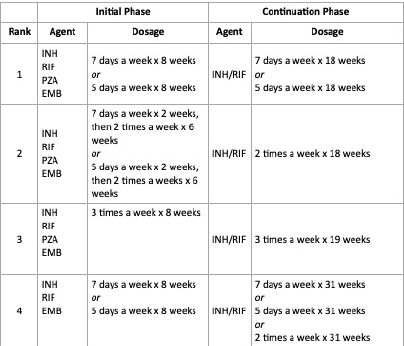
CHAPTER 3 PART 2
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
Clinical Findings for Streptococcus pyogenes
TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS
SCARLET FEVER
Seasonal occurrence
Involves children 5-10 years of age
Secondary peak at 12 and 18-20 years of age
TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS
Sign and Symptoms
sudden onset of fever, sore throat, headache, nausea, malaise, pain, and marked tonsillo-pharyngeal erythema
TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS
Complications:
sinusitis, otitis media, pertonsillar and retropharyngeal abscess, acute rheumatic fever, and acute glomerulonephritis
TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS
Diagnosis for TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS
Culture of specimen (swab)
Treatment for TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS
self- limited
DOC: PENICILLIN
ALT.: ERYTHROMYCIN or CLINDAMYCIN
Occurs in association with streptococcal pharyngitis
Scarlet Fever
Sign and Symptoms:
pinkish-red rash on the skin
spotted strawberry-like appearance of the tongue
skin peels off similar to sunburn (as the disease progresses)
Scarlet Fever
Treatment or DOC for Scarlet Fever
PENICILLIN G
“Pneumococci”
Gram (+),
encapsulated,
lancet-shaped diplococci
Alpha-hemolytic (causes partial hemolysis)
Normal inhabitants of the URT;
transient flora of the nasopharynx
Streptococcus pneumoniae
the virulence factor of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Capsule (anti-phagocytic)
Mode of Transmission:
Droplet respiratory secretions
Nasopharyngeal carriers (10% cases)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
clinical findings for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Chronic cardio-pulmonary disease
Otitis media ( middle ear)
Sinusitis (sinuses)
Mastoid
Meninges
follows URT infections
Begins with abrupt onset of fever and chills, cough and pleuritic chest pain
Sputum is RED or BROWN (“rusty”) in color
Chronic cardio-pulmonary disease
Laboratory Diagnosis for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Gram’s stain
Microscopic examination (sputum)
Capsular swelling test (Quellung Reaction)
Optochin sensitivity
Treatment and prevention for Streptococcus pneumoniae
DOC: PENICILLIN G
Alt.: CEFTIZOXIME and VANCOMYCIN
Prevention: PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE VACCINE
it is also called as “blood-loving”
Haemophilus
Haemophilus – “blood-loving”
Found on the mucous membranes of the URT
Most infections occur in children 6 months-6 years
Haemophilus infuenzae
the virulent factor of Haemophilus influenzae and the most virulent
Capsule (anti-phagocytic)
H. influenzae type b (encapsulated strain)
Mode of Transmission for Haemophilus influenzae
it enters the body through the URT
Clinical findings of Haemophilus influenzae
Sinusitis and Otitis media (2nd to Pneumococci)
Epiglottidis (exclusively caused by H. influenzae)
Meningitis (SSx: Fever, Headache, Stiff neck along with drowsiness)
Bronchitis and Pneumonia (commonly seen in elderly adults with chronic respiratory disease)
Laboratory Diagnosis for Haemophilus influenzae
Microscopic Examination
▪︎ SPECIMEN (Nasopharyngeal swabs, pus, blood, and spinal fluid)
Treatment and prevention for Haemophilus influenzae
DOC: AMPICILLIN (non beta-lactamase producing strains)
Newer Cephalosporins (all strains)
Prevention: H. influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (Hib vaccine) to children
Smallest free-living organisms that can self-replicate in laboratory media
Produces tiny colonies on special agar that have a "fried egg" appearance
Cell wall-less organism (cell membrane = sterol)
Part of mouth’s normal flora
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
mode of transmission for Mycoplasma pneumoniae
person-to-person (infected respiratory secretions)
Clinical findings for Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Atypical or Walking Pneumoniae
☆ Asymptomatic carriers
☆ Tracheobronchitis with low grade fever, pharyngitis, malaise and non-productive cough
