BIOL 2460 - chapter 15 - PARKS - MICROBIOLOGY
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parks UTA
Last updated 11:33 PM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
Disease
a condition where normal structure and/or function are damaged or impaired
2
New cards
Infection
invasion of pathogen or parasite that lead to disease
3
New cards
Signs
things that can be directly measured by clinician (e.g. blood cell counts, Heart rate, respiratory rates)
4
New cards
Symptoms
things felt by patient that cannot be clinically measured (e.g. nausea, headache, loss of appetite) (EXPRESSED BY PT)
5
New cards
Syndrome
groups of signs & symptoms that help indicate a particular disease
6
New cards
asymptomatic
only signs can be observed thru correct testing
7
New cards
Infectious
disease caused by direct effect of a pathogen
8
New cards
Communicable
capable of spreading person-to-person (contagious – easily spread) (STD’s/ HIV, Malaria)
9
New cards
Iatrogenic
acquired as result of medical procedure
10
New cards
Nosocomial
acquired from hospital setting
11
New cards
Zoonotic
acquired from animal (rabies, malaria, avian flu)
12
New cards
Non-communicable
obtained from non-living thing such as soil or contaminated object (tetanus, Sickle Cell Anemia)
13
New cards
Non-infectious
not caused by pathogen (Sickle Cell Anemia)
14
New cards
Infectious disease follow 5 stages:
Incubation, Prodromal, Illness, Decline, Convalescence
15
New cards
Incubation
initial entry of pathogen; replication begins; no signs or symptoms
16
New cards
Prodromal
Replication continues; host shows signs & symptoms
17
New cards
Illness
signs & symptoms are most severe in host (respiratory) (HIGHEST # OF PATHOGENS)
18
New cards
Decline
pathogen no. start to decrease; host’s immune system is weak and vulnerable to secondary infection (immunocompromised)
19
New cards
Convalescence
host starts to recover
20
New cards
Acute
relatively short (hours, days, week) (flu)
21
New cards
Chronic
longer time (months, years, lifetime) (TB, HIV, Hepatitis)
22
New cards
Latent
comes in episodes; pathogen replicates when disease is active (chickenpox and herpes)
23
New cards
Koch’s Postulates
determine whether a particular microorganism is a pathogen
1. The suspected pathogen must be found every case of disease and not be found in healthy individuals
2. The suspected pathogen can be isolated and grown in pure culture
3. A healthy test subject infected with the suspected pathogen must develop the same signs and symptoms of disease as seen in postulate 1
4. The pathogen must be re-isolated from the new host and must be identical to the pathogen from postulate 2
1. The suspected pathogen must be found every case of disease and not be found in healthy individuals
2. The suspected pathogen can be isolated and grown in pure culture
3. A healthy test subject infected with the suspected pathogen must develop the same signs and symptoms of disease as seen in postulate 1
4. The pathogen must be re-isolated from the new host and must be identical to the pathogen from postulate 2
