Plant Anatomy
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Allium root
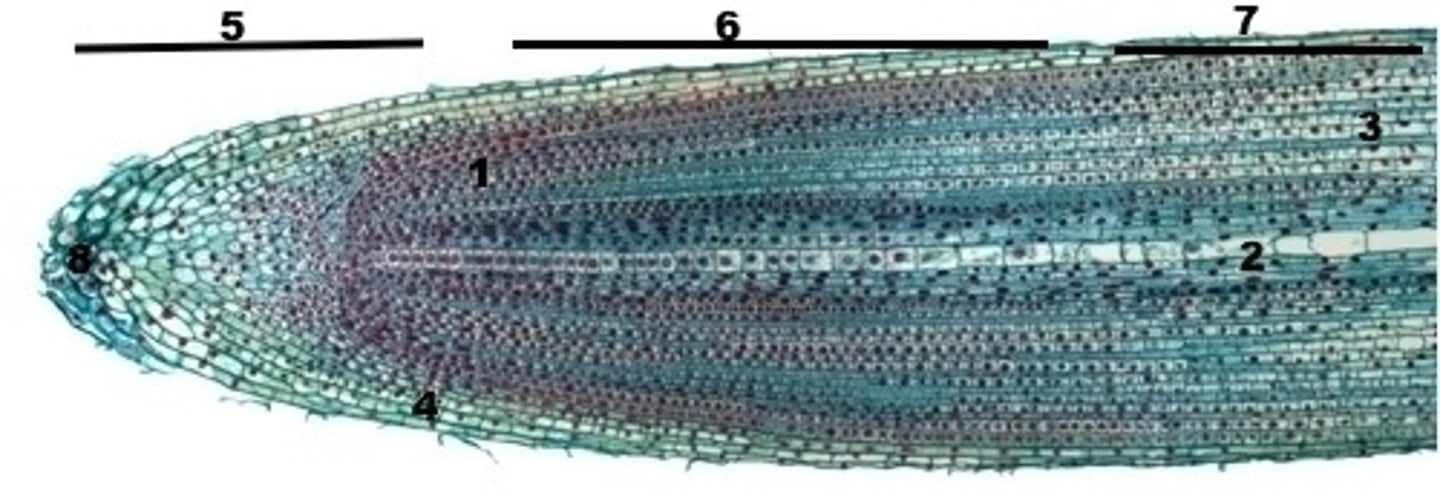
Label allium root
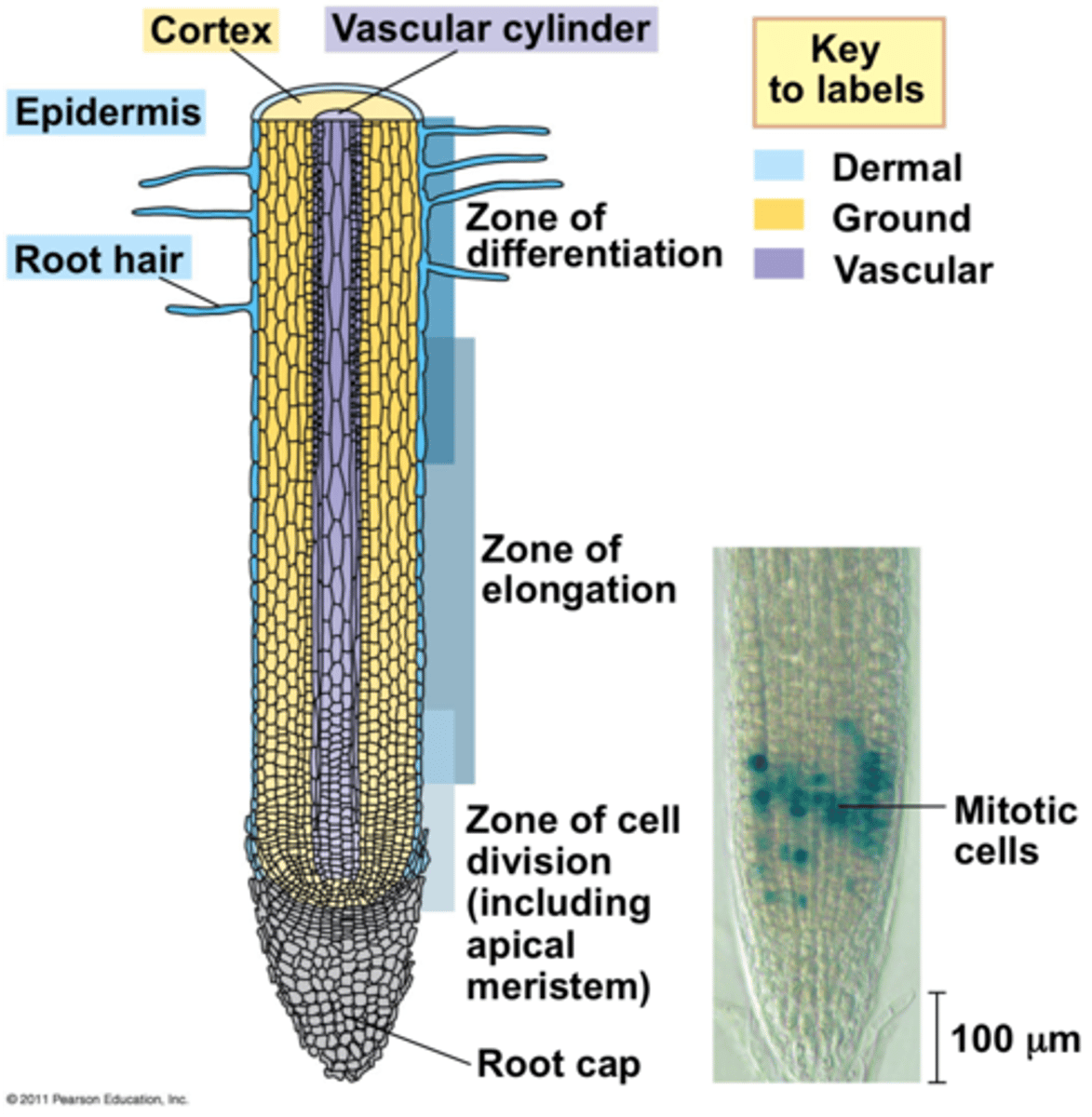
Zone of maturation definition
Region where xylem and phloem mature and absorption takes place
Region where root hairs are located
Purpose of root hairs
Increase the roots surface area for gathering minerals, water, and O2
Zone of elongation definition
