Written and Oral Communication
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
Writing: Conventional Stage
Fourth stage of writing (ages 6-7). Demonstrates more control over many aspects of the writing process.
Example.
Jane lost her cat named Tabby and it made her sad. She and her friends made sines with Tabby's pitcher. One of her friends found Tabby and Jane was so happy
Direct Quotation
an exact reproduction of the words of an author or a speaker that are set-off in quotation marks
Example.
Patrick Henry said, "Give me liberty, or give me death!"
Details
information about the setting, characters, actions, plot, etc. that helps the reader understand the story better
Mentor Text
books or other pieces of literature that are revisited throughout the school year for different purposes in literacy instruction
Example.
Due to its unique narrative and abundance of figurative language, Owl Moon by Jane Yolen is a popular mentor text to use in a language arts classroom.
Modeling
an instructional strategy in which the teacher demonstrates a concept or skill and students learn by observing
Example.
When a teacher encounters a difficult word in a text, she thinks aloud to model how she can use the context clues to discover the meaning.
Counterargument
expresses an opposing point of view
Expository Writing
a writing style in which students investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, and develop a clear argument
Example.
Newspaper articles, how-to manuals, and assembly instructions are examples of expository writing.
Plot
the events included in a story (may or may not be sequential)
Transitional Words
words or phrases that connect ideas, sentences, or paragraphs to help writing flow smoothly and clearly
Example.
Because of the fire in the building, the class had to meet elsewhere.
Audience (Rhetorical Situation)
the intended recipient of a written or verbal communication
Example.
When writing lesson plans, your students are your audience. A student writing a research presentation would have both his classmates and the teacher as an audience
Tense
words that indicate if a statement is referring to past time, present time, or future time
Example.
Past- She spoke. Present- She speaks. Future- She will speak.
Canva
an online content creation tool
Writing: Emergent Stage
Second stage of writing (ages 4-5). Understands that what is said (speech) can be written and that print moves from left to right rather than randomly on a page
Conflict (Narrative)
the challenge(s) the main character(s) need to overcome to achieve their goal
Informative Presentation
a presentation which demonstrates comprehension of a topic or process
Precise (Writing)
in writing, a sentence that contains specific details and avoids wordy descriptions
Example.
turquoise instead of light bluish green
Prewriting
the first step in the writing process when the writer decides on a central idea/topic for writing and formulates a thesis or main idea statement
Reliable Source / Credible Source
information presented in a professional way, with a formal tone, includes source documentation, and author and/or publisher information.
Example.
a textbook
Autonomy
student's ability to self-govern or self-motivate
Speaker (Rhetorical Situation)
the author of the text
First Person
tells the story from the narrator's perspective
Rubric
assessment tool that outlines specific criteria and performance levels for evaluating student work, providing clear guidelines and standards for both instructors and students to ensure consistent and objective grading
Bibliography
a list of all the sources explored in the research process
Writing: Pre-Conventional Stage
First stage of writing (ages 2-5). Child is aware that drawings and prints have specific meaning
Repetition
use of the same word, phrase, or idea to call attention to its significance
Speaking Rate
the speed at which a person speaks, usually measured in words per minute
Synthesis
the combination of ideas to form one theory
Writing Process
the steps a writer goes through to compose a finished, polished text
Example.
prewriting, drafting, revising, editing, publishing
Memorized Presentation
word-for-word delivery from memory
Descriptive Writing
used to create detailed descriptions of people, places, and things. Descriptive writing also develops the mood and atmosphere of the text
Context (Rhetorical Situation)
the social and historical circumstances in which a text is created and received
Dialogue
conversation between two or more characters
Graphic Organizer
a visual display of the relationships between facts and ideas
Example.
Graphic organizers, such as story maps, timelines, venn diagrams and K-W-L charts, help students organize information.
