Histology and Function of Urinary Organs, Kidney (Nephrons, Collecting Ducts, Ureters, Urinary Bladder, Urethra)
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
what are the major functions of the kidney?
remove metabolic waste from blood
regulate ions + acid/base
endocrine organ
when kidneys remove metabolic waste products from blood, what does heme get broken down into?
heme → bilirubin → urobilin
kidney plays major role in regulation of:
ion balance (Na+, K+, etc.)
acid-base balance
what do kidneys do as an endocrine organ?
regulate blood pressure (renin* secretion by modified smooth muscle cells)
regulate rbc production (erythropoietin* made by interstitial fibroblast-like cells)
activate vitamin D** (in proximal convoluted tubule cells)
which hormones are synthesized and released by the kidney?
renin
erythropoietin
which hormone is synthesized in skin but generated & released by the kidney in its active form?
vitamin D
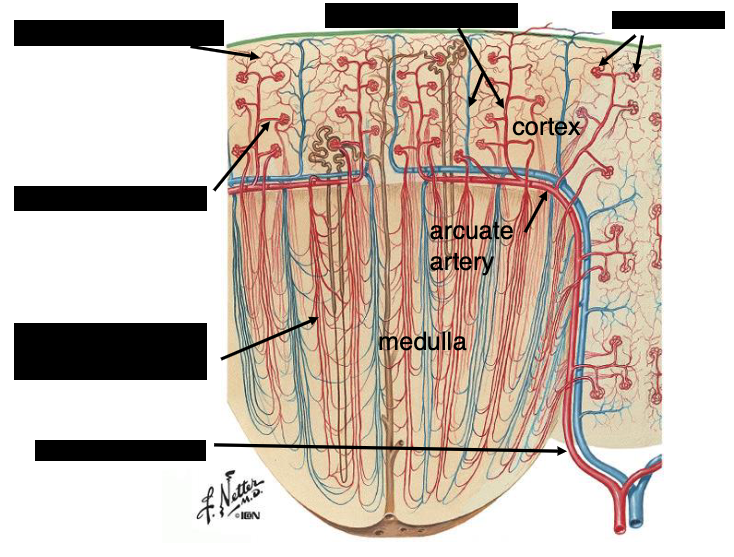
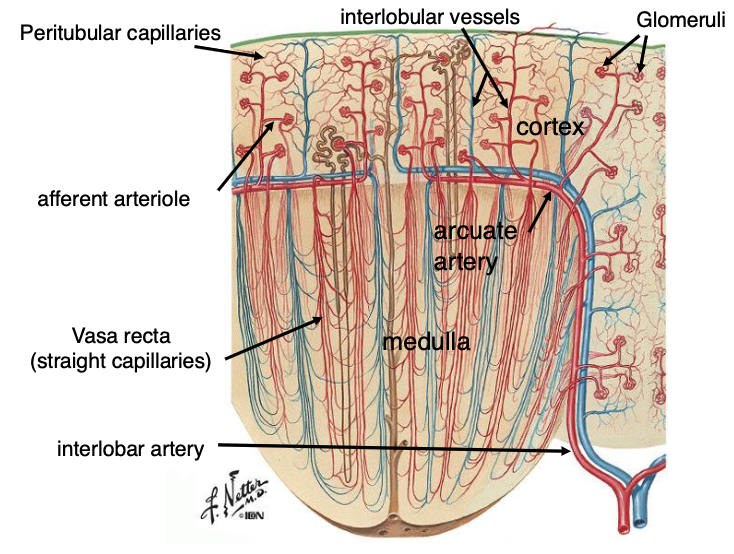
*interlobular vessels
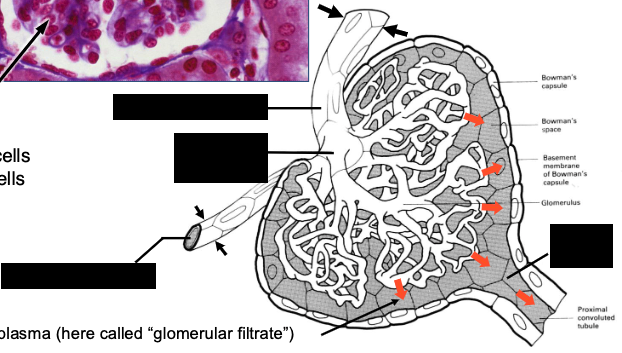
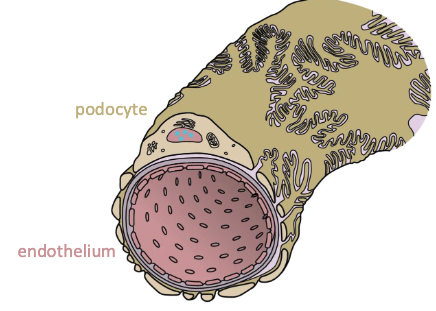
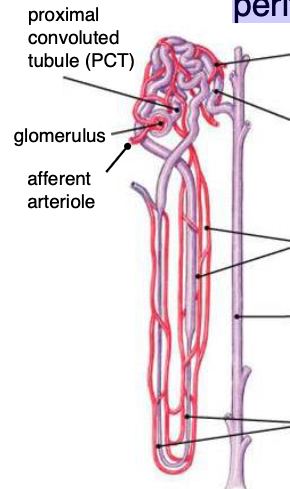
a renal corpuscle consists of…?
glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule (~1 million/kidney)
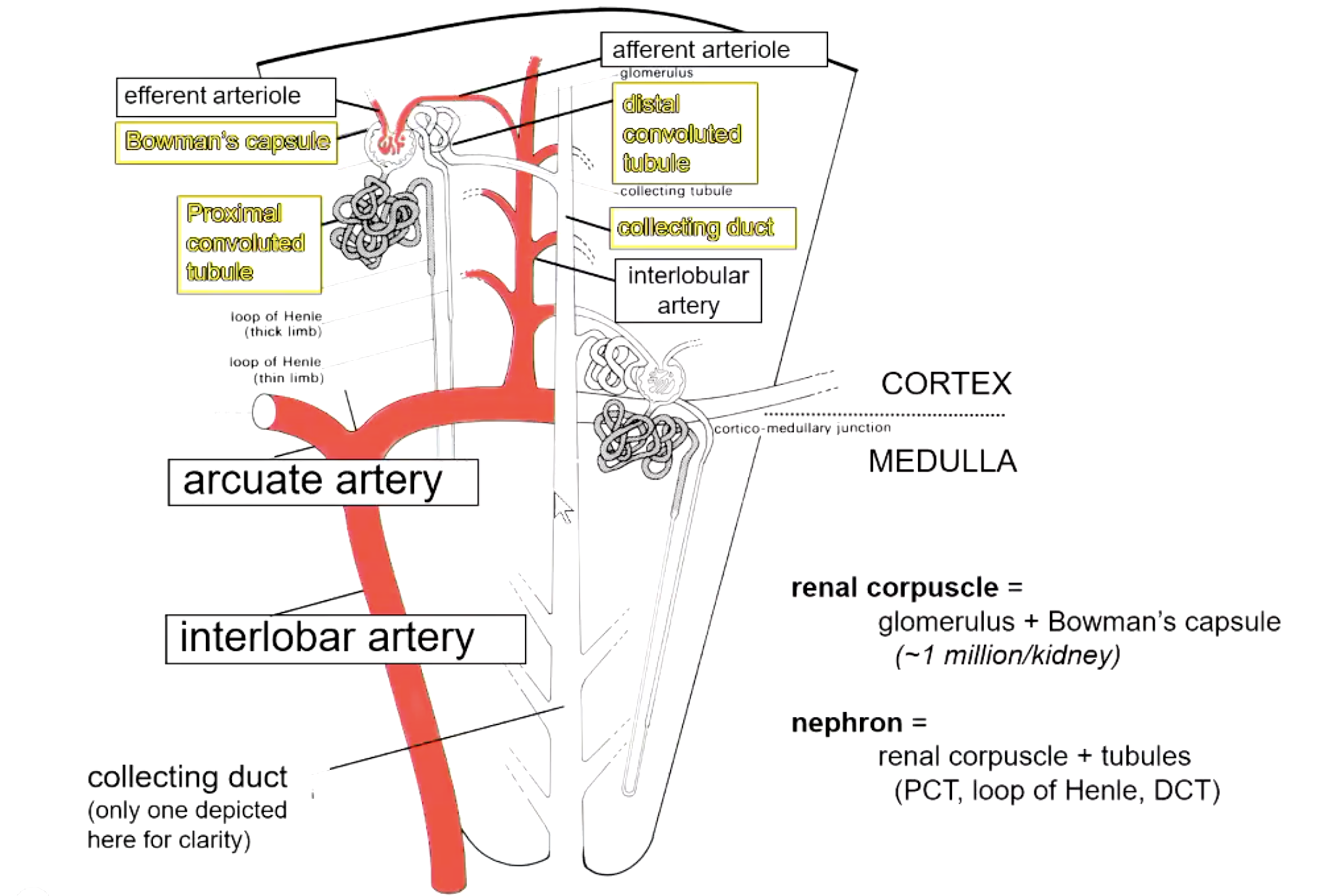
a nephron consists of…?
renal corpuscle + tubules (PCT, loop of Henle, DCT)
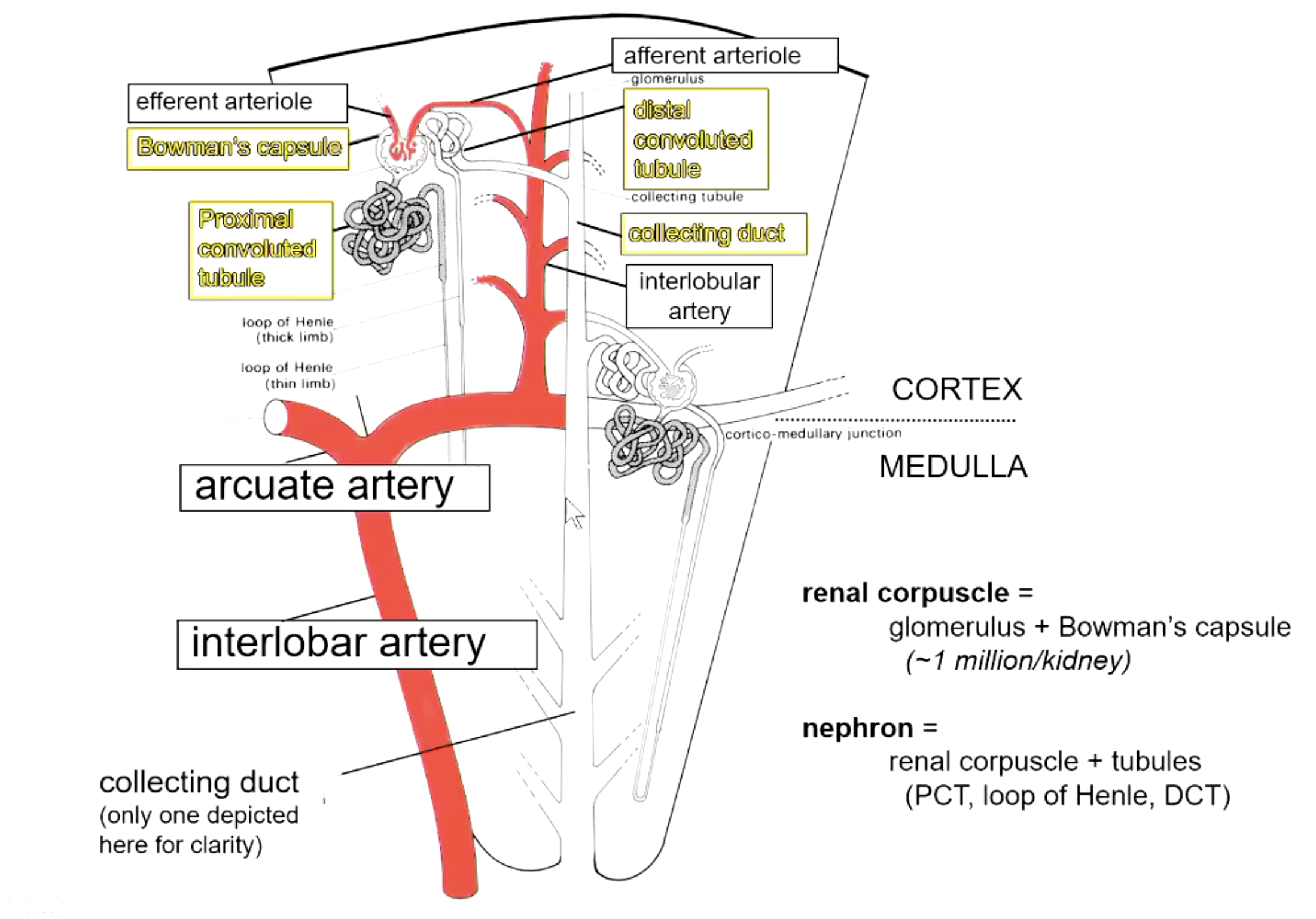
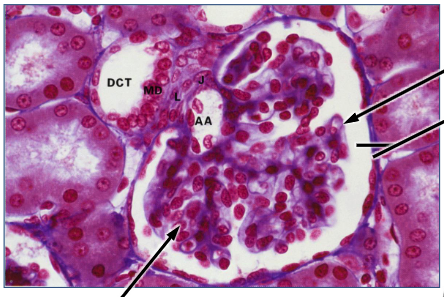
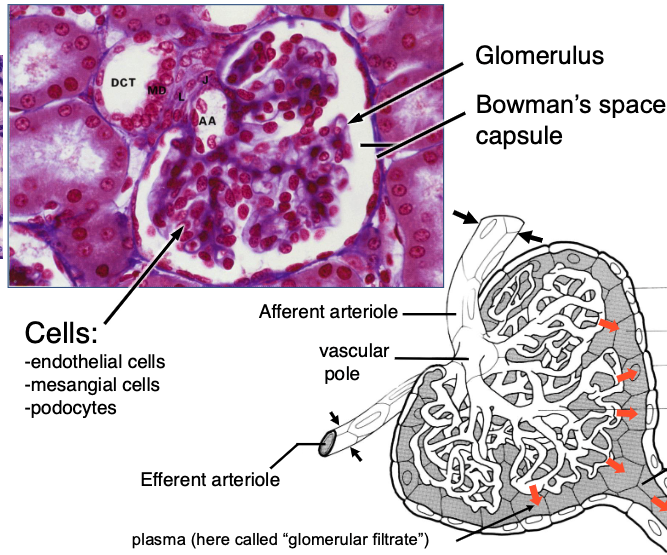
which diameter is larger? afferent vs efferent arteriole
afferent
because helps force fraction of plasma that goes into Bowman’s space
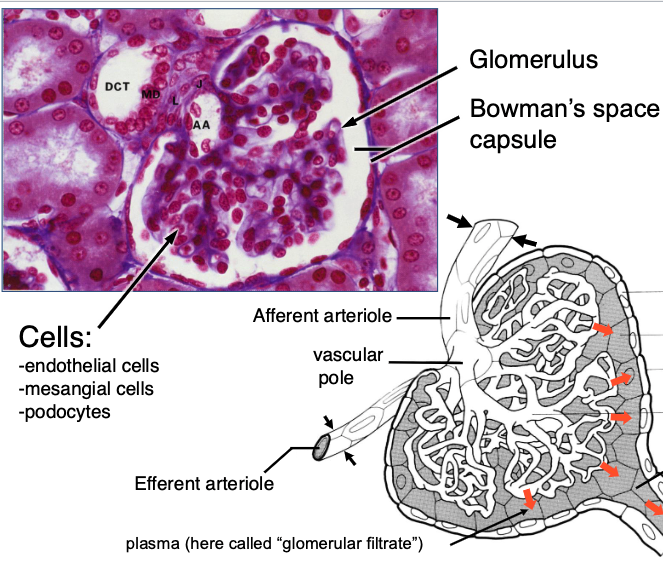
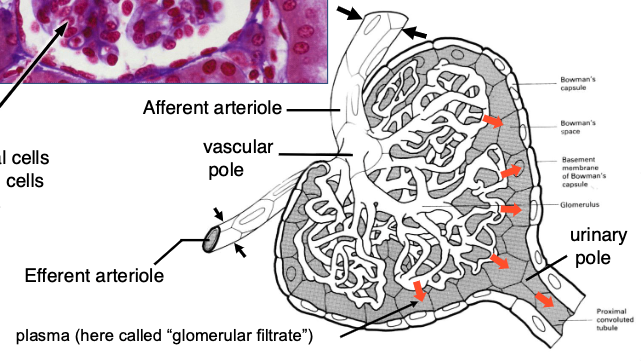
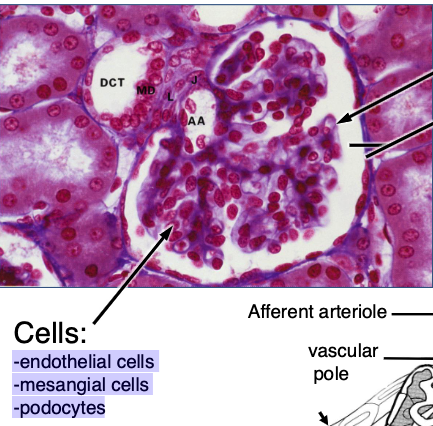