Region where cells elongate and push the apical meristem and root cap through the soil
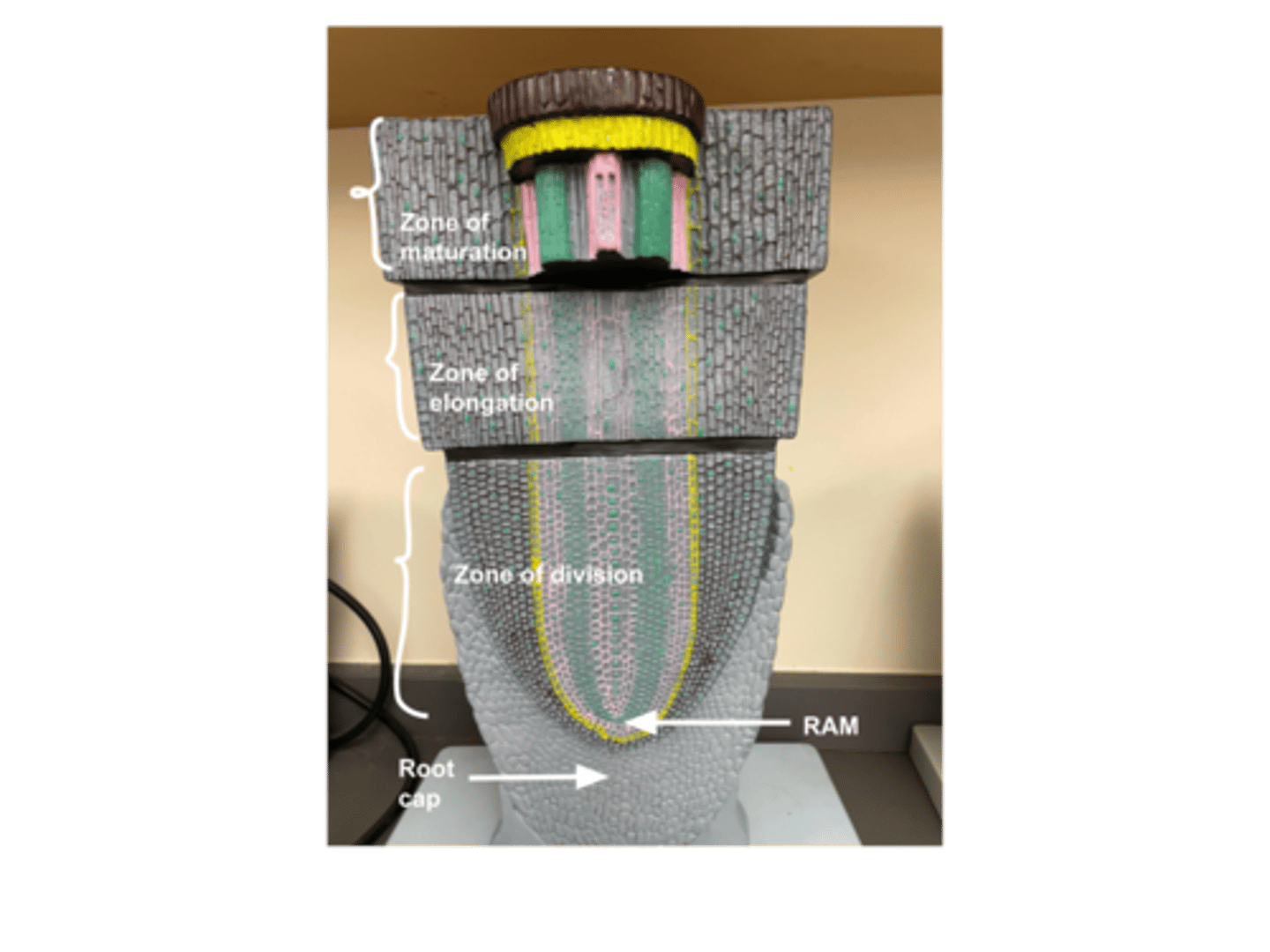
Zone of division
Houses the RAM and responsible for primary growth
Ensures growth by adding new cells by mitosis
Replaces sloughed off root cap cells
Root cap purpose
Protects the RAM and secretes a polysaccharide slime to lubricate the soil
What is located in the zone of maturation?
