Final Exam
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Population Health
The health outcomes of a group of individuals, including the distribution of those outcomes within the group
Socioecological Model of Health (SEM)
Conceptualizes health by focusing on factors affecting human health and the interplay between individuals, groups/communities, and broader physical, social, and political environments
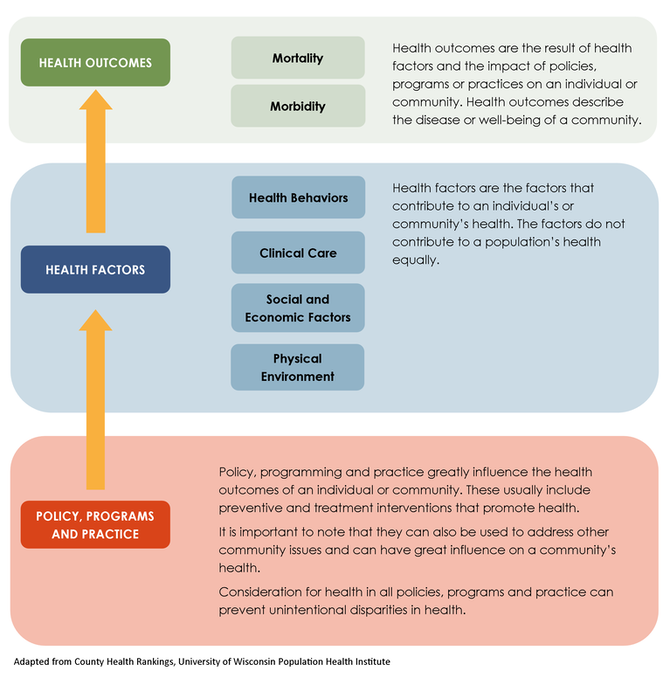
Center for Urban Population Health (CUPH)
Policies, programs, and practice form the base, fundamentally shaping the environment, which influences health factors, ultimately leading to health outcomes
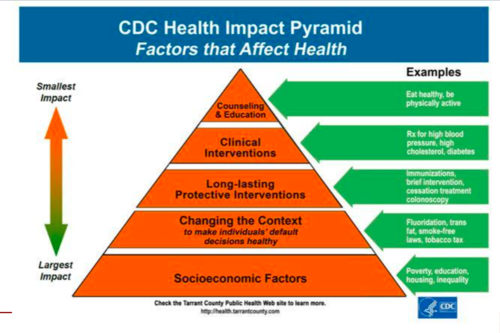
Health Impact Pyramid
As individual effort increases, the impact on population health decreases (Socioeconomic factors at base )
US Health Outcomes
- high infant mortality rate
- low life expectancy
- high spending on healthcare
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH)
economic stability, healthcare access/quality, neighborhood/built environment, social/community context
economic stability
Employment status, income level, housing stability, food security
education access and quality
High school graduation rates, health literacy, language and literacy skills
health literacy
Ability to understand medical information and make informed health decisions
healthcare access and quality
Insurance coverage, provider availability, transportation to care
neighborhood and built environments
Housing quality, transportation options, safety, access to healthy foods
social and community context
family support, community cohesion, cultural beliefs, social networks
SDOH Barriers in Getting Prescription
no insurance, no transportation, no time off work
SDOH Barriers in Picking Up Medication
pharmacy too far away, cannot afford copay, pharmacy hours don’t match work schedule, no ID/insurance card
SDOH Barriers in Taking Medication Directly
cannot read instructions, complex work schedules affecting timing, cultural beliefs about medications, no safe storage space
SDOH Barriers to Following Up on Medication
cannot afford follow-up appointments, lack of transportation to labs, work schedule
SDOH Barriers
create “cascading effects” that undermine entire treatment plan
Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs)
innovative community health pharmacy models that serve underserved populations and address social determinants of health barriers by using income-based sliding fee scales and integrating pharmacists into their healthcare teams
Health Disparities
Preventable differences in the burden of disease, injury, violence, or opportunities to achieve optimal health that are experienced by socially-disadvantaged populations
Health Equity
When every person has the opportunity to attain his or her full health potential" regardless of social position or other socially determined circumstances
Healthy People 2030 Initiative
US federal government's 10-year plan, led by DHHS, to improve the health and wellbeing of all Americans by setting data-driven national objectives and promoting health equity
Health People 2030 Goals
▪ Attain healthy, thriving lives free of preventable disease, disability, injury, and premature death.