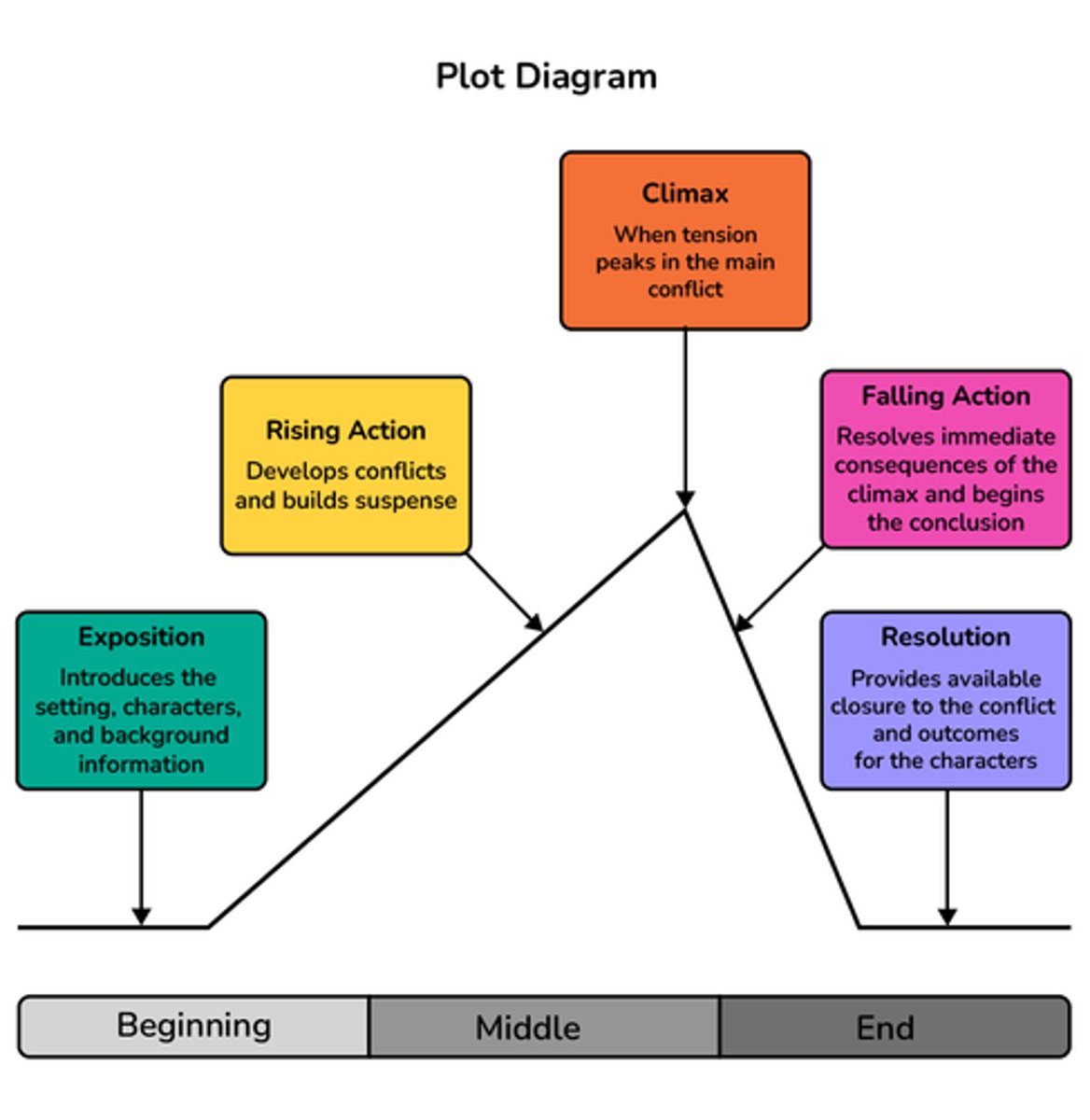
Plot Diagram
a graphic representation of the plot of a story
Example.
a plot triangle that outlines exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution
Peer Assessment
students evaluating their peer's learning and having their learning evaluated by peers
Problem and Solution
an organizational approach where the author presents a problem and possible solution
Concise (Writing)
in writing, a sentence that is brief but still contains all necessary information
Symbolism
an object stands for an idea or a greater meaning
Example.
dove = peace, red rose = love and romance
Prezi
a more interactive presentation software
Writing Workshop
an all-class writing project including instruction, writing time, conferencing, and sharing where students are guided through the process step-by-step
Exigence (Rhetorical Situation)
the problem or situation that prompted the speaker to write the text
Rhetorical Question
a question asked for effect rather than an answer
Shared Writing
a writing strategy where the instructor collaborates with students to draft a written text
Publishing
the final step in the writing process where the writer ensures the neatness and understanding of the final product
Writing: Proficient Stage
Fifth stage of writing (ages 7-9). Understands and is able to write for various purposes and audiences
Example.
The proficient writer can easily engage and work with the following types of writing: lists, invitations, letters, emails, narratives, descriptions, and expository
Accusative Case
nouns or pronouns that act as an object of a verb or preposition
Informative / Explanatory Writing
a writing style which demonstrates comprehension of a topic or process
Example.
In a science class, students write about a procedure that they performed and the results that they achieved.