what types of cells are found in the glomerulus?
-endothelial cells
-mesangial cells
-podocytes
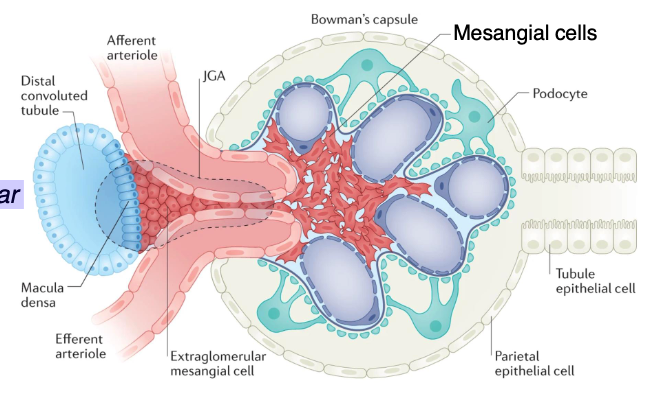
these are the functions of what type of cells?
-support
-phagocytosis
-repair
-contractile
-blood pressure monitoring (i.e. part of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
mesangial cells
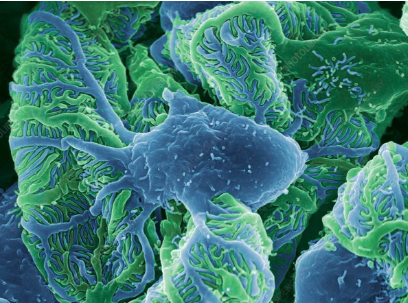
podocyte
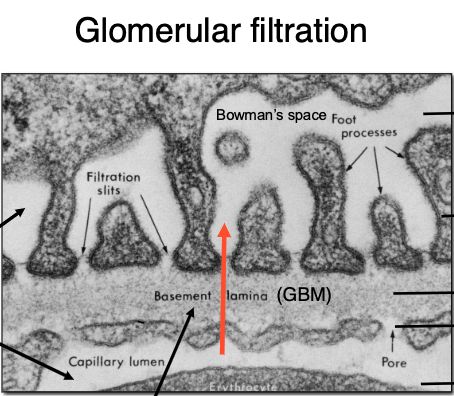
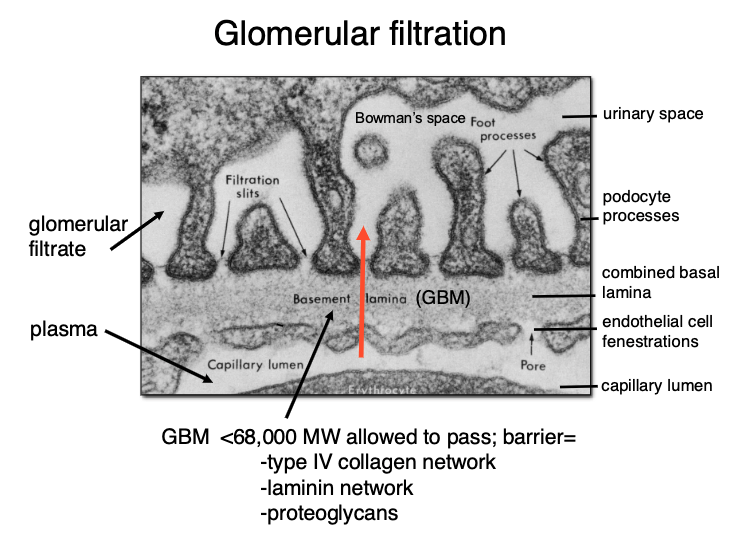
the glomerular basement membrane allows things <68,000 MW to pass. the barrier is composed of…?
