Lecture 19: Kidney Labs and Cysts
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Agenesis of the Kidney
Bilateral renal agenesis:
Incompatible with life and often associated with other congenital disorders
Potter’s Sequence
Unilateral agenesis:
Solitary kidney enlarges as a result of compensatory hypertrophy
Some patients develop progressive glomerular sclerosis and chronic kidney disease
Ectopic kidney
One or both kidneys fail to migrate and remain in the pelvis
Generally asymptomatic
Rarely a kidney will cross to other side (crossed ectopia)
Horseshoe Kidney
Kidneys fuse early in development
Migration arrested at inferior mesenteric artery
Abnormal anatomy can obstruct outflow
Azotemia
Elevation in blood levels of nitrogen containing compounds
Creatinine - Secreted by skeletal muscle
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)- Product of protein catabolism and breakdown
Uremia
Azotemia + clinical signs and symptoms
progressive weakness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, pruritis, tremors, altered mental status, eventually: stupor, coma, death
Dehydration, Edema, Hyperkalemia, Metabolic acidosis
Hyperphosphatemia, Hypocalcemia, Secondary hyperparathyroidism, Renal osteodystrophy
Anemia (low erythropoietin), Bleeding diathesis (platelet dysfunction)
Hypertension, Congestive heart failure, Cardiomyopathy, Pulmonary edema, Uremic pericarditis
Nausea and vomiting, Bleeding, Esophagitis, gastritis, colitis
Myopathy, Peripheral neuropathy, Encephalopathy
Sallow color, Pruritus, Dermatitis
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
High serum Phosphate + Low serum Calcium + High PTH
Kidney Injury
Decline in GFR
Dysregulation of fluid and electrolyte balance
Retention of metabolic waste products
Can result from glomerular, tubular, interstitial, vascular insult
Acute kidney injury (AKI)
Rapid decline in GFR (hours to days)
Generally reversible
Subacute kidney injury
Diminished GFR for 2 days to 3 months
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Diminished GFR that is persistently less than 60 mL/min for ≥3 months
End result of all chronic renal parenchymal diseases
End-stage renal disease (ESRD)
Terminal stage of CKD
GFR <5% of normal
Requires hemodialysis or transplant
Azotemia Causes
Prerenal disease: Decrease in renal perfusion caused by atherosclerosis, hypovolemia, NSAIDs (afferent arteriole vasoconstriction)
Intrinsic renal disease:
Glomerular disease
Renal vascular disease
Tubular and interstitial disease
Postrenal: Obstructive nephropathy
Prerenal Disease Causes
Cardiorenal Disease:
Systolic heart failure → decreased renal perfusion → reduced GFR
Hypotension, fatigue, dyspnea, peripheral edema
“Cardiorenal Disease” can also describe cardiac failure caused by increased Renin in renal disease
Hepatorenal syndrome:
Decompensated liver disease → portal hypertension + hypoalbuminemia
Fluid shift into ascites and portal circulation → decreased renal perfusion
end stage liver disease
Poor prognosis
Glomerular Filitration Rate
Good metric of kidneys functional status
