabetes?
Gestational, Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes
What is gestational diabetes?
Hormone made by placenta in pregnancy prevents the body from using insulin effectively so glucose builds up in blood instead of being absorbed by cells
What does gestational diabetes increase risk of?
Increases risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life by 60%
What are risk factors for developing gestational diabetes?
Overweight (obesity), family history of diabetes, having given birth previously to infant weighing greater than 9 pounds, age, race, prediabetes
What is Type 1 diabetes?
Happens due to autoimmune disease where immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys beta cells in pancreas, so pancreas can’t produce insulin at all
What increases risk of developing Type 1 diabetes?
Having an inherited link (genetics), so if parent or siblings has Type 1 diabetes risk increases for example
When is onset of Type 1 diabetes?
Usually diagnosed around puberty (when body starts attacking pancreas)
Is onset of Type 1 diabetes rapid or slow?
Rapid (patient goes from feeling fine to showing 3P symptoms in a week)
What is Type 1 ½ diabetes?
Exactly same as Type 1 diabetes, due to autoimmune disease where immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys beta cells in pancreas, so pancreas can’t produce insulin at all, but is diagnosed in late 20s (NOT puberty)
True/False: Type 1 diabetes and Type 1 ½ diabetes are exactly the same
False; although both Type 1 and Type ½ diabetes are due to autoimmune disease where immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys beta cells in pancreas, so pancreas can’t produce insulin at all, Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed in puberty whereas Type 1 ½ is diagnosed in late 20s
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Happens due to cells being resistant to insulin so insulin can’t attach to receptors which causing glucose to not be able to get into cells, even though body is still producing some insulin OR pancreas fails to produce enough insulin OR insulin is poorly utilized in body
What is onset of Type 2 diabetes?
Onset is slower and over time as insulin receptors become more resistant OR pancreas slowly fails to produce enough insulin
What are diagnostics?
Diagnostics are tests, procedures, and tools used to identify, monitor, and manage diseases or health conditions
What are diagnostics of diabetes (all types; type 1, type 2, and gestational)?
Fasting glucose level, random glucose level, oral glucose tolerance test, glycated hemoglobin (A1C), urinalysis, diabetes autoantibodies panel
What is fasting glucose level test?
Patient doesn’t eat or drink anything except water for 8 hours, then glucose is checked. If glucose is above 126 this first time, another fasting test has to be done at a different time to see if glucose is above 126 again. If 2 results come back over 126 mg/dl then patient has diabetes
What is random glucose level test?
Patient doesn’t fast prior to test (like in fasting glucose level test) and glucose is checked. If glucose is above 200 this first time, another test has to be done at a different time to see if glucose is above 200 again. If 2 results come back over 200 mg/dl then patient has diabetes
What is oral glucose tolerance test?
Patient drinks glucose and within 2 hours healthcare team sees what patient’s blood glucose levels are. Levels greater than 200mg/dl indicate client has diabetes
What is glycated hemoglobin (A1C) diagnostic?
Blood is drawn, send to lab, and lab tells patient a percentage of how well your blood sugar has been in past 2 to 3 months. For diabetics, a level between 6% and 7% means patient is managing diabetes well, but a level greater than 7% means patient needs help managing blood sugar
How is urinalysis performed to check for diabetes?
Normally, urine contains little to no glucose. When blood glucose levels rise above a certain threshold, kidneys cannot reabsorb the excess, causing it to "spill" into urine. Ketones are by-products formed when the body breaks down fat for energy because it cannot use glucose (due to lack of insulin). Their presence in urine, especially alongside high glucose, indicates severe, uncontrolled diabetes or Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
What is diabetes autoantibodies panel?
Detects antibodies in Type 1 diabetes that attack beta cells (insulin-producing) in pancreas
What is typical diagnostic test for gestational diabetes?