-type IV collagen network
-laminin network
-proteoglycans
water and nutrients get reabsorbed into…?
peritubular capillaries
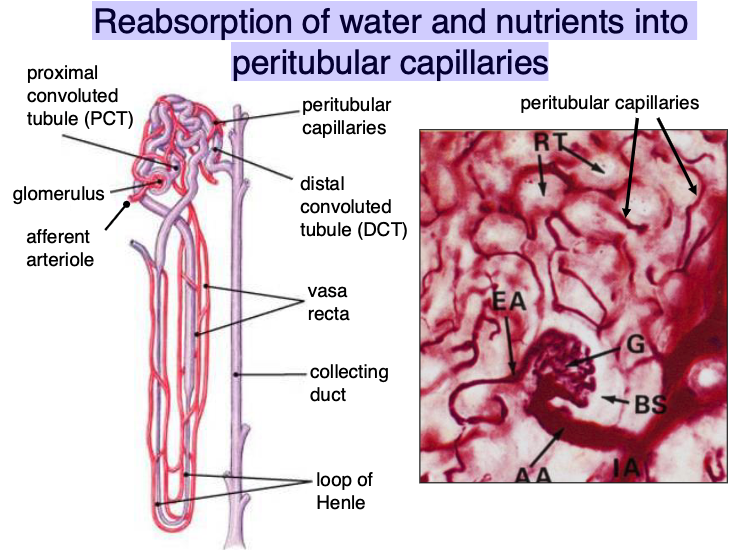
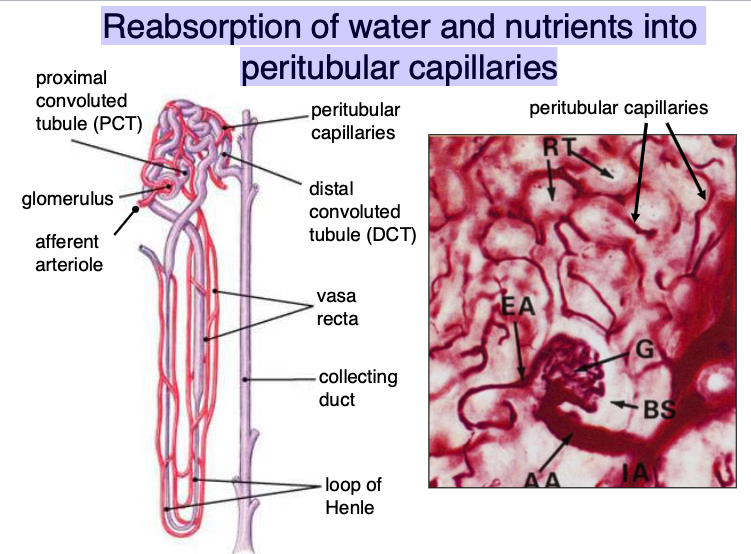
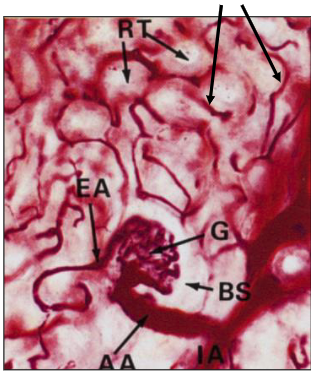
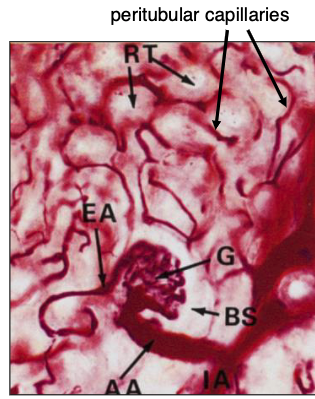
what does the proximal convoluted tube reabsorb?
80% of ultrafiltrate (analagous to small intestine)
what does the distal convoluted tube reabsorb?
mostly ions (analagous to large intestine)
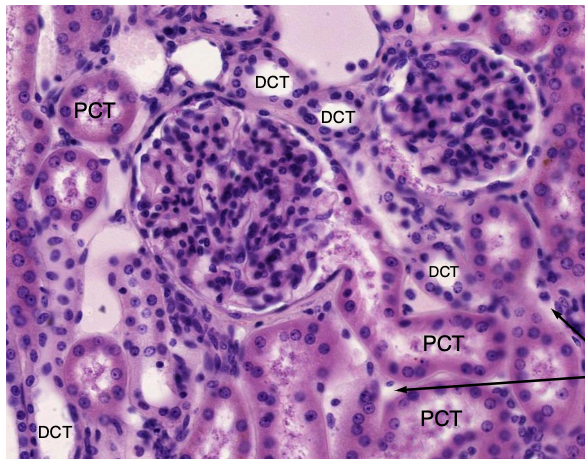
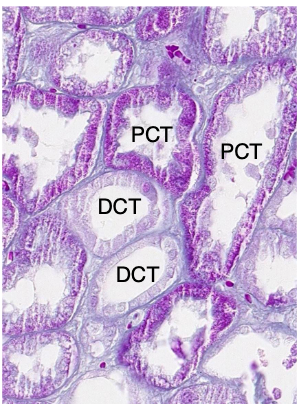
which convoluted tube has a brush border and abundant mitochondria?
PCT
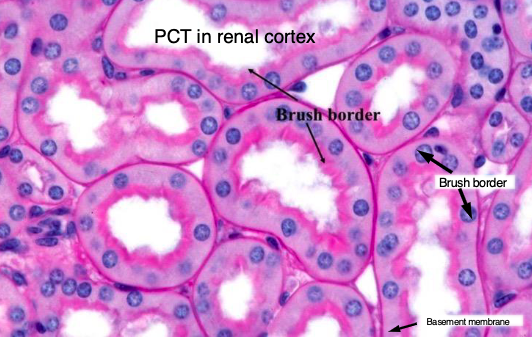
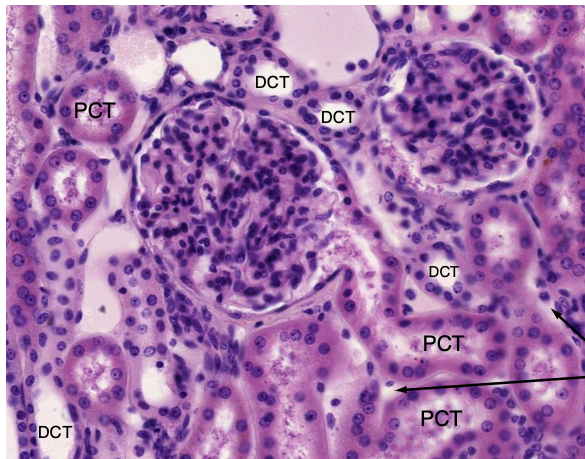
which convoluted tube has no brush border and fewer mitochondria?