Volume of fluid filtered by glomerulus per unit time
Creatinine or Cystatin C
BUN:Creatinine ratio in kidney injury
>20:1 pre-renal cause of renal injury
In dehydration, BUN is reabsorbed to retain fluid and maintain vascular pressure
12:1 to 20:1 intrarenal cause of renal failure
Urine Osmolality in AKI
Prerenal: >500 mOsm/kg - hypoperfused kidneys are trying to retain fluid
Intrarenal: <500 mOsm/kg - Renal tubules are unable to concentrate urine
Postrenal: Depends on tubule function
Fractional Excretion of Sodium (FENa)
Percentage of filtered sodium that is excreted in the urine
FENa < 1% - Prerenal disease
FENa > 1% - Renal disease (Acute tubular necrosis)
Post renal azotemia
Early disease: resembles prerenal azotemia
Later disease: tubular cells are damaged and it resembles intrinsic azotemia
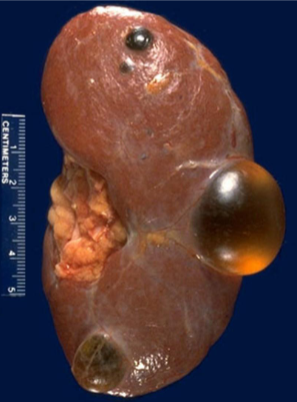
Simple Cysts
Simple Cysts
Single/multiple all sizes up to 10cm
Common with increasing age (>50)
Frequent incidental finding on imaging
Suspect ADPKD if 3 or more cysts or young individuals (<40)
Occasionally symptomatic - Hemorrhage, rapid distension and pain
Usually of no significance
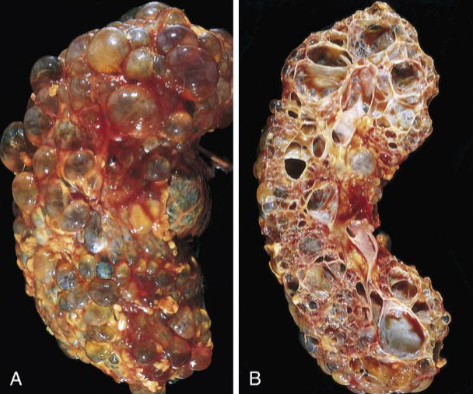
Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease
AD inheritance of pathogenic PKD1 or PKD2 LOF
Slower progression of CKD than other forms of ESRD
Spheroid cysts of variable size compressing intervening function nephrons
Generally asymptomatic until renal function declines in 30s-40s
May present with pain or hematuria
Association with liver cysts, berry aneurisms, mitral valve prolapse
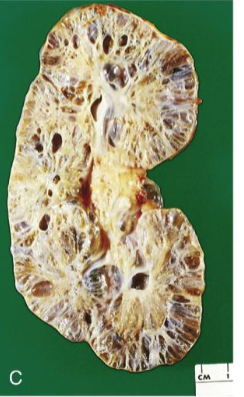
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal recessive inheritance of LOF PKHD1
Cysts are slender and at right angle with cortex
Oligohydramnios resulting from decreased urine output → pulmonary insufficiency
If a patient survives respiratory distress in the neonatal period, renal function may improve with maturity, but eventually kidneys fail
Liver involvement: congenital hepatic fibrosis and dilation of hepatic bile ducts
Medullary Sponge Kidney
Congenital multiple cystic dilations of the collecting ducts in the medulla
Increased risk of renal calculi, urinary tract infection, and mild hematuria
Incidental finding on radiology
Nephronophthisis
Rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by NPHP mutation → dysfunctional primary cilia (ciliopathy)
Can be sporadic (nonfamilial); familial (juvenile nephronophthisis); or part of a larger genetic syndrome
Variable number of small cysts in the medulla, usually concentrated at the corticomedullary junction
Progressive tubular atrophy involving medulla and cortex and interstitial fibrosis
May present with polyuria and polydipsia and progress to ESRD in childhood and adolescence
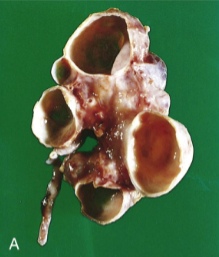
Multicystic Renal Dysplasia
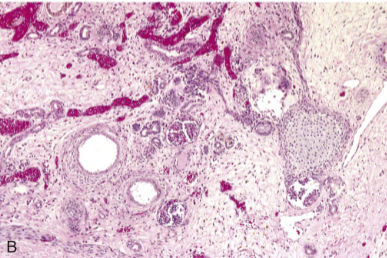
Multicystic Renal Dysplasia
Multicystic Renal Dysplasia
Sporadic, congenital maldevelopment of one (more common) or both kidneys
Kidney replaced by cysts of variable size separated by undifferentiated mesenchyme often with cartilage and immature collecting ducts
