Lec 9,10,11 - Clinical Pharmacology of Injectable Anesthetic Drugs
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1 - Dr. Clark-Price
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Define anesthesia?
insensitivity to pain, especially as artifically induced by the administration of gases or the injection of drugs before surgical operations
What are the 3 requirements of anesthesia?
unconciousness
analgesia
muscle relaxation or paralysis
T/F: Preanesthetics are only used to help the anesthetist.
FALSE - help both anesthetist & the patient
Preanesthetics imply the administration of what?
sedatives, tranquilizers, analgesics, & anticholinergics
What are the goals of administering premeds?
relieve anxiety, counteract unwanted side effects of anesthetic agents, reduce does of induction & maintenance agents, provide analgesia
T/F: Induction agents produce reliable sedation & anesthesia.
TRUE
Induction agents are administered to induce an unconcious state suitable for what?
intubation
Induction agents provide a transition to what?
inhalant anesthetics
T/F: Induction agents maintain anesthesia with intermittent bolus or constant rate infusion (CRI).
TRUE - movement towards CRI over inhalants due to negative environmental effects
What patient factors should be taken into consideration when deciding which anesthetics to use?
species, health status, medications, procedures, age, temperament
T/F: There are drug protocols that can safely and routinely be administered to all patients.
FALSE
What is the most important take away from selecting a drug for your patient?
IF YOU DON’T KNOW HOW A DRUG WORKS AND WHAT A DRUG WILL DO, DON’T GIVE IT TO A PATIENT
Most commonly, preanesthetics use _______ class of drug.
more than one
Define neuroleptanalgesia.
a state of quiescence, altered awareness, & analgesia produced by a coombination of neuroleptic agent and a narcotic (opioid) analgesic
Why is it imperative to avoid medical errors when administering anesthetics?
errors with the use of medications can result in extreme harm or death to a patient
Anesthetic and pain management drugs often have a ______ therapeutic margin.
narrow → check your labels and math!!!!
What are the 6 intravenous anesthetic agents?
propofol
alfaxalone
etomidate
dissociatives
opioids
barbituates
Intravenous anesthetic agents are used for what?
to induce an unconcious state or are administered by repeated injection & infusion to maintain the mental depression necessary for anesthesia
What are the ideal properties of injectable anesthetics?
water soluble, long shelf life, stable when exposed to heat & light, only small volume needed to produce anesthesia, large safety margin, short duration of anesthesia, no cumulative effects, readily metabolized into non-toxic metabolites, minimal withdrawl times, provide adequate analgesia, muscle relaxation, not create unpredictable life-threatening changes to CV or respiratory function
T/F: The ideal anesthetic does NOT exist.
TRUE
What are the 3 things to consider when choosing an anesthetic protocol?
select drugs that patient can compensate for adverse effects
utilize multiple drugs with different MOA
minimize dose as appropriate (to “effect” and nothing more)
Most induction agents exert their effet through interaction with the _________ complex.
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) → specifically through GABAA
The GABA complex is a transmembrane _____________ ion channel.
ligand-gated chloride
What is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS?
GABA
What is the MOA of the GABA complex?
activation of GABAA by GABA → increase chloride conductance → hyperpolarization of postsynaptic cell membrane → inhibits propagation of nerve impulse
Hyperpolarizing the postsynaptic cell membrane makes it more _______ and therefore ________ to activate.
negative
harder
The NMDA complex is a transmembrane __________ & __________ ion channel.
ligand-gated & ion-gated
The NMDA complex is mostly activated by _______ ions but is also activated by _______ ions.
calcium
sodium
What is the main endogenous agonist for the NMDA receptor?
glutamate
What co-agonist is required to open the NMDA ion channel?
glycine
Activation of the NMDA complex causes what?
depolarization & propagation of nerve impulse
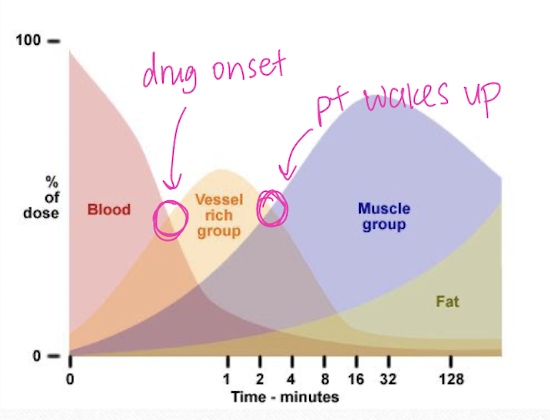
What is the major determinant in the delivery of injectable anesthetics to the CNS?