▪ Eliminate health disparities, achieve health equity, and attain health literacy to improve the health and wellbeing of all.
▪ Create social, physical, and economic environments that promote full health potential for all.
▪ Promote healthy development, healthy behaviors, and wellbeing across all life stages.
▪ Engage leadership and the public across multiple sectors to design policies that improve health
Populations at Risk for Pop. Disparities
Racial or ethnic minority groups, Sexual or gender minority groups, Socioeconomically disadvantaged populations, Individuals in rural environments with underserved healthcare, Elderly people, Persons with disabilities.
Causes of Health Disparities
often multifaceted or multifactorial, requiring multifaceted interventions to fully address them
Primary Drivers of Health Disparites
health behaviors, social/economic factors, structural racism/discrimination, historical/systemic, biological/physiological
health behaviors
choices we make are directly related to choices we have
Structural Racism and Discrimination
macro-level conditions that limit opportunities, resources, and wellbeing for individuals based on race or ethnicity
Allostatic Load
cumulative burden of chronic stress from both daily life and major life events
Native Americans Disparities
- higher mortality rate from diabetes
- alcohol induce diseases
- lower life expectancy (5.5 yrs lower)
Black/African American Disparities
- higher prevalence of HBP, diabetes, and stroke
- higher mortality for CVD and cancers
- infants w/ low birth weight
- pregnancy related-mortalities
Historical Redlining
ID areas based on population risk; led to neighborhood disinvestment
Pharmacisi’s Role in Population Health
serves as a bridge between individual patient needs and boarder community/systemic factors; most accessible healthcare provider; “on the front lines”
equity focused MTM Approach
Recognizes medication-related problems often have social and cultural roots requiring different solutions
Cultural Humility
lifelong practice of self-reflection to learn about biases; Recognizing you cannot be an expert in every culture, but approaching each patient with genuine curiosity, respect, and a willingness to learn from their experiences
Cultural Competence
ability to provide care to patients with diverse values, beliefs, and behaviors
LEARN model
Listen to patient perceptions
Explain your perceptions
Acknowledge differences
Recommend treatment
Negotiate agreement
explicit bias
conscious, openly expressed attitudes or beliefs that affect how individuals are treated
implicit bias
unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that healthcare professionals hold about certain groups of people; potentially leading to disparities in care
common types of bias
- racial and ethnic bias in pain management
- socioeconomic bias
- age and gender bias
systemic approaches for bias reduction
Standardized protocols, clinical decision support tools, regular training and self-reflection, diverse healthcare teams
clinical documentation as advocacy tool
Captures medical information, social determinants, and systemic barriers; creates an evidence base to influence policy and resource allocation
Population-level advocacy
Engaging with policymakers (legislative days), participating in professional organizations, working with community coalitions to address systemic issues
physical healthcare access
Geographic location, transportation infrastructure, parking, hours of operation
financial healthcare access
Insurance coverage, co-payments, deductibles, prescription costs, and hidden expenses
cultural healthcare access
Culturally appropriate services, language interpretation, culturally competent providers/staff
administrative healthcare access
Appointment scheduling systems, documentation requirements, bureaucratic processes overwhelming for those with limited health literacy
community level cultural factors
influence, collective health beliefs, social networks, traditional healing practices, community norms around help-seeking
Native Americans Cultural Considerations
traditional healing systems, intergeneration trauma, medical mistrust, tribal sovereignty, diversity
Community Health Workers (CHW)
trusted members of the community they serve who leverage their lived experience and specialized training to bridge the gap between healthcare systems and underserved populations by providing culturally appropriate health education, navigation, and advocacy
policy
law, regulation, procedure, administrative action, incentive or voluntary practice of governments or other institutions
law/statue
- from elected body (federal/state)
- acts on everyone
- enforceable by government (criminal or civil)
ordinance
