vasc final exam review questions
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
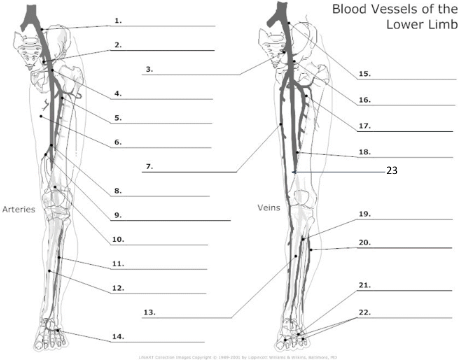
1
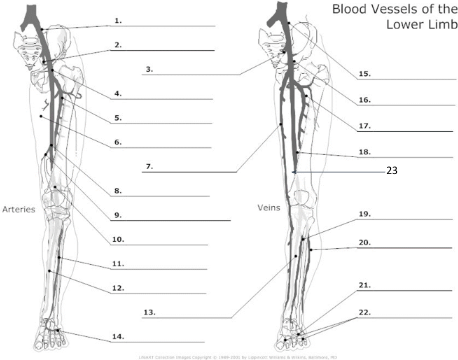
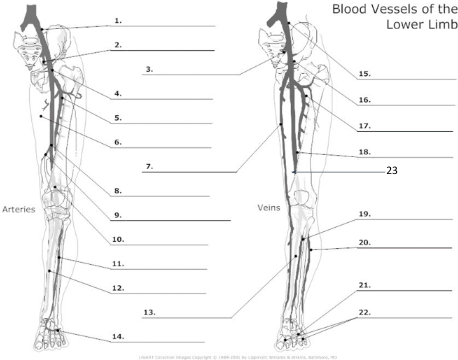
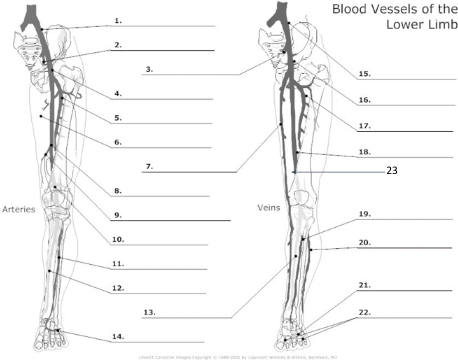
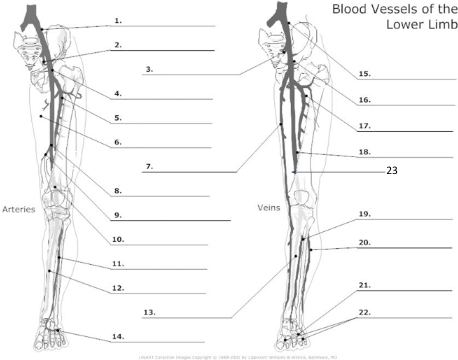
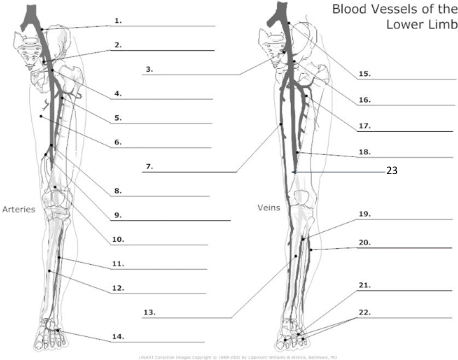
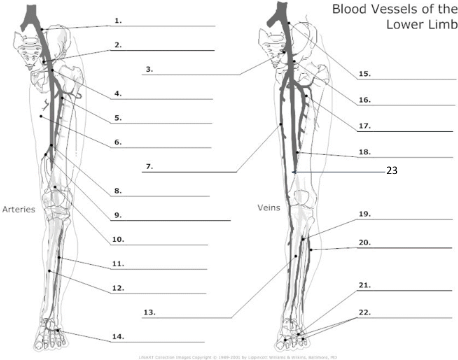
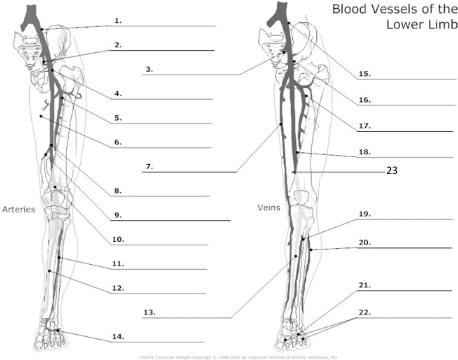
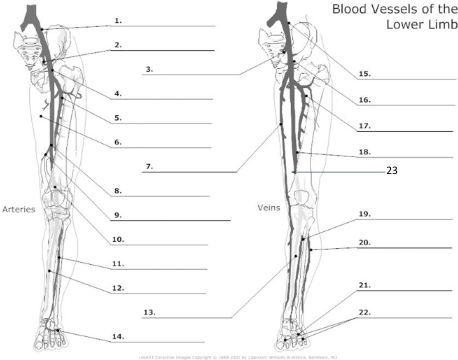
Common Iliac artery
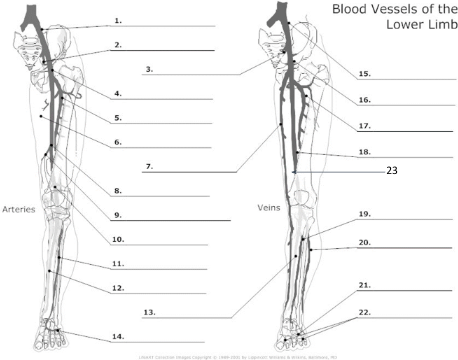
2
internal iliac artery
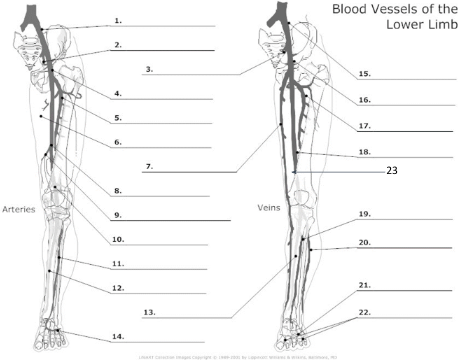
3
internal iliac vein
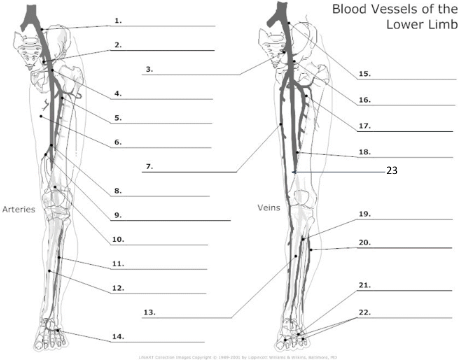
4
common femoral artery
5
proximal femoral artery
7
long saphenous vein
8
femoral artery
10
popliteal artery
11
anterior tibial artery
12
posterior tibial artery
21
plantar veins
15
common iliac vein
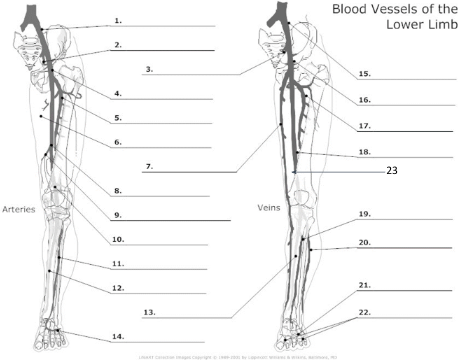
16
common femoral vein
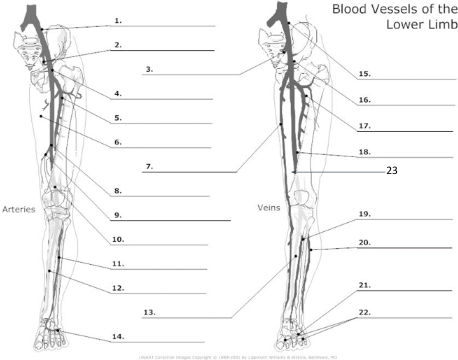
17
pfv
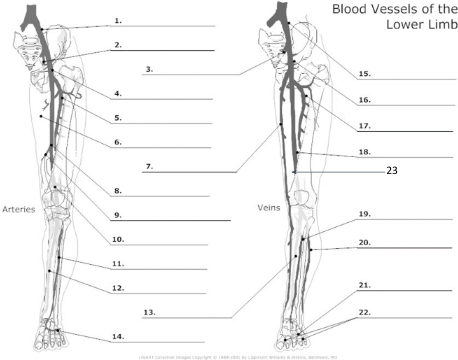
18
femoral vein
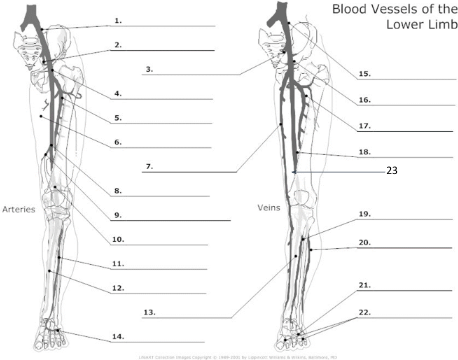
23
popliteal vein
what is the purpose of valsalva maneuver
to test efficiency of valves
what causes varicose veins
incompetent valves, increased pressure in superficial system
what is augmentation used for
to force a bolus of blood quickly up venous tree
what does a good augmentation response prove
lack of obstruction between the probe and area of squeeze
continuous, non-phasic flow in the common femoral vein when compressions did not reveal a DVT points to
DVT in ipsilateral iliac vein
if iliacs are not seen due to pt body habitus, gas, etc, how could you expand the test
