Gastrointestinal: Ingestion & Digestion Disorders
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Gastrointestinal (GI) Series
-Radiographic studies done with or without contrast that define anatomic or functional abnormalities
1.Upper GI Series- patient swallows and has xray done (takes pictures of upper GI throughout the day)
2.Lower GI Series - Barium Enema (looks at colon and inserted through rectum can cause white stools) (bowel prep)
-take lots of liquids and monitor for contrast elimination
GI series Indications
-Gastric ulcers
-peristaltic disorders
-tumors
-varices
-intestinal enlargements or constrictions
-C/O:
-abdominal pain
-altered elimination habits
- GI bleeding
when patients complain of abdominal pain or altered elimination habits what should you do?
-may need to do GI series because they are supposed to go every 3 days
-ask patient when was their last void?
Nursing actions are most prominent when during the GI series?
pre and post op
endoscopy
-Allows direct visualization of body cavities, tissues and organs
-diagnostic and therapeutic purposes
-can be M2A endoscopy where the person swallows a small camera
-risk for bleeding
-check for gag reflex once patient wakes up
colonoscopy
-after age 50
-patient should be on clear liquid diet so stools will be clear
-no red/orange/purple or green foods can be confused with blood
-no solid material should be in poop
-NPO the night before
-discontinue NSAIDS
colonoscopy and endoscopy require what type of sedation?
moderate
indications for endoscopy
-Potential Diagnoses
-Client Presentation
endoscopy nursing pre-procedure
-Verify informed consent is obtained for proper procedure
-Assess vital signs and verify allergies
-Assess history for risks of complications
-Evaluate baseline laboratory values and report unexpected or abnormal results
-verify F/E and chem 7
-Verify patient NPO status
how long should a patient be NPO for before an endoscopy
6-8 hrs
colonoscopy pre procedure
-consent
-drink alot of fluids
-make sure stools are clear
-NPO the night before
-give patient bedside camode because they will need to empty bowels alot
for colonoscopy how long before should a patient be NPO
NIGHT BEFORE
for a endoscopy which colors should the patient avoid consuming
-red
-orange
-purple
endoscopy during the procedure
left side lying with head elevated for the procedure
surgeon will order
-CBC
-electrolyte panel
-BUN/creatinine
-PT/PTT
- liver function
b4 and after procedures
post procedure endoscopic nursing actions
-Monitor vital signs
-Assess for complications (leaking/wound open)
-If biopsy taken, may have food restrictions
-make sure gag reflex returns
EGD and ERCP post procedure
-Withhold fluids until gag reflex returns
post procedure Colonoscopy/Sigmoidoscopy
-Monitor for rectal bleeding
-Instruct that there may be increased flatulence due to air instillation during the procedure
-check CBCs again after
chem 7 test includes
-creatinine
-potassium
-glucose
-sodium
can a patient drive or take uber after having a procedure?
no they need family to give them a ride
GI bleed interventions
-NPO
-NGT- to suction blood
-IV fluid
-two IV sites: one for blood the other for fluid and meds
-BLOOD
-cauterize bleeding site
-ligate bleeding vessels
what symptoms does a patient with GI bleed have
-bleeding
-cool/pale skin
