TACS revision
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Standard precautions
A group of infection prevention practices in any setting in which healthcare is delivered
5 moments of hand hygiene
Before touching a patient
Before carrying out a procedure
After body fluid exposure risk
After touching a patient
After touching patient surroundings
Temperature sites + average temperature
Tympanic: 36.64C
Oral: 36.57C
Axillary: 35.97C
Rectal: 37.04C
55-95bpm
Normal pulse rate
12-20 breaths per minute
Normal respiratory rate
>25 breaths per minute indicates
Tachypnoea
<8 breaths per minute indicates
Bradypnoea
Kortkoff sounds
sounds heard through the stethoscope when ausculating BP, caused by turbulent blood flow through a partially compressed artery
What causes HTN?
Stress/ anxiety
White coat HTN
Stimulants e.g. caffiene, cocaine, nicotine, amphetamine
Over-hydration/ full bladder
Salt, baking soda, liquorice
Cuff size too small
What do you do if BP is too high?
Check cuff size (not too small) and correct placement
Make sure patient is relaxed and arm supported
Measure again after 5 minutes of rest
What causes hypotension?
Relaxation/ prolonged bed rest
Heat
Recent meal
Dehydration
Serious illness
Endocrine/ neurological conditions
Cuff size too big
Location of aortic valve
2ics RSE
Location of pulmonary valve
2ics LSE
Location of tricuspid valve
4ics LSE
Location of mitral valve and apex beat
L5ics mcl
What does JVP assess?
Right atrial pressure
PPE that is part of standard precautions
Non-sterile gloves
Mask
Eye protection
Gown/ apron
Associated MSK symptoms
Pain
Discolouration
Stiffness
Joint swelling
Heat
Deformity
Weakness
Locking/ Instability
Altered functional capacity
Extra-articular symptoms
Associated CVS symptoms
Chest pain
Claudication
Dyspnoea (orthopnoea and PND)
Palpitations
Syncope/ pre-syncope
oedema
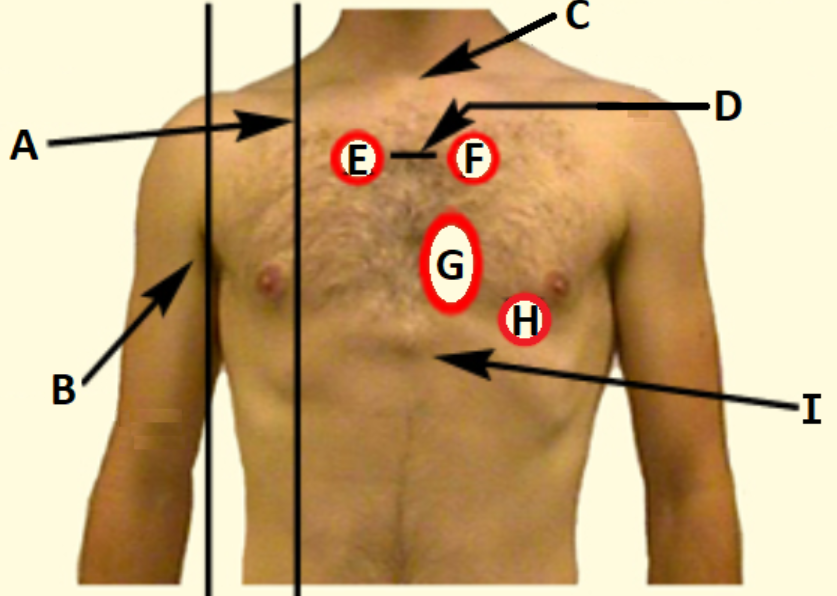
D
Sternal angle
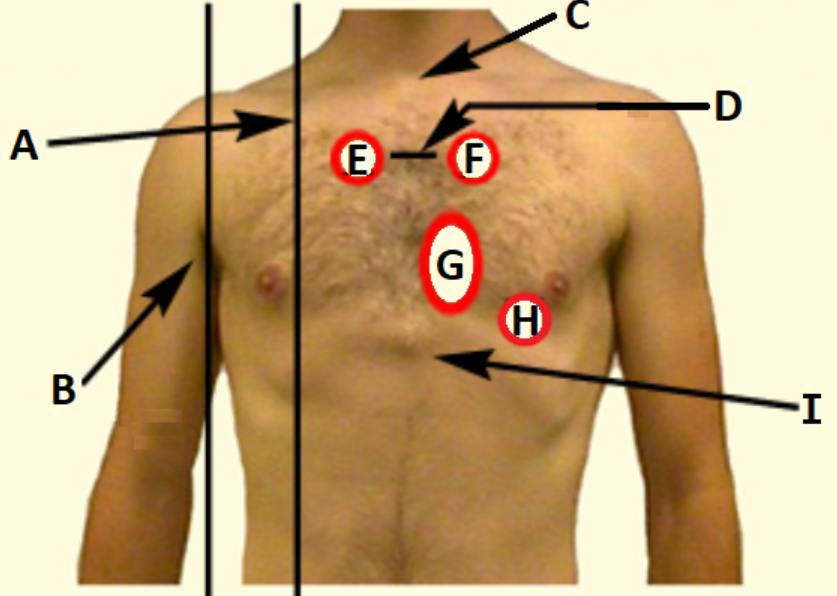
C
Suprasternal notch
Why is the internal jugular vein used to assess R atrial P?
No valves and drains directly into SVC
Parts of a CV examination
Look (praecordium): scars, pacemaker box, apex beat, muscle bulk and symmetry, JVP
Feel: apex beat, peripheral pulses, ausculatation, capillary refill
Informed consent
Process to respect the patient’s right to be informed, make their own decision, and refuse or accept care offered to them
Standard precautions include
Promoting safety climate
Respiratory hygiene
Hand hygiene
Assessing risk of exposure to body fluid and PPE
Patient care equipment
Environment cleaning
Relative degrees of movemet: shoulder + knee
Shoulder:
Flexion: 180°
Extension: 60°
Adduction: 50°
Abduction: 0-140°
Knee:
Flexion + exetension: 0-180°
Hyperextension: 10°
MCL + LCL: up to 10mm movement (20-30°)
ACL + PCL: <5mm
Waves observed in JVP
a + v wave
How does the height of the JVP change with inspiration?
Falls with inspiration due to increased volume of thorax
Associated RESP symptoms
Cough
Sputum
Haemoptysis
Chest pain
Wheeze
Hoarseness
Systemic symptoms
Dyspnoea
Grading of dyspnoea
Grade I: breathless when hurrying on flat or walking up slight hill
