5 Methylxanthines, B-phenethylamines Stimulants, Anorexients, ADHD
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
types of neurotransmitter receptors
ligand-gated ion channels, GPCRs
what are the monoamine neurotransmitters? are they excitatory, inhibitory or both?
- Ach, NE, E, dopamine, seratonin, histamine
- excitatory & inhibitory
is GABA excitatory, inhibitory or both?
inhibitory
is glutamate excitatory, inhibitory or both?
excitatory
CNS stimulants effects (intended effects and AE)
- increased alertness, decreased drowsiness & fatigue
- too much -> nervousness, anxiety, fatigue
CNS stimulants therapeutic uses
central sympathomimetic agents, antidepressants
methylxanthines examples
caffeine, theophylline, theobromine, aminophylline, pamabrom, dyphylline
methylxanthine MOA (3)
1. adenosine-1 (A1) antagonist, which increases cAMP (most important)
2. inhibits PDE, which increases cAMP
3. alters intracellular Ca2+ distribution
is caffeine acidic or basic? how does this affect solubility?
weakly basic, not very soluble at room temp
how to increase the solubility of methylxanthines
include acid to create a salt
caffeine indication
infant apnea, migraines (exedrin)
caffeine metabolism
oxidative demethylation
is caffeine lipophilic or hydrophilic? how does this effect CNS stimulation?
high lipophilicity due to methyl groups -> high absorption in BBB -> stimulates CNS
theophylline indications
bronchial asthma
theophylline administration
oral or IV
is theophylline acidic or basic? how does this affect solubility?
more acidic than caffeine -> more soluble than caffeine (but still limited water solubility at room temp, more soluble at warm temps)
theophylline metabolism
oxidative demethylation
what are salt derivatives of theophylline
aminophylline (2:1), oxtriphylline (1:1). pamabrom (1:1),
oxtriphylline indication
bronchial asthma (po or IV)
pamabrom indications
often used in combo with acetaminophen for back pain and menstural relief
dyphylline solubility compared to theophylline
better solubility -> doesn't need to be made into a salt
dyphylline indication
asthma, COPD
is theophylline a metabolite of dyphylline
no, dyphylline isn't dealkylated (not heavily metabolized)
is dyphylline stronger or weaker than theophylline? what is the benefit?
dyphylline is weaker -> less CNS stimulation, less likely to have excessive stimulation
doxapram administration
IV only
doxapram indication
