Investment Management Exam #1
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Real Assets
Assets used to produce goods and services
What is a limit order?
Execute only if you can meet my specified price (or better)
Financial Assets
Claims on real assets or the income generated by them.
Fixed-income (debt) securities
Pay a specified cash flow over a specific period
Equity
An ownership share in a corporation
Derivative Securities
Securities providing payoffs that depend on the values of other assets
Example of financial assets
Deposits, Pension funds, mutual funds, life insurance.
What are the roles of Financial Markets in the Economy?
Informational Role
Consumption Timing
Risk allocation and diversification
Separation of Ownership and Management
Liquidity
Payment mechanism
Asset Allocation
Allocation of investment portfolio across broad asset classes - % of fund in asset classes.
Top Down Investment Strategies
Security Selection
Choice of particular securities within asset class
Bottom up investment strategies
Security Analysis
Risk-Return Tradeoff
Higher expected returns means higher risk
Stock portfolios lose money an average of 25%
Bonds (Lower average rates of return(under 6%), Not lost more than 13% of value in any one year)
Market Efficiency
Competitive markets are where investors compete for profits
Competitive markets lead to market efficiency
No overvalued or undervalued securities in an efficient market.
Market price is right and no investor can consistently outperform the market
Market efficiency => Active vs. Passive Investment Management
Example of Active and Passive Investment Management
Active: Mutual fund or hedge fund
Passive: ETF
What are the major players in financial markets?
Business firms, households, governments, financial intermediaries(banks, investment companies, insurance companies)
Where can I invest my money?
1. Cryptocurrencies - Risk Level: Very High
2. Commodities - Risk Level: High
3. Emerging Market Equities - Risk Level: High
4. Individual Stocks (Equities) - Risk Level: High
