lecture 2 fermentation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
I: Microbial enzymes* acting on substrate
Proteolysis: digestibility, flavour and taste
Lipolysis: flavour
Amylolysis: digestibility, acid formation
Pectinolysis: digestibility
Cellulolysis: digestibility
2. Formation of metabolites
2. Formation of metabolites
Flavour compounds
• acids, alcohol, esters, acetoin
Colouring substances
• carotenoids
Vitamins
• B-vitamins
• yeast extract
Antimicrobial compounds
• acids, alcohols, carbon dioxide
• hydrogen peroxide
• reuterin, bacteriocins, killer-toxins
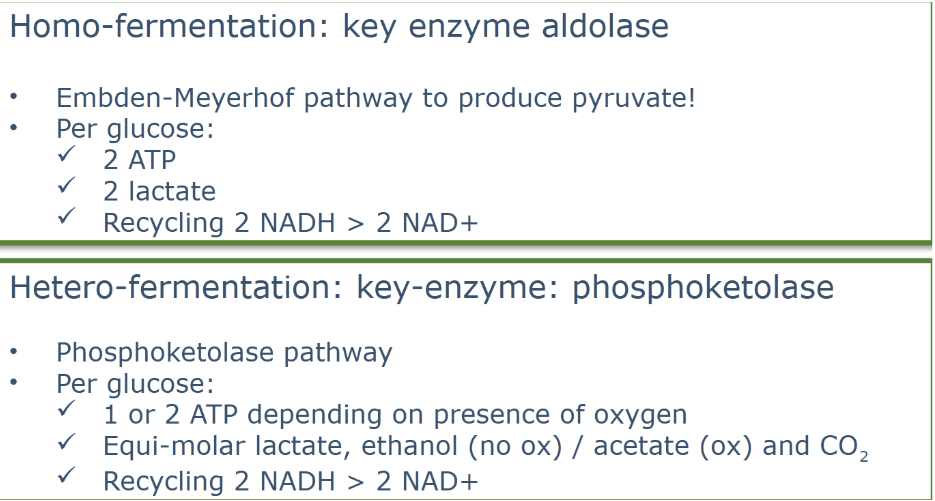
what are the main types of fermentation

Describe Lactic fermentation
Lactic ( Yoghurt, Cheese, Vegetables, Sausages)
Efficient conversion of carbohydrates into lactic acid. Microbes have transporters, simple sugars are converted into lactic acid and other organic acids. It is FAST and energetically inefficient