Grade II: breathless when walking with other people of own age or on ground level
Grade III: walks slower than peers, or stops when walking at own pace
Grade IV: stops after 100m or few minutes on surface level
Grade V: too breathless to wash/ dress
Normal amount of sputum produced per day
~100mL; clear
Assessment of sputum colour
Clear/ grey: COPD
White: asthma
Dark yellow/ green: bronchopulmonary infection
Yellow = live neutrophils (acute)
Green = dead neutrophils (chronic)
Yellow: RTI
Clear/ water: beoncho-alveolar cancer
Frothy + pink: pulmonary oedema
Rusty: pneumococcal penumonia
Causes of hoarseness
Acute inflammation of vocal cords OR chronic tumour on vocal cord or recurrent nerve palsy
Examination position of RESP assessment
patient lying on couch with bed head at maximal height
Causes of tracheal displacement towards side of lesion
Upper lobe collapse/ fibrosis; peneumonectomy
Casues of tracheal displacement away from side of lesion
massive pleural effusion or tension pneumothorax
Causes of tracheal displacement in either direction
upper mediastinal mass e.g. goitre, lymphoma, lung cancer
Sounds during lung field percussion
Resonant: over normally inflated lung fields
Dull: over solid structure e.g. liver, pulmonary consolidation, collapse, or fibrosis
Stony-dull: over fluid-filled areas e.g. pleural efusion (or bone)
Hyper-resonant: over completely hollow structures e.g. pneumothorax
Breath sounds on auscultation
Vesicular: normal and louder on inspiration
Bronchial: harsher and louder on expiration, audible gap between inspiration and expiration
Added sounds on auscultation
Crackles
Wheeze
Pleural friction rub
Avoid ausculation within __ of the midline
3cm
Associated GI symptoms
Mouth ulcers
Dysphagia
Indigestion/ heartburn/ GER
Nausea
Retching
Vomiting
Haematemesis
Abdominal pain
Melaena
Jaundice
Wind: belching or burping
Change in bowel habits e.g. diarrhoea, constipation, overflow diarrhoea, recetal bleeding, tenesmus, steatorrhea
7 F’s of abdominal distension
Fat
Fluid
Flatulence
Foetus
Faeces
“Frightfully” big tumour
“Phantom” pregnancy
Extra-abdominal organs assessed in GI assessment
Hands: clubbing, tobacco staining, palmar erythema
Face: jaundice, pallor, tobacco staining
Eyes: conjuctive pallor, jaundice in sclera
Mouth: dehydration, dentition
Skin: bruising/ petechiae, sratch marks, spider navi
Extra-abdominal organs that require special permission in GI assessment
Eyes
Mouth
Face (quizzes)
Gaurding
Contraction of the muscles in the abdomen, voluntary if the patient anticipates pain or involuntary in peritonitis
Rigidity
Constant involuntary contraction of the abdominal muscles associated with tenderness
Rebound tenderness
Tenderness elicitied by pressing firmly over an inflamed structure and suddenly withdrawing pressure
Borborygmi
Audible sounds madeby the GI tract (tummy rumbles)
Features of crackles (crepitations/ rales)
Non-musical sounds
Like velcro being pulled apart/ hair rubbed between fingers
Common causes: infection, LHF, COPD, pulmonary fibrosis
Features of wheeze (rhonchi)
Continuous muscial noises
Caused by vibration of narrow airways