24
New cards
Koch’s wrong assumptions
Pathogens are found only in disease individuals
All subjects are equally susceptible to infection
All pathogens can be grown in culture
All subjects are equally susceptible to infection
All pathogens can be grown in culture
25
New cards
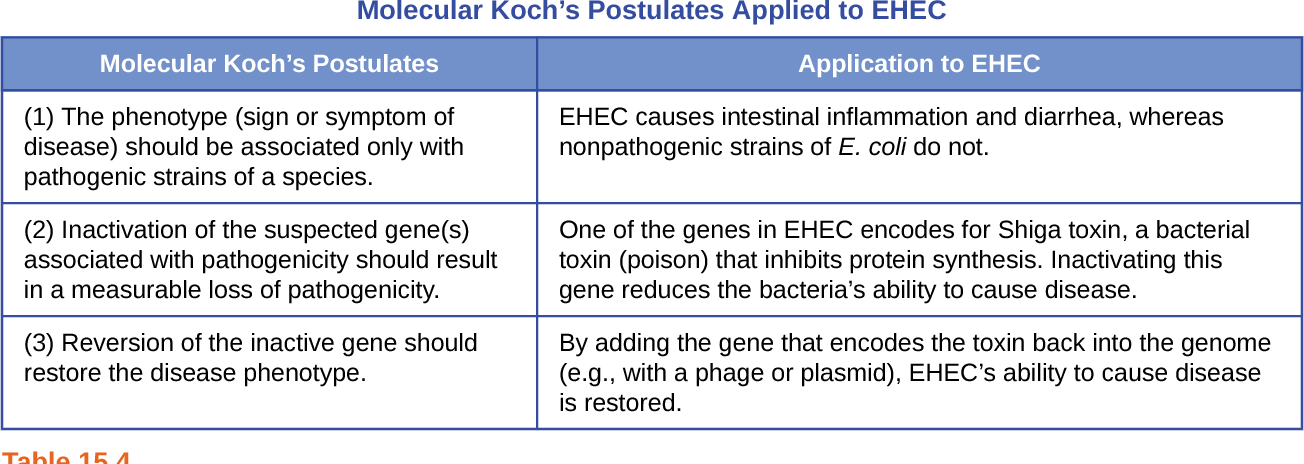
Molecular Koch’s Postulates
used to determine what genes contribute to a pathogen's ability to cause disease
26
New cards
Molecular Koch’s Limitations
1. genetic manipulation of some organisms isn’t possible with current techniques
2. some diseases do not have suitable animal models (HIV)
2. some diseases do not have suitable animal models (HIV)
27
New cards
Pathogenicity
ability of pathogen to cause disease
28
New cards
Virulence
degree of pathogenicity
Highly virulent – Bacillus anthracis induces severe signs & symptoms
Low virulent – Rhinovirus induces low signs & symptoms
Highly virulent – Bacillus anthracis induces severe signs & symptoms
Low virulent – Rhinovirus induces low signs & symptoms
29
New cards
Median infectious dose (ID50)
no. of pathogens required to infect 50% of those inoculated
30
New cards
Median lethal dose (LD50)
no. of pathogens required to kill
50% of those infected
31
New cards
Primary pathogen
can cause disease in a host regardless of host’s resident microbiota or immune system
- enterohemorrhagic E. coli (mainly due to Shiga toxin)
- enterohemorrhagic E. coli (mainly due to Shiga toxin)
32
New cards
Opportunistic pathogen
can only cause disease in situations that compromise the host’s defenses (e.g. protective barriers, immune system, or normal microbiota) (ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGE)
- Candida albicans with disrupted microbiota, UTI caused by E. coli
- STAPH infection, E. coli
- Candida albicans with disrupted microbiota, UTI caused by E. coli
- STAPH infection, E. coli
33
New cards
Stages of Pathogenicity
Exposure to host, Adhesion, Invasion, Infection, Transmission
34
New cards
Exposure/contact
pathogens must be exposed to portals of entry to begin adhesion
i.e. (eye conjunctiva, nose, mouth, placenta (TORCH), anus, urethra, vagina, insect bite, broken skin)
i.e. (eye conjunctiva, nose, mouth, placenta (TORCH), anus, urethra, vagina, insect bite, broken skin)
35
New cards
Adhesion
capability of colonization
Adhesins - molecules/structures that bind to certain host receptors
Biofilm - production of community glycocalyx
Adhesins - molecules/structures that bind to certain host receptors
Biofilm - production of community glycocalyx
36
New cards
Invasion
colonization is established
- Effector proteins are secreted to trigger entry –membrane ruffling (e.g. Salmonella & Shigella spp.)
- Surface proteins allow for binding to host cell, receptors that bind to epithelium cells and the cells allow them to enter (trojan horse approach)
~ some survive phagolysosomes within WBCs (e.g. Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
- Effector proteins are secreted to trigger entry –membrane ruffling (e.g. Salmonella & Shigella spp.)