Laboratory Diagnosis for Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Serologic Testing
Treatment and prevention for Mycoplasma pneumoniae
DOC: MACROLIDE or TETRACYCLINE
An opportunistic pathogen (community-acquired/nosocomial infections)
☆ Elderly patients
☆ Diabetics
☆ Alcoholics
☆ Chronic respiratory tract
Frequently found in the large-intestine
Found also in soil and water
Very large capsule (anti-phagocytic)
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Clinical findings for Klebsiella pneumoniae
Lobar Pneumonia – thick, bloody sputum (“currant jelly”)
Necrosis and abscess formation are common
Laboratory Diagnosis for Klebsiella pneumoniae
Differential Media: MacConkey’s Agar and EMB
Biochemical Tests
Treatment and prevention for Klebsiella pneumoniae
Highly resistant to antimicrobial drugs
DOC: Sensitivity Testing
Gram (-) rods
It can survive inside macrophages and alveolar cells
Legionella pneumophila
what is the virulence factor of Legionella pnuemophila
LPS
mode of transmission for Legionella pneumophila
Lakes,
streams,
air conditioners,
and water-cooling towers
clinical findings for Legionella pneumophila
Pontiac Fever
Legionnaire's Disease (Legionellosis)
A mild flu-like form of infection
Does not result in pneumonia
Abrupt but resolves completely in < a week
Pontiac Fever
Atypical type of pneumonia
Very high fever and severe pneumonia accompanied by mental confusion and non-bloody diarrhea
Can be fatal
Legionnaire's Disease (Legionellosis)
laboratory diagnosis for Legionella pneumophila
Dieterle and Warthin-Starry Silver Stains (Silver Impregnation Method)
Monoclonal or Polyclonal immunofluorescent
Antibody Staining
Treatment and prevention for Legionella pneumophila
Macrolides
Fluoroquinolones
Small,
encapsulated,
Gram (-) rod
Bordetella pertussis
Mode of Transmission for Bordetella pertussis
Airborne droplets ( severe coughing episodes)
Stages of Whooping Cough ( Pertussis)
Catarrhal Stage
Paroxysmal Stage
Convalescent Stage
stage of whooping cough where:
Most contagious (greatest number of Mos)
1-2 weeks
Mild URT infection with non-specific signs and symptoms
Catarrhal Stage
stage of whooping cough where:
5-20 forceful, hacking coughs with the production of abundant amounts of mucus that ends in a high-pitched indrawn breaths (“whoop noise”)
2-10 weeks
Patient may turn cyanotic, the tongue protrudes, the eyes bulge, and neck veins engorge
Paroxysmal Stage
stage of whooping cough where:
Reduction of symptoms leading to recovery
Patient is no longer contagious
Convalescent Stage
complications of Bordetella pertussis
Pertussis, like measles, can unmask underlying
tuberculosis
Convulsions may occur due to cerebral anoxia
during coughing spells
Blindness (from hemorrhages into conjunctiva
during paroxysms)
Pneumonia,
deafness, and
hernias
Laboratory Diagnosis of Bordetella pertussis
Culture of specimens (nasopharyngeal swabs – taken during paroxysmal stage)
☆ Regan Lowe Charcoal Medium
Treatment and Prevention of Bordetella pertussis
DOC: MACROLIDES (patients and exposed individuals)
Supportive care: Oxygen Therapy and Suctioning of mucus
Prevention: Acellular Vaccine
Acid-fast,
obligately aerobic bacillus
Cell Wall - Mycolic Acid
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
mode of transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Person-to-person (respiratory aerosols)
Fomites (utensils and galsswares)
transmitted through ingestion of contaminated cow’s milk —— GI tuberculosis
M. bovis
clinical findings of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis)
1° Infection/ Complex
2° Infection/ Reactivation Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Disseminated/ Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
Initial infection in childhood
May affect any part of the lungs (most cases – middle and lower lobes)
Ghon Complex (Lesion)
Asymptomatic (most ptx)
1° Infection/ Complex
Caused by Mos that have survived in the 1° lesion
Almost always begins at the apex (highest oxygen tension)
S/Sx: fatigability, afternoon rises in temp, weight loss, night sweats, loss of appetite, chronic non-productive cough with or without hemoptysis.