-dizziness
-tachycardia
-hypotension
what is the major risk factor for GI bleeds?
duodenal ulcers
which tests should be monitored for a patient with a GI bleed
-BP
-H/H every 6-8 hrs to check for improvement
-fecal occult blood/stool guiac test
what do we give in the IVs of GI bleed patient
-blood
-isotonic fluids (LR/NS)
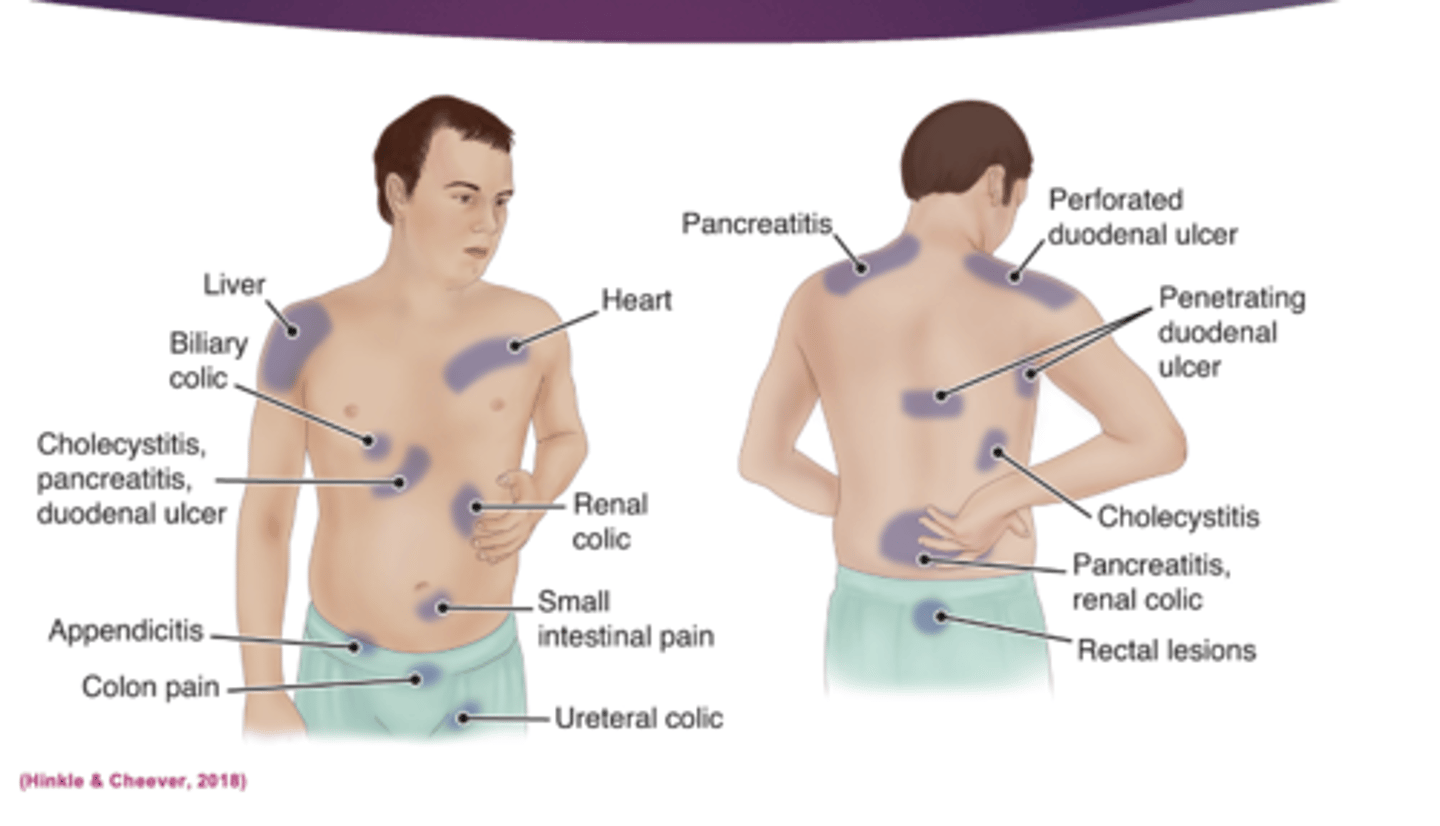
sites for referred abdominal pain
pain that starts in your thumb but moves to other areas
Hiatal Hernia
-Muscle weakness of the diaphragm at the esophageal hiatus
-muscle protrudes
diagnostic testing hernia
•X-rays
•Barium Swallow (swallow camera to monitor what is going on)
•Fluoroscopy
medical management hernia
-last resort
-Surgical hernia repair
hernia CM
-Pyrosis/Heartburn
-Regurgitation
-Belching
-Pain
-Dysphagia
-hiccups
-dental carries
when do symptoms worsen for a hiatial hernia
-after eating
-reccumbent
-side lying
monitor (hernia)
-Nutritional status
-Aspiration
-Pain
complications of hernia
-Strangulation (tight and closed)
-Incarceration
-Hemorrhage
hernia diet modifications
-Frequent small feedings that pass easily through esophagus
-NO:
-oil
-spicy food
-soda
-citrus
-Alcohol
hernia lifestyle changes
-Do not recline 1 hour after eating
-Elevate HOB 4-8"
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
-gastric content and enzyme leakage into the esophagus
-irritates the esophageal tissue
-limits ability to clear contents from esophagus
medical management of GERD
-DIET (small frequent meals)
-lifestyle changes (exercise)
-meds
-surgery
which foods should a GERD patient avoid (foods that affect LES pressure)
-dairy products
-chocolate
-coffee
-peppermint
-soda
-spicy food
-fried food
-sauces
untreated GERD can lead to
-inflammation
-breakdown
-long term complications including:
-adenocarcinoma of the esophagus
-barretts esophagus
GERD RISK FACTORS
-Diet
-Tobacco use
-Coffee Drinking
-Alcohol
-H. Pylori
Clinical Manifestation
-Dyspepsia
-Acid reflux
-Throat irritation
-Hypersalivation
-Eructation (belching)
-Flatulence
-Bitter taste in mouth
-Atypical chest pain
-Dysphagia
-Tooth erosion
-Hoarseness
GERD diagnostic testing
-EGD
-Esophageal manometry
-24 hour ambulatory pH monitoring
-Barium swallow
-TEST FOR H. PYLORI
GERD DIET
-low fat
-avoid foods that decrease LES pressure
-4-6 small meals
GERD lifestyle changes
-Maintain normal weight
-No smoking or alcohol
-Elevate HOB 6-8 inches
Education for GERD
-Avoid situations that causes esophageal irritation
-Avoid eating/drinking 2 hours before bedtime
-Elevate upper body on pillows
GERD complications
-Barrett’s epithelium (premalignant)
-esophageal adenocarcinoma
Reflux of gastric fluids can cause esophagitis, chronic condition resulting in continuing healing of inflamed tissue, replaces normal tissue with premalignant tissue or malignant adenocarcinoma
Gastritis
-Inflammation of the stomach mucosa
-A common GI problem (NSAIDS)
-Can be acute or chronic; non-erosive or erosive
non erosive
associated with infection by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)
Erosive
-associated with long-term NSAID use
-alcohol abuse
-gastric radiation therapy (burns the lining of the stomach)
acute
rapid
caused by :
-dietary indescretion
-meds
-alcohol
-bile reflux
-radiation therapy
-Ingestion of strong acid or alkali may cause serious complications.