5. High-Yield Bonds (Junk Bonds) - Risk Level: High
6. Real Estate - Risk Level: Moderate to High
7. Corporate Bonds - Risk Level: Moderate
8. Mutual Funds & ETFs - Risk Level: Moderate
9. Government Bonds (Sovereign Debt) - Risk Level: Low to Moderate
10. Investment-Grade Bonds - Risk Level: Low
11. Cash and Cash Equivalents - Risk Level: Very Low
12. Precious Metals - Risk Level: Low to Moderate
13. Certificates of Deposit (CDs) - Risk Level: Very Low
14. Savings Accounts - Risk Level: Very Low
Equity Securities
Common Stock & Preferred Stock
Common stock
Residual Claim & Limited Liability
Preferred Stock
Priority over common, Fixed dividends: limited gains, nonvoting, tax treatment: corporate tax exclusions on 70% of dividends earned.
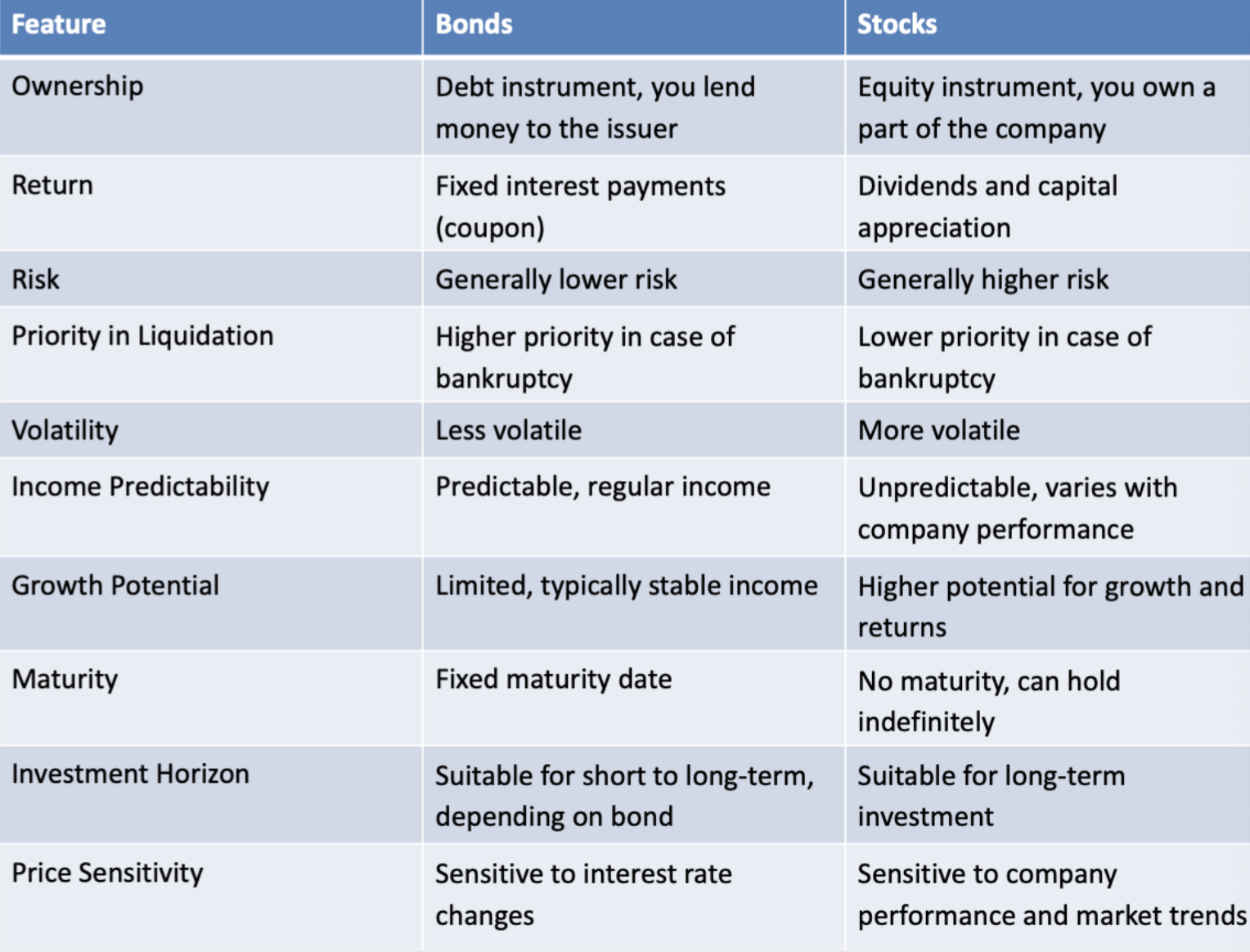
Bonds vs. Stocks
Photo
Money Markets
Subsection of the fixed-income market
Short-term
Highly liquid
Low risk
Often have large denominations
Money Market Securities
T-bills
Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
Commercial Paper or Bill
Repurchase Agreements (Repos)
Bankers' Acceptances
Eurodollar Deposits
Municipal Notes
Federal Funds
London Interbank Offer Rate (LIBOR)
Replaced by Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR)
Money Market Securities
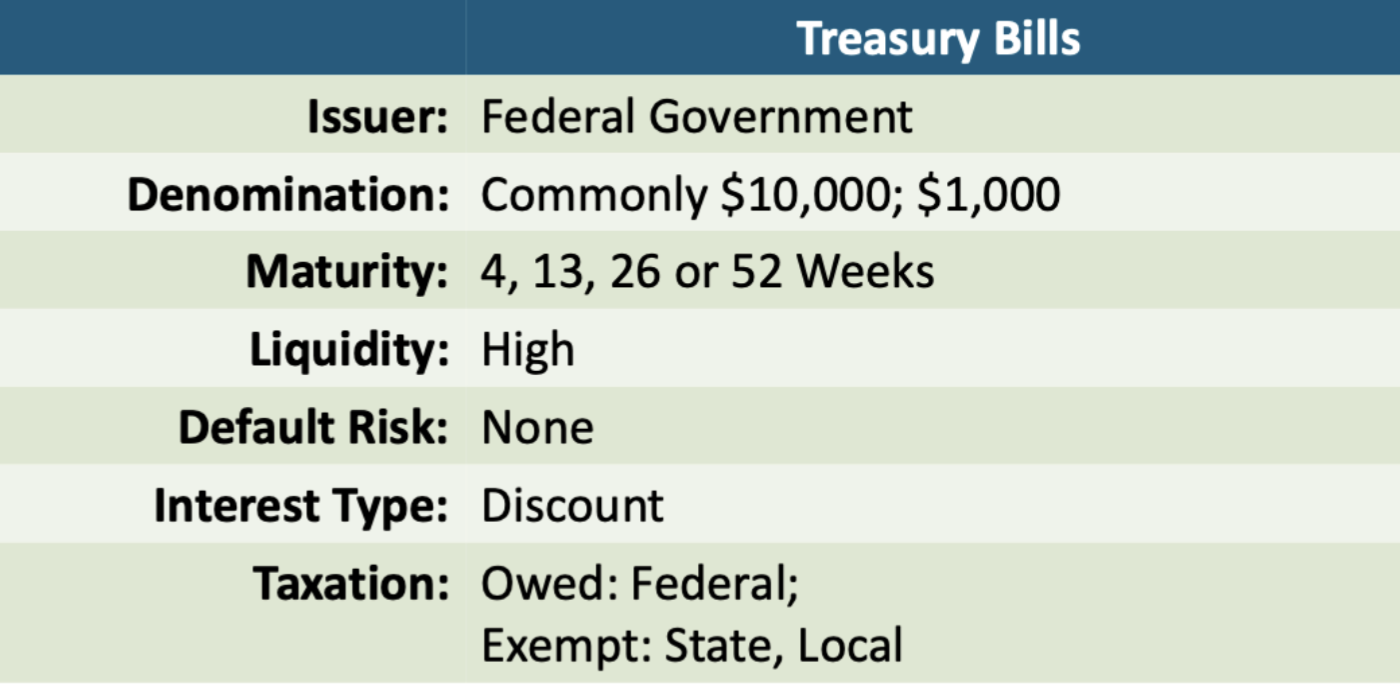
Treasury Bills
Look at the photo
Treasury Bonds
Ask prices are always above bid prices
Treasury Bills
Quoted in discount rates(not prices paid)
A high discount rate means a low price paid
Ask discounts are always lower than bid discounts
Bid price
Price paid if I sell
Ask price
Price paid if I buy
Bond Equivalent Yield
Can’t compare T bill directly to bond
360 vs. 365 days
Return is figured in par vs. price paid
Annualize investment gain to make them comparable
Derivative Asset/Contingent Claim
Security with payoff that depends on the price of other securities
Futures Contracts
Purchaser (long) buys specified quantity at contract expiration for set price
Contract seller (short) delivers underlying commodity at contract expiration for agreed-upon price.