DCT
what is the ratio of PCT:DCT?
3:1
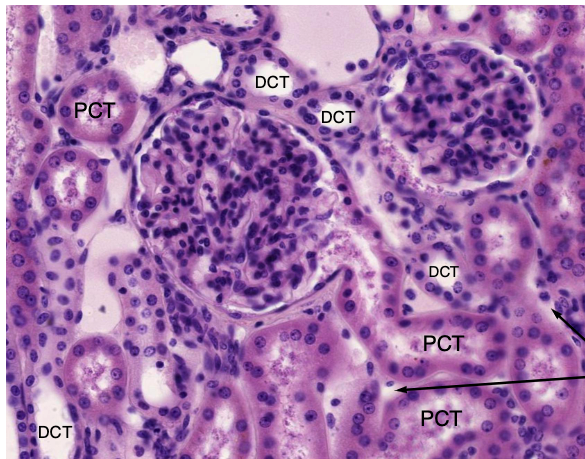
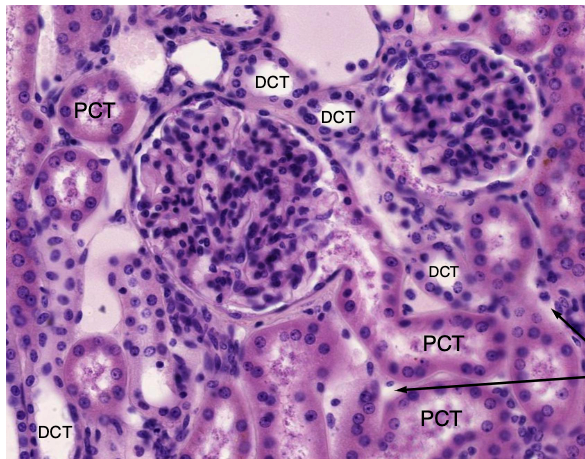
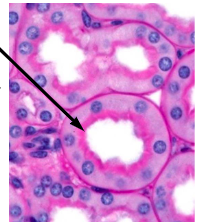
arrows pointing to peritubular capillaries
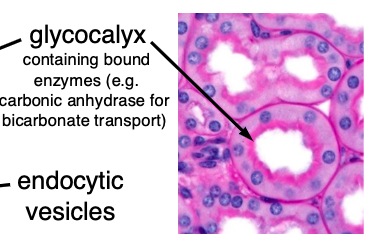
Renal PCTs possess brush borders with a _______ to facilitate reabsorption; waste products are not actively removed, they are just not selected
glycocalyx
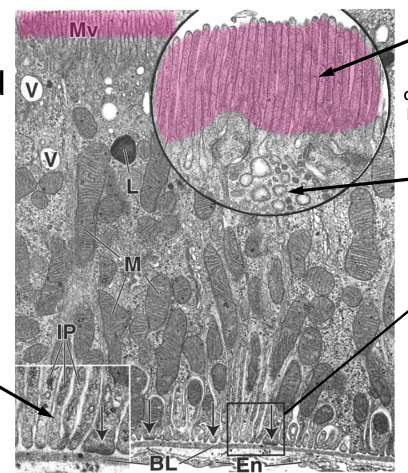
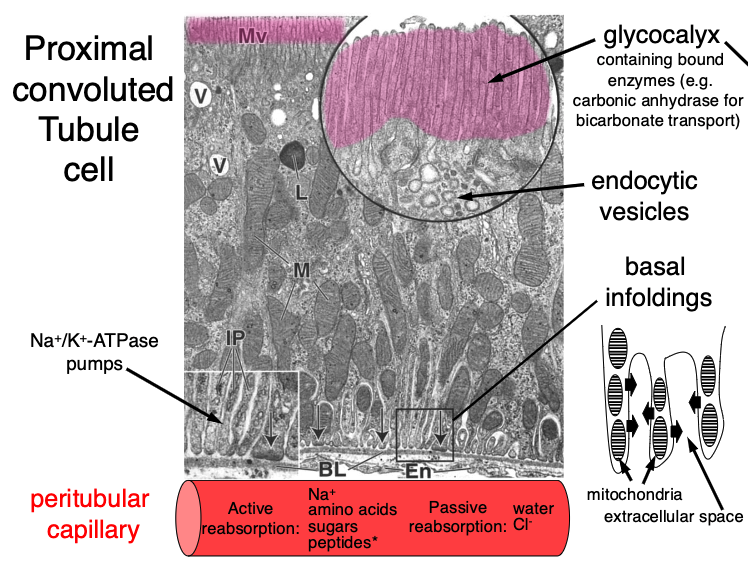
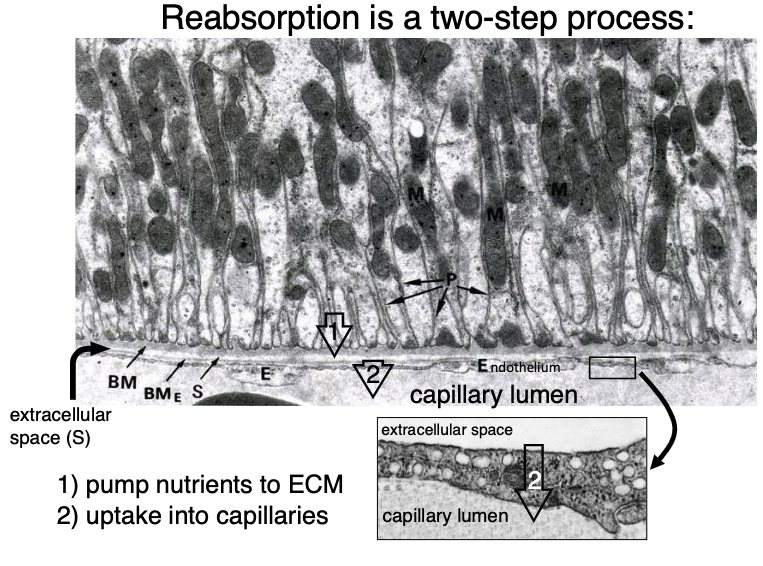
reabsorption is a 2 step process:
pump nutrient to ECM
uptake into capillaries
what is being actively reabsorbed into peritubular capillaries in PCT?