tissue blood flow
What structures receive injectable drugs first?
more vascular structures (ex = the brain)
What happens after injectable anesthetics are administered?
drug then redistributes away from vascular structures to less vascular structures
Explain the percentage of cardiac output in relation to injectable anesthetics.
blood → 75% vessel rich group (CNS) → 19% muscle → 6% fat → <1% vessel poor group
How is the action of injectable anesthetics terminated?
redistribution of drugs from vessel rich groups therefore reducing concentrations in the brain
Drugs _______ from receptors and follow _________ out of the CNS.
disassociate
concentration gradient
Redistribution of injectable anesthetics determines the ________ of a single dose of a drug. This varies patient to patient based on _________.
duration of action
health status (hyper dogs wake up faster)
What 3 things contribute to the termination of action of injectable anesthetics?
physical redistribution
metabolic degradation
renal excretion
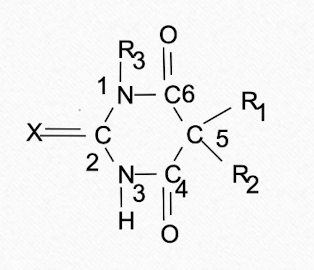
Barbituates are useful as both anesthetics and __________. They are derived from ________.
anticonvulsants
barbituric acid
T/F: Only some barbituates are DEA controlled substances.
FALSE - all are controlled
What are the 2 structural forms of barbituates?
oxybarbituates (x = oxygen at C2)
thiobarbituates (x = sulfur at C2)
Oxybarbituates are good for _______ while thiobarbituates are good for ________.
seizures
anesthesia
Substitution as the X carbon influences _________.
duration of action
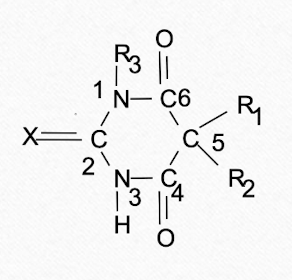
Which barbituate structure has a faster onset and shorter duration due to its increased tissue solubility (fat)?
thiobarbituates
What is the ultrashort acting thiobarbituate that is not available in the US, and is the only one used for induction?
thiopental
What is a short acting oxybarbituate found in euthasol?
pentobarbital (~1 day)
What is the long acting oxybarbituate?
phenobarbital (~2 days)
CNS potency is directly related to ___________.
lipophilicity
Oxybarbituates are (more/less) lipid soluble. This means they have (slower/faster) onset of action but (shorter/longer) duration of action.
less
slower
longer
T/F: Animals on barbituates for seizures will take MUCH longer to recover from anesthesia when barbituates are also used as an anesthetic.
TRUE - due to tissue saturation
Short and long acting barbituates rely on some metabolism by the _________ (minor).
liver
T/F: Barbituates can only be administered IV.
FALSE - can be given by all routes
What formulations of barbituates are most common?
oral & IV
Injectable formulations of barbituates given IM or intraperitoneal may cause severe ___________.
tissue irritation
Barbituates have a ________ volume of distribution.
very large → crosses placenta and BBB easily
What are the CNS effects of barbituates?
generalized depression
decreased CMRO2 (metabolic demand of O2 in tissues)
cerebral protection from ischemia
utilized for medically induced comas in humans
What effects do barbituates have on cardiovascular pump function?
decreased stroke volume & contractility
What vascular effects are seen with barbituates?
vasodilation → increased size of spleen (not favorable for abdominal surgeries)
Barbituates (increase/decrease) heart rate which can lead to arrhythmias. How is this decreased in animals?
increase
animal is pre-oxygenated and ventilated
What respiratory effects are seen with barbituates?
decreased rate and depth of breathing
apnea at induction → ONLY give to effect
What is a good rule of thumb to remember when administering barbituates?