acute gastritis CM
-epigastric pain/discomfort
-dyspepsia
-hiccups
-n/v/a
-Melena or hematochezia
chronic
over a period of time
-prolonged inflammation from repeated exposure to irritating agents or recurring episodes of acute gastritis.
-associated with autoimmune diseases
CHRONIC gastritis CM
-fatigue
-pyrosis
-belching
-sour taste in the mouth
-early satiety
-n/v/a
-May have vitamin deficiency due to malabsorption of B12
-intolerance of spicy foods
-epigastric pain relieved by eating
with gastritis when is the pain relieved
by eating
DIAGNOSTIC TEST
-endoscopy histologic examination of tissue specimen by biopsy
-CBC
-Testing for H. Pylori infection
ACUTE medical management
-Refrain from alcohol and food until symptoms subside
-If due to strong acid or alkali treatment to neutralize the agent
- avoid emetics (anything that causes vomit) and lavage
-Supportive therapy
Chronic Medical management
-Modify diet
-promote rest
-reduce stress
-avoid alcohol and NSAIDs
-Pharmacologic therapy
primary treatment of gastritis
identification and elimination of the causative factors
gastritis nursing management
-Monitor fluid intake and urine output
-Provide IVFs
-Monitor electrolytes
-identifying triggering foods
-Provide small, frequent meals and eat slowly
- avoid alcohol, caffeine, and foods that cause gastric irritation
-identifying reduction of stress
-Monitor for gastric bleeding and anemia
peptic ulcer disease
-Erosion of the mucosal lining of the stomach or duodenum
-epithelium is exposed to gastric acid and pepsin
-bleeding and perforation
perforation that extended through all layers and leads to
peritonitis
PUD is associated with
infection of H. pylori
if ulcer is in the stomach it causes pain
immedietly after eating
if ulcer is in duodenum causes pain
1-2 hrs after eating
PUD risk factors
-excessive secretion of stomach acid
-dietary factors
-chronic use of NSAIDs
-alcohol
-smoking
-familial tendency
CM PUD
-dull gnawing pain/burning in the mid-epigastrium
-heartburn
-vomiting may occur
LAB TESTS PUD
-H. pylori
- H & H
- Stool Hemoccult (FECAL OCCULT)
Diagnostic studies PUD
-Barium studies
-endoscopy (with possible biopsy)
LIFESTYLE CHANGES
-smoking cessation
-avoid alcohol
-avoid extremes of temperature
-coffee
-Bland nonirritating diet
-USE NATURAL SPICES (SCALLIONS, ONION, THYME)
PUD complications
-Hemorrhage/perforation
-Emergency situation
-Fluid deficit management
-NGT/Saline lavage
-EGD with laser treatment
GI bleeding etiology
-Gastritis
-hemorrhage from PUD
CM GI bleed
-Faintness/dizziness
-Nausea
-Tachycardia
-hypotension
-tachypnea
-Emesis
-Bright red
-Coffee-ground
-Small quantities: Passed in stool → tarry black (digested hemoglobin)
GI Bleed: Medical Management: Treatment of hemorrhagic shock
-Two, large-bore IV catheters
-Isotonic crystalloid solution for volume
-Blood products
-Endoscopic evaluation
-Injection of the bleeding site with epinephrine, gelfoam
-Cauterizing the site of bleeding
-Clipping the ulcer
arteriography
embolization for severe and persistent bleeding
GI bleed nursing management
-Monitoring and early recognition of complications
-Preventing and/or managing bleeding, perforation (check dressing for excessive blood)
-Possible surgical treatment
-Monitor lab values
-Testing for gross or occult blood in the stool
-Recording hourly urinary output to detect anuria or oliguria (should be eliminating well)
-Acid-suppressive agents
-NGT insertion-to decompress
-NPO-IVF
will physician let patient eat if they have GI issues
no
-NPO
Gastric Cancer risk factors
-Diet
-H. pylori
-Chronic inflammation
-Pernicious anemia
-Smoking
-Obesity
-Achlorhydria
-Gastric ulcers
-Previous partial gastrectomy
-Genetics
Adenocarcinoma
Begins with lesion in top layer of stomach, penetrates to stomach wall, and metastasis via lymphatic and vascular networks of stomach
CM cancer
-Pain relieved by antacids
-early satiety
-weight loss
-abdominal pain
-loss of appetite
-bloating
-N/V
Assessment and diagnostic findings cancer
-H&P
-EGD for biopsy and cytology
-Barium X-ray of UGI