Na+
amino acids
sugars
peptides (by endocytosis)
what is being passively reabsorbed into peritubular capillaries in PCT?
water
Cl-
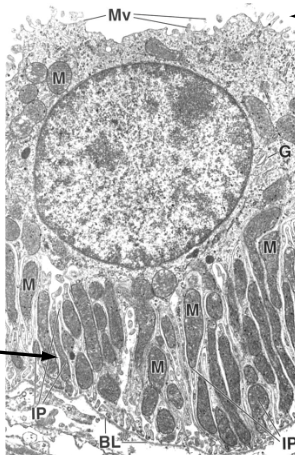
distal convoluted tubule cell
what is being reabsorbed into peritubular capillaries in DCT?
Na+
Na+/K+-ATPase in DCT are senstivie to…?
aldosterone (regulated by angiotensin II)
what is the function of the renal medulla?
-generation of salt gradient
-resorption of water
-acid-base balance
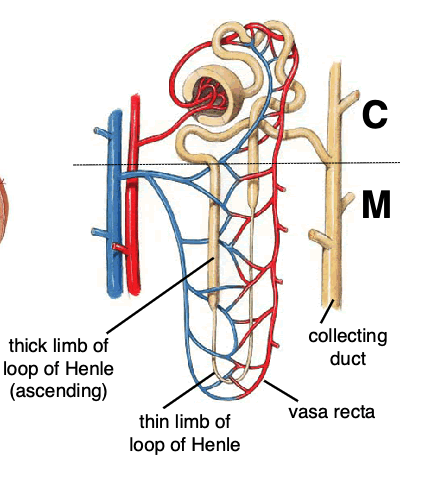
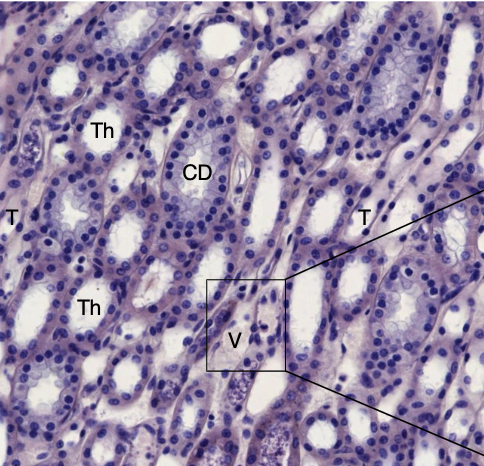
T – thin loop of Henle (moves plasma)
Th -thick limb of loop of Henle
V – vasa recta (moves blood)
CD – collecting duct
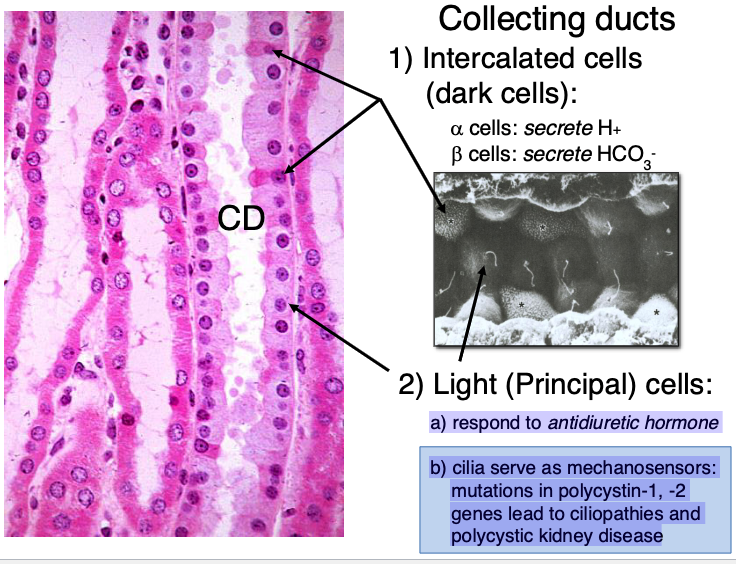
what type of cells are found in collecting ducts?
intercalated cells (dark cells)
light (principal) cells
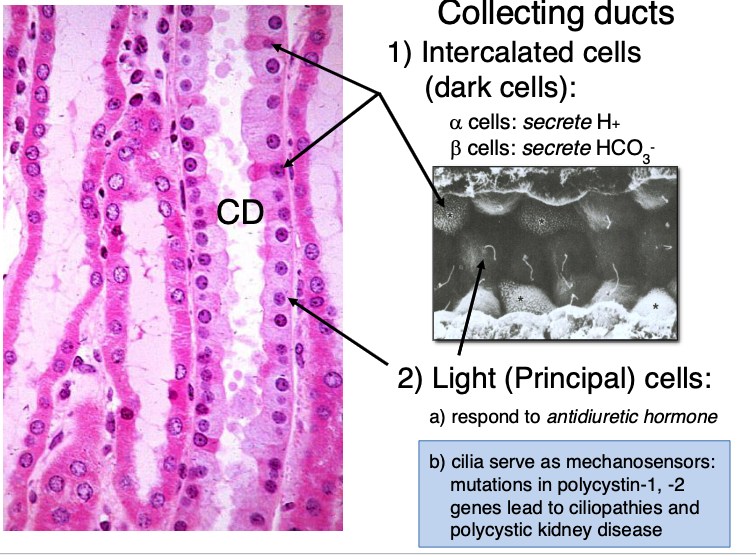
there are alpha and beta intercalated/dark cells. what do each secrete?
alpha cells: secrete H+
beta cells: secrete HCO3-
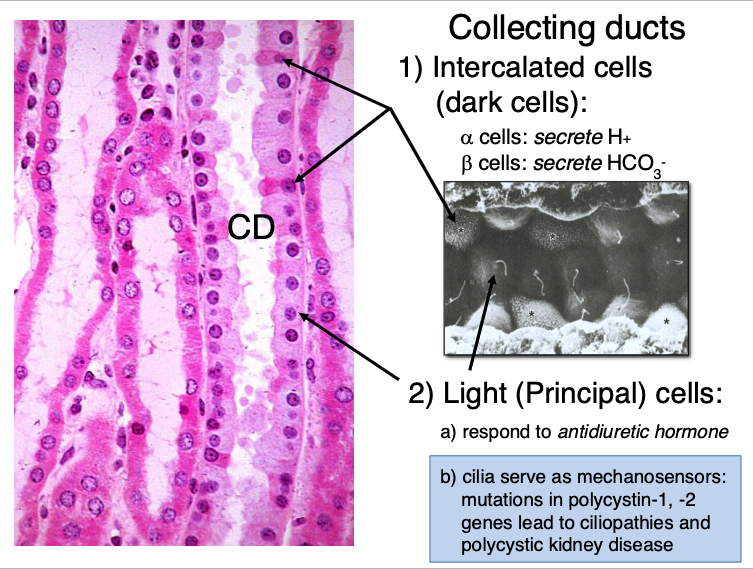
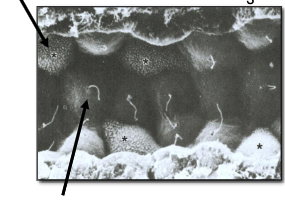
what do light (principal) cells in collecting ducts do?
