The Industrial Revolution
3.0(1)Studied by 14 people
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:49 PM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 6 reasons the IR started in Britain?
natural resources, large supply of labour, pro-business gov’t, capital, colonies, industrial enlightenment
2
New cards
What are the natural resources?
coal = energy → fuel→ steam engine → machines
iron → cast-iron = products + factories
iron → cast-iron = products + factories
3
New cards
What is the pro-business gov’t?
businessmen + landowners → parliament that creates laws that favour business
4
New cards
What is the capital?
non-anglican restricted from gov’t → turned to business = $ → invest into industrial development
5
New cards
What are colonies?
Britain has biggest colony = raw resources + wealth
India + usa = cotton → textile industry → mass production
India + usa = cotton → textile industry → mass production
6
New cards
What is the industrial enlightenment?
capitalist ($) + scientists (ideas) = invention
7
New cards
What is the large supply of labour?
Agriculture rev = skilled workers → cities → factory workers
8
New cards
What was it like before the AR in farming?
subsistence farming, 3 crop rotation
9
New cards
what does enclosing fields mean?
limiting access to peasants → work in cities or hired labour on farm
10
New cards
What was it like after enclosing fields in the AR?
Land under tight control = more productive → food production → money
11
New cards
What was the seed drill?
3 in 1 actions = increase in food production and prevented natural effects
12
New cards
What was the Rotherham plough?
iron blade = easy to use and only 2 horses and 1 person → cut cost and labour time
13
New cards
What are the benefits of the 4 crop rotation system?
turnips = better crops, more food → pop increase, livestock food
14
New cards
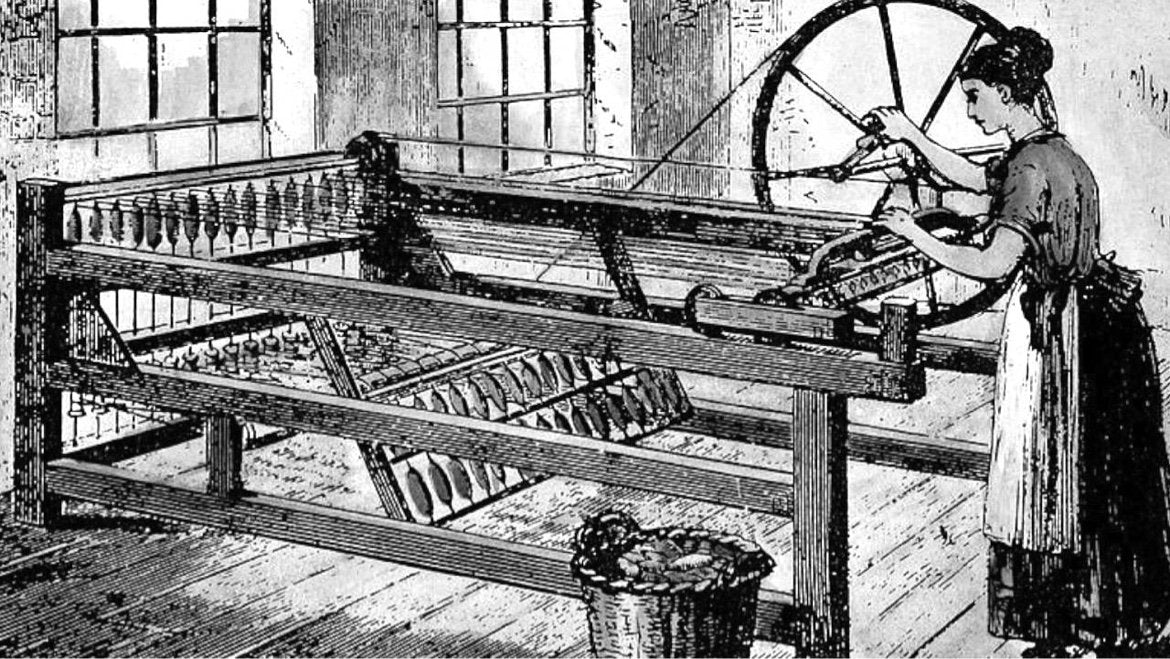

What is this?
the spinning jenny, could spin multiple spindles
15
New cards
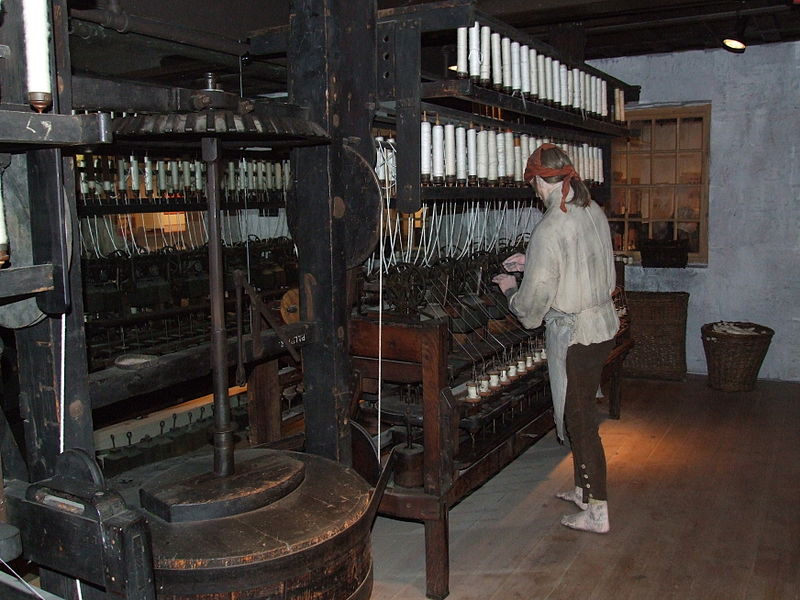