- Surface proteins allow for binding to host cell, receptors that bind to epithelium cells and the cells allow them to enter (trojan horse approach)
~ some survive phagolysosomes within WBCs (e.g. Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
37
New cards
Infection
1. Local infection – small area of body
2. Focal infection – pathogen or toxin spreads to secondary location
3. Systemic – occurs throughout body (ex. Septicemia, chicken pox)
2. Focal infection – pathogen or toxin spreads to secondary location
3. Systemic – occurs throughout body (ex. Septicemia, chicken pox)
38
New cards
Primary infections can lead to ________ infection of different pathogen
secondary
i.e. HIV lowers immune system and opens door for yeast and others; rhinoviruses can lead to bacterial pneumonia
i.e. HIV lowers immune system and opens door for yeast and others; rhinoviruses can lead to bacterial pneumonia
39
New cards
Transmission
Portals of exit: eye (tears), mammary glands, placenta, vagina, skin (flakes), urethra (urine), nose, mouth (saliva & sputum), ear (wax), needle (blood), anus, insect bite, and broken skin
40
New cards
Virulence factors
pathogen product that assists in ability to cause infection and disease
Adhesion factors, Exoenzymes, Toxins, Immune evasion
Adhesion factors, Exoenzymes, Toxins, Immune evasion
41
New cards
Adhesins
proteins that aid in
attachment to host cell receptors; initiate biofilm formation in some species
i.e. viral, fungal, bacterial, fimbriae or pili
i.e. viral, fungal, bacterial, fimbriae or pili
42
New cards
-bacteremia
bacteria in blood
43
New cards
-viremia
viruses in blood
44
New cards
toxemia
toxins in blood
45
New cards
septicemia
bacteria present and multiplying in blood (active)
46
New cards
Patients with __________ can lead to shock (life-threatening decrease in BP)
septicemia
47
New cards
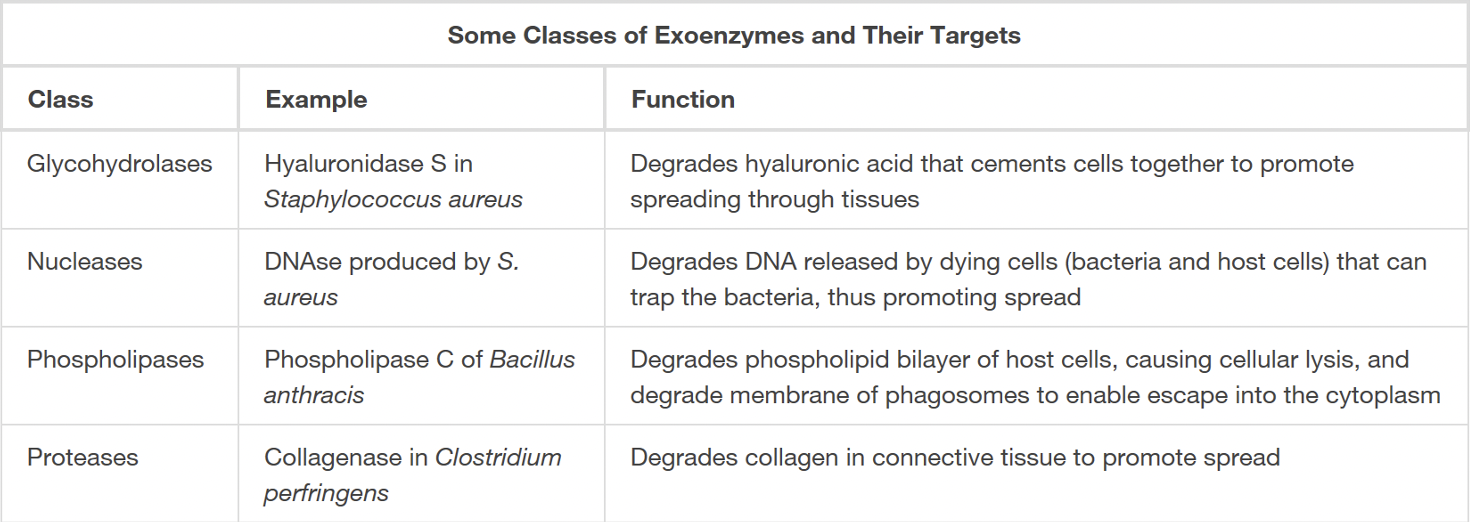
Exoenzymes