a) respond to antidiuretic hormone
b) cilia serve as mechanosensors: mutations in polycystin-1, -2 genes lead to ciliopathies and polycystic kidney disease
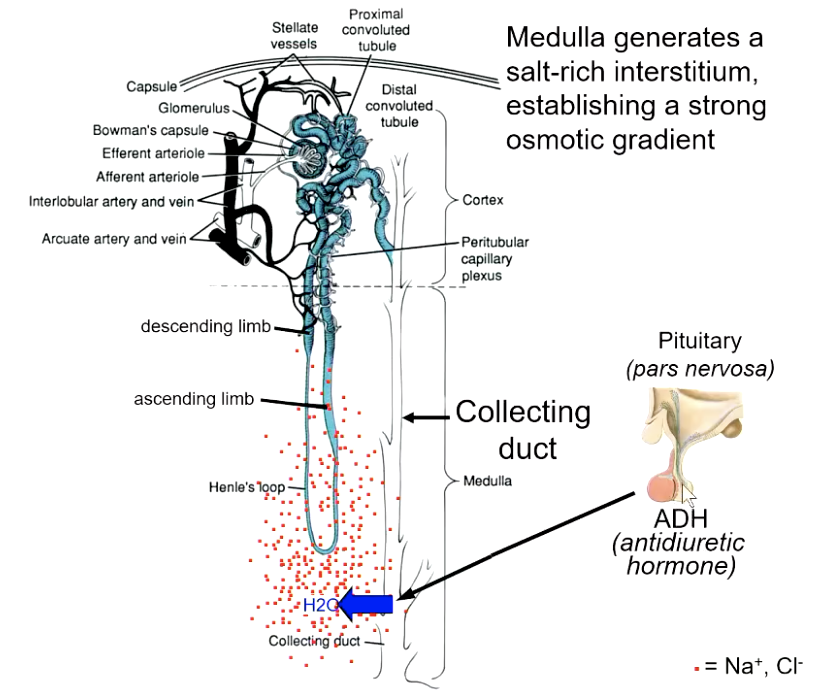
Medulla generates a ________, establishing a strong osmotic gradient
salt-rich interstitium (whole point is to concentrate urine)
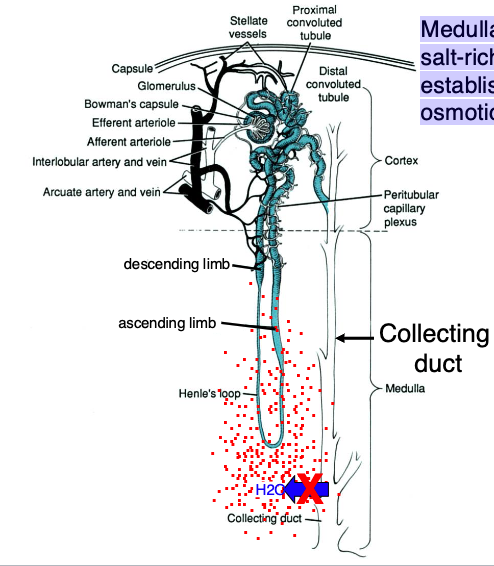
how does alcohol affect the collecting duct / urine concentration system?
prevents release of ADH which keeps collecting duct channels closed (pass much more diluted urine that u should = hangover)
collecting duct cells in the medulla are not normally permeable to water. to become permeable, they require…?
antidiuretic hormone (ADH) released by posterior pituitary
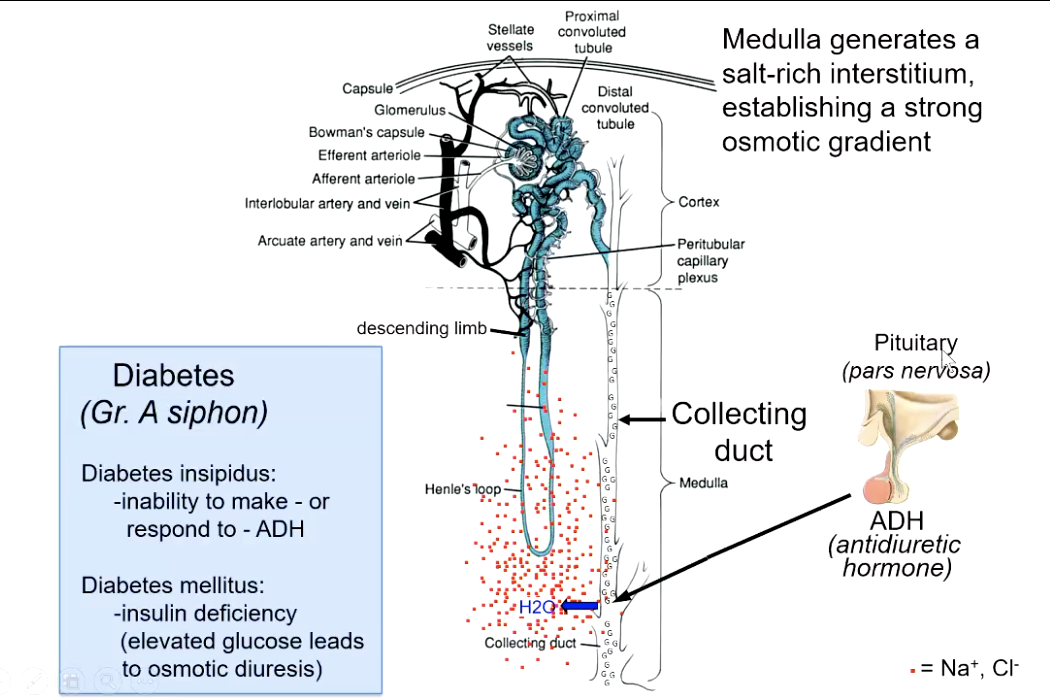
what condition is the inability to make or respond to ADH?
diabetes insipidus (pass diluted urine)
what is the condition caused by insulin deficiency which elevates glucose levels leading to osmotic diuresis?
diabetes mellitus
glucose is also osmotic (cancels out the salt gradient leading to passing of diluted urine)
kidney stones or renal calculi are crystals that form from…?
calcium oxalate (80% of cases)
or
uric acid precipitates
kidney stones (renal calculi) can be caused by…?