Oral glucose tolerance test
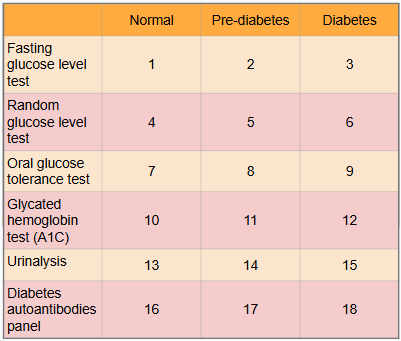
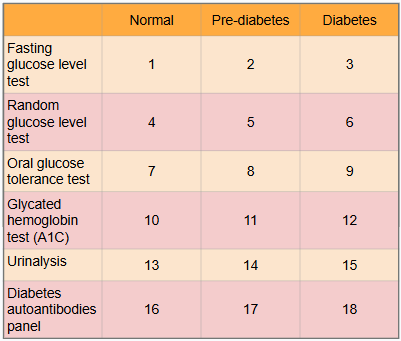
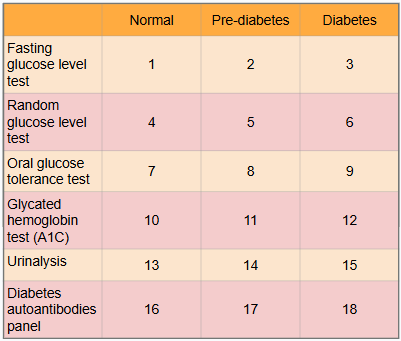
What is this?
Ranges of results to aid in diagnosis of diabetes
What is meant by the “normal” category?
Expected range for healthy adults with no pre-diabetes or diabetes present
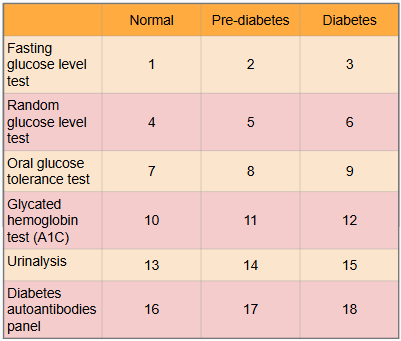
What is #1?
Less than 100 mg/dl
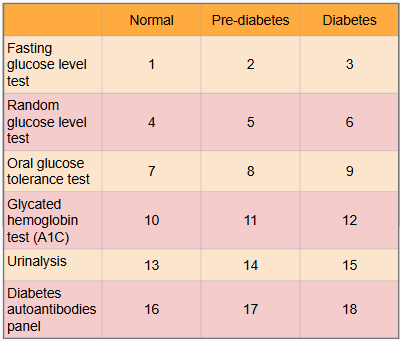
What is #2?
100 to 125 mg/dl
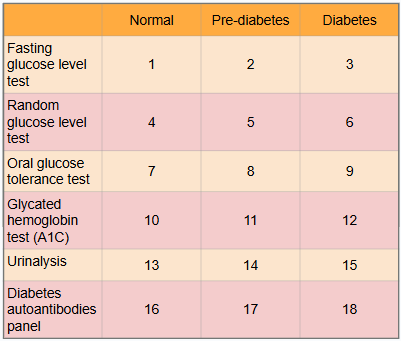
What is #3?
Greater than or equal to 126 mg/dl
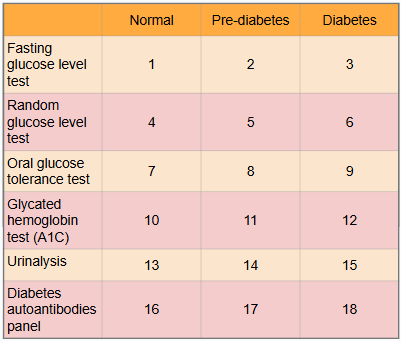
What is #4?
Less than or equal to 115 mg/dl
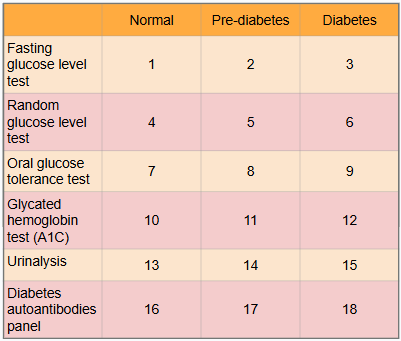
What is #5?