“the bigger the dose and the faster you give it, the more likely to have problems” → pt will stop ventilating voluntarily
What is the rate of onset of thiopental, and when is recovery from this drug seen?
30-60 seconds
recovery in 10-30 mins (dose dependent)
Repeated doses of thiopental can result in _______ recovery.
prolonged (hours)
Thiopental can only be administered _____. The high pH results in a very ________ solution meaning perivascular injections results in tissue _________.
IV
caustic
damage & sloughing
Pentobarbital is a (oxy/thiobarbituate) and can be used for ________ anesthesia. However, due to its (short/long) recovery time, it is rarely used clinically for anesthesia - research animals/ less developed countries.
oxybarbituate
injectable
long
Pentobarbital has a _______ onset of action and a ________ duration of action.
quick (30-60 s)
moderate (30-240 mins)
What can result in a very rough recovery from pentobarbital?
incoordination
Pentobarbital is the main ingredient of ________.
euthanasia solutions
How does death via pentobarbital occur?
from cardiorespiratory collapse after unconsciousness
T/F: Both formulations of Pentobarbital for euthanasia and anesthesia are DEA controlled substances.
TRUE
Phenobarbital is a _____ acting (oxy/thiobarbituate).
long
oxybarbituate
Phenobarbital is not used as an injectable anesthetic, rather it’s main use is as a _________ agent.
oral anticonvulsant
T/F: Phenobarbital can be administered IV for immediate control of seizures though the IV preparation is difficult to obtain.
TRUE
Propofol is a chemically distinct _______ anesthetic.
phenol
Propofol results in a ______ awakening from anesthesia.
rapid
One pro of using propofol is that patients return to conciousness with _____________ effects.
minimal residual
What MOA does propofol use?
GABAA agonist
What are the chemical properties of propofol.
emulsion → soybean oil, egg lecithin, & glycerol
NO preservative
supports bacterial growth
use within 8 hours after opening vial
What is special about Propoflo 28?
preservative with 28 day shelf life after opening
Propofol may only be administered _____.
IV → perivascular inj does NOT cause tissue irritation, it has no anesthetic effects
Propofol _____ crosses cellular membranes, making for _______ induction and recoveries.
rapidly
smooth & rapid
Propofol has an induction time of less than _______ and lasts for about _______.
60 s
20 mins
Recovery from propofol is via ________.
redistribution
What tissues metabolize propofol? When is this useful?
liver, lung, kidney, & blood stream
for patients with hepatic disease (less stress on liver)
What are the cardiovascular effects seen with propofol?
hypotension → arterial & venous vasodilation
What are the respiratory effects seen with propofol?
strong respiratory depressant
dose dependent
some become cyanotic (preoxygenate)
Propofol (does/does not provide) analgesia.
does NOT
What are some species specific concerns when using propofol in cats?
phenol can cause oxidative injury to cats’ RBCs with repeat usage = Heinz body anemia
What are some species specific concerns when using propofol in horses?
side effects similar to other species HOWEVER in adults:
large volume needed for induction may cause excitement thus resulting in potential injury if used as sole agent
How can you prevent the potential excitement related injuries caused by propofol use in horses?
combine with other sedative/ anesthetic medications
Alfaxalone is an injectable _________, similar in structure to ________, that has anesthetic properties.
neurosteroid
progesterone
Well developed metabolic pathways in mammals given Alfaxalone result in (rapid/slow) clearance from circulation & (short/long) duration of effect.
rapid
short
What MOA does alfaxalone use?
GABAA agonist
Alfaxalone is available in a ____ solution and is NOT _____ soluble.
1%
water
When in a formulation with ________, sugar molecules _______ alfaxalone, making it water soluble.
cyclodextran
hides
Alfaxalone (does/does not) contain preservatives.
does NOT → utilize up to one week
T/F: Alfaxalone can only be used for a few species.
FALSE - can be used in many species
How is alfaxalone prepared?
clear, colorless solution in multi-dose vial
How can alfaxalone be administered? How does this vary across species?
IV or IM (no tissue irritation)
dogs → IM difficult due to large volume needed
cats → IM use 1 mL or less
reptile/amphibians → IM or intracoelomic