Biochem Exam 1 Important Info
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Things she said to memorize
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What type of bond hold monomers together?
Covalent bonds (strong)
What type of bond holds supre and macromolecules together?
Noncovalent, weak bonds like hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions.
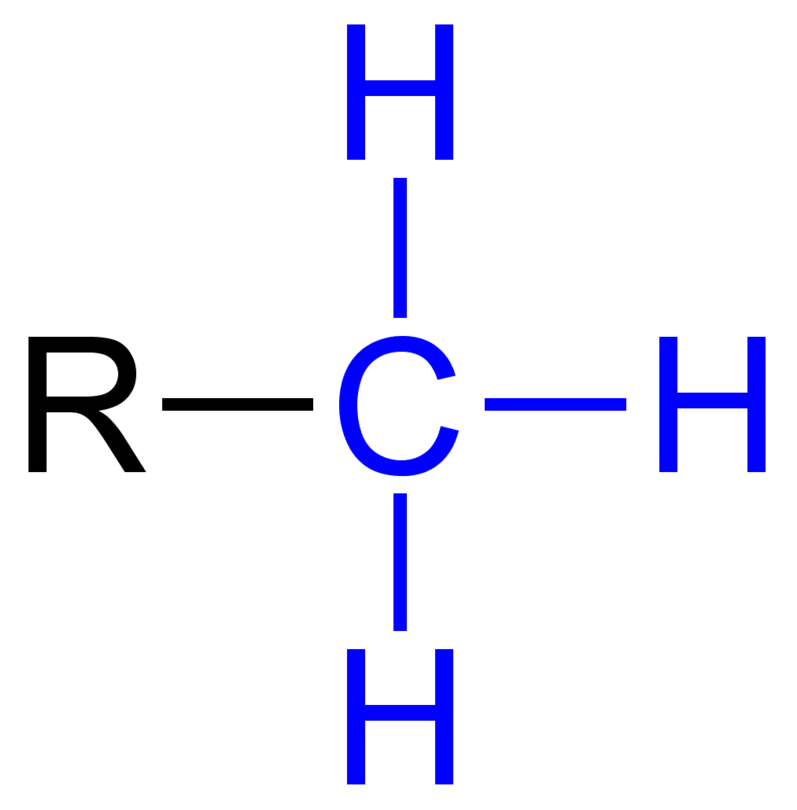
Group Name?
Methyl
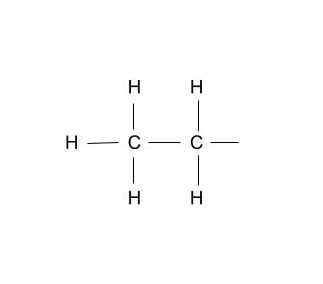
Group Name?
Ethyl
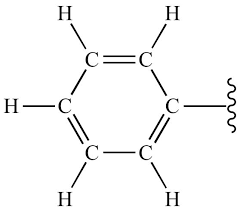
Group Name?
Phenyl
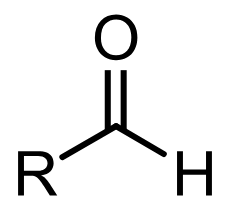
Group Name?
Aldehyde (carbonyl type)
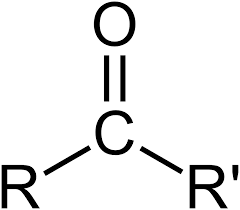
Group Name?
Ketone (carbonyl type)
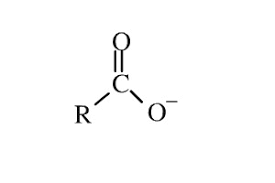
Group Name?
Carboxyl
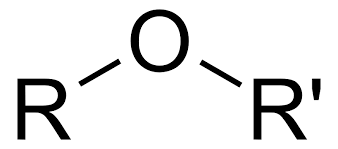
Group Name?
Ether
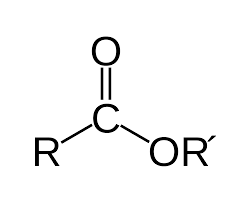
Group Name?
Ester
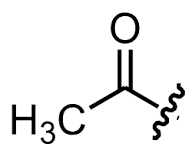
Group Name?
Acetyl
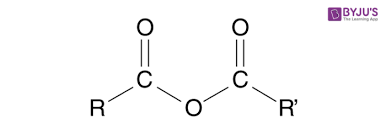
Group Name?
Anhydride
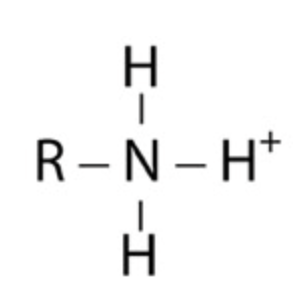
Group Name?