-CT scan
-CBC
-Tumor markers
medical management of GC
-MULTIMODAL uses all 3
-surgery
-chemo
-radiation
obesity
-abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health
-BMI exceeding 30
-BMI exceeding 40 considered to have severe or extreme obesity
risks for obesity
-complex & multifactorial; behavioral, environmental, physiological, and genetic factors
-Associated with increased risk of mortality
medical management of obesity
-life-style modifications
-pharmacotherapy
-nonsurgical interventions
-bariatric surgery
bariatric surgery
preformed only after nonsurgical methods have failed.
selection criteria for bariatric surgery
-Include BMI >= 40 without excessive surgical risk
-BMI >= 35 and one or more severe associated obesity conditions
-BMI >=30 with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome
-Ability to perform ADL and self-care
-Failure at nonsurgical attempts at weight loss
-Expectations that will adhere to postoperative care, follow-up visits, and recommended medical management
post operative nursing care
-Reducing Anxiety
-Relieving Pain
-Ensuring Fluid Volume Balance
-Prevention Infection/Anastomotic Leak
-Ensuring Adequate Nutritional Status
-Supporting Body Image Changes
-Ensuring Maintenance of Bowel Habits
post op complications/Monitoring and Managing Potential Complications
-Monitoring and Managing Potential Complications
-Hemorrhage
-VTE
-Bile Reflux
-Dumping Syndrome
-Dysphagia
-Bowel and Gastric Outlet Obstruction
Dumping syndrome
Rapid transit of food bolus from stomach into small intestine causes a rapid and exuberant release of metabolic peptides
-associated with sweets and sugars
CM manifestations dumping syndrome
-Symptoms occur 15 minutes – 2 hours after eating
-Tachycardia, dizziness, sweating, N/V, bloating, abdominal cramping, diarrhea
-Symptoms resolve upon defecation
-Reactive hypoglycemia
The RN charge nurse is making assignments. Staffing includes a registered nurse with 5 years of medical-surgical experience, a newly graduated registered nurse, and two unlicensed assistive personnel (UAPs). Which client should be assigned to the most experienced nurse?
1.The 39-year-old client diagnosed with lower esophageal dysfunction reporting pyrosis.
2.The 54-year-old client diagnosed with Barrett’s esophagus scheduled to have an endoscopy this morning
3.The 46-year-old client diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease wheezing in all five lobes
4.The 68-year-old client 3 days postoperative for hiatal hernia needs to be ambulated four times today
3.The 46-year-old client diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease wheezing in all five lobes
The nurse is planning care of a client diagnosed with lower esophageal sphincter dysfunction. Which dietary modifications should be included in the plan of care? Select all that apply.
1.Allow any of the client’s favorite food as long as the amount is limited
2.Have the client perform eructation exercises several times a day
3.Eat four to six meals a day and limit fluids during mealtimes
4.Encourage the client to consume a glass of red wine with one meal a day
5.Maintain an ideal body weight with a healthy diet and exercise
3.Eat four to six meals a day and limit fluids during mealtimes
5.Maintain an ideal body weight with a healthy diet and exercise
A nurse in the emergency department is completing an assessment of a client who has suspected stomach perforation due to a peptic ulcer. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? (Select all that Apply)
A. Rigid abdomen
B. Tachycardia
C. Elevated blood pressure
D. Circumoral cyanosis
E. Rebound tenderness
A. Rigid abdomen
B. Tachycardia
E. Rebound tenderness
A nurse is teaching a client who has a new diagnosis of dumping syndrome following gastric surgery. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
A.Eat three moderate-sized meals a day.
B.Drink at least one glass of water with each meal.
C.Eat a bedtime snack that contains a milk product.
D.Increase protein in the diet.
D.Increase protein in the diet.