- from elected legislature or council (local)
- acts on everyone in local jurisdiction
- enforceable by local government (civil penalty = fine)
regulation
- from non-elected bureaucratic organization
- acts on those specified
- enforceable by government (civil penalty = fine)
rule
- from public or private organization (health system)
- acts on those operating within organization
- enforceable by organization (may be consequences if violated)
guidance document (clinical guidlines)
- from any organization with vested interest
- acts on those specified in document
- voluntary, not enforceable by government
Policy Process
Problem Identification
Policy Analysis
Strategy and Policy Development
Policy Enactment
Policy Implementation
Evaluation
infrastructural policy
Creates or strengthens fundamental public health structures; enabling public health statues
interventional policy
modifies health risk factors
intersectoral policy
implemented by a NON-health agency for non-health purposes, but can affect health outcomes
de-regulation
Providing access, distributing equipment, making resources available, or removing previous regulations
direct regulation
forces a behavior
indirect regulation
often related to liability
money tool for pop health
taxes, incentives, and spending
rescue imperative (rule of rescue)
preference for emergency fixes rather than prevention
technological imperative
Cutting-edge biomedical technology has greater appeal than population-based interventions
visibility imperative
Public/population health practices are often INVISBLE until a crisis occurs.
partisanship
New federal legislation can be hampered by disagreements
health care systems
Organizations of people, institutions, and resources that deliver healthcare services to meet the health needs of a target population-
National Quality Strategy (NQS)
- developed by AHRQ due to lack of a national plan for quality
- order as a part of ACA
- includes 3-6-9 framework
3-6-9 Framework for NQS
All health systems must adopt three aims focusing on six priorities, using nine levers (tools) to improve healthcare quality
3 Aims of NQS
better care, healthy people/communities, and affordable care
6 Priorities of NQS
Health and wellbeing; prevention and treatment of leading causes of mortality; person and family-centered care; patient safety; effective communication and care coordination; affordability
9 Levers (tools) of NQS
Measurement and feedback (publicly available data); learning and technical assistance; certification, accreditation, and regulation; consumer incentives and benefit designs; payment models (influencing clinician reimbursement); health information technology and innovation/diffusion (interoperability); workforce development
Accountable Care Organizations
A group of providers that collectively accepts responsibility for improving the overall health status, care efficiency, and healthcare experience for some defined population
ACO vs HMO
no restriction of provider for ACOs; ACOs focus on outcomes
Patient-Centered Medical Homes (PCMHs)
A care delivery model, typically operating within an ACO. The patient is at the center of all shared decision-making with a primary care provider (PCP), and all other clinicians report back to the PCP
Medicare Part A
hospitalizations, funded by federal payroll tax
Medicare Part B
regular coverage (Outpatient care, checkups, ambulatory services); Requires monthly premium
Medicare Part C
Private health plan alternative to traditional Medicare. Requires opting in and often higher monthly premiums
Medicare Part D
Prescription medications. Requires monthly premium
Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
insurance program for low-middle income children; funded by state taxes and federal allotment
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)
insurance programs for those with approved disability funded by payroll tax; administered by federal government
Medicaid
public health insurance program for those with low-income (state-run, federally supported)
Affordable Care Act (ACA)
most comprehensive piece of US healthcare designed to improve population health by expanding insurance coverage, regulating insurers, protecting consumers, and reforming care delivery systems
Economic Theory of Disparities in Quality of Care
spending primarily via a third party (insurance) rather than the consumer creates misaligned incentives for care quality and consumption
ACA provisions
insurance regulations, consumer protections, mandates, public coverage expansion
upstream determinant
include broad social and structural influences on the health of a population
downstream determinants
factors that are closer to the individual (i.e., risk behavior, disease/injury, and mortality)