Basic Organic
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Hydrocarbons
Compound of Hydrogen and Carbon only
Saturated
Only single bonds
Unsaturated
Containing a multiple carbon-carbon bond
Homologous series
A series of organic compounds w/ the same functional group and similar chemical properties but with each successive member differing by CH2
Functional group
The part of the organic molecule responsible for its chemical reactions
Aliphatic
Containing carbon atoms joined together in straight or branched chains
Alicyclic
Containing carbon atoms joined together in a ring that is not aromatic
Alkanes
The Hydrocarbon homologous series with single carbon to carbon bonds and the general formula CnH2n+2
Alkenes
The hydrocarbon homologous series with at least one double carbon to carbon bond
Alkynes
The hydrocarbon homologous series with at least one triple carbon to carbon bond
Alkyl groups
A side chain formed by removing a hydrogen atom removed from an alkane parent chain
For example CH3, C2H5; any alkyl group is often shown as R
General Formulae
Simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series eg Alkanes: CnH2n+2
Empirical Formula
Shows simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element present in the compound
Molecular Formula
Shows number and type of atoms of each element present in a molecule
Displayed formula
Formula showing relative positions of all atoms in a molecule + the bonds between them
Skeletal Formula
Simplified organic formula w/ Hydrogen atoms removed from alkyl chains, leaving just a carbon skeleton and associated functional groups
Structural Isomers
Molecules w/ same molecular formula but different structural formula
First 10 alkanes
Methane
Ethane
Propane
Butane
Pentane
Hexane
Heptane
Octane
Nonane
Decane
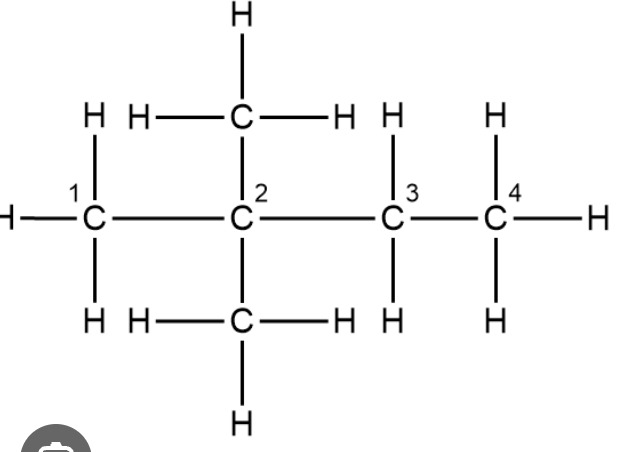
Naming Branched Alkanes
Suffix -ane
Identify longest continuous chain of carbon atoms: e.g 4 - But-
Identify side chains/ which no. carbon the chains are on. e.g 2 methyl side chains on carbon 2/3 (used lowest 2): 2,2-dimethyl
Combine suffix, stem and side chains: 2,2,-dimethylbutane
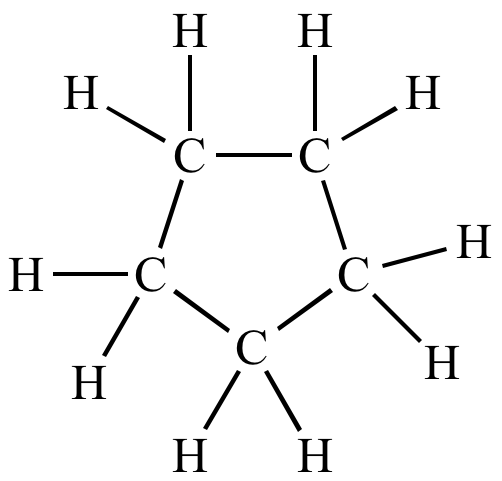
Naming Alicyclic Alkanes
Longest chain
Add cyclo
e.g Cyclopentane
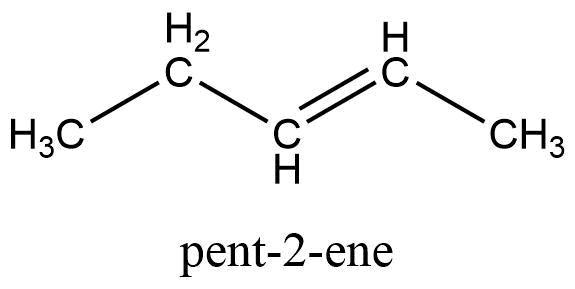
Naming Alkenes
Suffix -ene
Longest Carbon Chain: e.g 5: pent-
Identify space of double bond: e.g between c2 and c3: 2-
Combine: pent-2-ene
Naming Alcohols
Functional group -ol
Longest chain: e.g 4: Butan-
Which carbon: 2-
Combine: butan-2-ol
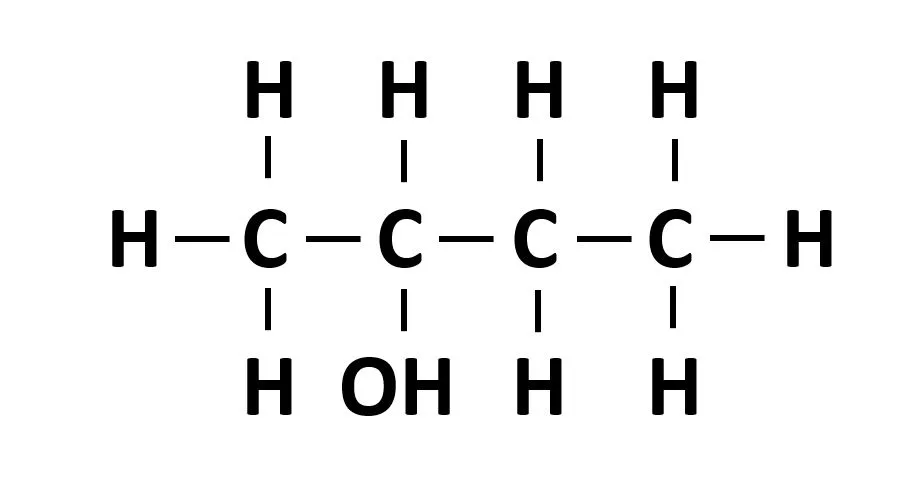
Naming Alehydes
Functional Group -al
Longest chain: e.g 3: propan-
Propanal

Naming Organic compounds w/ Multiple Functional groups
Longest Chain: e.g 4, Butan-
Functional groups: e.g Halogen on C2: 2-chloro, Methyl on C2: 2-methyl
Stem + prefixes (alphabetical order) e.g 2-chloro-2-methylbutane

Bond Angles in Alkanes
109.5º due to each C pair being surrounded by 4 bonding pairs in 4 sigma bonds
Effect of chain length on bpt
London forces are between molecules
As chain length increases, molecules have larger SA - more surface contact possible between molecules
London forces greater → more energy required to overcome
Bpt increases with chain length
Effect of branching on bpt
Isomers of alkanes: same molecular mass
Branched lower bpts