There is no indication for pre-diabetes in random glucose level test
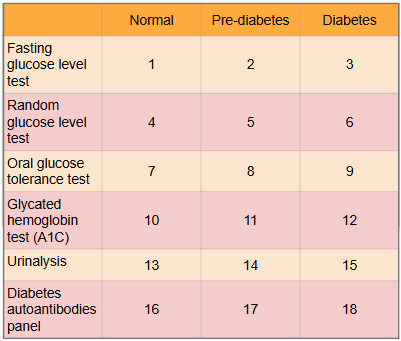
What is #6?
Greater than 200 mg/dl
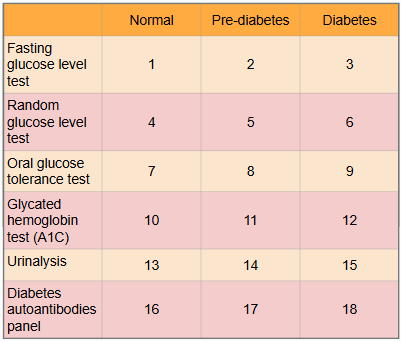
What is #7?
Less than or equal to 139 mg/dl
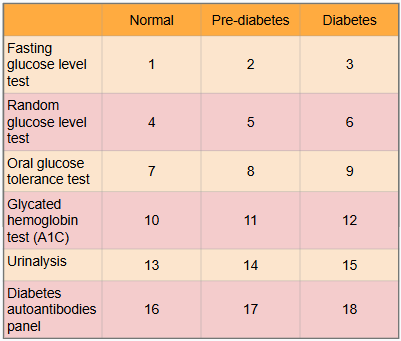
What is #8?
140 to 199 mg/dl
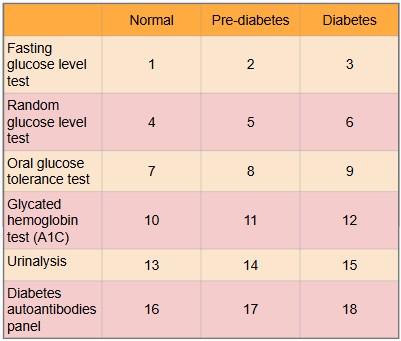
What is #9?
Greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl
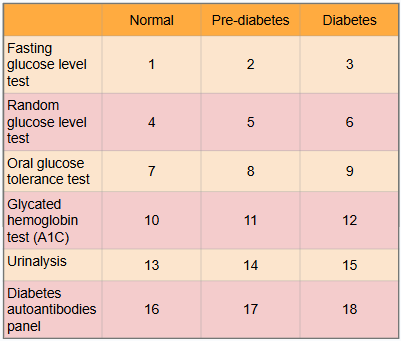
What is #10?
Less than 5.7%
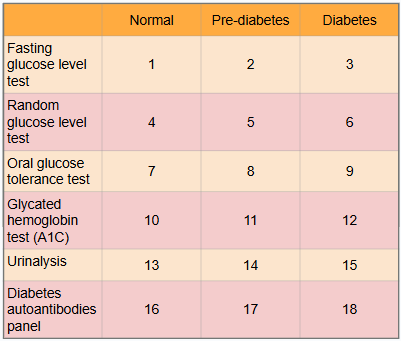
What is #11?
5.7% to 6.4%
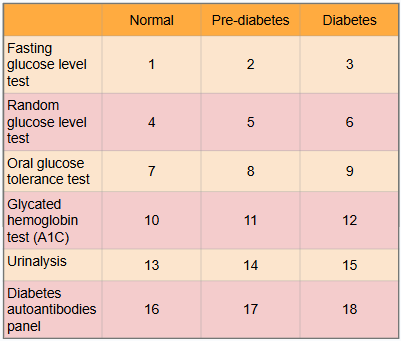
What is #12?
Greater than or equal to 6.5%
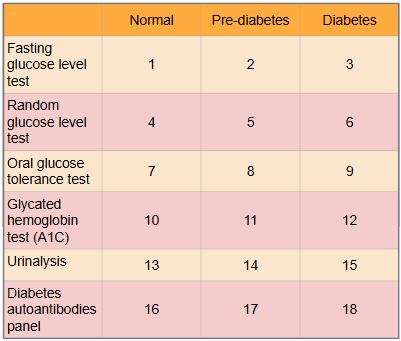
What is #13?