Xylem and phloem
root hairs
Root model longitudinal section
Root model cross section
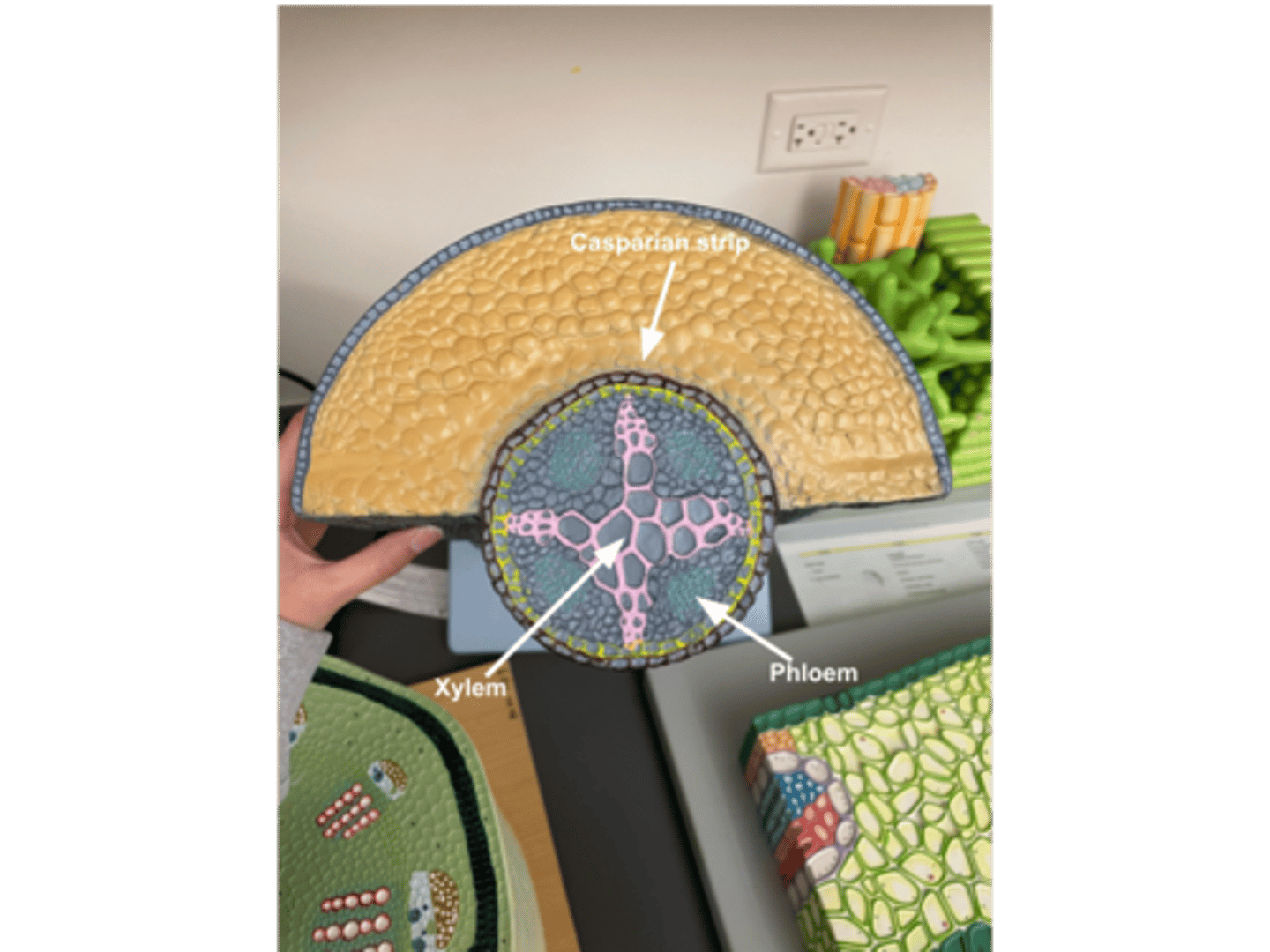
Significance of casparian strip
◦Waxy barrier attached to the cell walls in roots