respiratory stimulation after anesthesia or drug overdose
doxapram metabolism (what phase & reactions)
oxidative phase 1 reactions (oxidation, hydroxylation, dealkylation)
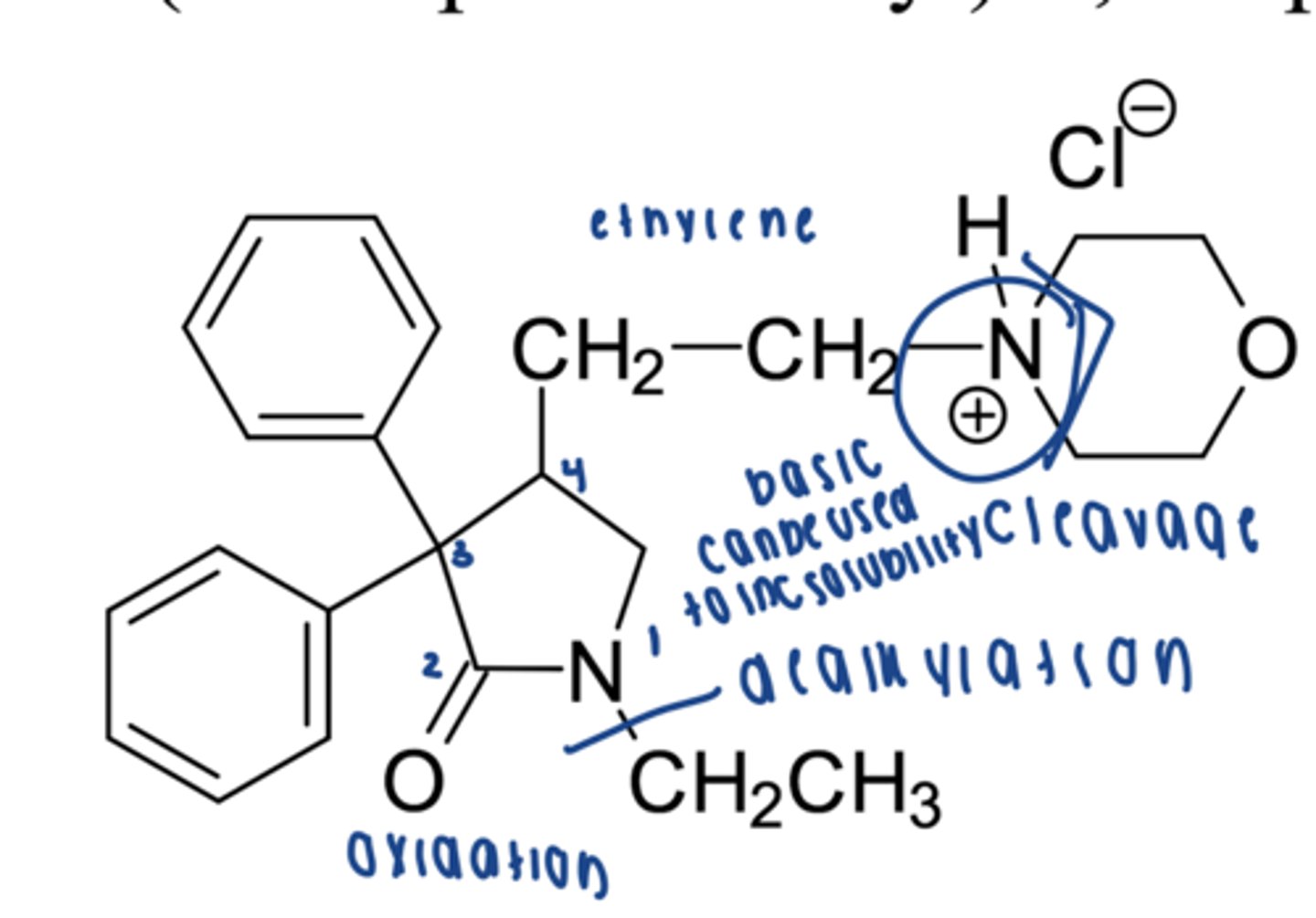
modafinil indication
narcolepsy, OSA
is modafinil racemic? if so, is one enantiomer more potent than the other?
yes, R isomer is more potent than S
what is armodafinil?
R enantiomer of modafinil
modafinil metabolism
hydrolysis, oxidation of sulfide
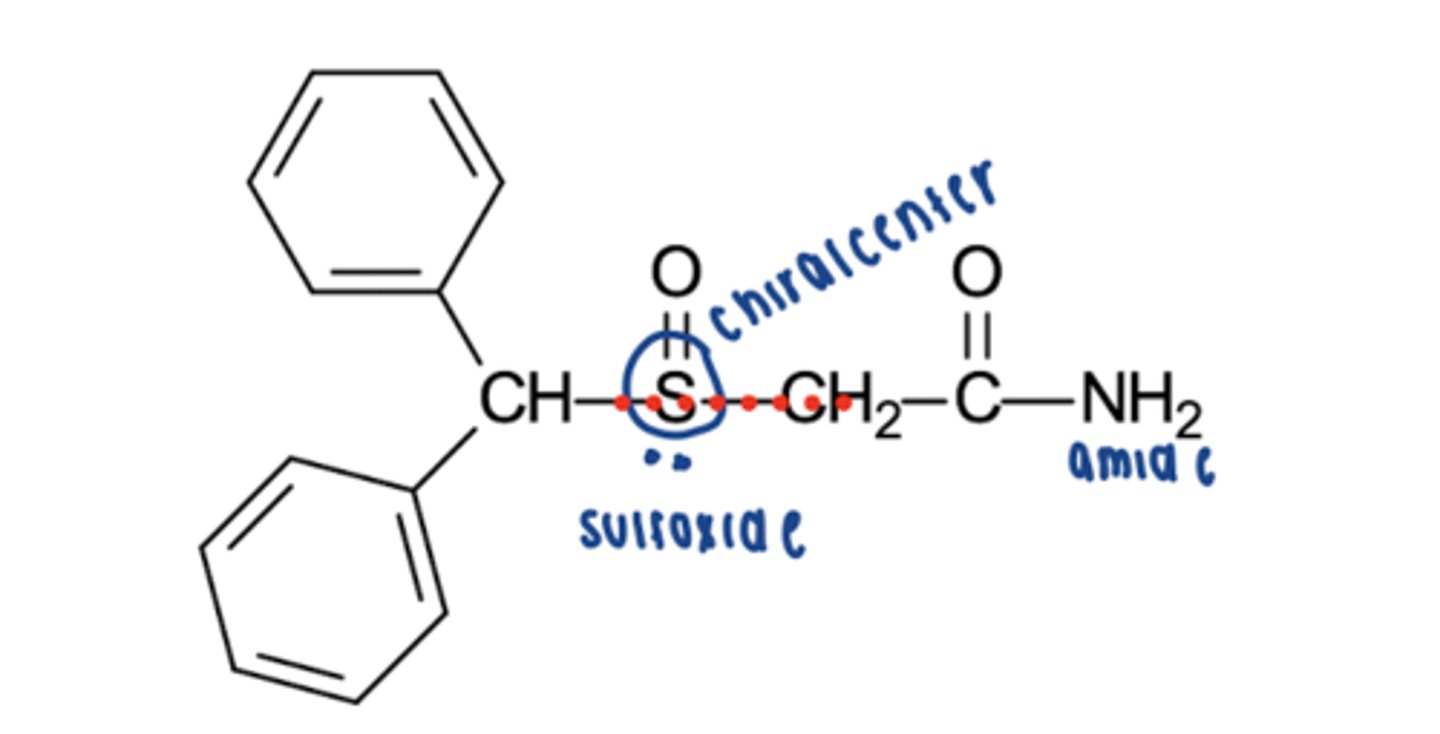
pitolisant HCL MOA
H3 inverse agonist and antagonist -> increases histamine release
pitolisant HCL administration, metabolism
- oral
- metabolized by CYP2D6
pitolisant HCL indications
narcolepsy, cateplaxy
solriamfetol structure
phenethyl amine
solriamfetol stereochemistry
R isomer only
solriamfetol indications
narcolepsy, OSA (obstructive sleep apnea)
solriamfetol longevity and half life
lasts for 9 hours, half life is 7.1 hours
is sodium oxybate a CNS depressant or stimulant
CNS depressant (strong sedative)
sodium oxybate MOA
GABA B and GHB agonist
sodium oxybate indications
narcolepsy (only inhibitory drug used), cateplaxy
sodium oxybate is the synthetic form of ...
GHB
when is sodium oxybate administered