There is typically no glucose, and small amounts of ketones may be normal after long periods without food, during a ketogenic diet, or during pregnancy
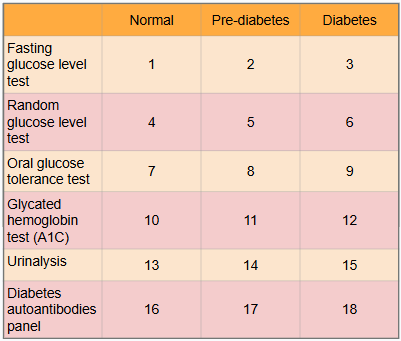
What is #14?
There is no in between normal and diabetes for urinalysis
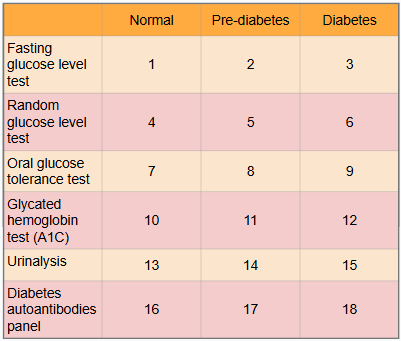
What is #15?
Presence of glucose and ketones in urine (moderate to large amounts)
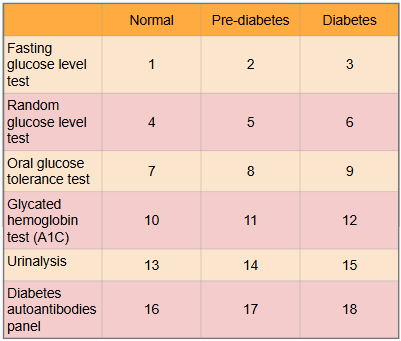
What is #16?
No presence of autoantibodies, but Type 2 diabetes would indicate no presence of autoantibodies as well, so this test only works for Type 1 diabetics
What is #17?
There is no in between as patient either has autoantibodies or doesn’t
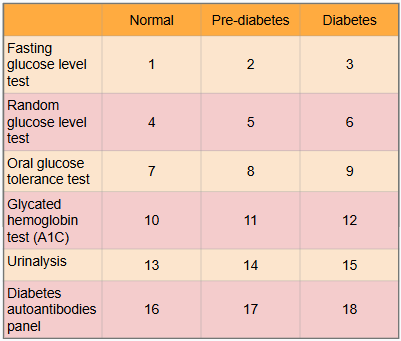
What is #18?
Presence of autoantibodies in Type 1 diabetic (Type 2 diabetic would show negative results to presence of autoantibodies)
True/False: Diabetes autoantibodies panel would show positive presence of autoantibodies in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics
False; diabetes autoantibodies panel would only show positive presence of autoantibodies in Type 1, NOT Type 2 diabetics
What does unit mg/dl stand for?
Milligrams per deciliter, a unit of measure representing the concentration of a substance (typically blood sugar or cholesterol) in a specific volume of fluid
True/False: Each diagnostic test (fasting, random, A1C, autoantibodies, urinalysis, OGTT) usually needs to be repeated on a second day to diagnose diabetes
True!
What are signs and symptoms of Type 1 diabetes?
Weight loss, fatigue, increased frequency of infections, rapid onset, insulin dependent, familial tendency, polyuria (increased urination), polydipsia (increased thirst), polyphagia (increased hunger)
What are 3 big P symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia (increased urination, increased thirst, increased hunger)
Why do Type 1 diabetics have an increased frequency of infections?
Hyperglycemia weakens immune system defenses, specifically impairing white blood cell function (neutrophils) and reducing the body’s ability to fight bacteria. Additionally, high glucose levels provide an ideal environment for pathogen growth, while associated vascular issues and neuropathy can hinder (slow) healing
True/False: 3 big P symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes include polynocturia, polynatremia, polyphobia
False; 3 big P symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes include polyuria (increased urination), polydipsia (increased thirst), polyphagia (increased hunger)
Does diabetes mellitus reference Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes?
