Biology 2E - Chapter 3 - Biological Macromolecules Readthrough Notes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
1
New cards
DNA in prokaryotes
is not enclosed in a membranous envelope
2
New cards
DNA in eurkaryotes
* Is contained in the nucleus
* forms a complex with histones to form chromatin
* forms a complex with histones to form chromatin
3
New cards
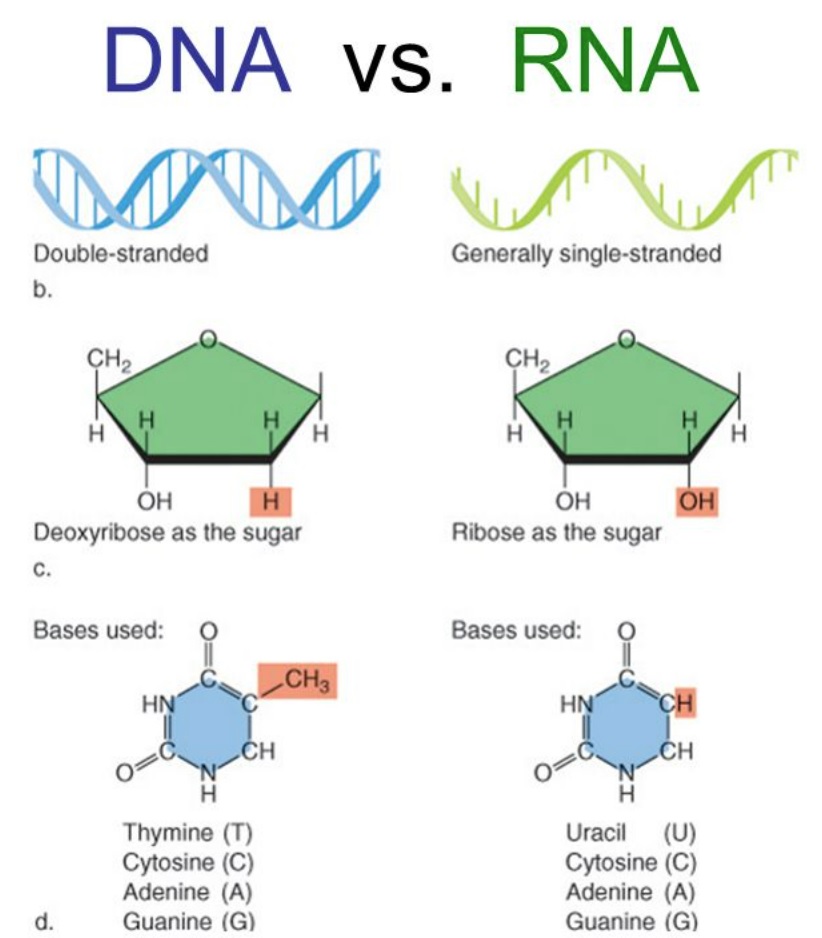
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
* DNA contains all the genetic content of an organism and controls all cellular activities by turning genes on or off
* Sugar is deoxyribose
* Double stranded
* Bases ATGC
* RNA is mostly involved in protein synthesis
* Sugar is ribose
* Single stranded
* Bases AUGC
* Sugar is deoxyribose
* Double stranded
* Bases ATGC
* RNA is mostly involved in protein synthesis
* Sugar is ribose
* Single stranded
* Bases AUGC
4
New cards
What composes a nucleotide?
* nitrogenous base
* pentose sugar (five carbon)
* phosphate group
* pentose sugar (five carbon)
* phosphate group
5
New cards
What are the four possible nitrogenous bases in DNA?
* (A) Adenine
* (G) Guanine
* (C) Cytosine
* (T) Thymine
* (G) Guanine
* (C) Cytosine
* (T) Thymine
6
New cards
Why are ‘nitrogenous bases’ considered bases?
Because they contain and amino group that has the potential of binding an extra hydrogen, and thus decreasing the hydrogen ion concentration in its environment, making it more basic.
7
New cards
What is the difference between purines and pyrimidines?
* Purines primary structure is 2 carbon-nitrogen rings
* Pyrimidines primary structure is 1 carbon-nitrogen ring
* Pyrimidines primary structure is 1 carbon-nitrogen ring
8
New cards
What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA vs. RNA
* DNA - ATGC - All The Good Code
* RNA - AUGC - All Uther Good Code
* RNA - AUGC - All Uther Good Code
9
New cards
Which nitrogenous bases are purines?