Forces water and ions into the xylem
◦Materials are forced across plasma membranes rather that following cell walls
Prevents water and minerals from leaking out of the xylem
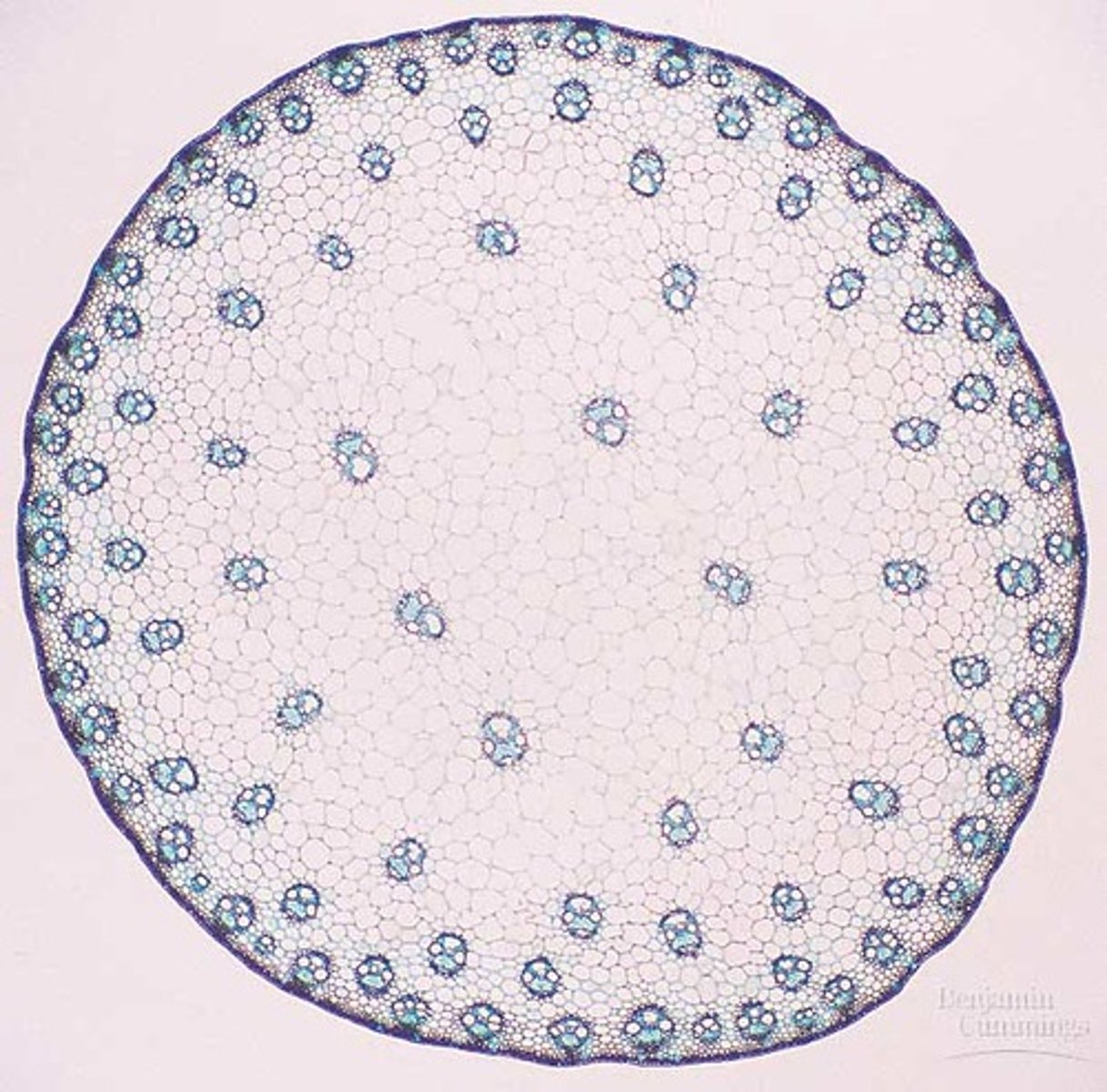
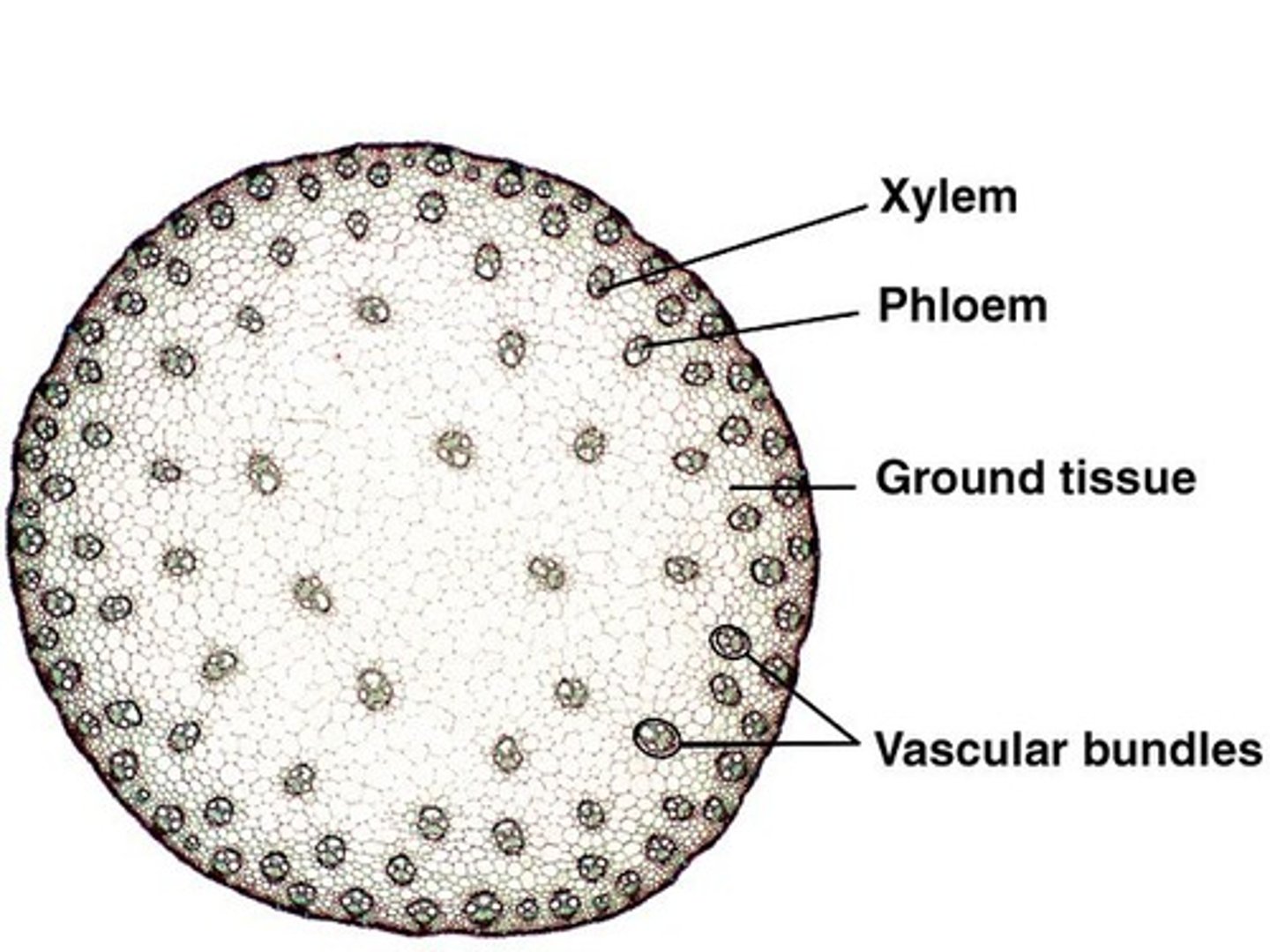
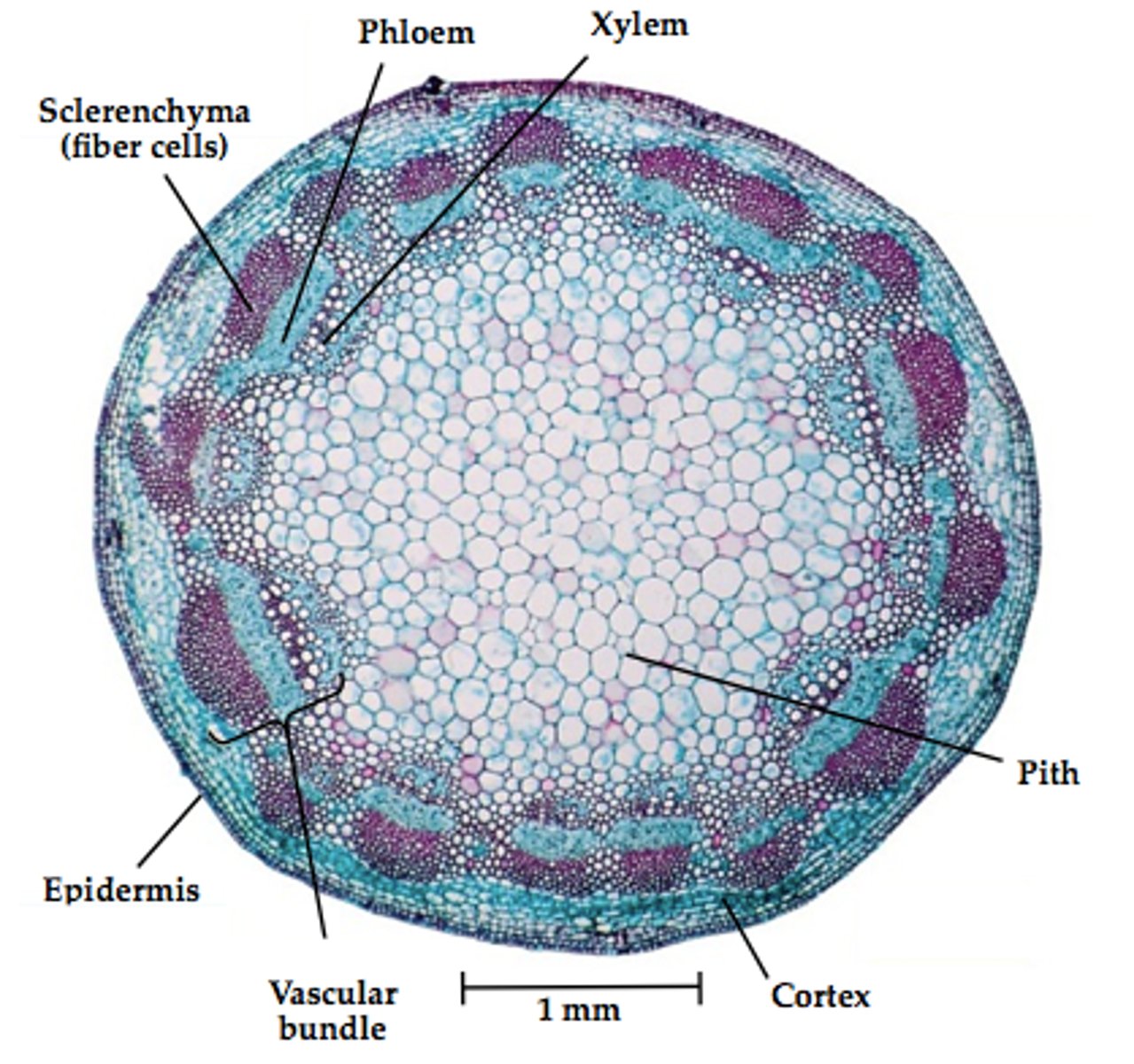
Monocot stems are known as a
atactostele
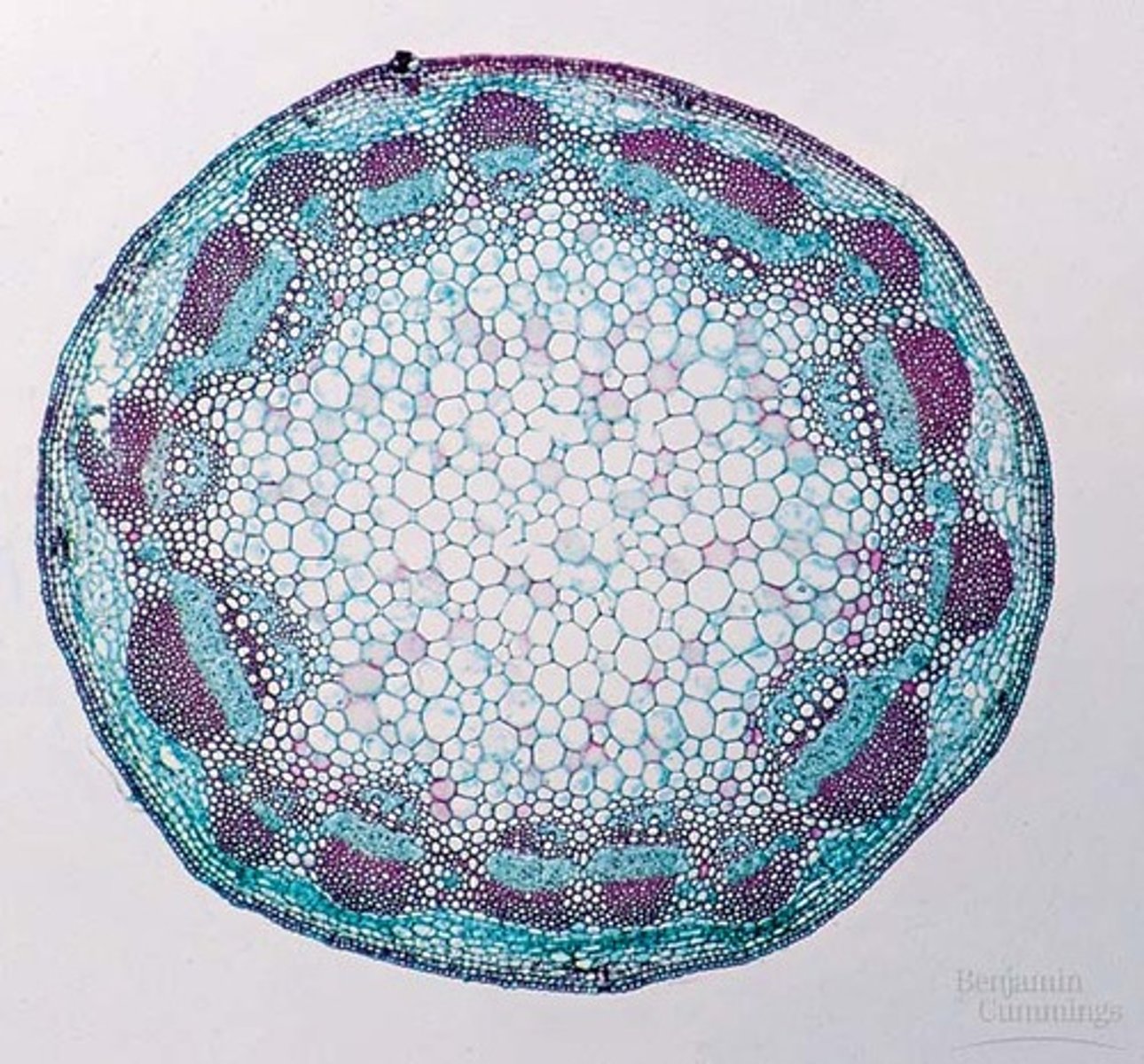