examine IVC below liver for phasicity
aortic flow above renal arteries
low resistant, medium pulsatility
aortic flow at infrarenal portion and iliacs
high resistant, higher pulsatility
while exercise what kind of flow would aorta and distal iliacs have
low resistant flow
fasting state in SMA will show what kind of pattern
high resistant, low diastolic
post prandial flow in SMA would show what pattern
low resistant flow, high diastolic
renal flow is normally
low resistance
the upper limits of normal PSV in main renal artery is
< 180cm/s
what is the formula for RI
PSV-EDV / PSV
what is the normal range for renal RI
0.4-0.7
what is the acceptable renal artery to aorta ratio
< 3.5
what indicates a hemodynamically significant MRA stenosis
intrarenal tardus parvus waveform
what is the most common cause of renal artery stenosis
atherosclerosis
emboli or insitu thrombus causes what condition in the kidney
infarct
a malformation that causes arterial pulsations within renal venous tree is called
arterial venous fistula
how much flow does the portal vein supply to the liver
70%
normal blood flow velocity of the ______ is 13-23cm/s with an average of 18cm/s
portal vein
the normal PSV in hepatic artery of a fasting adult is
30-40cm/s
the normal EDV in hepatic artery of fasting adult is
10-15cm/s
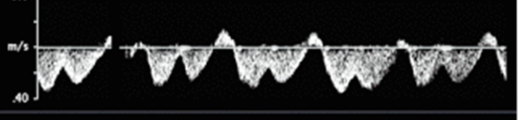
is this a normal waveform seen in hepatic veins
yes
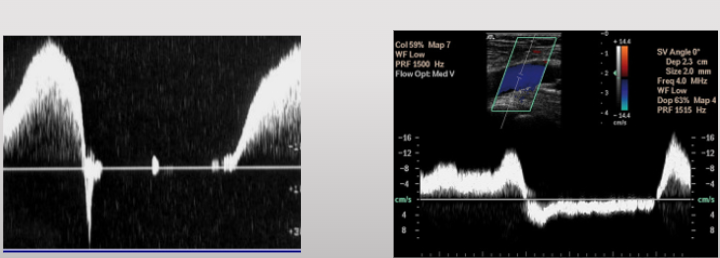
what does this waveform represent
non-phasic continuous flow
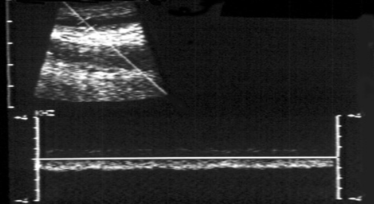
which one represents an incompetent valsalva
right
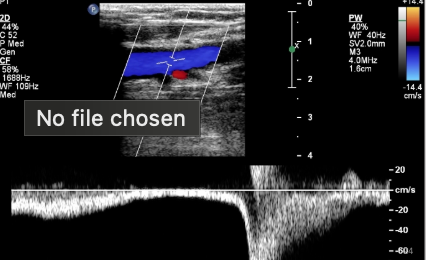
what does this represent