Heard throughout lung fields, usualy in expiration
Common causes: asthma, COPD
Features of pleural friction rub
Like leather rubbed together/ creaking sound
Due to thickened, inflamed surfaces rubbing together
Associated w pleuritic pain
Common causes: PE, pneumonia
Causes of reduced breath sounds
Reduced conduction of sound (obesity, thickened chest wall, pleural effusion, pleural thickening, pneumothorax)
Reduced airflow (COPD, collapse by foreign body/ cancer)
Causes of asymmetrical absent breath sounds
Unilateral pleural effusion/ pneumothorax
Collapse due to major obstruction of bronchus by foreign body or carcinoma
Parts of closing the session
Contracts
Safety nets
Summary
Final check
Associated neuro symptoms
Pain (head, face, neck, back)
Change in LoC, syncope
Dizziness/ vertigo
Seizures
Weakness
Nausea/ vomiting
Motor impairment (gait, speech, dysphagia, involuntary movement, bladder/ bowel)
Change in cognition
Sensory impairment (loss, vision, hearing, smell, taste)
Normal chest expansion
>5cm normal
Causes of symmetrical reduced chest expansion
Asthma
Emphysema
Causes of unilateral reduced chest expansion
Consolidation
Pneumothorax
Localised collapse
Pleural effusion
Causes of back pain radiating to leg
Disc prolapse
Cauda Equina Syndrome
Characterstics of focal seizures
Aura
Motor features (e.g. limb jerking)
Transient loss of awareness or responsiveness
Positive Romberg’s sign
Worsening balance when the eyes are closed (loss of proprioception)
Features of nominal dysphasia
Cannot name objects
Speech and lanuage normal, fluent
Uses long phrases to descibe one word
Athetosis
Slow writhing movements often seen in cerebral palsy
Red flag features for headaches
New headache in older person (>50yrs)
History of trauma
Sudden onset esp if no history of headache
Severe debilitating pain (SAH)
Features of raised ICP
Red flag symptoms for headaches
Change in LoC
Fever, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, neck stffness
Weight loss
Changes in mood or personality
Focal neurological deficit
Changes in cognitive function
Causes of true vertigo
Acue labrynthitis (inflammation of inner ear)
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (short-lived intense vertigo)
Meniere’s disease (acute attacks of vertigo, fluctuating tinnitus, increasing deafness, pressure in inner ear)
Acoustic neuroma (benign slow growing tumour)
Parts of cognitive examination
Orientation to person, place, and time (date)
Eye response in GCS
4 = spontaneous
3 = to sound
2 = to pressure
1 = no response
Verbal response in GCS
5 = orientated
4 = confused
3 = words
2 = sounds
1 = no response
Motor response in GCS
6 = obeys commands
5 = localising
4 = normal flexion
3 = abnormal flexion (decorticate)
2 = extension (decerebrate)
1 = no response
Features of decorticate response (abnormal flexion)
Slow sterotyped movement
Elbows flexed and forearms across chest
Hands pronated
Thumb and fingers flexed
Legs extended
Feet plantarflexed
Features of decerebrate response (extension)
Elbows extended
Arms adducted and internally rotated
Wrist, thumbs and fingers flexed