Amino (prontonated)
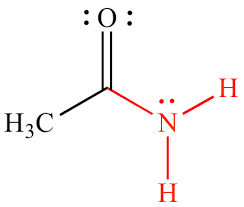
Group Name?
Amido
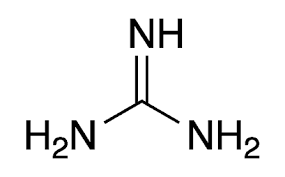
Group Name?
Guanidium
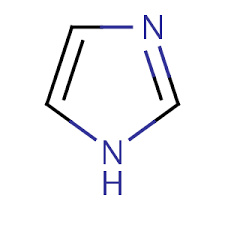
Group Name?
Immidazol
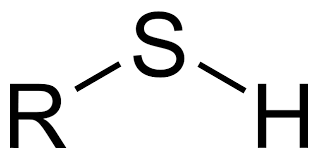
Group Name?
Sulfhydryl
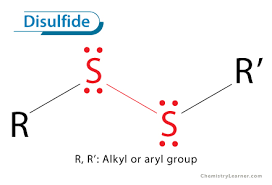
Group Name?
Disulfide
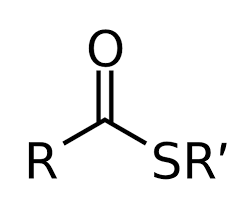
Group Name?
Thioester
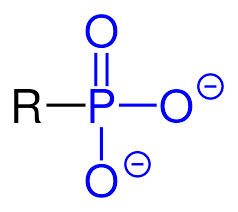
Group Name?
Phosphoryl
How does cell size/weight impact suface area/volume ratio?
As size increases, the ratio decreases (inverse relationship)
Formula for Gibbs Free Energy?
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS ( + S and - G = favorable)
Formula for Equilibrium Constant (K)?
K = Products / Reactants
Gibbs in terms of Equilibrium
ΔG° = -RT ln(K)
Which element cannot be a hydrogen bond donor and why?
Carbon, because it does not have a dipole stronger than nitrogen or oxygen.
What is the ion product of water (Kw)?
1.0 × 10^-14 M² = [H+][OH-]
What is the formula for pH?
pH = -log[H⁺] = log 1/[H+]
What is the formula for the acid dissociation constant (Ka)
Ka = ([H⁺] x [A⁻]) / [HA]
Pka Formula?
pKa = -log₁₀(Ka)
When does pH = pKa?
At the midpoint, when [HA] = [A-]
What is a Zwitterion?
Amino acid with a chargo amino group or a carboxyl salt
Isoelectric point formula?
pI = (pKa1 + pKa2) / 2,
What does cysteine do?
It can ionize the side chain at high pH and oxidize to form disulfide bonds.
How to find the number of residues in a protein?
Molecular weight of the protein / 110
How to find the number of possible peptide sequences?
Number of sequences = (number of possible of amino acids)(peptide length)
Which bond is the phi angle?
N-alpha C bond
What bond is the psi angle?
The alpha C-C (the one that is double bonded to O) bond
What bond is the omega angle?
The C (the one that is double bonded to O) -N bond
What is the acronym for amino acid residues in alpha helix secondary structure?
Kristin Has Marvelous LACE Q-tips (uppercase letter = AA)
What is the acronym for amino acid residues in beta sheet secondary structure?
IVY For The Win (uppercase letter = AA)
What is the acronym for amino acid residues in reverse turns?
SPDNG (uppercase letter = AA)
What does is mean if nH is equal to or less than 1?
There is no cooperativity
What does is mean if nH is greater than 1?
There is will be cooperativity; nH= the number of binding sites that will be impacted
What type of reaction occurs for the oxidoreductases enzyme (Class 1)
Transfer of electrions (hydride ions or H atoms)
What type of reaction occurs for the Transferases enzyme (Class 2)
Functional group transfer between two different molecules
What type of reaction occurs for the Hydrolases enzyme (Class 3)
Hydrolysis (transfer of functional groups to water)
What type of reaction occurs for the Lyases enzyme (Class 4)
Cleavage of C-C, C-O, C-N or other bonds via elimination, cleaving double bonds or rings, or addition of groups to double bonds.
What type of reaction occurs for the of the Isomerases enzyme (Class 5)
Transfer of groups within molecules to yield isomeric forms.
What type of reaction occurs for the Ligases enzyme (Class 6)
Formation of C-C, C-S, C-O, and C-N bonds via condensation reactions coupled to cleavage of ATP or a similar cofactor.
