Heating/Cooling Curves
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
The lower the kinetic energy of a substance, the ___ attraction between its molecules
stronger
True or False; The solid state of matter is unique because all molecular motion stops
False
All molecular motion does not fully stop, but while in a solid state of matter the molecules will vibrate acutely
True or False; Phase transitions occur at precise temperatures
True
As heat is turned up under a pot of boiling water, the temperature will _____ until all the water has become gas.
remain constant
Why does temperature remain constant during a phase change?
Because the energy gained or lost is all used by molecules transitioning from one phase to another
At 150 seconds a pot water has just reached a boil. If the heat is left on, what will happen to the temperature and volume of water in the pot
The temperature will remain constant, and the water volume will increase
Which of the following statements is most accurate
a) When liquid water is heated, the molecules move faster
b) When liquid water is heated, the molecules collide more often
c) When liquid water is heated, collision between molecules are more violent
d) All of the above
D
Describe/explain the process of warm water freezing into ice
Water molecules slow down until they begin to attract together
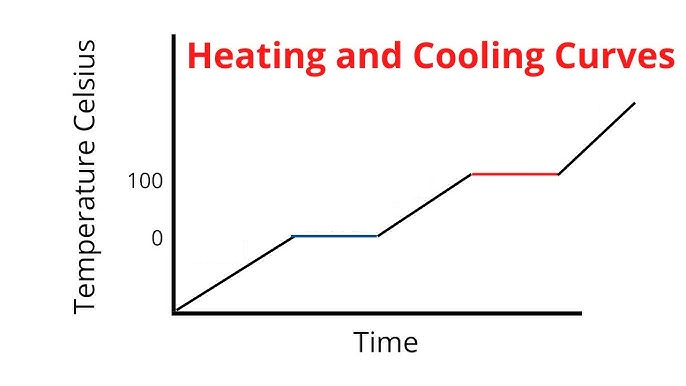
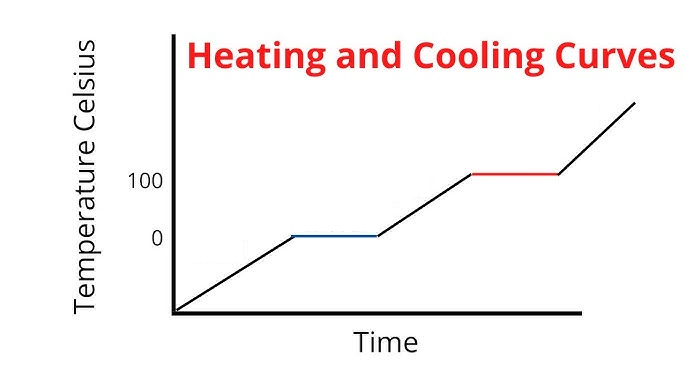
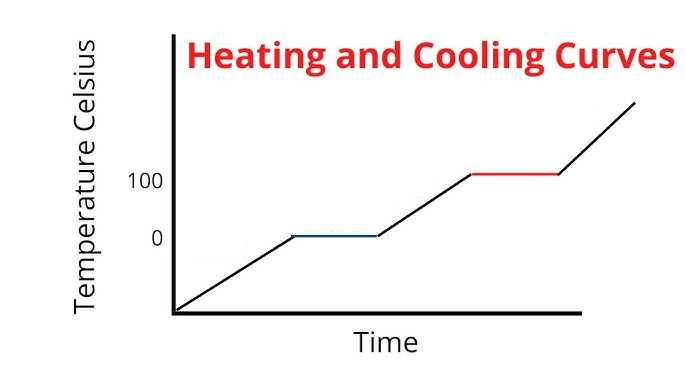
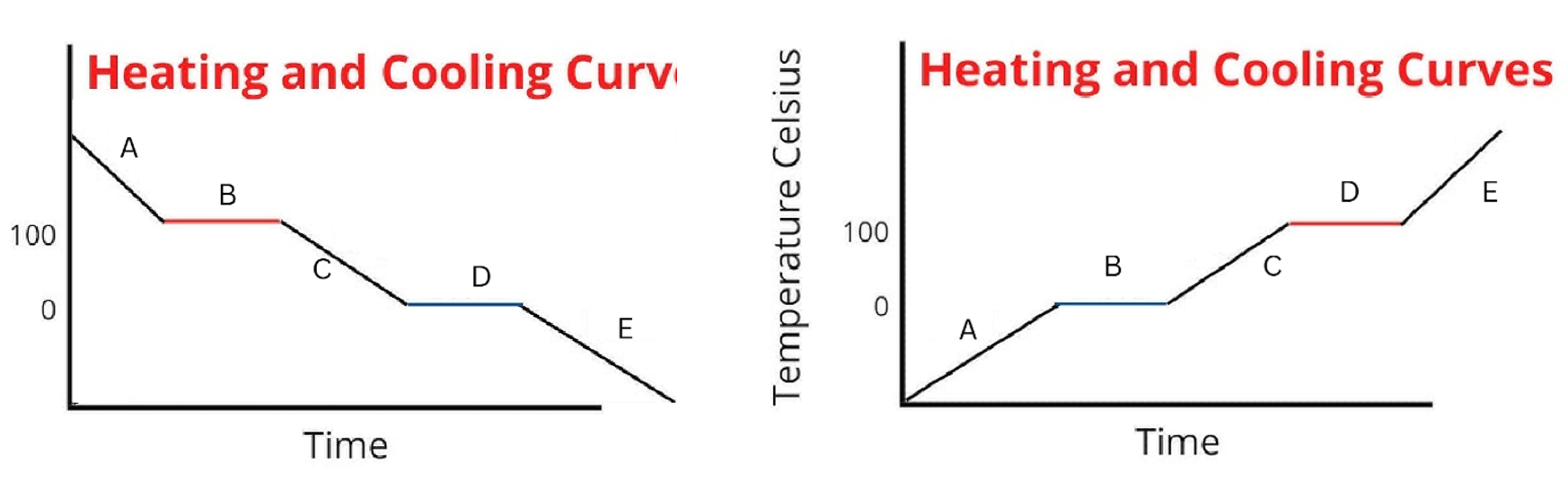
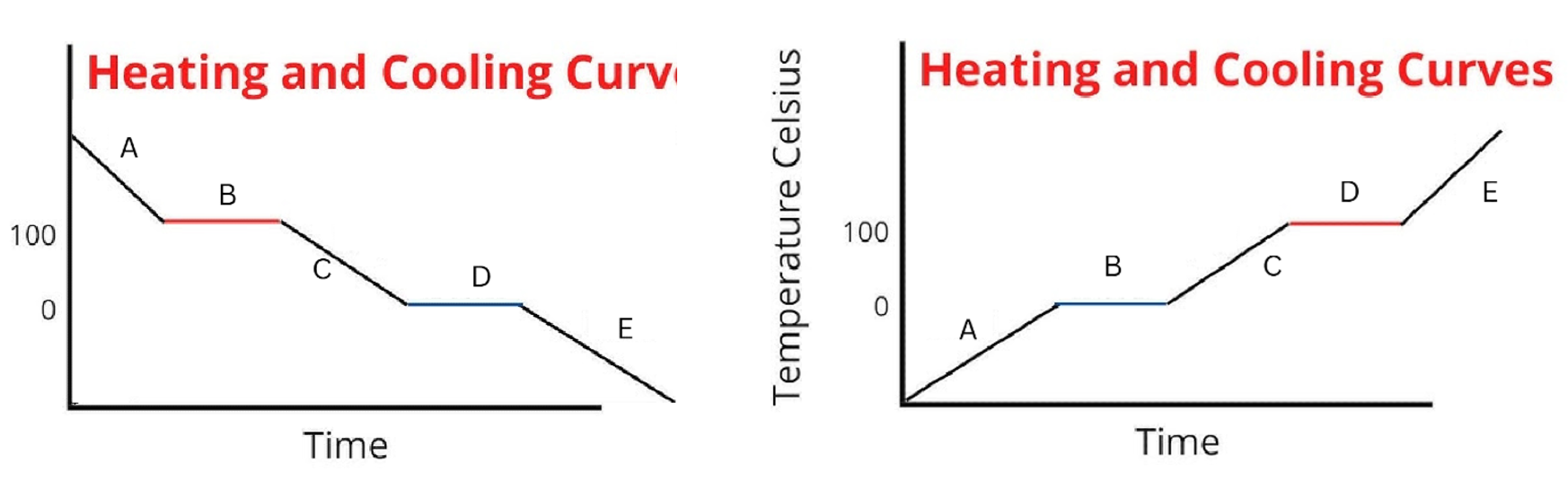
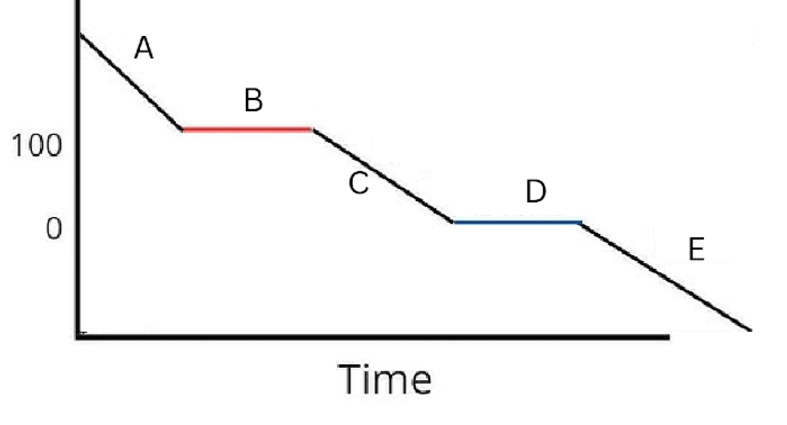
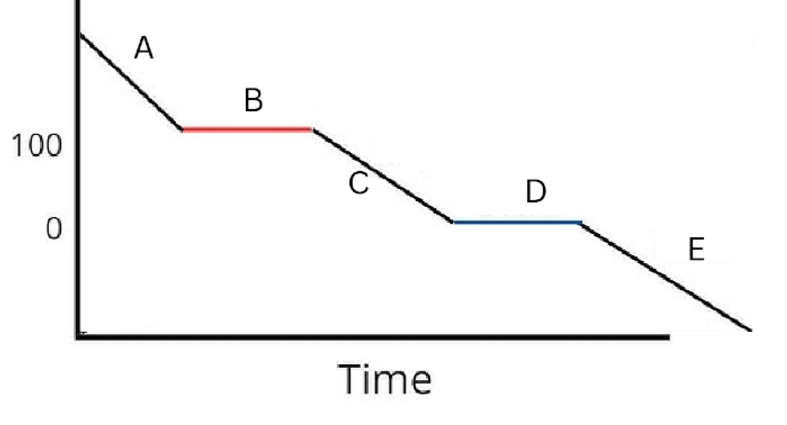
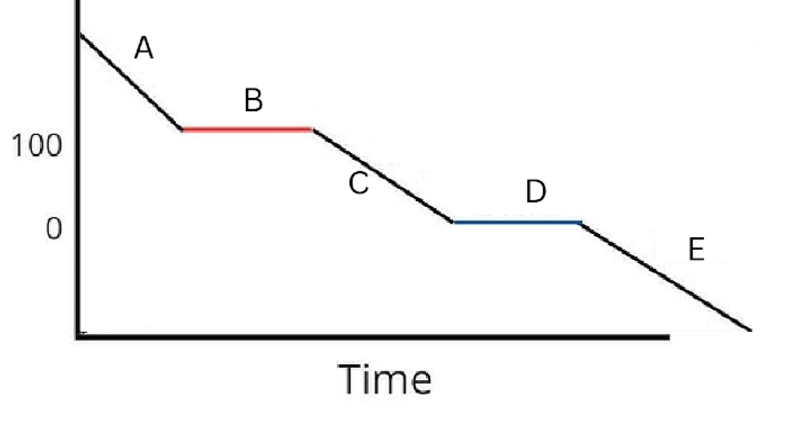