extracellular enzymes used to invade host tissues
i.e. glycohydrolases, nucleases, phospholipases, proteases
i.e. glycohydrolases, nucleases, phospholipases, proteases
48
New cards
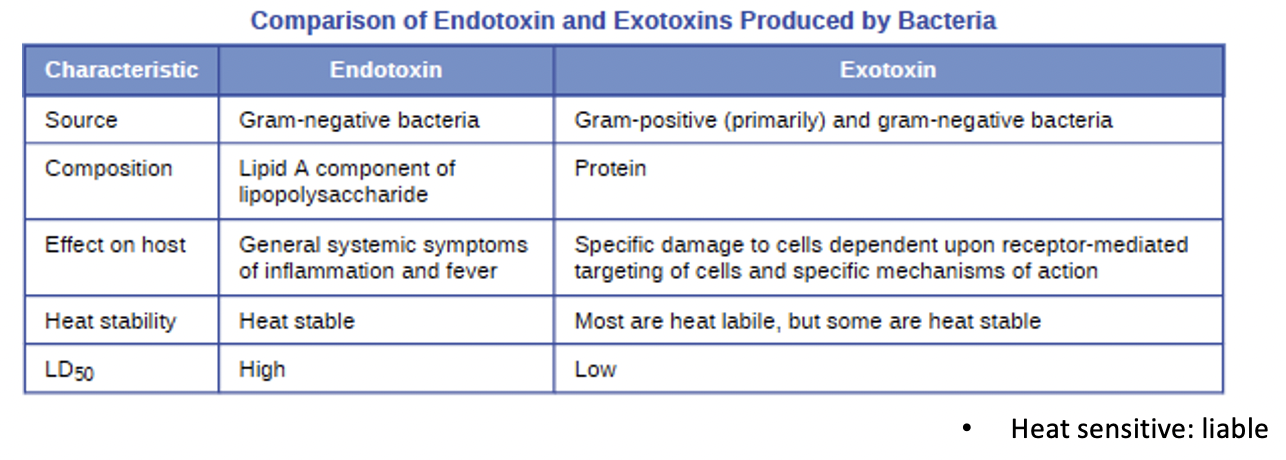
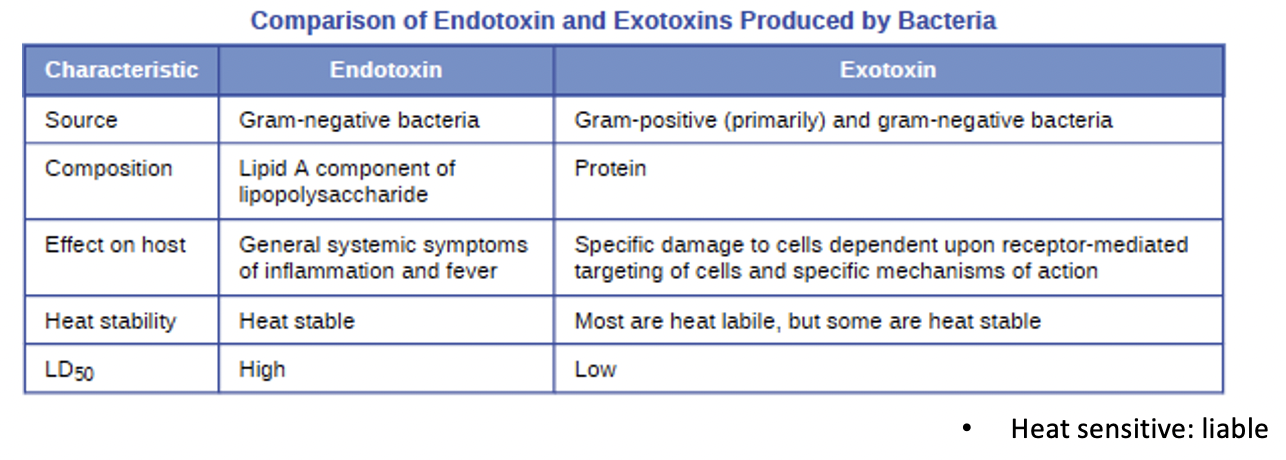
Toxins
biological poisons that assist in ability to invade and cause tissue damage (toxigenicity)
49
New cards
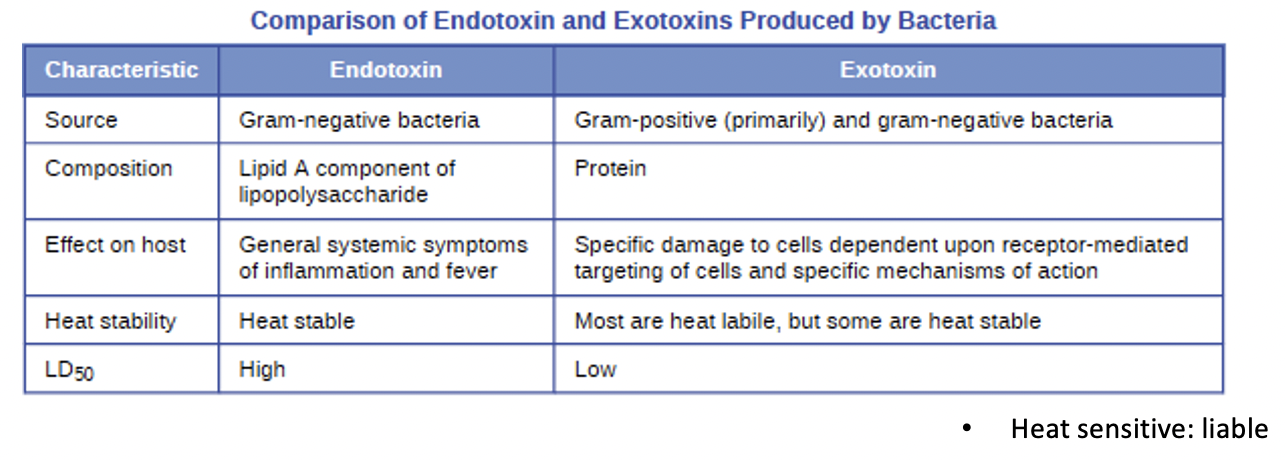
Endotoxins
lipopolysaccharides (in G-) that triggers host inflammatory responses; can cause sever fever and shock
50
New cards
Exotoxins
proteins mostly produced by Gram (+); Targets receptors on specific cells; can be further divided
51
New cards
Detecting endotoxins
1. Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) Test: blood cells of the horseshoe crab mixed with patient’s serum; observed chromogenically or by coagulation
2. ELISA – enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: uses antibodies to detect endotoxins
2. ELISA – enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: uses antibodies to detect endotoxins
52
New cards
Intracellular targeting - EXO
with A & B regions for activity and binding; Ex. diphtheria & botulinum toxin
53
New cards
Membrane-disrupting - EXO
aka phospholipases that degrade bilayer membrane; Ex. Bacillus anthracis & Rickettsia spp.
- Hemolysins and Leukocidins: can target RBC, WBC, and other cells
- Hemolysins and Leukocidins: can target RBC, WBC, and other cells
54
New cards
Superantigen - EXO
trigger excessive production of cytokines by immune cells;
Ex. Staphylococcus aureus and Toxic Shock Syndrome (causing high amounts of S. aureus since it is cultivated by blood
Ex. Staphylococcus aureus and Toxic Shock Syndrome (causing high amounts of S. aureus since it is cultivated by blood
55
New cards
Host evasion
mechanisms to evade phagocytosis
- Capsules that enlarge bacterial cell so phagocytes cannot
engulf pathogens
- Proteases digest host antibody molecules