2° Infection/ Reactivation Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Multiple disseminated lesions
Initial organs affected – lymph nodes
Scrofula – aggregation and ulceration in the lymph nodes
Forms: TB meningitis, TB osteomyelitis (Pott’s
disease), GI TB, Oropharyngeal TB, Renal TB, GU TB, PerIcardial TB
Disseminated/Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
Diagnosis for Mycobaterium tuberculosis
Acid-Fast Staining of Sputum
☆ 2 collections – 0 hr and 1hr
☆ Medium: Lowenstein-Jensen
Chest X-ray
Tuberculin Skin Test (Mantoux – intradermal test)
treatment and prevention for Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine
clinical findings for Bacillus anthracis
ANTHRAX
Cutaneous
Gastrointestinal
Pulmonary/Inhalation Anthrax (Woolsorter’s Disease)
edema, enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes (Chest X-ray - widening of the mediastinum), bloody pleural effusion, septic shock, and death
complications of Bacillus anthracis
Hemorrhagic meningitis
Hemorrhagic mediastinitis
treatment for Bacillus anthracis
DOC: CIPROFLOXACIN
Alt.: DOXYCYCLINE
Bacterial Infections of the GIT
Gastritis
Enteritis
Colitis
Gastroenteritis
Hepatitis
Dysentery
how does disease occur in the GIT?
Pharmacologic Action
Toxins
Local Inflammation
Invasion of the alimentary tract by microbes
Deep Tissue Invasion
Spread of the MO to the adjacent tissues
Perforation
Normal Flora spills into sterile areas
alter normal intestinal function without lasting damage to their targeted cells
Ex: Vibrio cholerae (Cholera toxin–epithelial cells)
Toxins
usually limited to the epithelial layer but may spread to the deeper tissues.
Ex: mouth (periodontitis) and intestine (dysentery)
Invasion of the alimentary tract by microbes
enters the bloodstream
Ex: Strongyloides stercoralis (burrowing through the intestinal wall called POLYMICROBIAL SEPTICEMIA)
Spread of the MO to the adjacent tissues
invades deep tissues
Ex: perforation of the inflamed appendix- peritonitis
Normal Flora spills into sterile areas
Causative agents of Dental Caries (tooth decay)
Streptococcus mutans (primary)
Actinomyces
Lactobacilli
prevention of Dental Caries
Minimal ingestion of sucrose,
Brushing,
Flossing,
Regular dental visits,
use of fluoride, chlorhexidine (mouthwash)
inflammation and degeneration of structures that support the teeth
Periodontal Disease
the causative agent of Periodontal Disease
Streptococci
Actinomycetes
Anaerobic Gram (-):
Prevotella
Bacteroides
Fusobacterium nucleatem
Reversible inflammation of the gums
Bleeding of the gums while brushing the teeth
Gingivitis
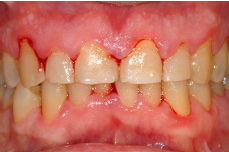
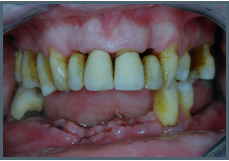
Severe/chronic gum disease
Bone destruction and tooth loss
Gums are inflamed and bleed easily
Periodontitis
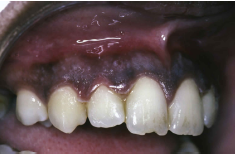
Serious, pain that prevents normal chewing
Halitosis
Prevotella intermedia (primary)
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis / Vincent’s DSE / Trench Mouth
Virulence Factors:
Rapid Motility (penetration of the lining of the stomach)
Urease Production (production of large amounts of ammonia from the urea (neutralization of gastric acid))
Helicobacter pylori
mode of transmission of Helicobacter pylori
Ingestion
Person-to-person via the saliva
clinical findings of Helicobacter pylori
Gastritis
Peptic Ulcer
laboratory diagnosis for Helicobacter pylori
Histologic examination
Culture
Measurement of antibody levels