Formative Assessments
ongoing evaluations to monitor student progress
Example.
using exit tickets to check understanding of the day's lesson
Compare and Contrast
an organizational approach where the author provides similarities and differences about two ideas
Extrinsic / External Motivation
the motive for the activity comes from outside the individual
Impromptu Presentation
unplanned and unrehearsed
Recursive
repeated application of a process, such as writing
Point of View
the style of narration used to tell a story
Example.
first person, third person limited, third person omniscient
Demonstrative Pronoun
this, that, these, those
Example.
These boxes are ready for shipment. Those boxes aren't.
Narrative Text
fictional stories, plays, and poems; usually contain some element of plot or conflict
Example.
Peter Pan, Romeo and Juliet
Paraphrase
to express the meaning of a text in different words, often used in research writing
Articulation
the clear and precise pronunciation of words
Compound-Complex Sentence
two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause
Example.
While we are in town, we should stop at the hardware store, and you can buy a new hammer.
Anecdote
a short retelling of a story used to emphasize or reinforce a point
Keyword (Research)
specific, relevant search terms
Balanced Feedback
teachers let students know both their strengths and weaknesses when giving feedback
Personification
giving human traits to inanimate, non-living objects
Example.
The stars seemed to dance in the glow of the moon.
Compound Sentence
two independent clauses joined by a comma and coordinating conjunction
Example.
Dogs are mammals, but lizards are reptiles.
Volume (ELA)
the loudness or softness of a person's voice when speaking
Emotional Language
language that is used to make the audience feel certain emotions, such as happiness, anger, sympathy, or fear
Imperative Sentence
sentence that gives a command or request
Example.
Sit in your chair.
Primary Purpose / Author's Purpose
why the author wrote a text
Example.
Charlie wrote an OpEd for the paper to convince people to stop littering.
PowerPoint
Microsoft's presentation software
Citation
reference to a source of information, such as a book, article, or website, used to support a statement or claim, typically including details like the author's name, the title of the work, and the publication date
Storyboard
a sequence of images or descriptions that represent the plot of a narrative
Writing: Transitional Stage
Third stage of writing (ages 5-6). Writes a single letter (often the beginning consonant of the word) to represent an entire word or syllable; begins to understand and use basic punctuation
Ethos
rhetorical appeal focused on the speaker's credibility and relatability
Argumentative Writing
writing meant to persuade the reader to agree with the conclusions of the author
Extemporaneous Presentation
prepared and practiced but delivered with a natural, flexible tone
Revising
reviewing the draft and making necessary corrections for sentence usage, organization, coherence, and audience
Dialogue Tag
followed or preceded by a comma or punctuation mark, with quotation marks around the quotation
Example.
As Mark exited the highway, he thought, "I hope this is the right way."
Cause and Effect
a writing method in which the author explains reasons why something happened or the effects of something that has happened
Example.
A politician's speech in which all of the bad actions of an opponent are listed to argue that the politician should be elected instead.
Chronological Order
an organizational approach that follows an orderly progression of events based in time
Portfolio
collection of student's work and achievements that is used to assess past accomplishments and future potential; can include finished work in a variety of media and can contain materials from several courses over time
Nonverbal Communication
facial expressions, gestures, physical actions
Characterization
the details an author uses to build a character (appearance, personality, thoughts, actions)
Citation Style
a set of guidelines for citing the basic information required to identify and locate a specific publication within a written work
Third-Person Limited
narrator is outside of the story and has limited access to the minds and motivations of characters
Onomatopoeia
words that make the sound of what the text is describing
Example.
The buzzing bee flew into the room.
Stylistic Choice
deliberate decision an author makes to enhance the narrative with a deeper message
Example.
allusion
Thesis Statement
a statement included in the introduction of a paper which makes a specific claim and provides a preview as to what will follow in the paper
Example.
A science student writes the following thesis statement in response to the question, "Is global warming a problem?" "Environmentalists agree that global climate change is an issue that needs to be addressed immediately."
Writing Conference
an individual meeting with students to discuss their drafts to help them revise their work before submitting a final product, and to help the teacher assess student understanding and modify instruction as needed
Pathos
rhetorical appeal focused on the emotions a speaker is evoking
Drafting
Term definition.
the second step in the writing process where the writer brings together similar ideas and organizes them into paragraphs
Cultural Language Variations
factors in a student's life lead to cultural variations in language
Example.
dialect
Interrogative Sentence
a sentence that asks a question
Example.
How long will it take to get there?