- Mycolic acid in acid fast bacteria (M. tuberculosis) helps evade
phagolysosomes
- Coagulase pos. microbes can coagulate blood cells to keep immune cells out of reach
- Alteration of cell surface proteins to hide from immune cell
recognition (antigenic variation)
- Capsules that enlarge bacterial cell so phagocytes cannot
engulf pathogens
- Proteases digest host antibody molecules
- Mycolic acid in acid fast bacteria (M. tuberculosis) helps evade
phagolysosomes
- Coagulase pos. microbes can coagulate blood cells to keep immune cells out of reach
- Alteration of cell surface proteins to hide from immune cell
recognition (antigenic variation)
56
New cards
Antigenic drift
result of point mutations causing slight changes in spike proteins (H & N)
57
New cards
Antigenic shift
major change in spike proteins due to gen reassortment
58
New cards
Mycotoxins
adhesins, exoenzymes, & toxins
produced by Claviceps purpurea and Aspergillus spp. that contaminate grains & other staple crops
- Many properties are also similar to bacteria (adhesins, exoenzymes, & toxins)
produced by Claviceps purpurea and Aspergillus spp. that contaminate grains & other staple crops
- Many properties are also similar to bacteria (adhesins, exoenzymes, & toxins)
59
New cards
Protozoans
Adhesins, toxins, antigenic variation
Unique features for attachment – Giardia lamblia uses adhesive disk of microtubules to attach to intestines
Unique features for attachment – Giardia lamblia uses adhesive disk of microtubules to attach to intestines
60
New cards
Helminths
- “Glycan gimmickry” – mimic host cells to evade immune system
- Tissue penetration commonly achieved w/ proteases (e.g. worms that burrow into skin)
- Schistosoma mansoni degrades host antibodies to halt immune defense
- Tissue penetration commonly achieved w/ proteases (e.g. worms that burrow into skin)
- Schistosoma mansoni degrades host antibodies to halt immune defense