Dicot stems are known as
eustele
monocot stem
dicot stem
monocot stem labeled
dicot stems
monocot leaf microscope
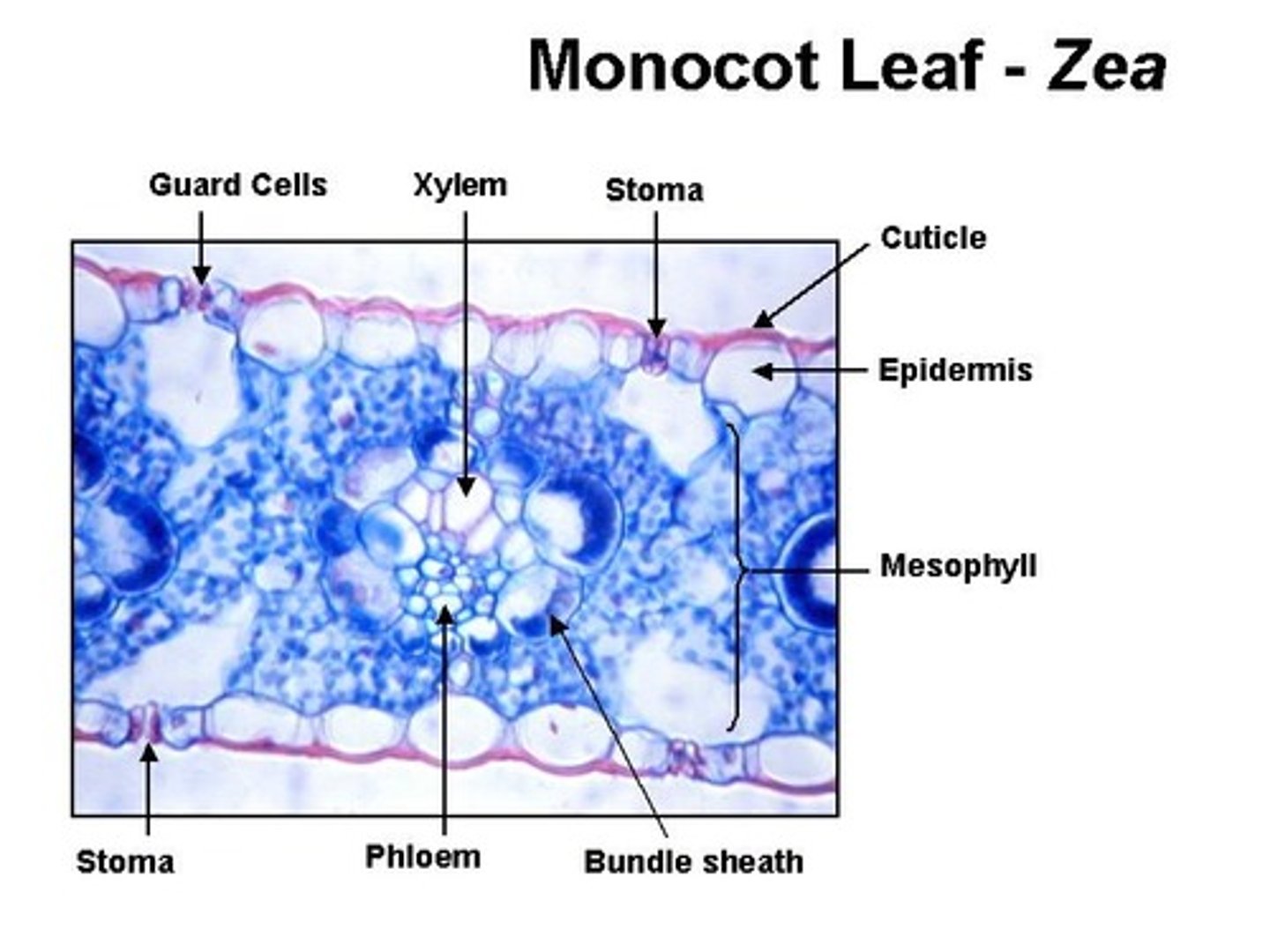
monocot leaf

