20.2 heart valves and circulation of blood
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
what happens to blood as the ventricles contract?
as each of the ventricles contract it pushes blood into the ventricles or our into an artery
when do heart valves open and close?
walves open and close in response to pressure changes as the heart contracts and relaxes
valves ensure what?
valves ensure one way flow of blood
valves open to
let blood through
valves closes to prevent what?
valves close to prevent back flow
what are the names of the atrioventricular valves?
tricuspid (R), bicuspid (L)
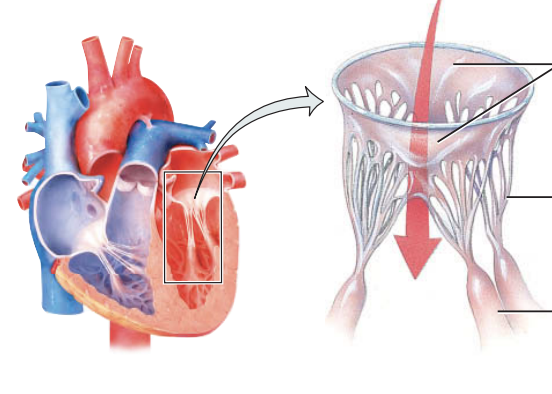
what do the AV valves look like when they are open
ends of the cusps project into the ventricle
what do the components of the ventricles look like when the ventricles are relaxed?
papillary muscles relaxed
chordae tendineae slack
how does blood move from atria?
blood moves from higher pressure in the atria to lower pressure in the ventricles through open AV valves
what happens to parts of the ventricles when the ventricles contract?
blood pressure drives the cusps up until they are closed
papilary muscles contract, tightening chorade tendineae
what does the tightening of the chordae tendineae by the papillary muscles prevent?
back flow
if AV valves or chordae tendineae damaged what happens?
back flow during ventricular contraction
what do the semilunar valves do?
SL valves allow ejection of blood from the heart into the arteries
what do the SL valves prevent?
back flow into the ventricles
when do the SL valves open?
the SL valves openwhen pressure in the ventricles exceeds the pressure in the arteries
what happens to blood flow when ventricles relax?
blood flows back to the heart
what is stenosis?
the narrowing of a heart valve opening that restricts blood flow
what is insufficiency?
filure of a heart valve to close completely
what is mitral stenosis?
scar formation or a congenital defect causes narrowing of the mitral valve
what is a cause of mitral insufficiency? (backflow into l. atrium)
mitral valve prolapse
what is the most common valve disorder?
mitral valve prolapse
what is aortic stenosis?
aortic valve narrowing
what is aortic insufficiency?
backflow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle
what is an example of an infectious disease that damage or destroy valves?
Rheumati fever: acute systemic inflammatory disease occurring after strep throat
what two circuits does the heart pump into with each beat?
systemic and pulmonary circuits
the left side of the heart pumps into what circuit?
systemic circuit - to receive oxygenate blood from the lungs
what do arteries give rise to in the systemic circuit?
arterioles leading to systemic capillaries
what happens in the walls of systemic capillaries?
exchange of nutrients and gases
blood unloads oxygen and takes CO2
what happens after blood flows through the capillaries?
blood enters systemic venules which carry deoxygenated blood away and merge to form systemic veins
what circuit does the right side of the heart pump through?
pulmonary circuit - receives all deoxygenated blood returning from the systemic circuit
what happens to CO2 in pulmonary capillaries?
in pulmonary capillaries blood unloads CO2, which is exhaled, they pick up O2 from inhale
what is coronary circulation?
the myocardium’s own network of blood vessels
the coronary arteries branch from?
the aorta and encircle the heart
where does blood go when the heart relaxes?
when the heart relaxes the high pressure of blood in the aorta propels blood through coronary arteries into c. veins
what do the left and right coronary artery do?
supply blood to the myocardium
what does the anterior interventricular branch (artery) do?
supplies blood to the walls of both ventricles
where does the right coronary artery supply blood to?
supplies atrial branches to the right atrium
where does the posterior interventricular branch (artery) supply blood?
supplies walls of the two ventricles with oxygenated blood
where does the marginal branch (artery) supply blood?
transports oxygenated blood to the wall of the right ventricle
what is anastomosis?
an end to end union or joining of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, or nerves
what do anastomosis do when there is a block?
provide oxygen to the heart through a different route
what are the different routes of anastomosis called?
collateral circulation
does myocardium have any anastomoses?
myocardium has a lot of anastomoses
where does deoxygenated blood drain?
from the myocardium into the coronary sinus
where does blooc from the coronary sinus empty?
into the right atrium
what are the principal veins that carry blood into the coronary sinus?
great cardiac vein, middle cardiac vein, small cardiac vein, and anterior cardiac veins
great cardiac vein drains blood were?
L & R atrium and ventricles
where does the middle cardiac drain?
drains areas of the L & R ventricles
where does the small cardiac vein drain?
drains the right atrium and ventricles
where do the anterior cardiac veins drain?
drains the R ventricles and open directly to R atrium
what causes further damage to the heart with a coronary artery is blocked?
reperfusion
what is reperfusion?
reestablishment of blood flow, leading to further tissue damage
what causes the further tissue damage of reperfusion?
the un paired electron of free radicals forming in reintroduced oxygen
what enzymes does the body produce to make free radicals less reactive?
superoxide dismutase, catalase
what nutrients remove free radicals from circulation?
Vitamin E, C
zinc
beta -carbonate
selenium
what is a partial block in a coronary artery?
myocardial ischemia - lowers blood flow to the myocardium
what does myocardial ischemia cause?
hypoxia
what is angina pectoris?
“strangled chest” the pain associated with myocardial ischemia
what is silent myocardial ischemia?
an ischemia episode without pain
what is myocardial infraction?
complete obstruction in blood flow of the coronary artery
what happens as a result of MI?
tissue death of the area with block
depending on location of tissue death potential for sudden death b/c ventricular fibralation
treatments for MI are?
injection of thrombolytic agent (clot dissolving):
streptokinase
heparin
coronary angioplasty
coronary artery bypass grafting