What type of reaction occurs for the Translocases enzyme (Class 7)
Movement of molecules or ions across membranes or their separation within membranes.
What is the relationship between activation energy and reaction rate?
They have an inverse relationship; as activation energy increases, reaction rate decreases (slows).
What is the Michaelis-Menten formula in terms of kcat?
V0 = kcat [Et] [S] / km + [S]
What is the Michaelis-Menten Equation?
V0 = Vmax [S] / Km + [S]
What is the relationship between Vmax and kcat?
Vmax = kcat [Et]
What is the pka of NH3+? (the end amino for calculating pI)
9.69
What is the pka of COOH? (the end amino for calculating pI)
2.18
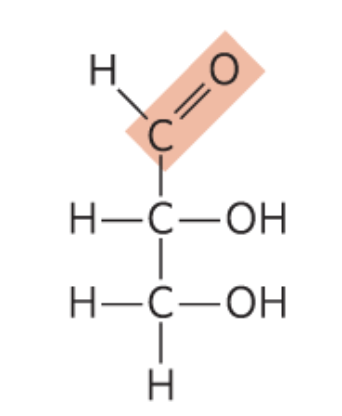
What monosccaride is this?
D-Glyceraldehyde
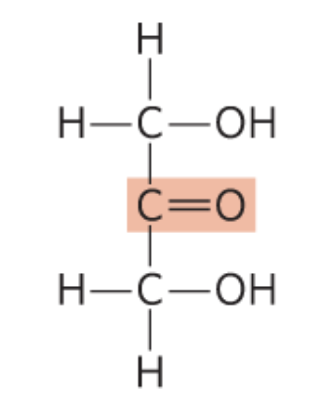
What monosccaride is this?
Dihydroxyacetone
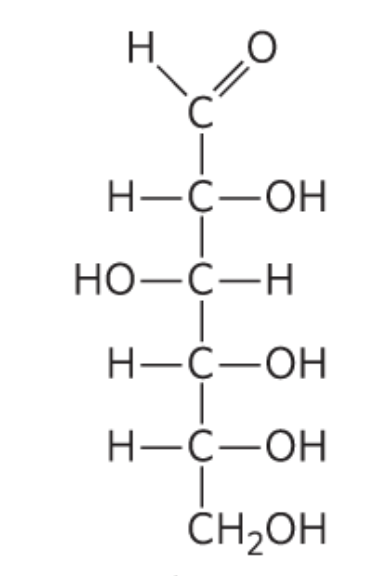
What monosccaride is this?
D-Glucose
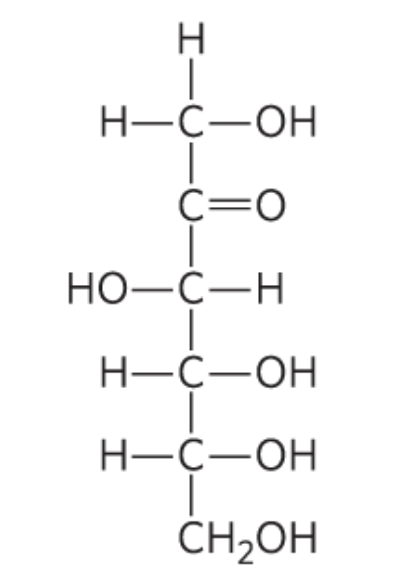
What monosccaride is this?
D-Fructose
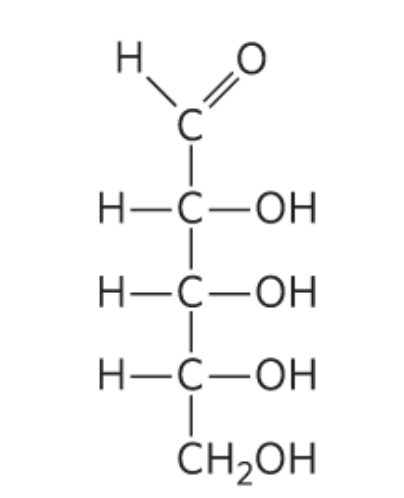
What monosccaride is this?
D-Ribose
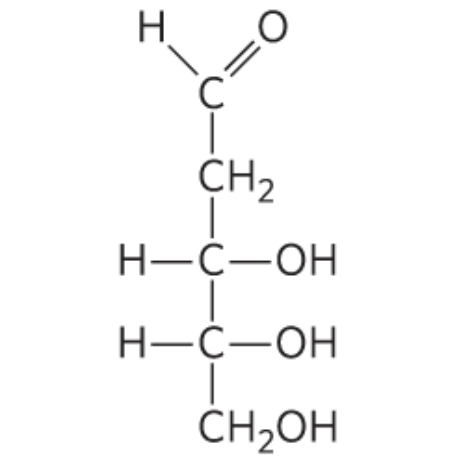
What monosccaride is this?