What is this?
the water frame, 100 spindles, water powered = bigger buildings → first factories
16
New cards

What is this?
the spinning mule, 1300 spindles
17
New cards
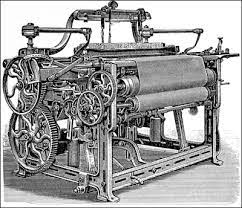
What is this?
the power loom, weave threads
18
New cards
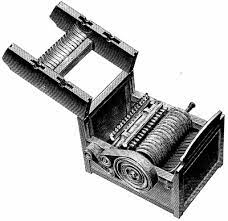
What is this?
the cotton gin, harvest cotton
19
New cards
What is the cottage industry?
goods were sold and produced locally and in a small scale
20
New cards
Why was the cottage industry ineffective?
could not keep pace with growing demand by pop increase
21
New cards
What is the factory industry?
factories = goods produced on large scale
22
New cards
Why were factories built in cities?
cities were built on water = water power, transportation → shipping goods
23
New cards
How was the pop. utilized and infleunced by factories?
AR = skilled workers in cities for factories,
success of factories = pop increase
success of factories = pop increase
24
New cards
How did the factory system advance the IR?
factories in city = mass production + pop increase
25
New cards
Why was child labour needed?
high demand in factories + low wages → children, family couldn’t afford child, some jobs are only for children
26
New cards
What were the 2 waves of children?
1\. orphans → state-sponsored slavery
2\. every child → cheap labour
2\. every child → cheap labour
27
New cards
What is state-sponsored slavery?
work instead of social welfare, orphans not paid but given basic needs
28
New cards
What were the children’s attitudes about going to work?
Propaganda = possibility of independent worker, education, meals, housing, skills
29
New cards
What types of child labour jobs are there?
chimney sweeper, textile factory worker, miner trapper boy
30
New cards
Why did the gov’t respond to child labour?
grown up children formed unions, Oliver Twist, Sadler report = investigation → public shock → pressure
31
New cards
Because of the pro-business gov’t, many wanted to follow the economic policy… which means…
laissez-faire/no gov’t regulations bc regulations cut into profit
32
New cards
What were the working conditions for the workers?
low wages, long hours, abuse, unions illegal
33
New cards
What did the gov’t do with child labour?
education replaces labour
34
New cards
What was the significance of child labour in the development of the factory system?
capitalists needed cheap labour to expand, low wages = no cut in profit, some jobs are just for children
35
New cards
Who were the upper class?
society, big network, old rich (inherited) or new rich (factory owners)
36
New cards
Who were the middle class?
grew during the IR, father worked in professions or business
37
New cards
Who were the lower middle class?
white-collar workers
38
New cards
Who were the working class?
worked in trades or factory, farmers, 80%, blue-collar workers, skilled/unskilled/casual labour
39
New cards
What was the energy development?
hand powered → water → coal/steam
40
New cards
What are the benefits of iron?
easy/cheap to produce, build factories, England has huge supply
41
New cards
What was the problem in the mines with water?
water leaked into coal lines = consistent removal → harder deeper down = can’t get coal
42
New cards
What was the solution in the mines with water?
Newcomen made steam engine → adapted to power machines
43
New cards
What was the significance of the steam engine in the textile factory?
factories didn’t need water power → built everywhere = faster + mass production
44
New cards
Who and what are the significance of the adapted steam engine?
James Watt made it efficient → trains
45
New cards
What is the significance of trains?
travel industry, army travel, info/mail travel, raw resources → factories → goods → market → sold = profit, allowed the mass production of goods to be moved
46
New cards
What was the standardization of time?
railroads switched to Greenwich mean time from local time (varied) → synchronized time all around the world
47
New cards
Why was there railroad time?
confusing, accidents,
48
New cards
What is the significance of steamships?
raw resources brought to England by colonies faster
49
New cards
What is the significance of canals?
linked river systems together = reduced cost by 75% + one barge = 100 horses
50
New cards
What was the negative to the transformation of energy?
coal demand staggered = intensive mining → exploits enviroment
51
New cards
What was the positive to the transformation of energy?
England became global superpower
52
New cards
What are the 4 positive effects of the IR?
class structure, labour unions, role of women, urbanization
53
New cards
What are the 5 negative effects of the IR?
daily life, working conditions, life expectancy, living conditions, seperation of work and home
54
New cards
What is the development in class structures?
2 classes (wealthy/peasent) → 3 classes (upper/middle/working)
55
New cards
What was the development in the role of women?
paid 1/2 of men → feminist movements for equality
56
New cards
What was the development in urbanization?
rural → city =massize growth in city pop
57
New cards
What was the development in the rise of labour unions?
no gov’t regulations → unions for shorter hours, higher pay, safety, education, healthcare
58
New cards
What was the development in daily life?
for working class life deteriorated when in cities, life was a routine of hard work, poorhouses
59
New cards
What was the development in life expectancy?
decreased for working class, 25%-33% died before 5
60
New cards
What was the development in living conditions?
cities: crowded, dirty, polluted, no proper streets/sewage, no clean water, slums, disease spread
61
New cards
What was the development in working conditions?
large labour supply = conditions of work set by factory owners : long days/week, low pay, division of labour (monotonous), very dangerous
62
New cards
What was the development in separation of home and work
in cottage era: families worked in unit to provide with equal gender roles
in factory era: work and home separated → decline of female’s economic role
in factory era: work and home separated → decline of female’s economic role
63
New cards
What was the development in socialism?
Robert Owen wanted to improve workers’ lives → rejected laissez-faire bc it didn’t address social concerns
64
New cards
What was the development in new laws after the first wave of the IR?
correct social concerns: child labour → education, labour unions are legal, cities got sanitation and better planning