Kidney will eventually involute
Associated with agenesis or atresia of ureter
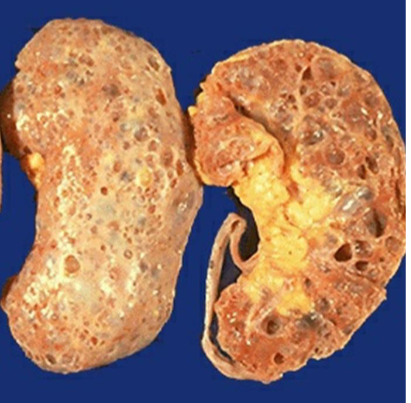
Acquired Cystic Disease
Acquired Cystic Disease
ESRD patients with prolonged dialysis
Small cysts
lined by either hyperplastic or flattened tubular epithelium
Often contain calcium oxalate crystals
Generally asymptomatic, but sometimes cysts bleed, causing hematuria
100-fold increased risk of renal cell carcinoma
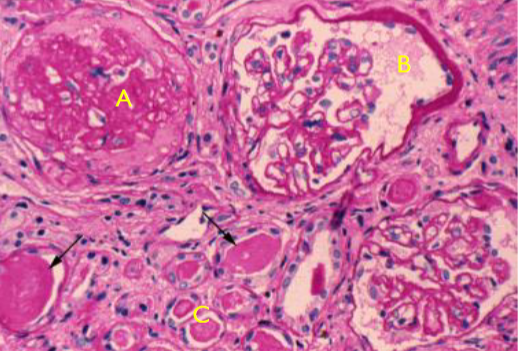
Nephrosclerosis
A. Globally sclerotic glomeruli
B. Shrunken glomeruli
C. Tubular atrophy
Nephrosclerosis
Renal pathology associated with sclerosis of renal arterioles and small arteries
Strongly associated with hypertension and diabetes
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis in response to hypertension, decreases blood flow to glomerulus
Micro vascular damage in diabetes contributes to decreased blood flow
Vascular disease leads to local ischemia, glomerulosclerosis and chronic tubulointerstitial injury
Gradual loss of kidney function, reduced kidney size and granular gross appearance
Common cause of ESRD
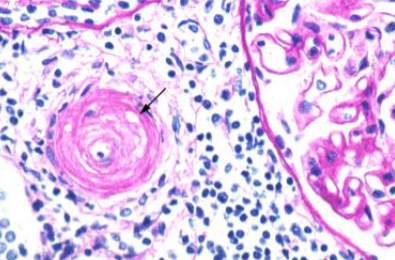
Acute Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis
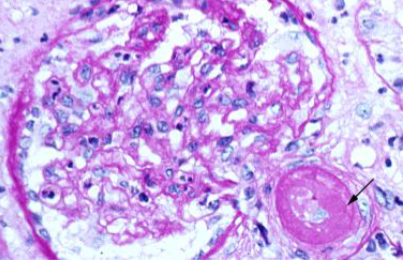
Acute Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis
Acute Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis
High blood pressure (SP >180) causing end organ damage to the kidneys
“Onion skinning” of small renal arterioles
Causes acute or chronic kidney injury
Kidney injury contributes to worsening hypertension via increased Renin
Antihypertensive therapy may transiently worsen renal blood flow and reduce GFR
May require dialysis
Renal Artery Disease
Atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia of one or both renal arteries
Juxtaglomerular cells produce renin in response to decreased blood flow (stretch receptor) increasing blood pressure
Treatable with ACE or ARB blockade or reversible with stenting
Bilateral renal artery stenosis due to atherosclerosis is a reversible cause of CKD
Kidneys have no collateral circulation and are susceptible to thromboembolic disease
thrombotic microangiopathies
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) and Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome (HUS) → thrombi in capillaries and arterioles (including renal arterioles)
Thrombi partially obstruct arterioles and shear red cells (schistocytes) leading to microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
Free Hemoglobin may cause direct damage to renal tubules
Thrombi in arterioles cases local necrosis and damages tubules and glomeruli
Can progress to renal failure
Sickle Cell Nephropathy
HbS crystalizes in response to hypoxia, oxidative stress or dehydration
The renal medulla is hypertonic causing dehydration of cells pushing HbS molecules closer together in a hypoxic environment leading to sickling
Hematuria and a diminished concentrating ability (hyposthenuria)
Patchy papillary necrosis
Proteinuria is common in sickle cell disease