night
how to improve the stability of B-phenylethylamines so that they can cause CNS stimulation
1. adding methyl group to alpha carbon -> resistant to MAO metabolism -< cross BBB
2. adding OMe to aromatic ring -> cross BBB
3. size of N group -> the bulkier the N, the less likely it will cross the BBB (no more than 1 methyl on the amine)
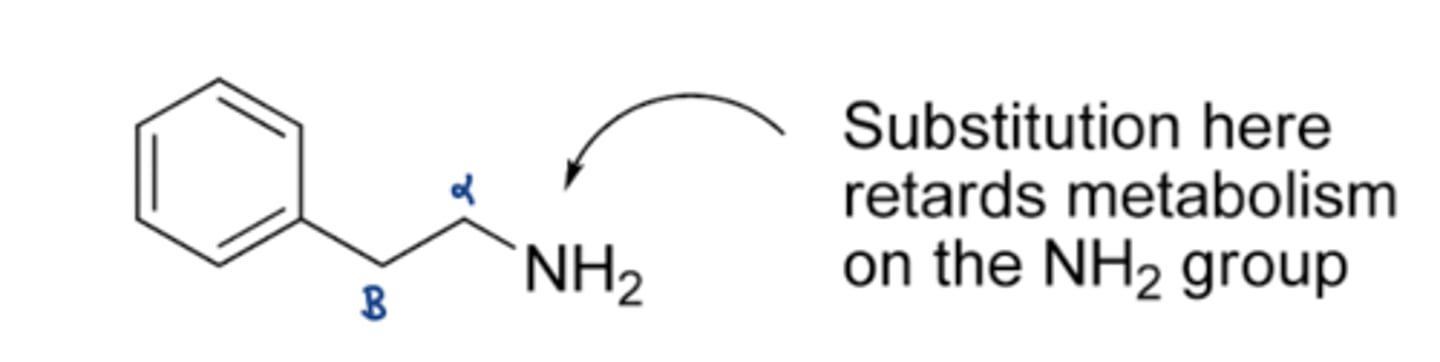
B-phenylethylamines MOA (4)
1. indirect CNS stimulation via adrenergic sympathetic NS (mimic NE, dopamine, serotonin)
2. promotes release of neurotransmitters & prevent reuptake of neurotransmitters
3. weak MAO inhibitors
what CNS structures do B-phenylethylamines stimulate
cortex, brain stem, medulla
B-phenylethylamines AE
hypertension (due to sympathetic stimulation)
B-phenylethylamines metabolism (location and reactions)
- in liver
- oxidative phase 1 reactions (aromatic hydroxylation, hydroxylation at benzylic position (a from benzyl), N-dealkylation, deamination)
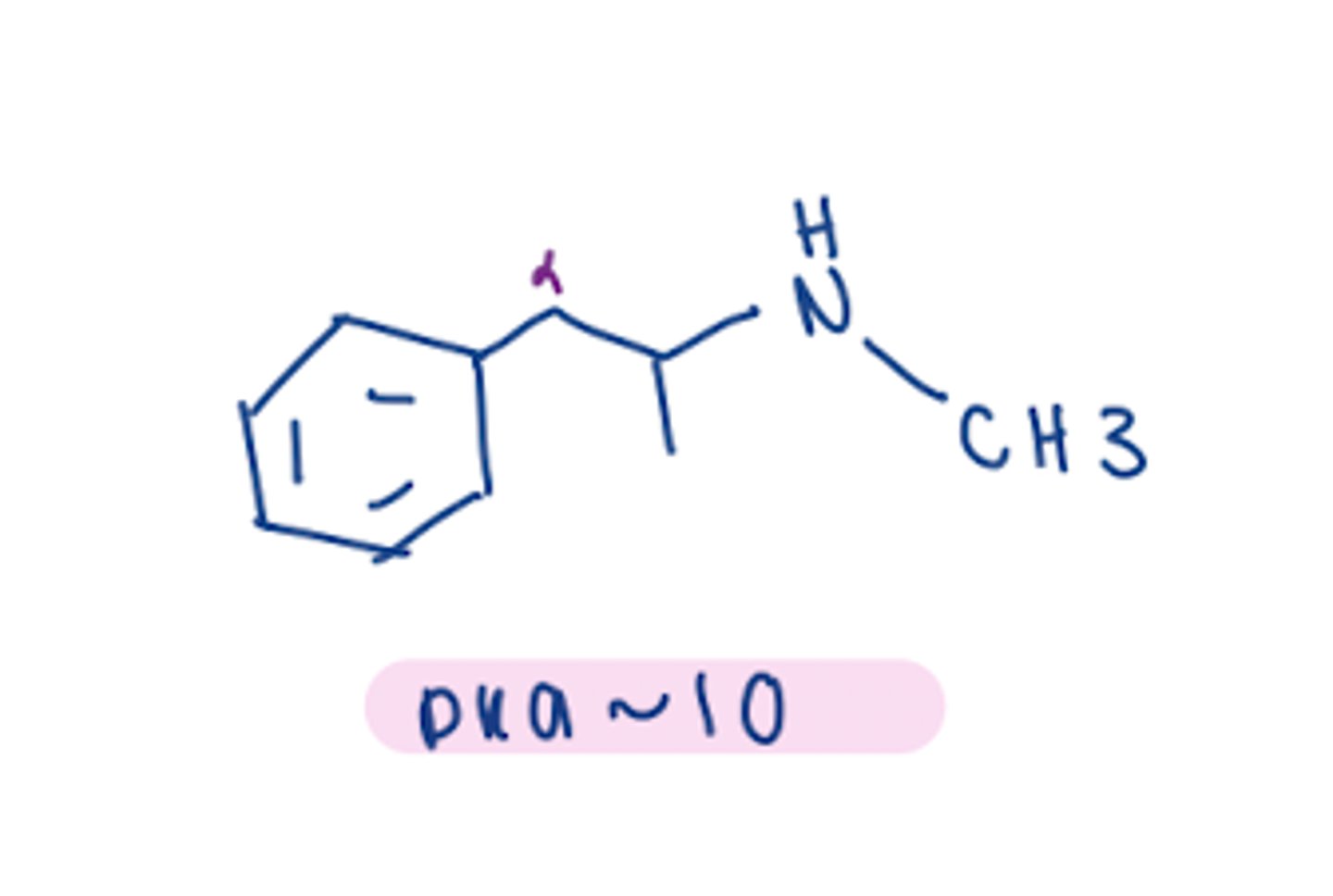
how does urine pH affect half-life of unchanged B-phenylethylamines
B-phenylethylamines are basic -> increased urinary pH -> longer half life
since B-phenylethylamines have abuse potential, how can an overdose be treated?
