Mechanics of Human Movement Final part 2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What makes up the axial and appendicular skeleton?
axial: skull, vertebrae, ribs 74 bones
appendicular: extremities, shoulder girdle, pelvis 126 bones
Adult skeleton = 206 bones (6 auditory)
What is the function of the skeletal system?
biomechanical: levers, supports
physiological: protection, storage of fat and minerals, blood cell formation
What is human bone composed of?
water
minerals (resist compression), what bone mostly made of
protein (collagen, resist tension)
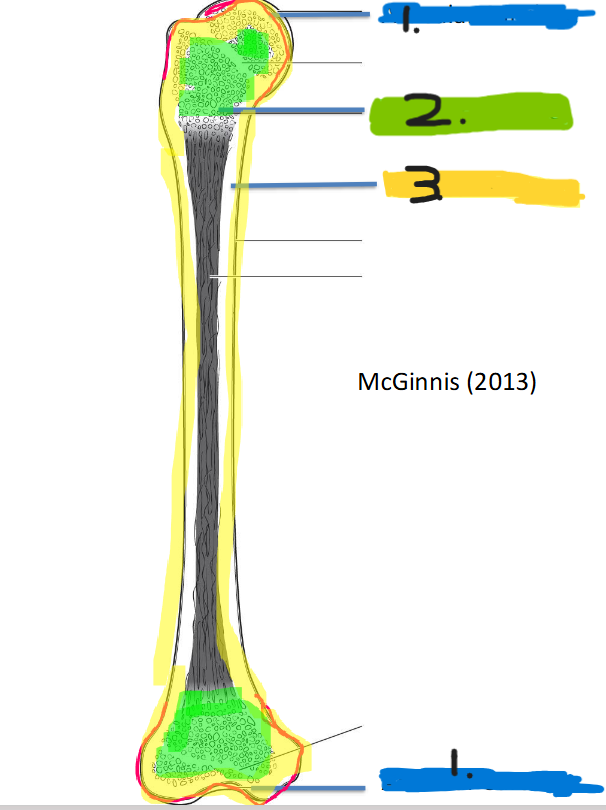
label
articular cartilage
cancellous bone
cortical bone
Cortical bone
compact
low porosity
shaft of long bones
Trabecular (cancellous) bone
less compact
high porosity (spongy)
ends of long bones, vertebrae
What does isotropic mean?
materials have the same mechanical properties in every direction of loading
synthetic materials are isotropic
What does anisotropic mean?
different mechanical properties depending on the direction of load
connective tissue and biological tissue are anisotropic
When is bone the strongest and weakest?
bone is strongest in compression
bone is weakest in shear
Are tension forces between compression and shear?
yes
What is Wolff’s law?
bone strength increases and decreases as the functional forces on the bone increase and decrease
bone in a healthy person will adapt to the loads under which it is placed
Describe the structure of Trabecular (cancellous) bone
system of columns of bone
the main columns are based on the direction of loading. Support the main loading (compression or tension)
main columns are tied together with smaller transverse trabecular
How does age affect bone?
decrease bone mineral density
trabeculae lose thickness
some transverse trabeculae disappear
Who does osteoporosis affect?
type 1 (post-menopausal): 40% of women > 50 years
type 2 (age associated): most women and men after age 70
How is trabecular (calcaneus) bone affected by osteoporosis?
less porosity (spongy)
hollow
air pockets
Do bones need be under stress to develop?
yes
How do bones respond to weight bearing exercise?
larger the forces acting on the skeletal system, greater bone development
What does the national institute of osteoporosis and related bone disease recommend people do?
walk
hike
jog
climb stairs
dance
What does the SCSM recommend?
weights-bearing endurance activities, activities that involve jumping, resistance exercise
moderate to high intensity for bone-loading forces. weight bearing endurance activities 3-5 times per week; resistance exercise 2-3 times per week
30-60 minutes
what is joint stability?
resistance to movement in planes other than those defined by specific joint
movement of articulating surfaces away from each other through sliding and pulling apart
Characteristics of tendons
attach muscle to bone
transmit tensile load from muscle to bone to produce joint stability or motion
provide mechanical pulleys
motor control
characteristics of ligaments
connect bones to bones
mechanical joint stability
guide joint motion
contribute to proprioception/position sense
composition of ligaments
type 1 collagen fibers that are not completely parallel
bear tensile loads in long direction
can bear smaller tensile loads in other directions
more elastin than tendons
Ligaments
prevent dislocation when force trying to pull bones apart
necessary when bone configuration not stable
not good with shear forces
Characteristic for healing
poor blood supply = bad healing
bone have better blood supply than ligaments
grades of tears
grade 1: very mild and can potentially heal on its own
grade 2: more damage and this will take much longer to repair itself. therapy advised
grade 3: complete tear. surgical intervention typical
factors affecting biomechanical properties
age: decreased stiffness, strength, and ability to withstand deformation
Pregnancy and postpartum period: increased laxity of tendons and ligaments in the pubic area during later stages of pregnancy
Mobilization/Immobilization: increased strength/stiffness with mobility, decrease with immobility
composition of tendons
parallel fibered collagenous network
type 1 collagen sustains large tensile loads
elastin: 2% of the dry weight
muscles
contraction typically pulls bones closer together
help make joint stable (good) but may increase joint compression to unsafe levels (bad)