Both
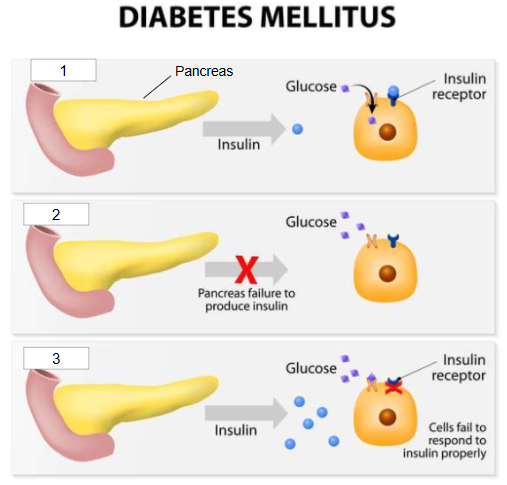
What is #1?
Healthy, functioning pancreas
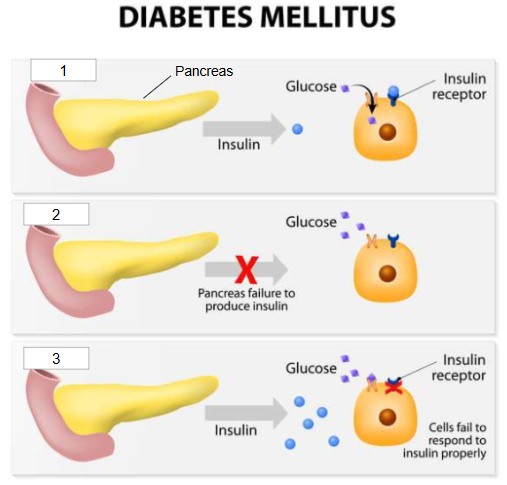
What is #2?
Type 1 diabetes
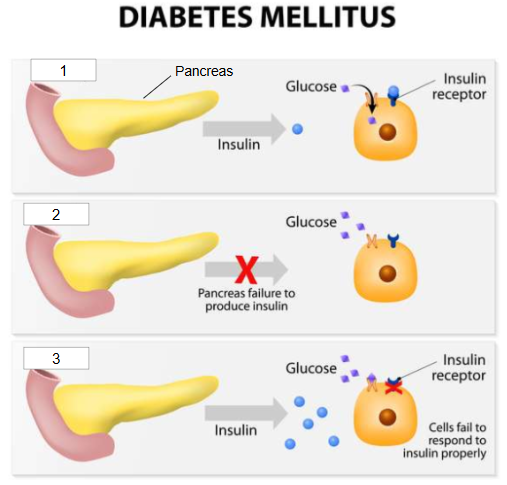
What is #3?
Type 2 diabetes
What are risk factors for Type 2 diabetes?
Have family history of diabetes, have BMI greater than or equal to 23, lead inactive lifestyle, have high blood pressure, have abnormal blood cholesterol/lipid levels, have history of gestational diabetes, are greater than or equal to 40 years old, have impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose
True/False: Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include having family history of diabetes, have BMI greater than or equal to 23, lead inactive lifestyle, have high blood pressure, have abnormal blood cholesterol/lipid levels, have history of gestational diabetes, are greater than or equal to 40 years old, have impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose
False; these are risk factors for TYPE 2 diabetes; having family history of diabetes, have BMI greater than or equal to 23, lead inactive lifestyle, have high blood pressure, have abnormal blood cholesterol/lipid levels, have history of gestational diabetes, are greater than or equal to 40 years old, have impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose
What are signs and symptoms of Type 2 diabetes?
Hypertension, fatigue, decreased energy, obese, recurrent infections, polyuria, polydipsia, fasting blood sugar (FBS) greater than 126 mg/dl
What is hypoglycemia?
Blood sugar level below 70 mg/dl, abnormally low blood sugar
What is hyperglycemia?
Blood sugar level between 130 to 140 mg/dl, or greater than 180 mg/dl 1 to 2 hours after a meal; high blood sugar
What is metabolic syndrome?