administer ammonia chloride (NH4Cl) -> in the liver, metabolizes to urea + H30, which acidifies urine pH -> decreases half-life
what enantiomer of B-phenylethylamines is typically more potent and used
S enantiomer
what B-phenylethylamines are used as CNS stimulants
amphetamine, dextroamphetamine, methamphetamine
what is dextroamphetamine
the S-enantiomer of amphetamine
amphetamine, dextroamphetamine indication
ADHD
what is the major metabolite of amphetamine? is it active?
inactive phenylacetone (from MAO)
methamphetamine indications
- ADHD > 6 yo
- short term weight loss when other therapies haven't worked
is methamphetamine or amphetamine more active
methamphetamine
what enantiomer of methamphetamine is used?
S enantiomer
B-phenethylamine anorexiants examples
phentermine, benzphetamine, diethylproprion, phendimetrazine
B-phenethylamine anorexiants MOA
1. modulate NE, 5-HT, and dopaminergic pathways -> promotes release & prevent reuptake of neurotransmitters
2. inhibition of nutrient absorption from intestines, inhibition of lipid biosynthesis, enhancement of lipolysis, and delay of gastric emptying
how do N-substituents affect the abuse potential of B-phenethylamine anorexiants
the bulkier the N groups, the less abuse potential
phenteramine indication
appetite suppressant
do B-phenethylamine anorexiants or CNS stimulants have more abuse potential
B-phenethylamine CNS stimulants
why does phenteramine have a reduced abuse potential (schedule 4)
ion exchange resin -> slow release
how is phenteramine eliminated? can it be deaminated by MAO?
eliminated unchanged (MAO can't deaminate it because there's no H group on adjacent C?)
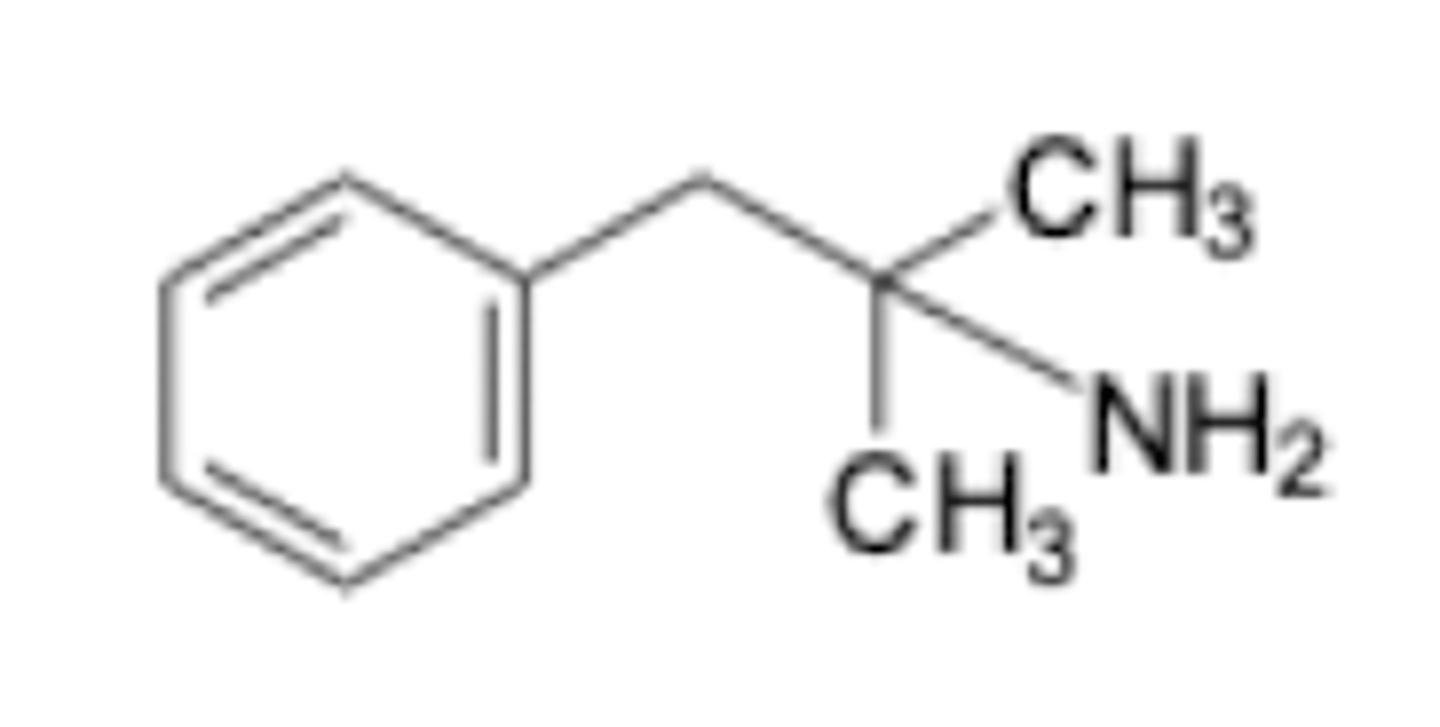
benzphetamine HCL indication
appetite suppressant
benzphetamine HCL metabolism
N-dealkylation, N-demethylation, aromatic hydroxylation
does phenteramine or benzphetamine HCL have more abuse potential? why?
benzphetamine HCL has higher abuse potential because it can be dealkylated to methamphetamine
diethylpropion HCL indication
weight loss
how do diethylpropion's side effects compare with phenteramine and benzphetamine
diethylpropion has less side effects
diethylpropion metabolism
N-dealkylation
is diethylpropion racemic?
yes
which CNS stimulant anorexiant is a prodrug? how is it activated?
phendimetrazine, activated by N-methylation
phendimetrazine stereochemistry