treatment for Helicobacter pylori
Triple Therapy
Proton pump inhibitor ( OMEPRAZOLE) + Macrolide ( CLARITHROMYCIN) + AMOXICILLIN
Similar symptoms occur in several members of a group who share the same meal
Onset of symptoms occurs a few hours after food ingestion
Bacterial Enterocolitis ( Food poisoning)
the 3 mechanisms of Bacterial Enterocolitis ( Food Poisoning)
Ingestion of preformed toxin may be present in contaminated food ( Staphylococcus aureus, Vibrio, and Clostridium perfringens)
Infection by toxigenic organisms
Infection by an enteroinvasive organism
Gram (+) aerobic bacillus
Bacillus cereus
clinical findings of Bacillus cereus
Emetic Type
Diarrheal Type
incubation period (1-6 hours)
nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and occasionally diarrhea
self-limited (recovery: 24 hours)
source: re-warmed rice and pasta dishes
Emetic Type
incubation period (6-24 hours)
profuse diarrhea with abdominal pain and cramps
Enterotoxin may be produced in the intestine
Source: meat, poultry, and vegetables
Diarrheal Type
laboratory diagnosis for Bacillus cereus
Isolation of the organism from the suspected food samples followed by culture
treatment and prevention for Bacillus cereus
Fluid and electrolyte replacement
Self-limited
Preventive Measures:
1. Preventing contamination by soil
2. Rice should not be kept warm for long periods
Causes food poisoning with the shortest incubation period (Average: 2 hours)
Enterotoxins – produced when the MO grows in food-rich in CHO and CHON
Staphylococcus aureus
mode of transmission for Staphylococcus aureus
Ingestion of contaminated food – salads, custards, milk products, and processed meat
Carriers and individuals shedding human lesions
Fomites contaminated with human lesions
clinical findings for Staphylococcus aureus
Vomiting and Nausea (more prominent than diarrhea)
Toxin – acts on neural receptors in the gut
laboratory findings for Staphylococcus aureus
Isolation of the organism from the suspected food samples followed by culture
treatment and prevention for Staphylococcus aureus
Self-limited
Fluid and electrolyte replacement
Preventive Measures:
cleanliness
hygiene
aseptic management of lesions
mode of transmission for Clostridium perfringens
Ingestion of preformed toxin from food-contaminated soil containing the MO’s spores – meat dishes
clinical findings for Clostridium perfringens
Incubation Period: 9-15 hours
Watery diarrhea with abdominal cramps
Self-limiting (24 hours)
treatment and prevention for Clostridium perfringens
Fluid and Electrolyte replacement
Preventive measure:
adequately cook food before consumption
Marine organism – bacterial gastroenteritis associated with seafood.
Curved, Gram (-) coccobacillus
Halophilic (requiring 80% NaCl solution for growth)
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
toxin that can is present in Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Kanagawa hemolysin (enterotoxin similar to the cholera toxin)
mode of transmission for Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Ingestion of raw or undercooked seafood (shellfish – oysters)
Philippines - milkfish
clinical findings for Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Mild to severe watery diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and fever
Self-limited (3 days)
laboratory diagnosis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Culture (Thiosulfate–citrate–bile salts–sucrose agar) TCBS Agar