Legs extended
Interpreting GCS severity
13-15: mild head injury
9-12: moderate head injury
3-8: severe head injury
Pressure points in GSC exam
Supraorbital notch pressure
Trapezius squeeze
Upper limb reflex locations
Biceps (C5, C6)
Triceps (C7, C8)
Brachioradialis (C5, C6)
Lower limb reflex locations
Knee jerk/ patllar reflex (L3, L4)
Ankle jerk/ achilles reflex (L5, S1)
Plantar reflex (S1, S2)
Lesions in the brain which can cause sensory disturbances
Brainstem
Thalamus
Sensory cortex
Vibration sense positions moving proximally
End of great toe/ toenail
MTP of big toe
Medial malleolus
Tibial tuberosity
Anterior iliac spine
Parts of CN V examination
Sensation
Corneal reflex
Motor (jaw opening)
Jaw reflex
Parts of CN IX, X, XII examination
Cough
Speech/ articulation
Uvula movement
Gag reflex (if indicated)
Tongue appearance and movement
Conductive deafness
Abnormal conduction of sound anywhere from the external auditory meatus to stapes (includes blockage from otitis media and earwax)
Sensorineural deafness
Abnormal conduction of acoustic vibration and neural impulses by the cochlear and vesitbulocochlear nerve to the brain
Normal (+ve) Rinne’s test
Air conduction better than bone conduction
Abnormal (-ve) Rinne’s test usually indicates
Conductive hearing loss (bone conduction greater than air conduction)
Weber’s test in conductive hearing loss
Sound localises to affected ear
Weber’s test in sensorineural hearing loss
Sound localises to normal ear
Why is the weber’s test louder in the affected ear in conductive hearing loss?
Masking (no masking effect from environmental noise)
Occlusion (sound cannot dissipate out of auditory canal which increases cochlear stimulation)
‘Lowest line read’ in visual acquity test
The last line that can be read with 2 errors or less
The finger should be held approximately __cm from the patient when testing eye movement
30cm
The torch should intially be held __cm away from the face when testing the light reflex
10cm
Hand positioning when testing orbicularis oculi (CN VII)
Left hand: fingers and thumb at the eyebrow
RIght hand: fingers and thumb just below the eye
Hand positioning when testing buccinator (CN VII)
3 fingers on each cheek, length of fingers (rather than fingertips)
Types of tuning forks used in CN VIII exam
256Hz or 512Hz
Abnormal Rinne’s test suggesting severe sensorineural hearing loss
Cannot hear both bone and air conduction
Patient does not hear tuning fork when placed on mastoid AND beside external auditory meatus
Cough heard in laryngeal nerve problem (CN X)
Non-explosive/ bovine cough
Wheeze
High-pitched squeek caused by turbulent flow of air through constricted airways, heard louder on expiration
Stridor
Inspiratory wheeze which may indicate upper airway obstruction
Process of assessing tracheal position
Right middle finger above suprasternal notch
Right index finger and ring finger to right and left of trachea
Hand positioning during chest expansion
Fingers towards mid-axillary line
Fingers firmly and gently applied to lateral chest wall
Thumbs towards the spine, almost meeting and midline and hovering slightly off chest