what are types of lactic acid bacteria
1. Homofermentative: mainly 1 product
-Homolactic fermentation: only lactate made
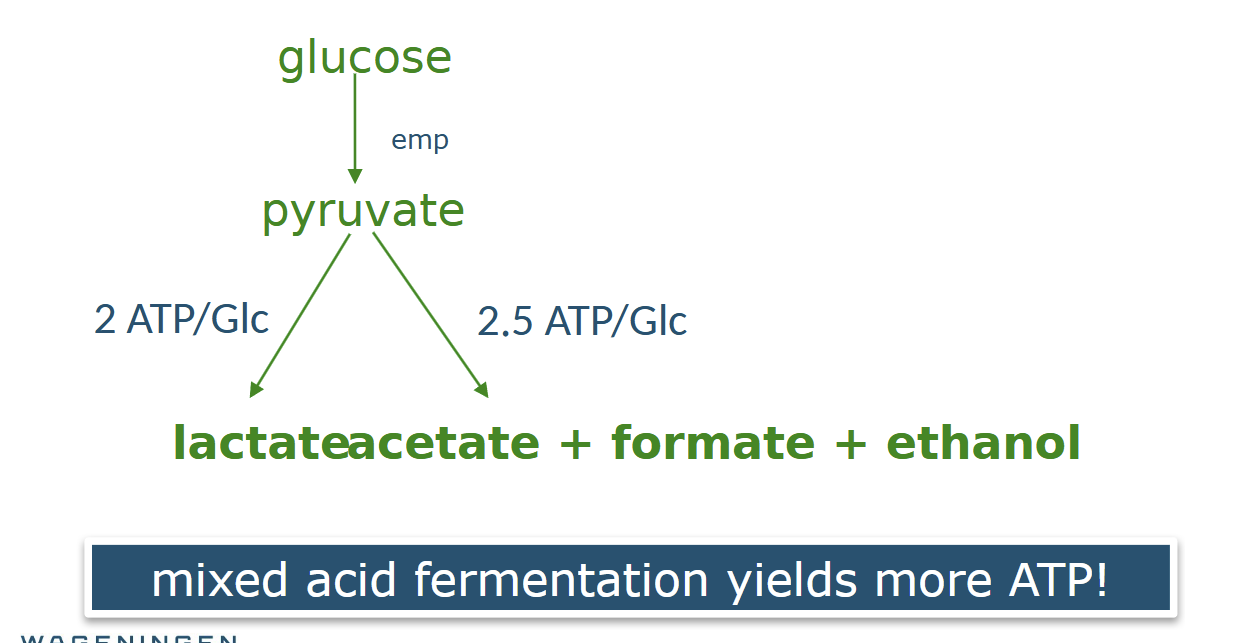
- Mixed acid fermentation: many organic acids
2. Heterofermentative: several main products
Heterofermentative
2.Heterofermentative : several main products made, co2 made
- ethanol ( no 02)
- acetate (02 present)
- 1 atp (no 02)
- 2 atp (02)
Homofermentative
1. Homofermentative: mainly 1 product
-Homolactic fermentation: only lactate made
- Mixed acid fermentation: many organic acids
Can switch from homolactic to mixed acid fermentation
When? conditions with limited substrate and during slow growth
why? more energy efficient
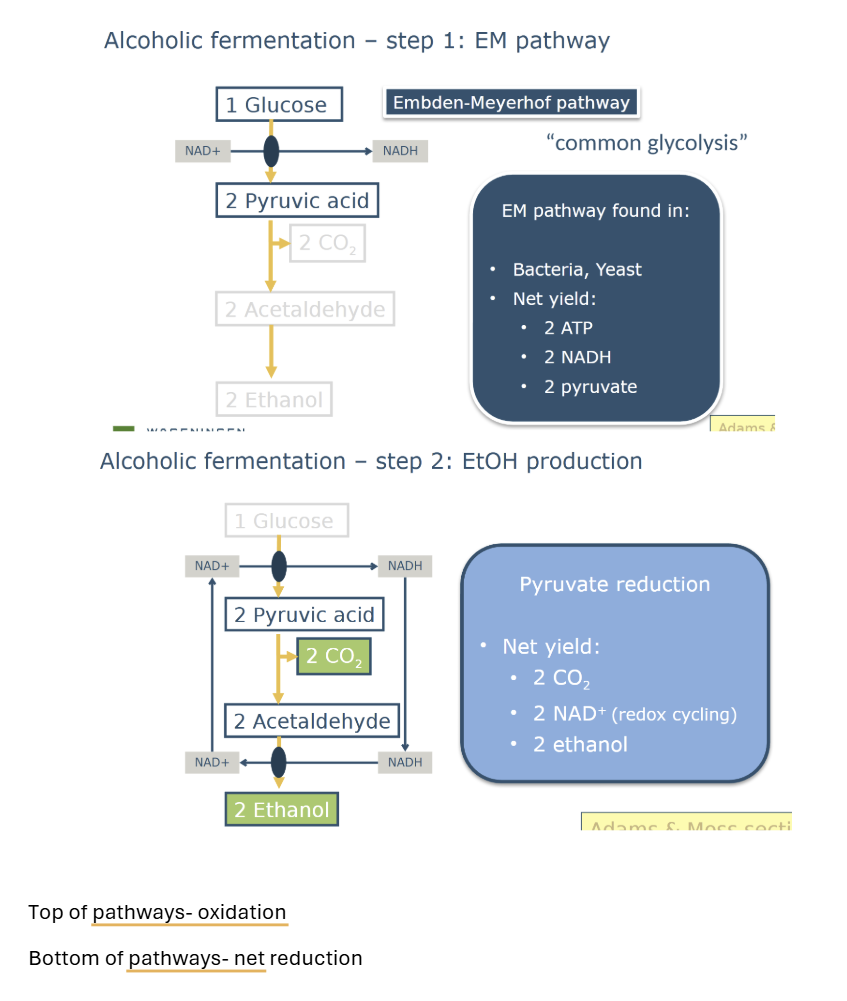
describe em pathway alcoholic fermentation