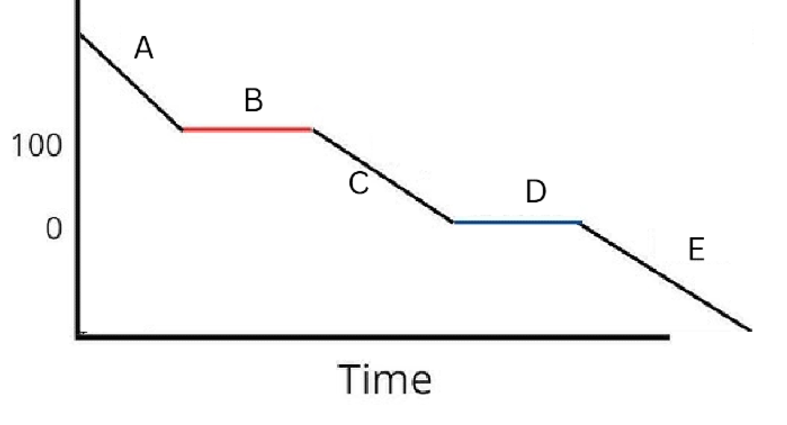
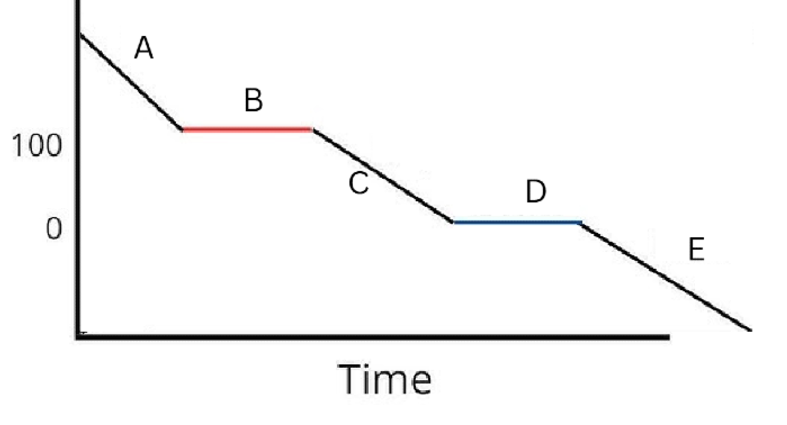
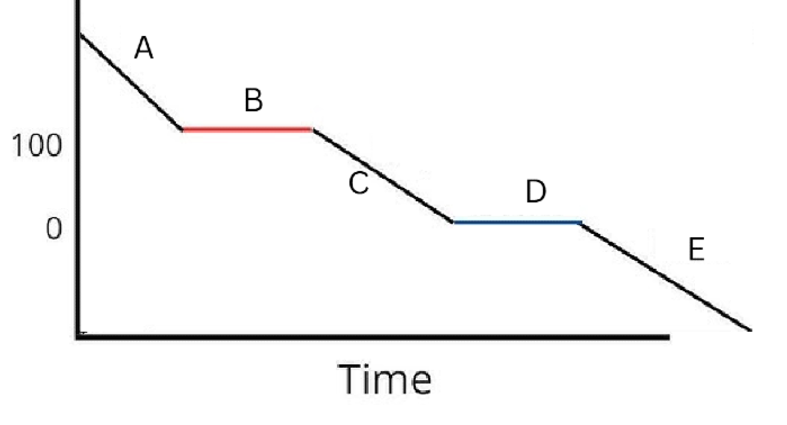
Label the phases in this graph
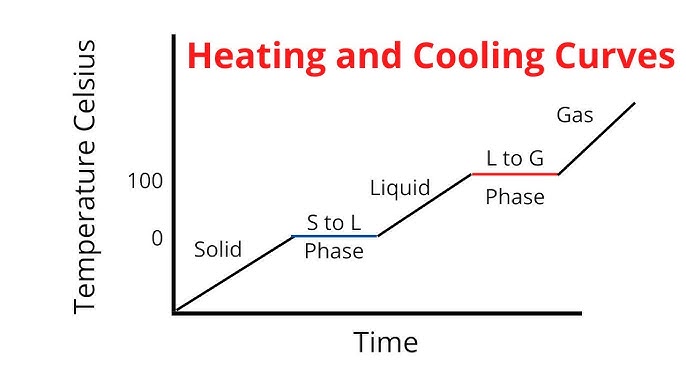
Label any Kinetic Energy increase/decrease and any Potential Energy increase/decrease
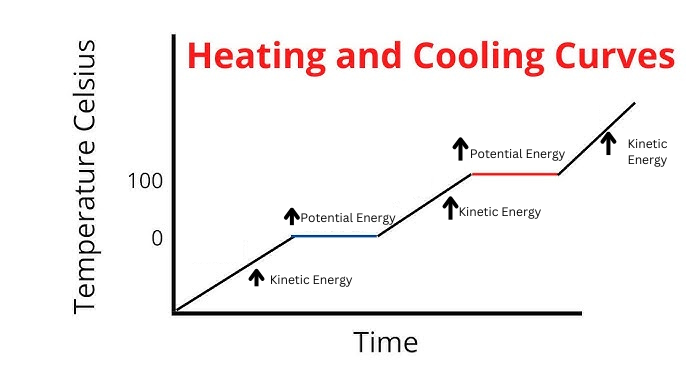
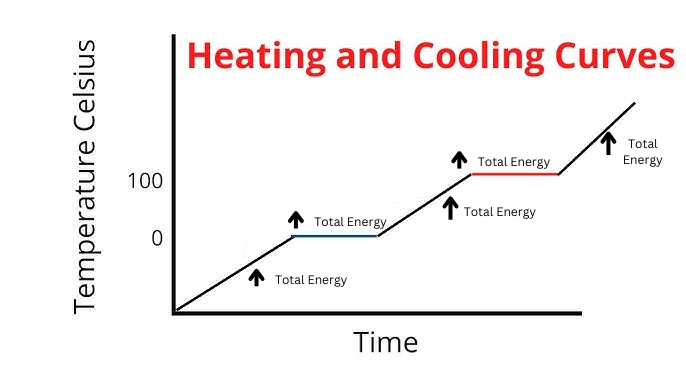
Label where Total Energy increases
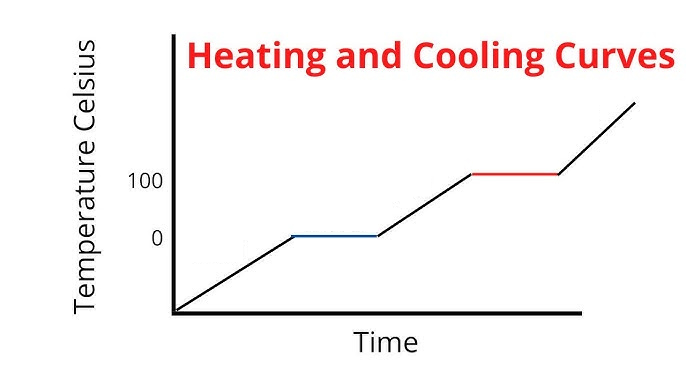
Label where Temperatures increase/decrease as well as Phase Changes
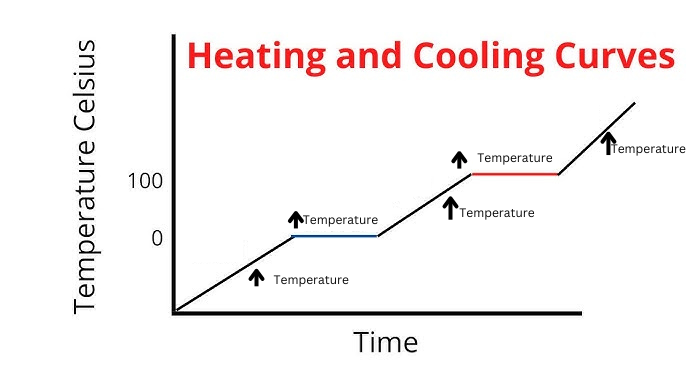