* (A) Adenine
* (G) Guanine
* (G) Guanine
10
New cards
Which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines?
* (C) Cytocine
* (T) Thymine
* (U) Uracil
* (T) Thymine
* (U) Uracil
11
New cards
Identify the prime connection points of the carbon atoms in
* 1’
* 2’
* 3’
* 4’
* 5’ - Phosphate residue attaches
\
* 2’
* 3’
* 4’
* 5’ - Phosphate residue attaches
\
12
New cards
What is a 5’-3’ phosphodiester linkage?
The phosphate residue attaches to the hydroxyl group of the 5’ carbon of one sugar and the hydroxyl group of the 3’ carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide.
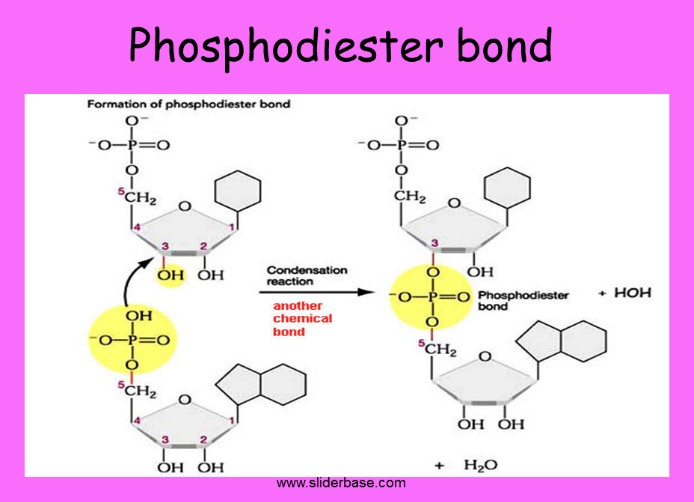
13
New cards
What is antiparallel orientation? Why is it significant?
* The two helical strands of DNA run in opposite directions but match the parallel strand so that the 5’ carbon on one faces the 3’ carbon on the other.
* Important for replication and nucleic acid interactions.
* Important for replication and nucleic acid interactions.
14
New cards
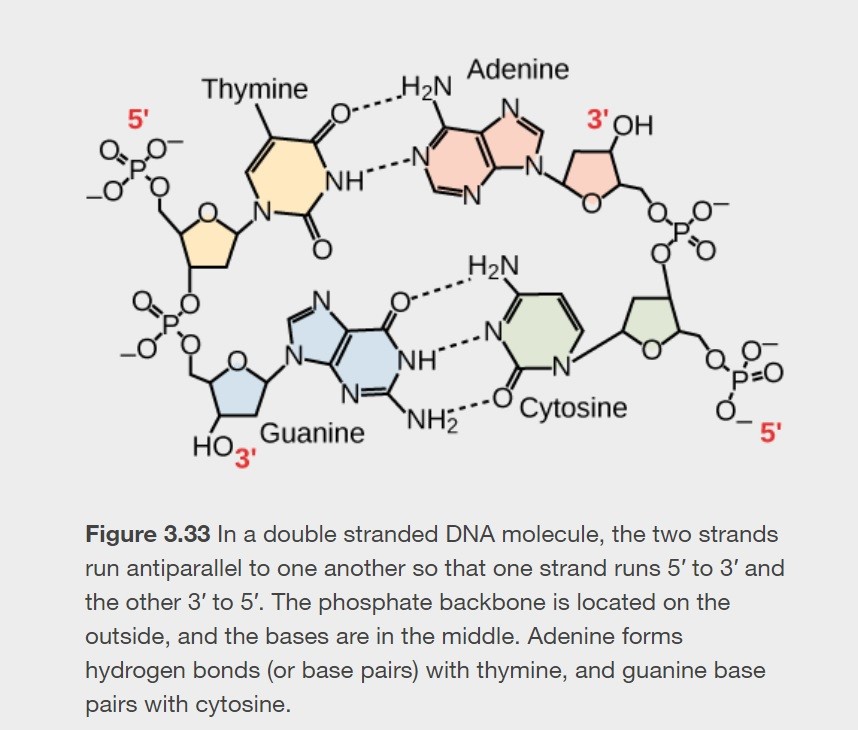
In DNA, what are the allowable base pairings?
* A - T
* G - C
* G - C