Cluster of 4 conditions that occur together and significantly increase the risk of diabetes, stroke, and heart disease
What are 4 conditions in metabolic syndrome that significantly increase the risk of diabetes, stroke, and heart disease?
Abdominal obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia, high lipid levels
True/False: Abdominal obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and high lipid levels are 4 conditions in metabolic syndrome that significantly increase the risk of diabetes, stroke, and heart disease
True!
What is metabolic syndrome also called?
Syndrome X
What is acronym for metabolic syndrome?
AHHL (abdominal obesity, hyperglycemia, hypertension, lipids increased)
What does BMI (body mass index) have to be greater than to count as abdominal obesity?
Greater than 25
What are acute complications of diabetes mellitus (type 1 or type 2)?
Hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS/HHNS)
What does HHS/HHNS stand for?
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome
True/False: Any sickness can wreck havoc on blood sugar levels in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes
True
What could cause hypoglycemia?
Too much insulin, skipped a meal (or insufficient food), excessive vomiting, excessive exercise
What can signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia appear just like?
Stroke (or someone really drunk)
Why should diabetics check blood sugar after exercising?
Exercise increases glucose uptake by muscles and can cause hypoglycemia
Is onset of hypoglycemia fast or slow?
Fast, onset is 1 to 3 hours
What are signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia?
Anxious, sweaty, hungry, confused, blurred or double vision, shaky, irritable, cool and clammy skin
What complication does the mnemonic “cool and clammy, need more candy” indicate?
Hypoglycemia
What complication does the mnemonic “hot and dry, they’re on a sugar high” indicate?
Hyperglycemia
What is mnemonic for hypoglycemia?
Cool and clammy, need more candy
What is mnemonic for hyperglycemia?
Hot and dry, they’re on a sugar high
What should nurse do if someone comes into hospital with symptoms including anxiety, sweaty, hungry, confused, blurred or double vision, shaky, irritable, cool and clammy skin?
Check blood glucose levels to confirm or rule out diabetes as symptoms can mimic a stroke or someone really drunk
What does patient with hypoglycemia need?
Needs blood sugar increased, so give glucose continuously so they don’t keep bottoming out
What does DKA stand for?
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Which type of diabetics, Type 1 or Type 2, are more likely to get diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
DKA happens more in Type 1
True/False: Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) happens more in Type 2 diabetics, whereas hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS/HHNS) happens more in Type 1 diabetics
False; diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) happens more in Type 1 diabetics, whereas hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS/HHNS) happens more in Type 2 diabetics
What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Develops when the body can't make enough insulin, so body begins to break down fat as fuel, which causes a buildup of acids in blood, called ketones. If it's not treated, buildup can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis
What are causes of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Illness, improper management of diabetes, newly-diagnosed Type 1 diabetic, GI upset, lack of insulin
True/False: Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) isn’t that serious so doesn’t require immediate treatment
False; diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a critical condition that requires immediate treat plus onset is quick
Is onset of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) rapid or slow?
Quick, onset is 4 to 10 hours
What are signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Breath smells like juicy fruit gum, Kussmaul respirations, thirsty, dehydration, tachycardia, hypotension, acidosis, high blood sugar over 240 mg/dl, hyperkalemia, polyuria
What are Kussmaul respirations?
Abnormal breathing pattern characterized by rapid, deep breathing at consistent pace, and is sign of medical emergency
What do Kussmaul respirations indicate?
Metabolic acidosis (type of this is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA))
Why does breath smell like juicy fruit gum in those who have diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Due to high glucose levels
What does blood sugar test result of greater than 240 mg/dl or no result indicate?
Indicates diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS/HHNS)
Why would no result of a blood sugar test indicate diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS/HHNS)?
Because glucose levels are so high that glucometer cannot read them
Why is hypotension sign of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Fluids are pulled into bloodstream, which causes excretion to the max (polyuria), and this causes massive dehydration as well as hypotension
True/False: In diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), fluids are pulled into bloodstream, which causes excretion to the max (polyuria), and this causes massive dehydration as well as hypotension
True
What is criteria to aid in diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
pH is less than 7.3, HCO3 (bicarbonate) is less than 18, urinalysis shows positive for ketones, blood sugar is greater than 240 mg/dl