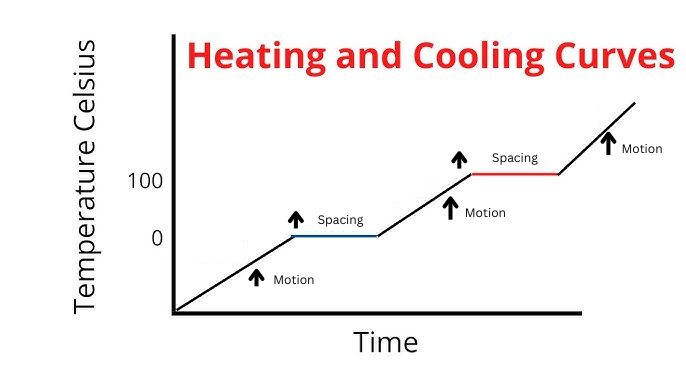
Label Spacing Increase/Decrease as well as Particle Motion Increase/Decrease
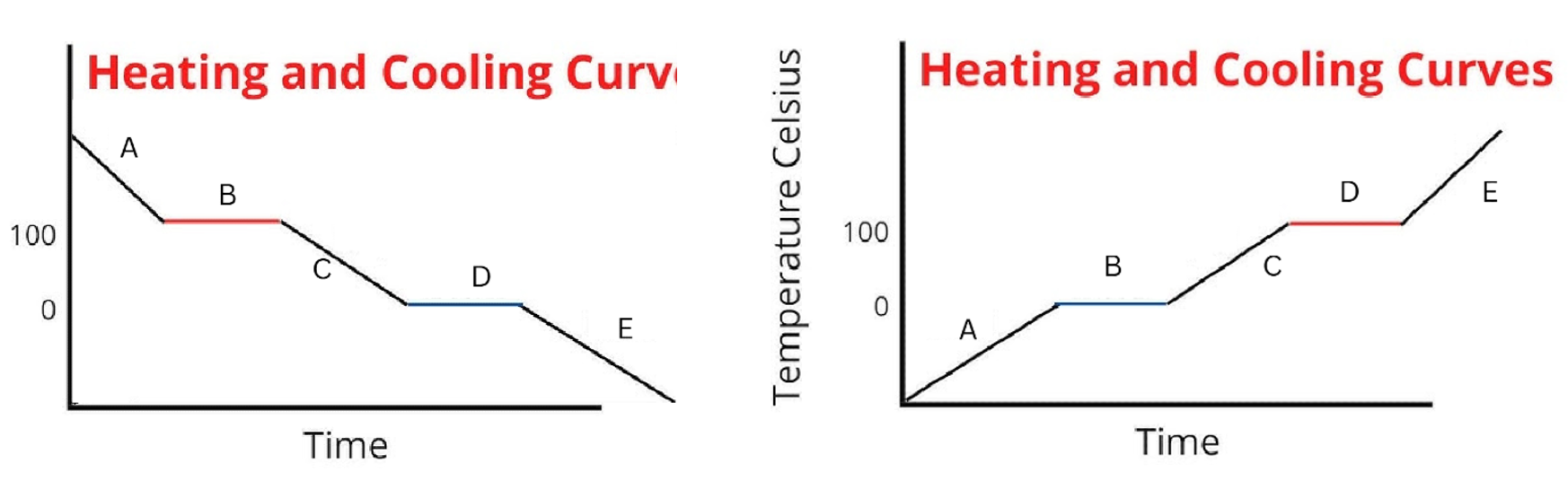
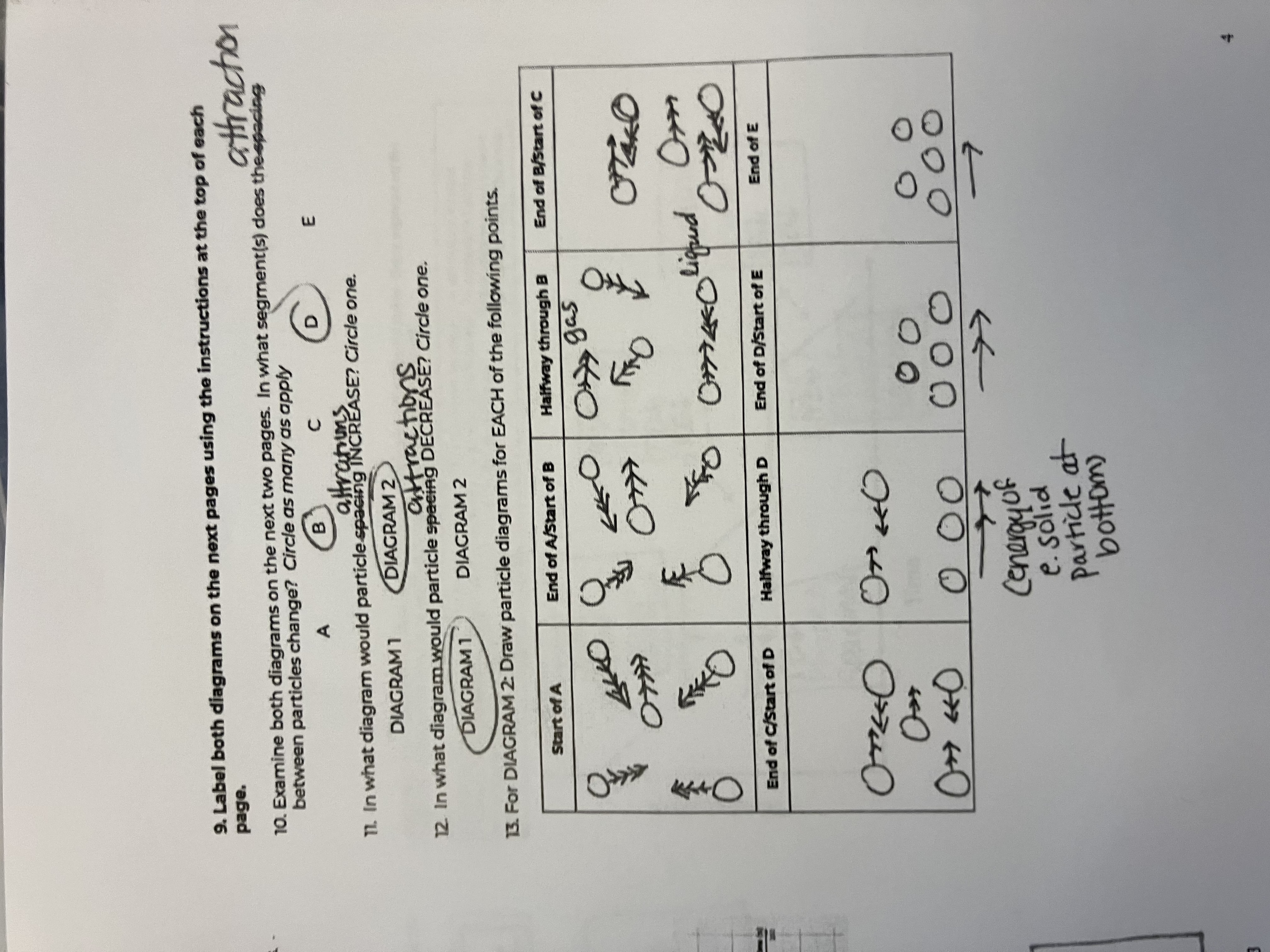
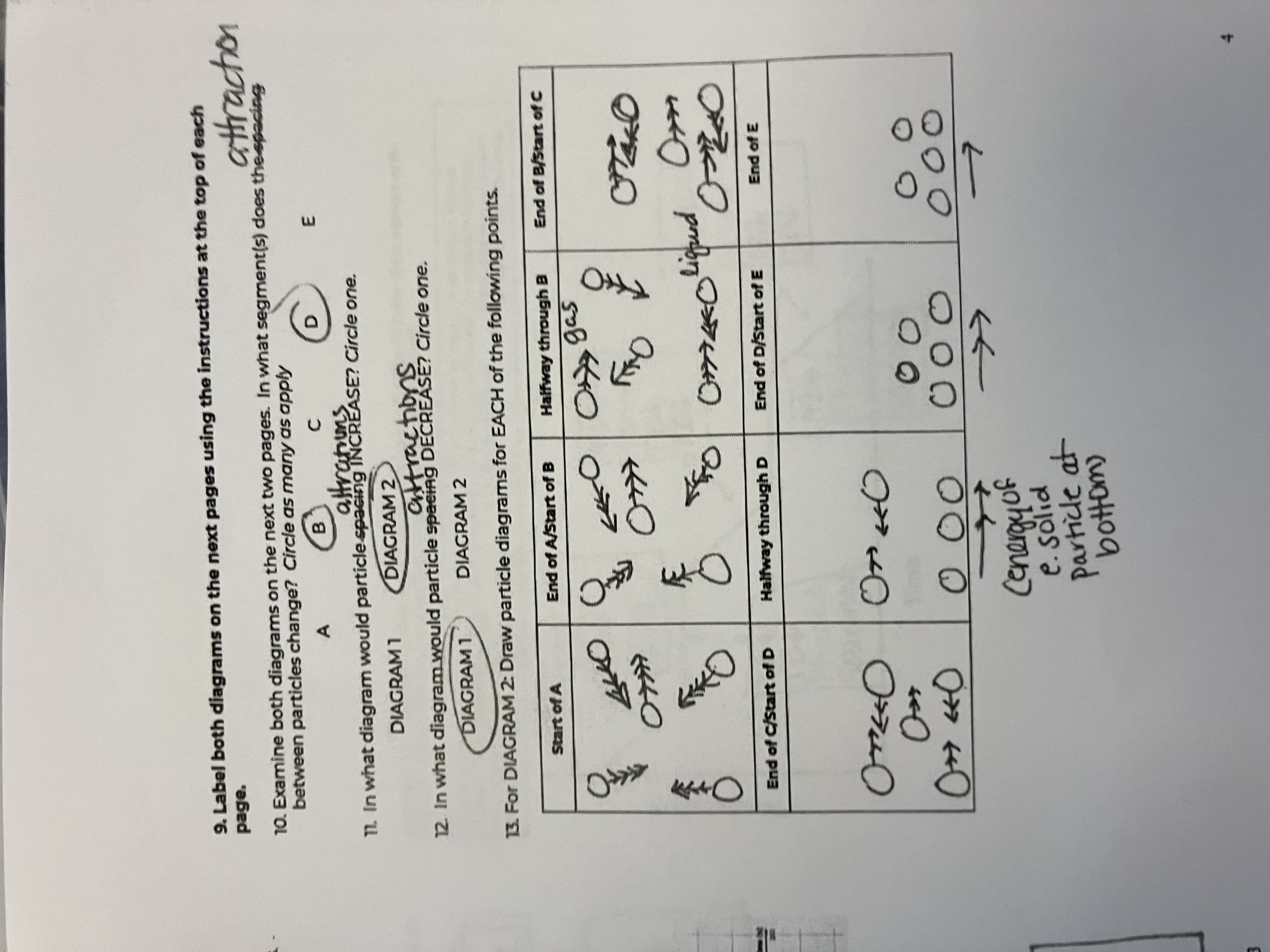
Between the 2 diagrams, what segments do the attractions between particles change
B and D
In what diagram would particle attractions INCREASE
diagram 1
In what diagram would particle attractions DECREASE
diagram 2
For this diagram draw the points for the Start of A
starts as a gas, big spacing, arrow has more heads than in diagram because of peak in speed