Paralanguage
includes intonation, pitch, and volume
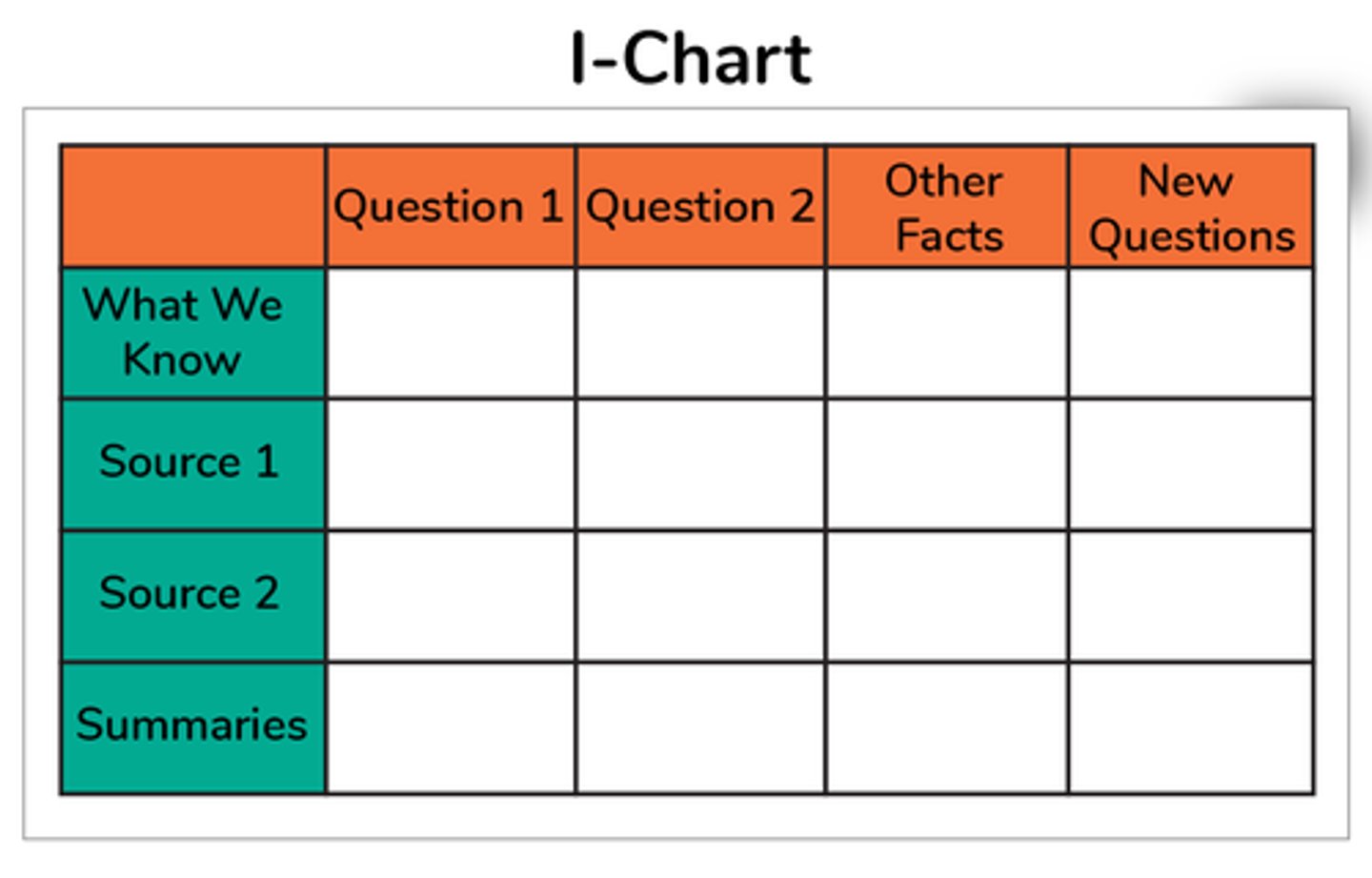
I-Chart
type of graphic organizer used for inquiry and research; organizes information by planning, interacting, and integrating/evaluating
Clause
a phrase that contains a subject and a verb
Self-Assessment
process where individuals reflect on their own performance, abilities, or understanding of a topic, typically using criteria or standards to evaluate themselves, fostering self-awareness, self-regulation, and continuous improvement
Unreliable Source
information presented in an informal way without documentation, and no author/publisher information
Example.
anonymous blog article
Anaphora
the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of sentences, clauses, or phrases one after another in a text
Example.
I have faith in my team. I have faith in my coach. I have faith in myself.
Irony
an incongruity between what the reader expects the author to mean and what they actually mean
Declarative Sentence
a sentence that makes a statement or gives an opinion
Example.
I love my job.
Alliteration
a sentence or phrase in which most of the beginning letters or sounds begin with the same consonant sound
Example.
Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.