medical sciences 3
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is the cranial nerve supplys hearing and balance?
CNVIII Vestibulochlear Nerve.
What are the 3 distinct parts of the ear?
outer, middle, inner
What is the cerumen and what does it do?
(earwax)
sticky and forms a barrier to protect the tymphanic membrane from dirt, insects etc.
has antimicrobial properties to inhibit bacteria/fungi growing
helps the ear to self-clean as old cerumen is trasnported out of the canal with the trapped debris.
What is the eustachain tube, where is it and what does it do?
in the middle ear
conncects the middle ear to the nasopharynx
typically closed, when open there is unequal pressure across the tymphanic memebrane e.g at high alititude.
What is in the outer ear?
aurcile- the visible structure on the side of out head
external auditory meatus- the channel that runs down into our ear
tympanic membrane (ear drum) at the end of the EAM, seperates the outer and middle ear.
where is the external auditory meatus and what does it do?
EAM
Outer ear.
- Extends from the auricle to our tympanic membrane
- Lined with skin, contains glands that screte cerumen (ear wax)
What is the tympanic membrane and where is it?
outer ear
Oval shaped
- Separates out the outer and middle ear
- Can be viewed with a special ear scope on ear examination
- Vibrates with incoming sound waves.
What is the middle ear, what is it made up of?
Ossicles- chain of 3 smaller bones, malleus, incus, stapes.
lies within the temporarl bone of the neurocranium
is an airfilled space
eustachian tube.
what are ossicles and where are they?
Within the middle ear
chain of 3 small bones
malleus (hammer)
incus (anvil)
stapes (stirrup)
Ossicles are connected to each other with synovial joints so they can vibrate to transmit sound
malleus is first in the chain and is on contact with the tympanic membrane
the stapes is the last in the chain and connects to the orval window.
What is the inner ear, what is it made up of?
also known as the labrynith, sits within the temporal lobe
contains the organs of hearing and balance
3 main structures:
1. vestibule
2. semicircular canals- responsible for balance
3. Cochlea- part of the ear that helps us to hear.
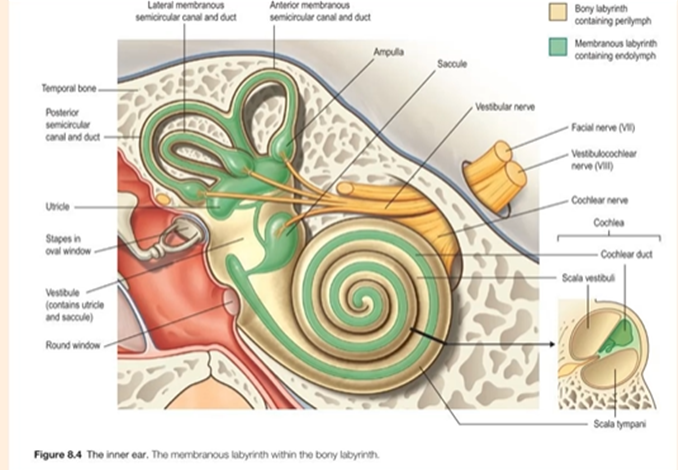
What are the round and oval windows, where are they?
2 windows are openings in the bone sepearting the middle and inner ear
the oval window recieves vibrations from the stapes bone and trasnmits them into the fluid filled cochlea
the round window act as a pressure release valve and bulges outwards when fluid is displaced in the cochlea.
What is residual volume?
The quantity of air left in our lungs after forced exhalation
(we cannot completley empty the lungs when we bretahe out because they would collapse)
What is tidal volume?
The quantity of air moving in and out of our lungs during each breath cycle, about 500mls at rest.
What is vital capacity?
the maximum quanity of air that can be moved in and out of the lungs during a breath cycle.
Explain the proccess of inhalation
-

Diaphragm contracts external intercostal muscles contract- ribes move upwards and outwards as a unit
- Both increase the volume of the thoracic cavity- so pressure decreases in the alveoli, bronchioles, and brochi causing air to rush in to equalise the pressure.
- The lungs move with the ribs as they are attached via the pleural membrane.
Explain the proccess of exhalation (relaxed)
1. External intercostal muscles relax- rib cage recoils downwards and inwards
+ diaphragm muscle relaxes and returns to neutral position
2. This decreases the volume in the thoracic cavity and so increases pressure in alveoli, bronchioles and bronchi. Therefore air rushes out as an exhaled airstream to equalize the pressure
3. The lungs move with the ribs as they are attached via pleural membrane.

explain the proccess of exhaltion with force
- Abdominal muscles and internal intercostals also contract to squeeze air out with pressure
(important when looking at coughing/phonation)