S,S
phendimetrazine indication
short term therapy of obesity
what is the non-CNS-stimulant weight loss drug
orlistat
orlistat MOA
irreversible inhibitor of pancreatic lipase -> prevents absorption of fatty acids and MAG -> increases excretion of fat
what part of orlistat interacts with pancreatic lipase
lactone
is orlistat avaliable OTC
yes
MOA of ADHD drugs
CNS stimulants inhibit dopamine transport away from synapse -> increased available dopamine
ADHD drugs
methylphenidate (dexmethylphenidate), serdexmethylphenidate, lisdexamfetamine, atomoxentine, viloxazine
which enantiomer of methylphenidate is more potent? what is it called?
- R,R (threo) isomer is more potent than S,S (erythro) isomer
- R,R is called dexmethylphenidate (Focalin)
methylphenidate (Ritalin) and dexmethylphenidate (Focalin) indications
narcolepsy, ADHD
methylphenidate major metabolites and whether they're active or inactive
- inactive: ritalinic acid, lactam
- active: p-hydroxy
Azstarys components
serdexmethylphenidate (schedule 4) + dexmethylphenidate (schedule 2)
what component of Azstarys is a prodrug? how is it activated
serdexmethylphenidate -> hydrolysis releases dexmethylphenidate at a slow rate
lisdexamfetamine indication
ADHD in children, binge eating disorder in adults
lisdexamfetamine stereochemistry and structure
dextral - steroid center in S configuration
is lisdexamfetamine a prodrug? how and where is it activated? what is it activated to?
yes, activated by hydrolysis in RBC -> releases dexmethylphenidate
what ADHD drugs are selective NE reuptake inhibitors (sNRIs) (not CNS stimulants)
atomoxetine, viloxazine
are sNRIs controlled substances?
no
atomoxetine indication
ADHD
atomoxetine metabolism
oxidative phase 1 reactions, mainly hydroxylation & glucoronidation on phenyl ring
is viloxanzine indicated for depression
not anymore, it used to be but was withdrawn
viloxanzine indication
ADHD, narcolepsy, cachexia
viloxanzine metabolism
hydroxylation of aromatic ring
viloxanzine selectivity
- very selective for NE (high Kd)
- not as selective for seratonin and dopamine (low Kd)
schedule 2 controlled substances CNS stimulants
ADHD: amphetamine, dexamphetamine, methamphetamine, methylphenidate, Azstaryz, lisdexamfetamine
schedule 3 controlled substances CNS stimulants
- CNS depressant: sodium oxybate
- anorexient: benzphetamine, phendimetrazine