DRIs
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
science based reference values for nutrients to meet adequacy and prevent chronic disease in healthy populations
DRIs are reference values for ________ intakes and ____ ______ levels of nutrients
recommended intakes; safe upper levels
DRIs impact food & nutrition _____
policy
DRIs serve as standards for nutrient intakes for:
healthy persons in the US & Canada
DRI values are based on:
average requirements
Individual requirements or adverse intake levels may:
be more or less than the DRI values
Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010
basis for federal nutrition policy & education
MyPlate Food Guidance System
provides food-based guidance to implement the recommendations of the DRIs and DGs
Nutrition Facts Food Label
consumer tool found on most food products
How do DRIs, DGs, MyPlate, and food labels work together? (use fiber as example)
1. DRIs: provide "Adequate Intake" fiber recommendation
2. DGs: recommends 3+ oz of whole grains/day
3. MyPlate: provides recommended whole grain amount based on individual calories level
4. Food label: contains information to help identify "whole grain"
FNB
Food and Nutrition Board
IOM
Institute of Medicine
Who developed the DRIs?
the FNB under the IOM
The ____ were developed first and aimed to ______
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs), 1989; prevent deficiencies
The _____ were developed in 1997 and aimed to _____
DRIs;
- decrease risk of chronic disease
- avoid excess consumption
DRIs include 4 nutrient intake values:
- EAR
- RDA
- AI
- UL
Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
the amount that meets the optimal nutrient needs of half the individuals in a specific group
Health professionals use _____ to develop RDAs and plan diets for groups of people
Estimated Average Requirements (EARs)
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs)
levels of nutrient intake adequate to meet the needs of nearly all healthy people in the US (97-98%)
RDAs are set for:
protein, carbohydrates, many vitamins & minerals
3 steps when setting RDAs:
1. Estimate average need for a group (EAR)
2. Add 30-50% to cover needs of nearly all
3. Possibly add more to account for absorption
Accurate view of optimal nutrient intakes (diagram)
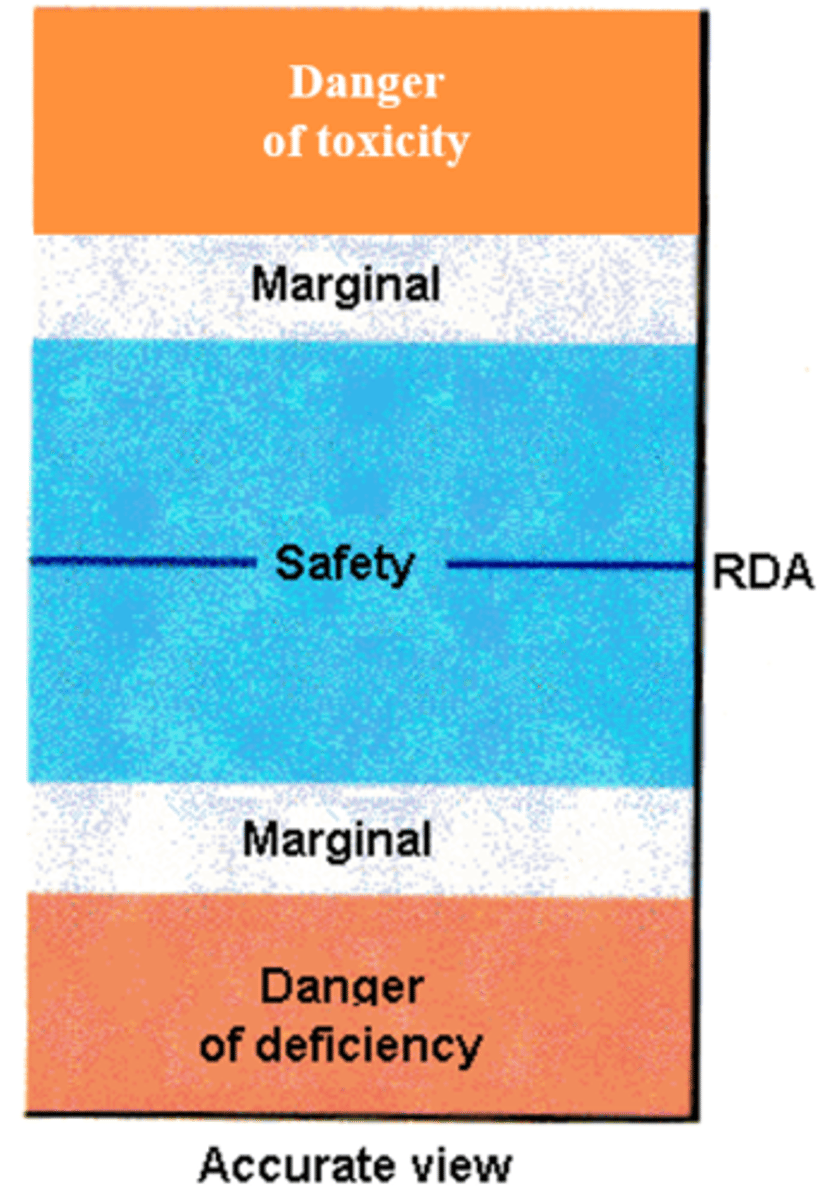
Adequate Intake (AI)
similar to RDA but lacks enough scientific evidence to set an RDA
5 nutrients that have AIs instead of RDAs:
- calcium
- vitamin K
- vitamin D
- fat
- fiber
Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)
total intake from food, fortified food, and supplements should not exceed this amount, or adverse health effects may result
--> not a recommended amount!
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDR)
acceptable ranges of what % of total kcal should come from each macronutrient
AMDR of fat = ___ % of total kcal
20 - 35%
AMDR of protein = ___ % of total kcal
10 - 35%
AMDR of carbohydrates = ___ % of total kcal
45 - 65%
DRIs
Dietary Reference Intakes
RDA
Recommended Dietary Allowance
EAR
Estimated Average Requirement
AI
Adequate Intake
UL
Tolerable Upper Intake Level