monocot leaf (only need to know stomata, xylem, and phloem)
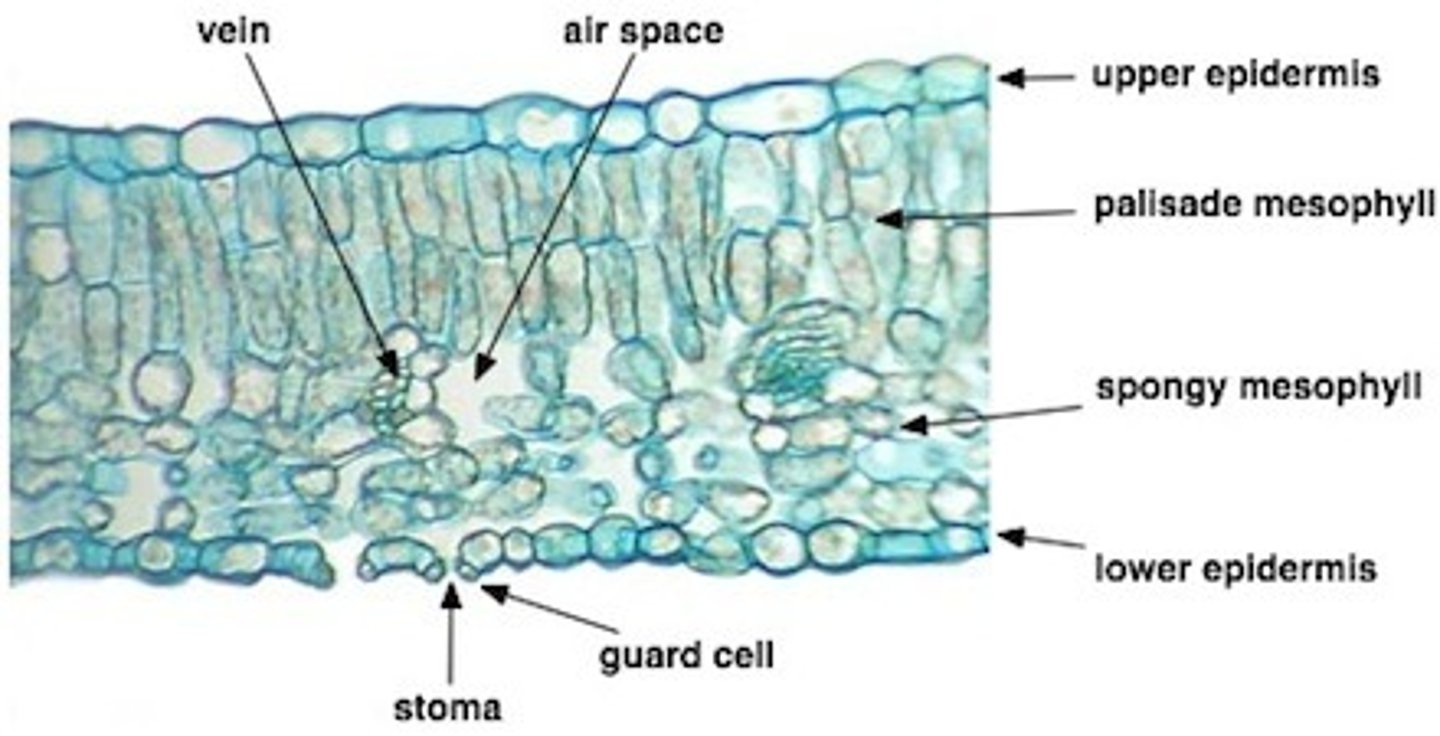
dicot leaf microscope
dicot leaf

dicot leaf
Dicot stem model
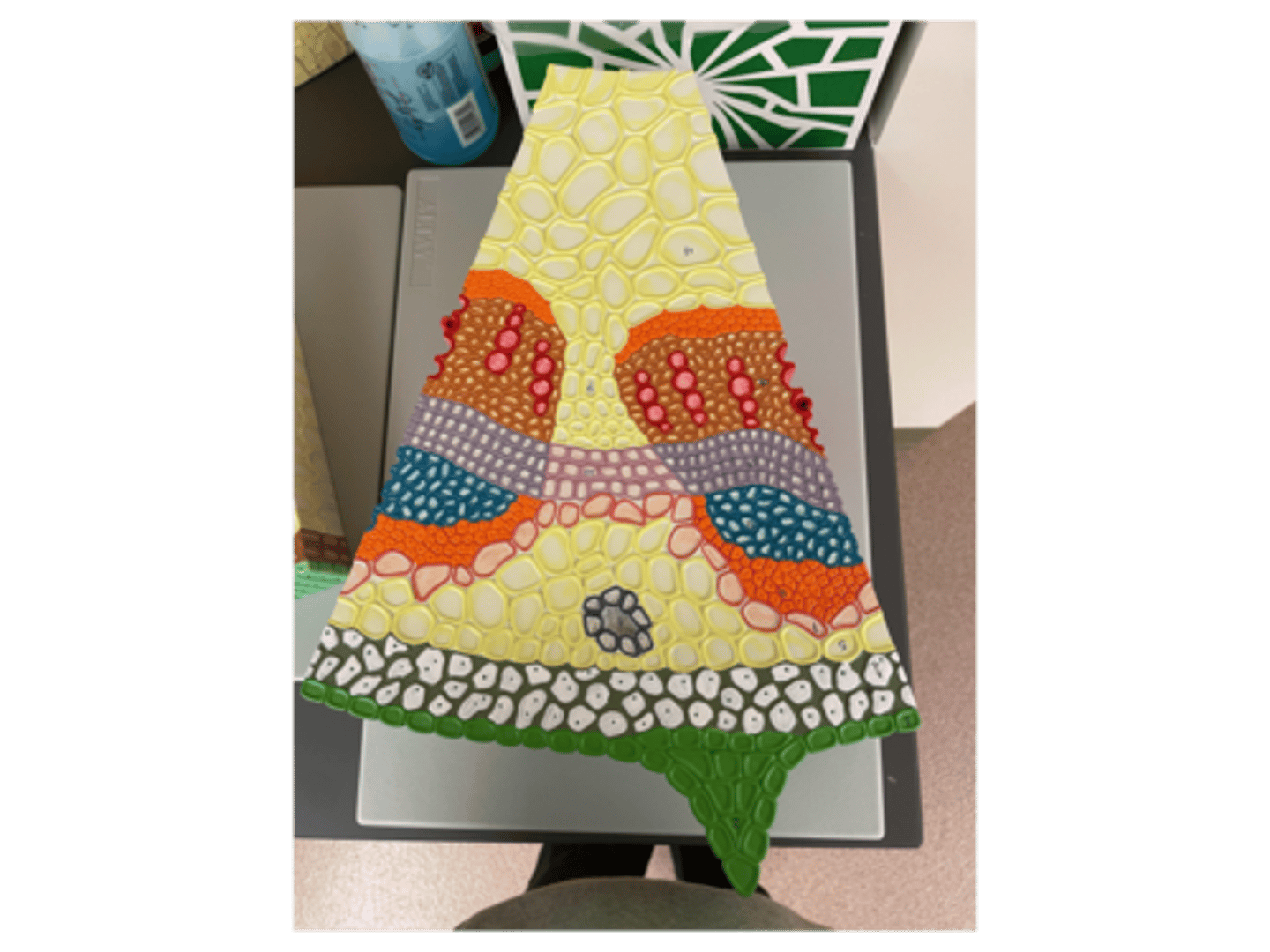