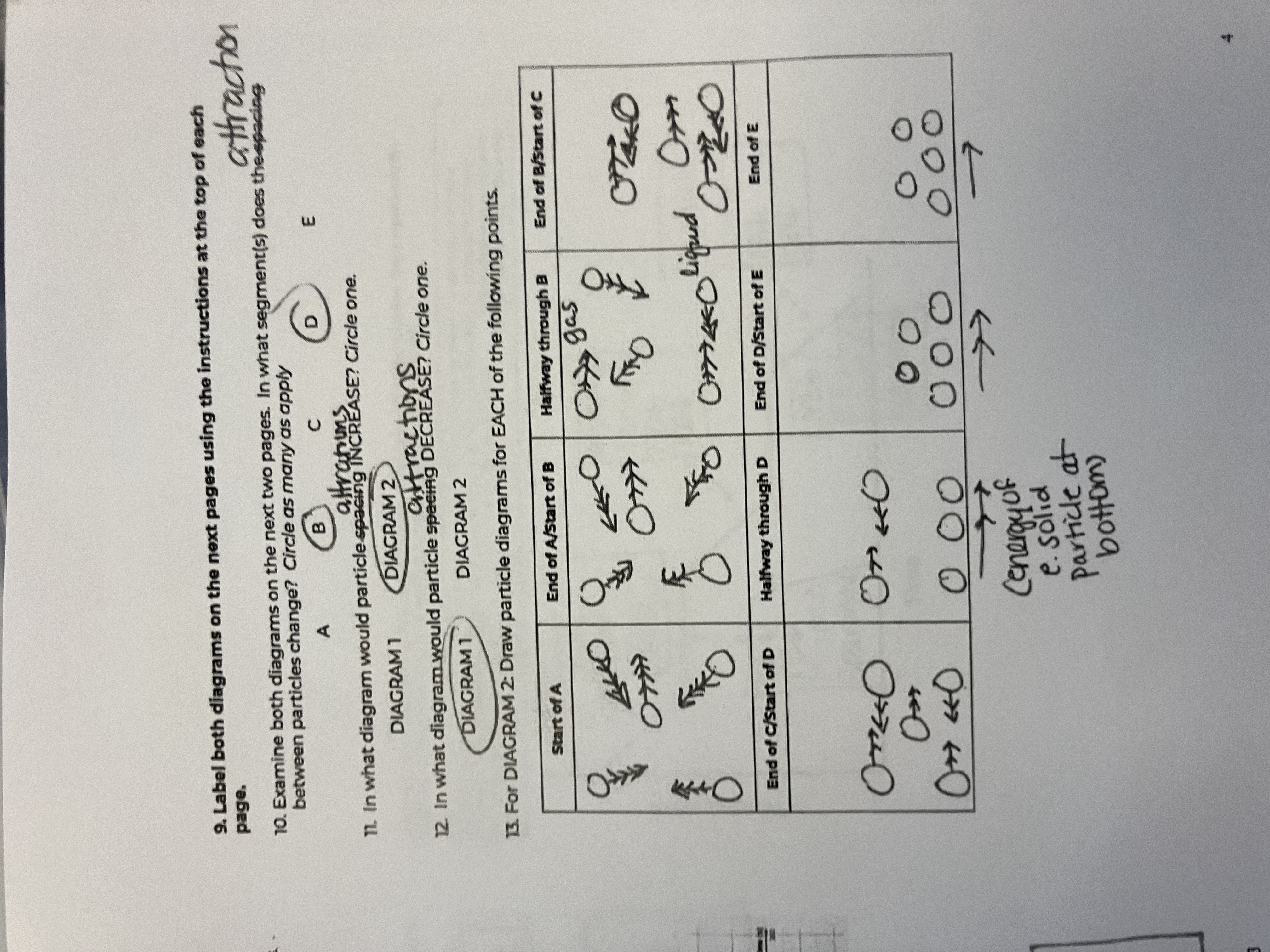
For this diagram draw the points for the End of A/Start of B
Still a gas, but speed goes down
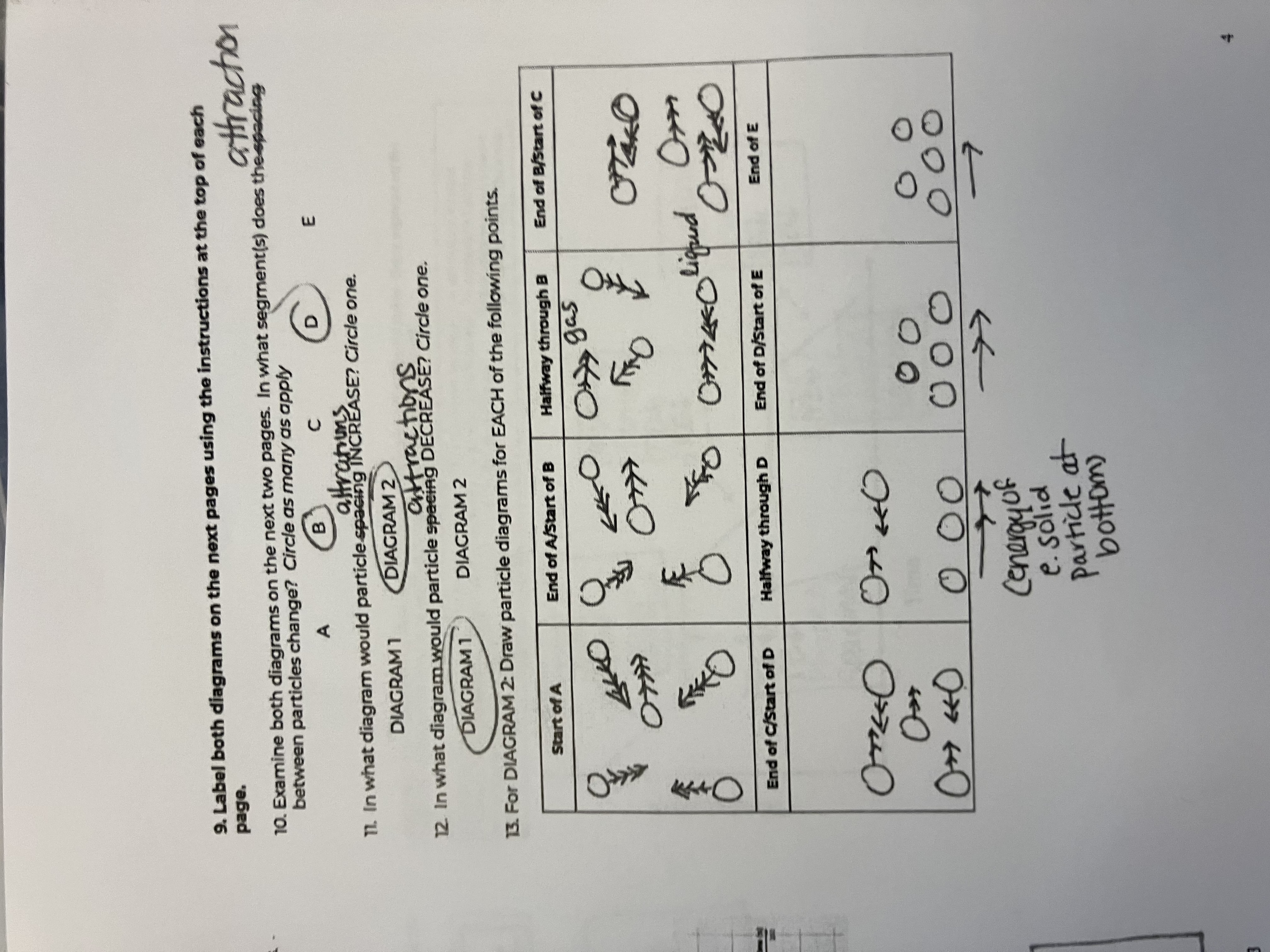
For this diagram draw the points for the Halfway through B
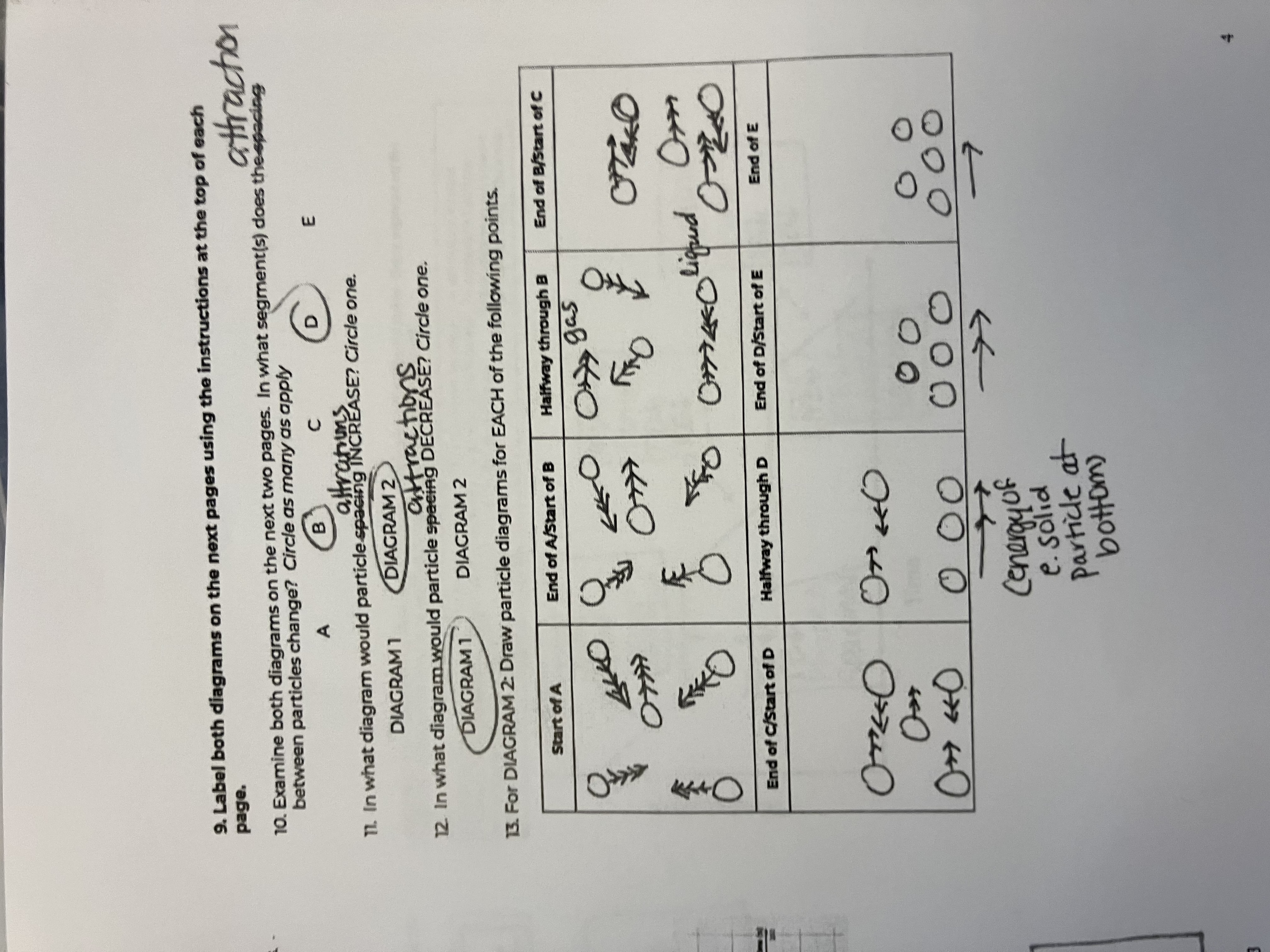
For this diagram draw the points for the End of B/Start of C
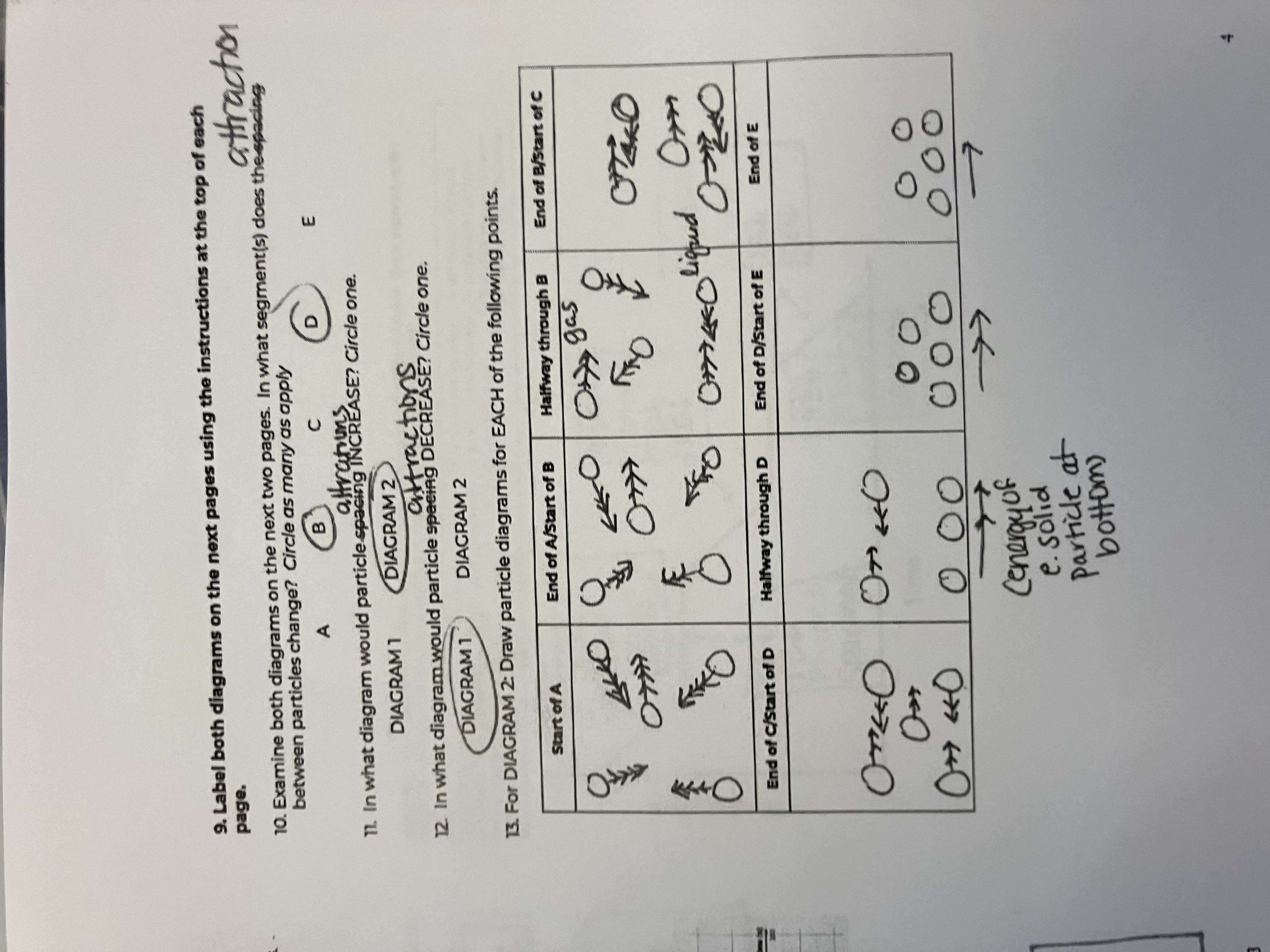
For this diagram draw the points for the End of C/Start of D
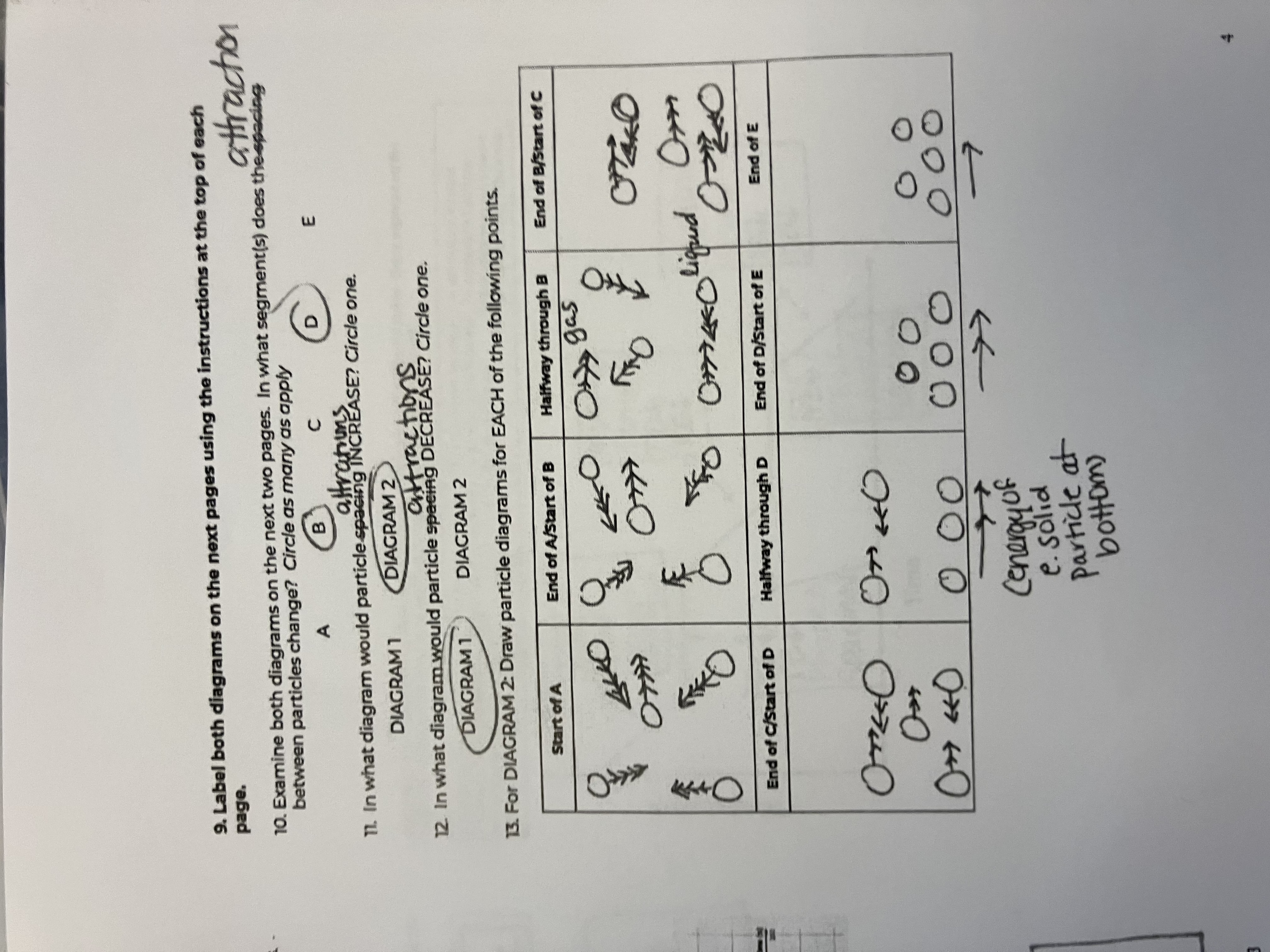
For this diagram draw the points for the Halfway through D