augmentation
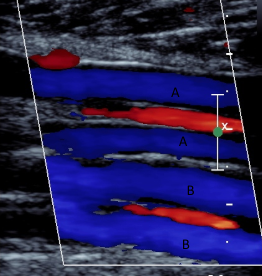
what does A represent in this photo
posterior tibial veins
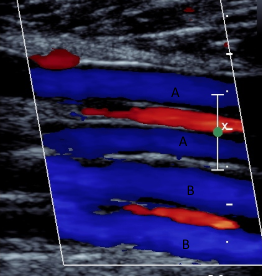
what does B represent in this image
peroneal veins
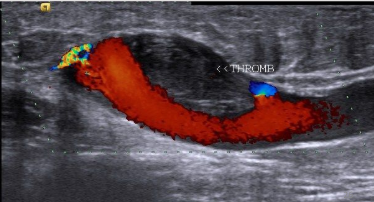
what category of thrombus is this
subacute
when the intimal wall pulls away from the muscular wall in an artery this indicates a
dissection
what is Paget-Schroetter syndrome associated with
strenuous upper body exercise or repetitive movements
what can be a cause of upper extremity DVTs
VADs
what are 3 uses for VADs
chemotherapy
nutritition
other meds
when is lymphedema in the arm most commonly seen
following mastectomy with removal of lymph nodes in the axilla
does right replaced hepatic artery or left replaced hepatic artery occur more commonly
right replaced
what artery does RRHA arise from
SMA
RRHA passes ______ to the portal vein
posterior
what is the size of the normal splenic vein
< 10mm
what is the term sinistral used for
left-sided splenic vein thrombosis
what is a sonographic sign useful in determining if a DVT is chronic
presence of collaterals
what is the sonographic appearance of a chronic clot
hyperechoic, calcified, thickened walls, atrophic vessel
if a D-dimer assay is negative does that mean there is unlikely a DVT
yes
what is primary varicose veins
incompetent SFJ valve
what is secondary varicose veins
history of DVT/occlusion or incompetent deep venous valves
what increases the risk of DVT
bowel disease (ulcerative colitis)
what can also increase risk of DVT
pregnancy
post partum period
OC
cancer
what does ABI stand for
ankle-brachial index