Embden-Meyerhof pathway is the main metabolic route to provide
pyruvate for ethanol production
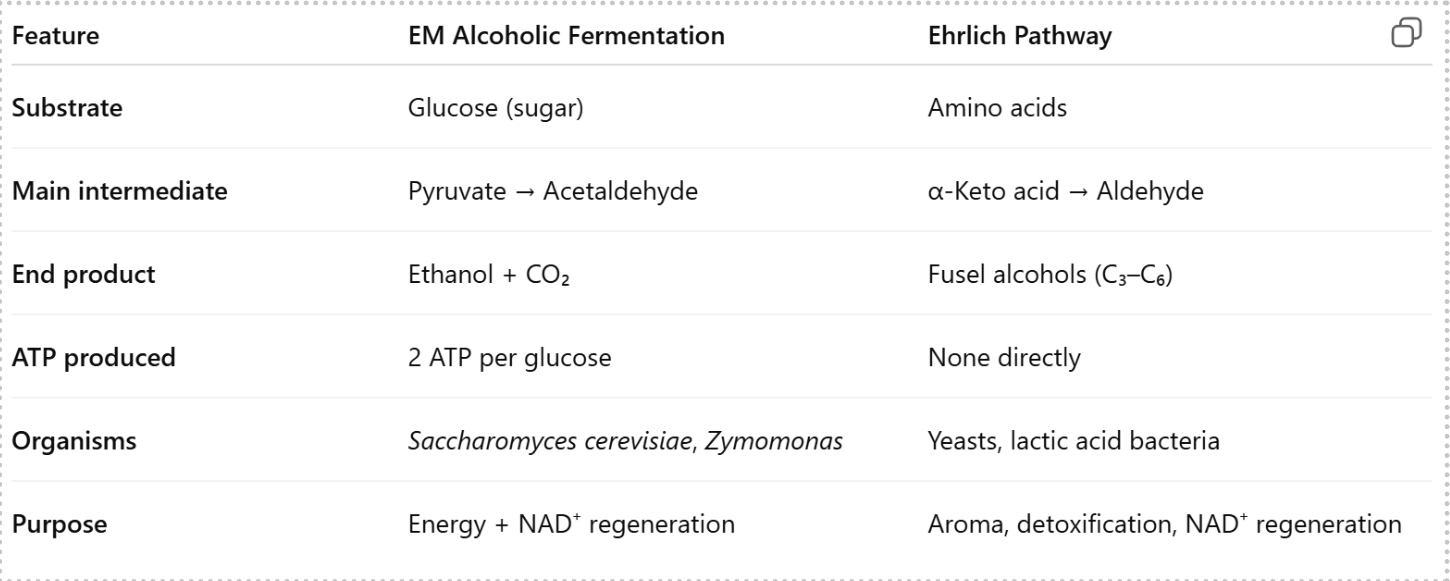
whats the difference between EM pathway and Ehrlich pathway
explian the Ethanol tolerance importance for activity in ripening phase
As ethanol concentration rises during fermentation (especially in wine), many microorganisms stop growing — but the yeast must remain active to finish converting sugars to alcohol and to survive the final stages.
So, yeast strain’s ethanol tolerance is crucial for successful wine fermentation and aging.
Many yeast species have high ethanol tolerance
what are yeast cells efficient producers of
Yeast cells are efficient producers of ethanol and CO
what does amino acid degradation lead to
Amino acid degradation leads to production of higher alcohols (fusel
alcohols) and thus aroma!