For this diagram draw the points for the End of D/Start of E
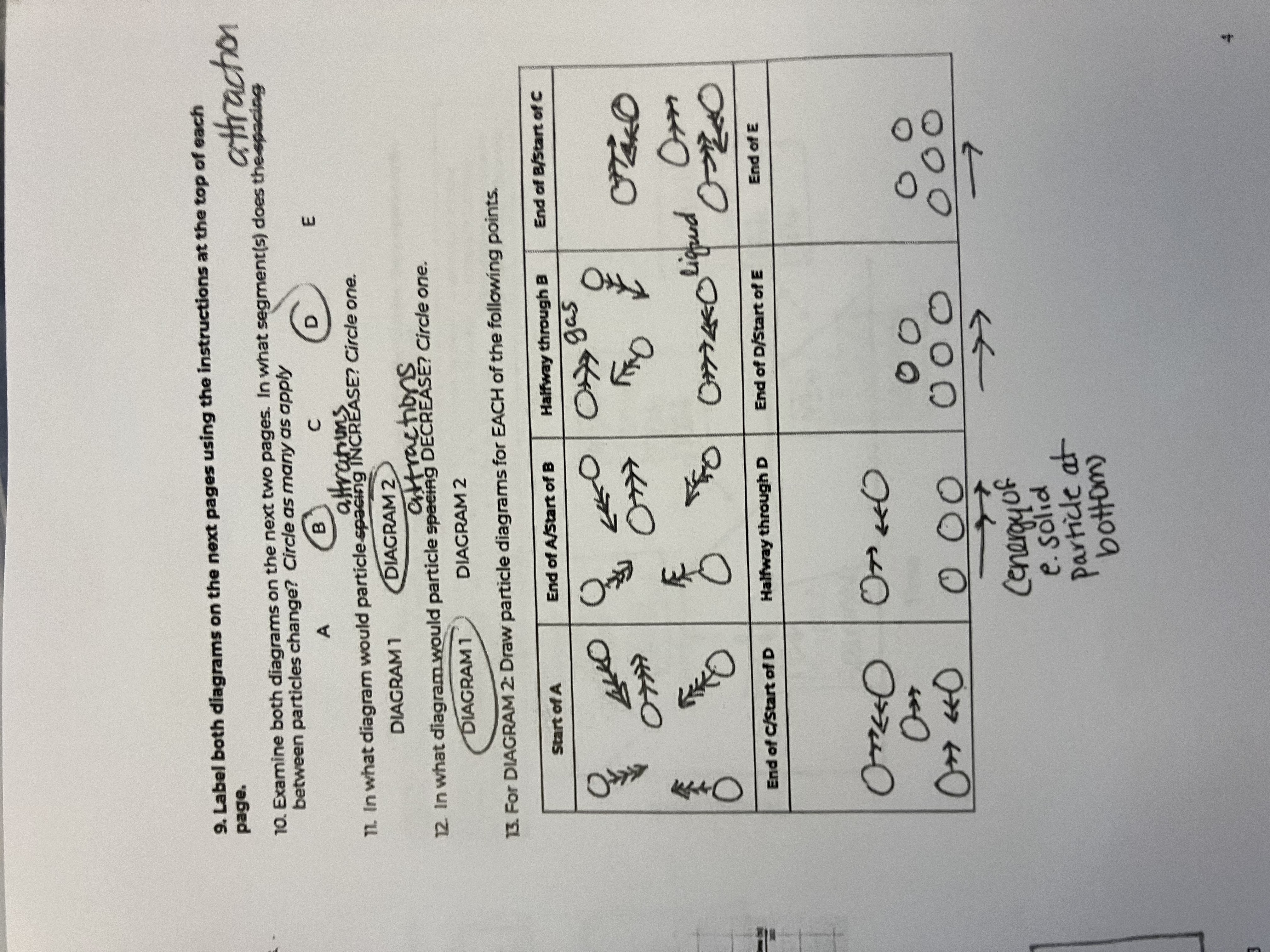
For this diagram draw the points for the End of E
How much energy must be absorbed by a 60 g sample of ice at -15*C that melts and then warms to 25.0*C

Suppose that a burner transfers 25,000J of energy to 100 g of water at -14*C. What mass of the water would melt?

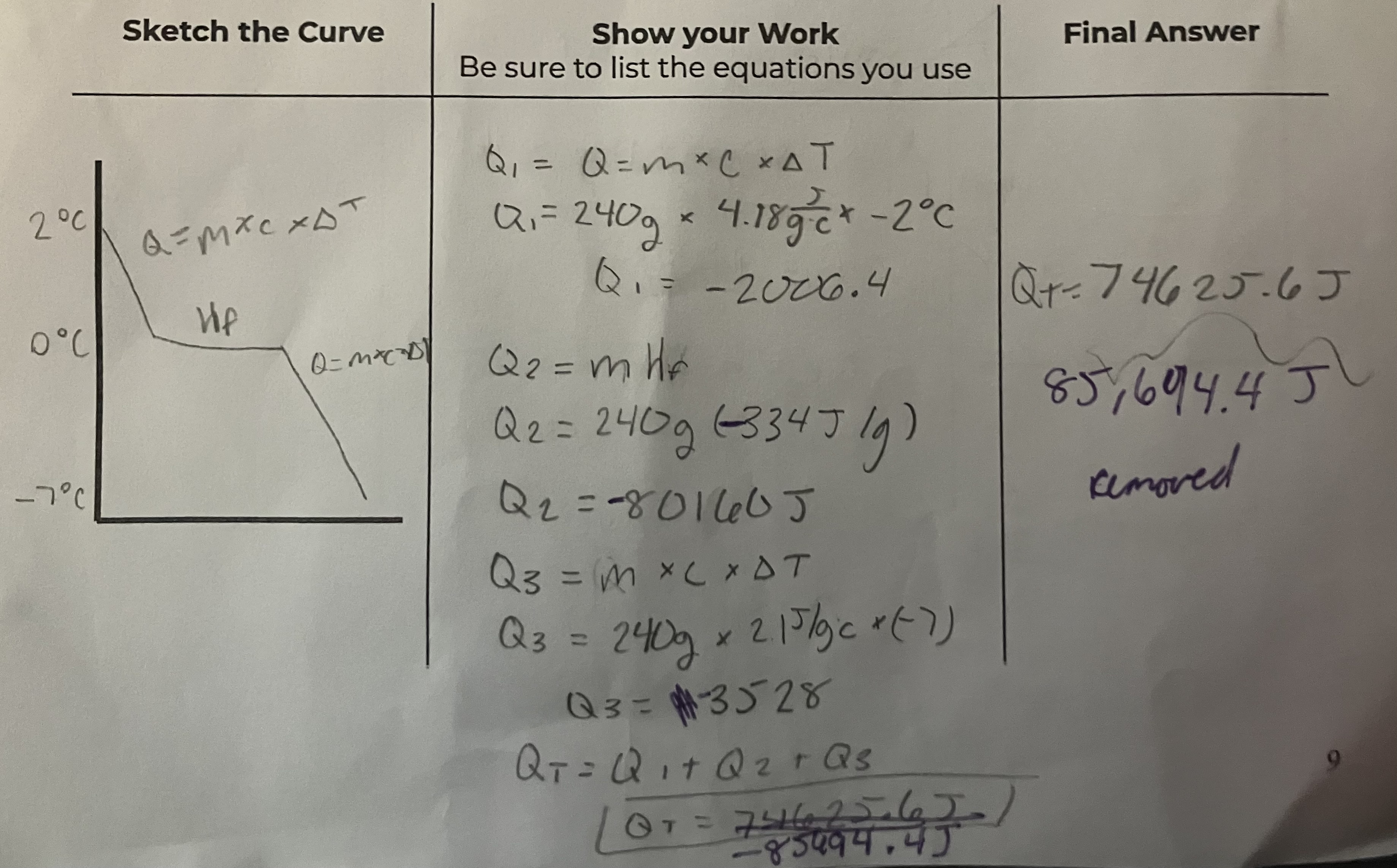
A 12oz water bottle (assume m = 240 g) at 2*C is placed in a freezer where the temperature is -7*C. How much energy must be removed from the water for it to reach this temperature.
65,000 J of energy is added to 150 g of ice at 0.0*C. What is the final temperature of the water.

250 J of energy is removed from a 4 g sample of water at 60*C. Will the sample of water freeze?

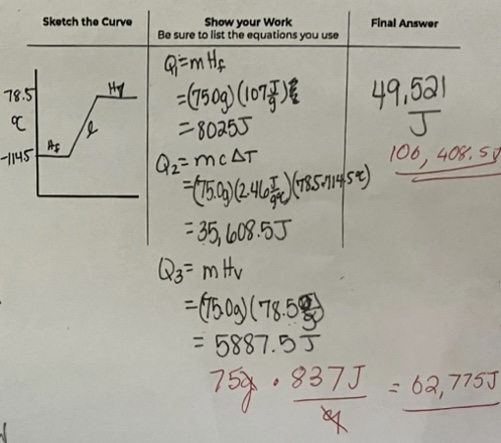
A750.0 g sample of solid ethanol starts at its freezing point (-114.5*C). Calculate the total heat energy required to completely vaporize the sample.
Point of Vaporization: 78.5*C
Heat of Fusion: 107.0 J/g
Heat of Vaporization: 837 J/g
Specific Heat capacity: 2.46 J/g*C