Call option
Right to buy an asset at a specified price on or before a specified expiration date
Put option
Right to sell an asset at a specified exercise price on or before a specified expiration date.
Holding-Period Return
Rate of return over given investment period.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
Per period rate x Periods per Year
Effective Annual Rate
Actual rate an investment grows
Is there a numerical measure of dispersion to quantify risK?
Variance and standard deviation.
Measuring Risk
In finance, risk refers to the degree of uncertainty and/or potential financial loss inherent in an investment decision.
Investment risk depends on the dispersion or spread of possible outcomes.
Probability distribution
Possible outcomes with probabilities
Expected Return
Mean value
Variance
Expected value of squared deviation from mean
Standard deviation
Square root of variance
Value at risk (VaR)
Measure of downside risk
Worst loss with given probability usually 1 % or 5%
Risk-free rate
Rate of return that can be earned with certainty
Risk Premium
Expected return in excess of that on risk-free securities
Excess return
Rate of return in excess of risk-free rate.
Risk aversion
Reluctance to accept risk. Higher reward to accept higher risk.
Risk vs. Return Trade offs
Look at the image
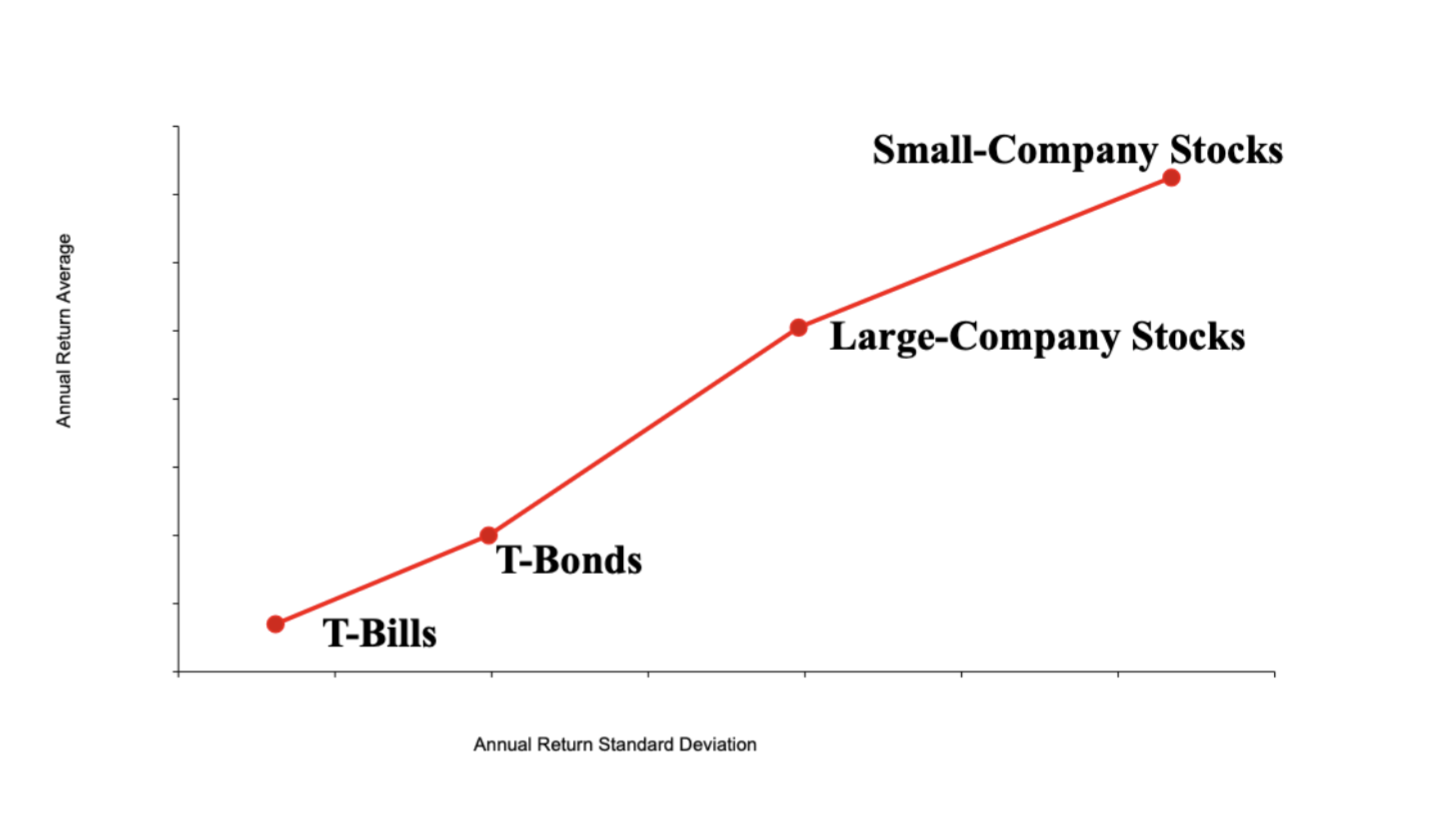
Sharpe Ratio
A statistic commonly used to rank portfolios in terms of this risk-return tradeoff. A higher ratio indicates a better reward per unit of standard deviation and a more efficient portfolio.
Primary Market
Market for new issues of securities
Secondary Market
Market for already-existing securities
How firms issue securities
Privately held firms
Publicly Traded Companies
Initial Public Offerings (IPO)
What is an Initial Public Offering (IPO)?
Issuer and underwriter put on “road show”
Purpose: Bookbinding and pricing
Underpricing
Post-initial sale returns average 10% or more “winner’s curse”
Easier to market issue => costly to issuing firm
Direct Search Markets
Buyers and sellers locate one another on their own.
Brokered Markets
Third-party assistance in locating buyer or seller
Dealer Markets
Third party acts as intermediate buyer/seller
Auction Markets
Brokers and dealers trade in one location. Trading is more or less continuous.
What are the types of trades that investors execute?
Market Order
Price-contingent Order
What is a market order?
Means to execute immediately at the best available price.
Price-contingent order