2-Deoxy-D-Ribose

What is the name of this Fatty Acid?
n-hexadecanoic acid

What is the name of this Fatty Acid?
n-octadecanoic acid
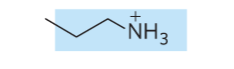
what is the name of the glycerophospholipid with this head group?
Phosphatidylethanolamine (head group = ethanolamine)
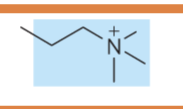
what is the name of the glycerophospholipid with this head group?
Phosphatidylcholine (head group = choline)
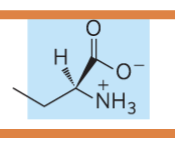
what is the name of the glycerophospholipid with this head group?
Phosphatidylserine (head group = serine)
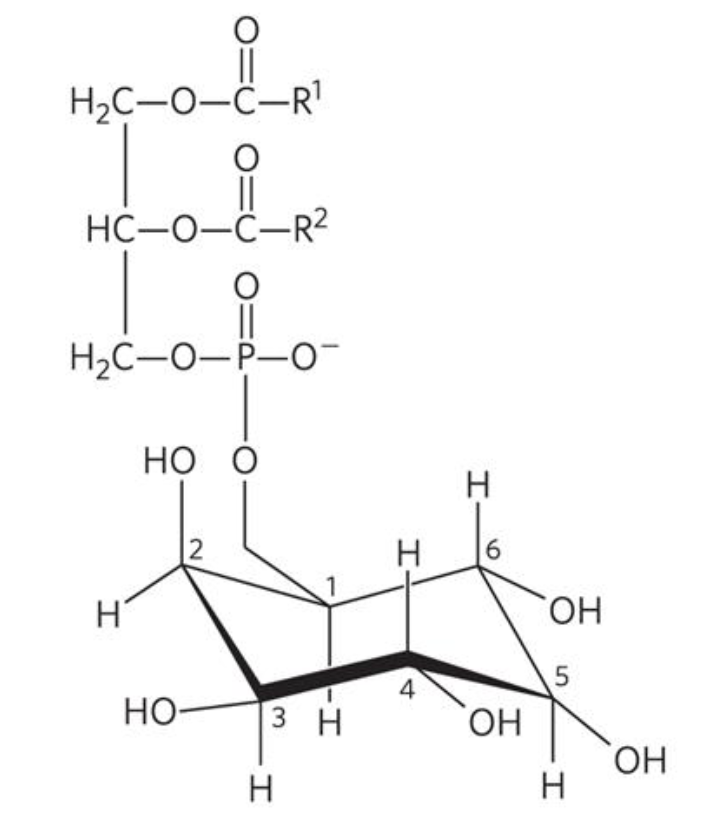
What is the name of this structure?
Phosphatidylinositol
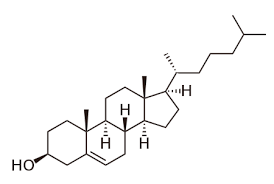
What is the key derivative of sterols?
Cholesterol
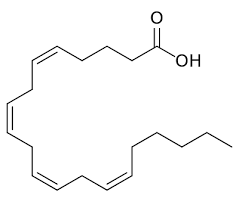
What is the name of this strucute and what type of lipid is it?
Arachidonic acid from eicosanoids
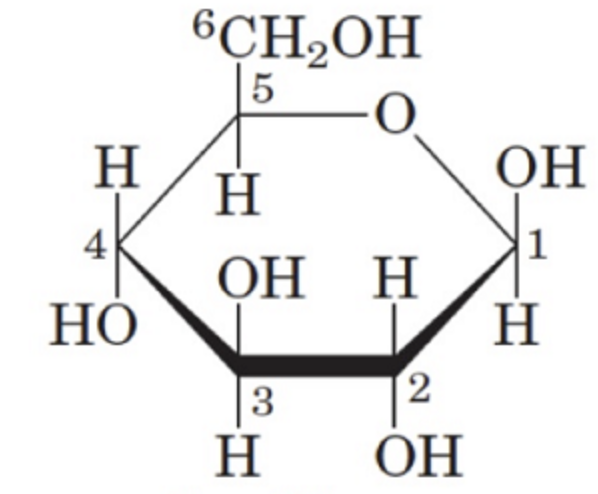
What is the name of this structure?
B (beta)-D-glucose