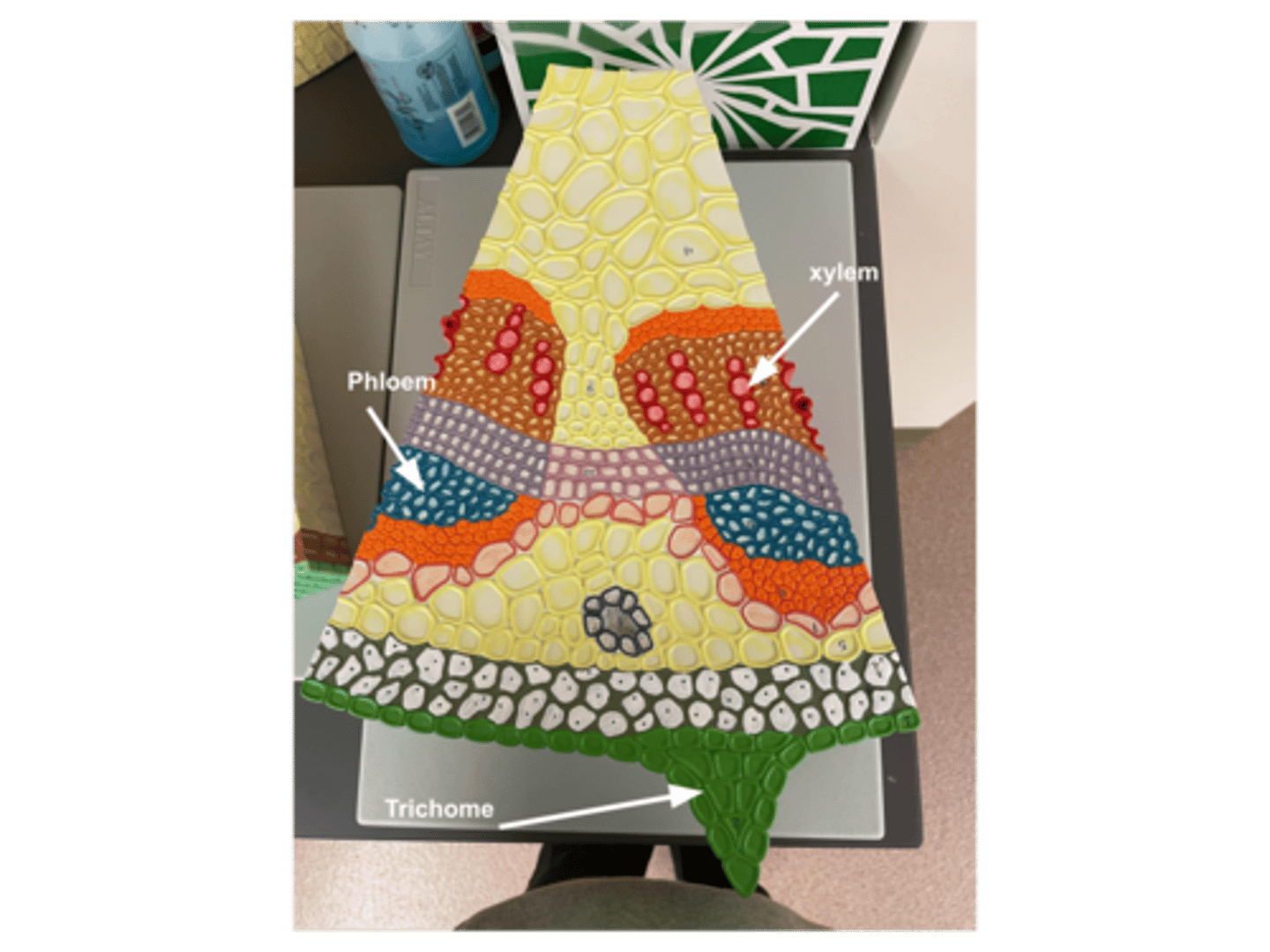
Dicot stem model labeled

monocot stem model
same thing as dicot stem model but no pith. i gave up.
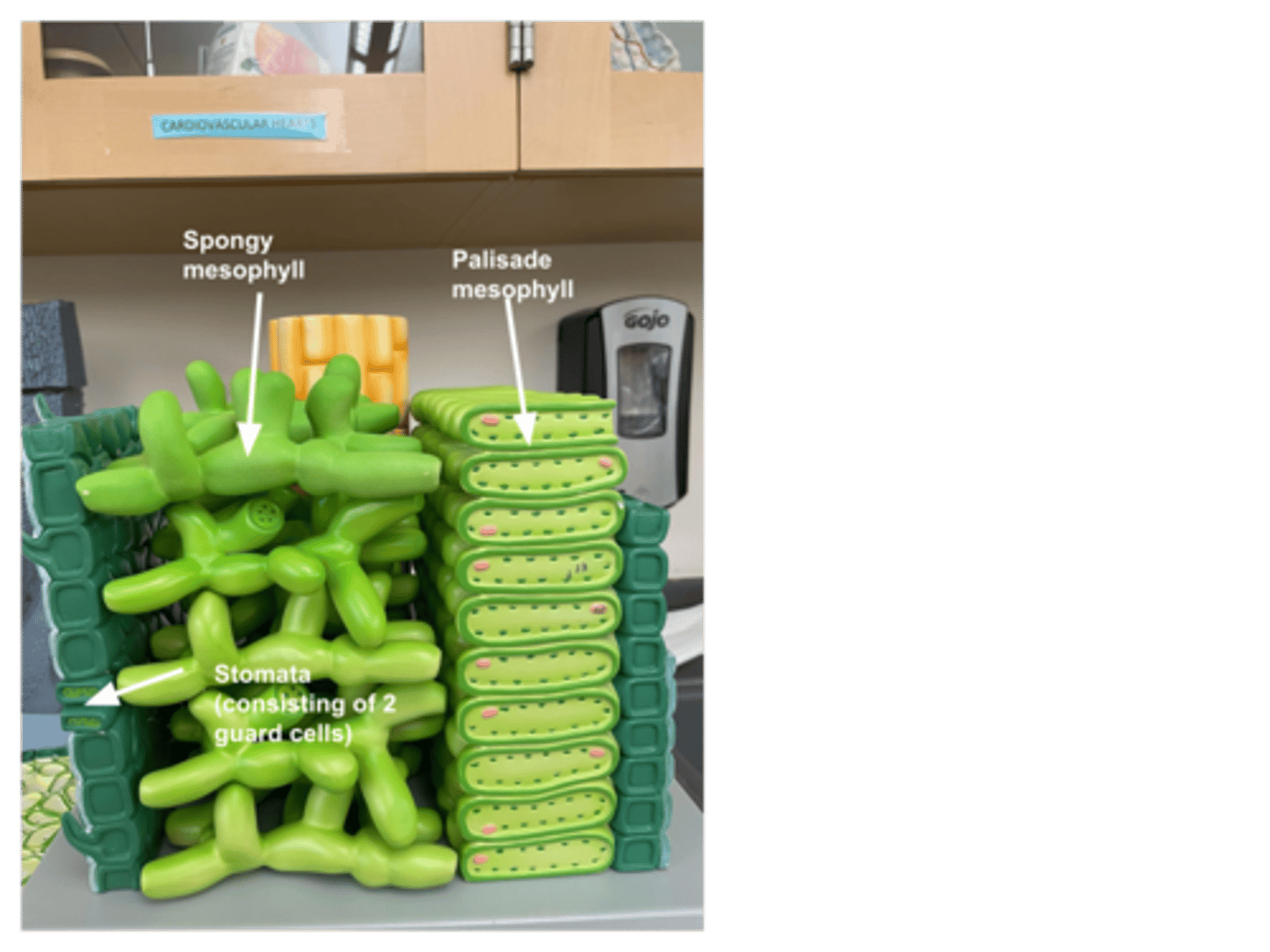
Leaf model