Limit order: specifies price at which investor will buy/sell
Stop order: not to be executed until price point hit.
Broker
Buy and sell on behalf of their clients, earns commissions.
Dealers
Buy and sell for their own account, earn profits = bid-ask spread.
Trading Costs
Commission: Fee paid to broker for making transaction. Spread: Cost of trading with dealer. Combination: on some trades both are paid.
Buying on margin
Investors borrows cash from a broker to purchase stocks.
Stocks are used as collateral.
The investor profits from the price difference if the stock price increases.
Short selling
An investor borrows shares from a broker sells them with the hope of buying them back at a lower price (to return to lender)
The investor profits from the price difference if the stock price declines.
Maintenance Margin Requirement (MMR)
Minimum value before additional funds must be added.
Margin Call
Notification from broker that you must put up additional funds or have position liquidated.
If Equity / Stock Value <= MMR
then margin call occurs
Short Sales
Borrow stock from broker, the liability is the borrowed stock. Broker sells stock, and deposits proceeds as Cash. Broker post margin in margin account. Required initial margin and margin call as before. Liable for any cash flows - dividend on stock.
Covering or closing out position
Buy stock; broker returns title to original party.
What are investment companies?
Financial intermediaries that invest the funds of individual investors in securities or other assets. Functions: record keeping and administration, diversification and divisibility, professional management, lower transaction costs.
Net asset value (NAV)
Assets minus liabilities per share.
Open end fund
A fund that issues or redeems its shares at NAV
Closed end fund
Shares are traded at prices that can differ from NAV and may not be redeemed.
Types of Investment Companies
Unit Investment trusts
Managed Investment Companies
Commingled Funds
Real Estate Investment Trusts
Hedge Funds
Costs of Investing in Mutual Funds
Annuaal fees
Loads
Soft Dollars
Annual fees
Paid Each year as a % of funds invested - expense ratios, management fees…. for marketing/distribution costs.
Operating Expenses
Costs in incurred by mutual fund in operating portfolio
Front-end load
Commission or sales charge paid when purchasing shares
Back-end load
“Exit fee incurred when shares
Soft dollars
Value of research services brokerage house provides “free of charge” in exchange for business.