is ABI reliable for documenting the presence of lower extremity arterial diseae
YES
what is an ABI > 0.9 indicative of
hemodynamically significant stenosis
a major cellular component of blood is
erythrocyte
auscultatory consequence of turbulent flow
bruit
hemodynamics definition
physical principles concerned with the study of blood circulation
fluid system produces hydrostatic pressure
what type of flow exhibits a constant velocity across a vessel
plug flow
microcirculation consists of
arterioles, capillaries, venules
which portion of circulatory system exchanges vital nutrients with tissue cells
capillaries
what will remove aliasing
decrease depth of sample volume
when does a positive doppler shift occur
received frequency is higher than transmitted frequency
if received and transmitted frequencies are identical what happens
no doppler shift
what is a major advantage of continuous wave doppler
ability to measure high velocities
what is required for blood flow to occur
pressure gradient
speed at which blood travels through a vessel is dependent on
left ventricular output
noise in doppler signal is known as
clutter
the nyquist limit is equal to
½ of PRF
what converts doppler shift information into visual spectral display
fast fourier transformation
what overcomes aliasing
increase PRF
increase doppler angle
adjust baseline lower
resistance to blood flow is proportional to the
length of vessel
what is the simplest form of doppler
continuous wave
colour doppler frequency shifts are obtained using
autocorrelation
power doppler imaging displays the signals
amplitude
smaller arteries commonly demonstrate ___ flow
laminar