low fluid intake, high protein diets, refined sugars
blockage of urine outflow caused by kidney stones may lead to
hydronephrosis
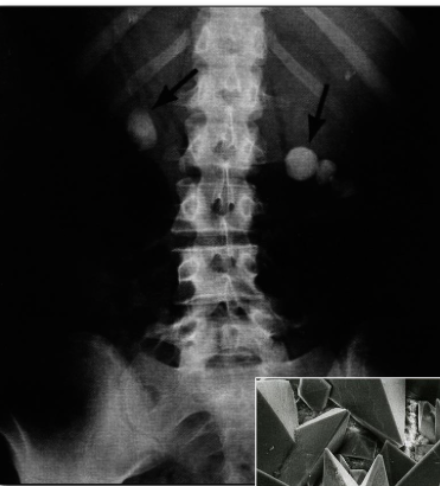
kidney stones
blood pressure monitoring is done via:
arterial pressure in afferent arteriole
ion concentration in DCT
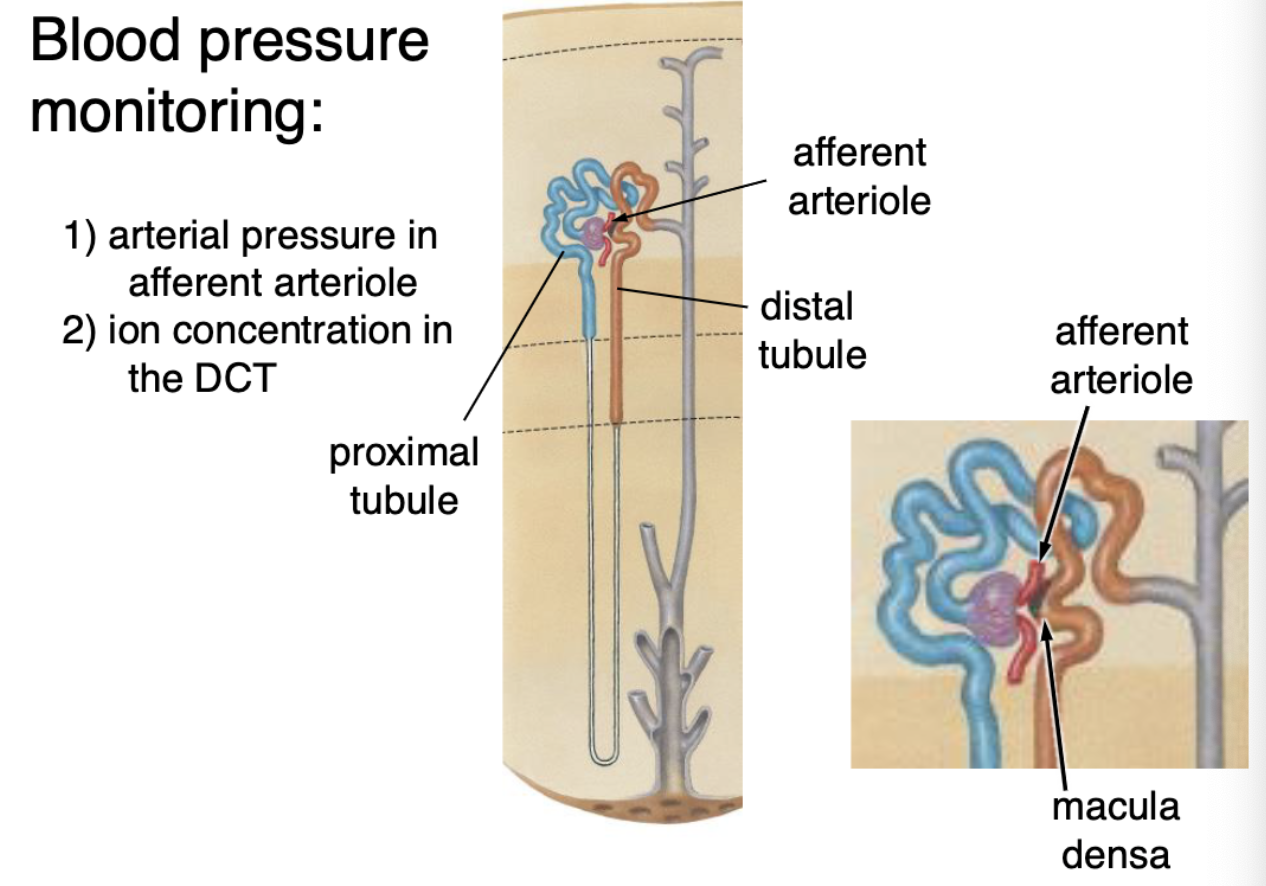
what cells make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
JG cells
macula densa
lacis cells
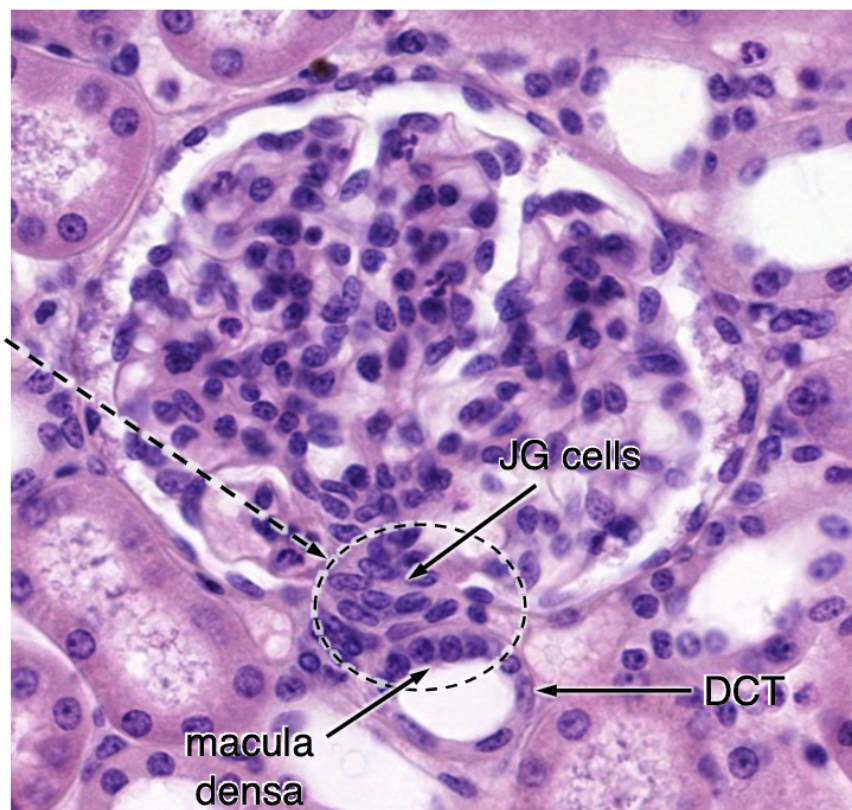
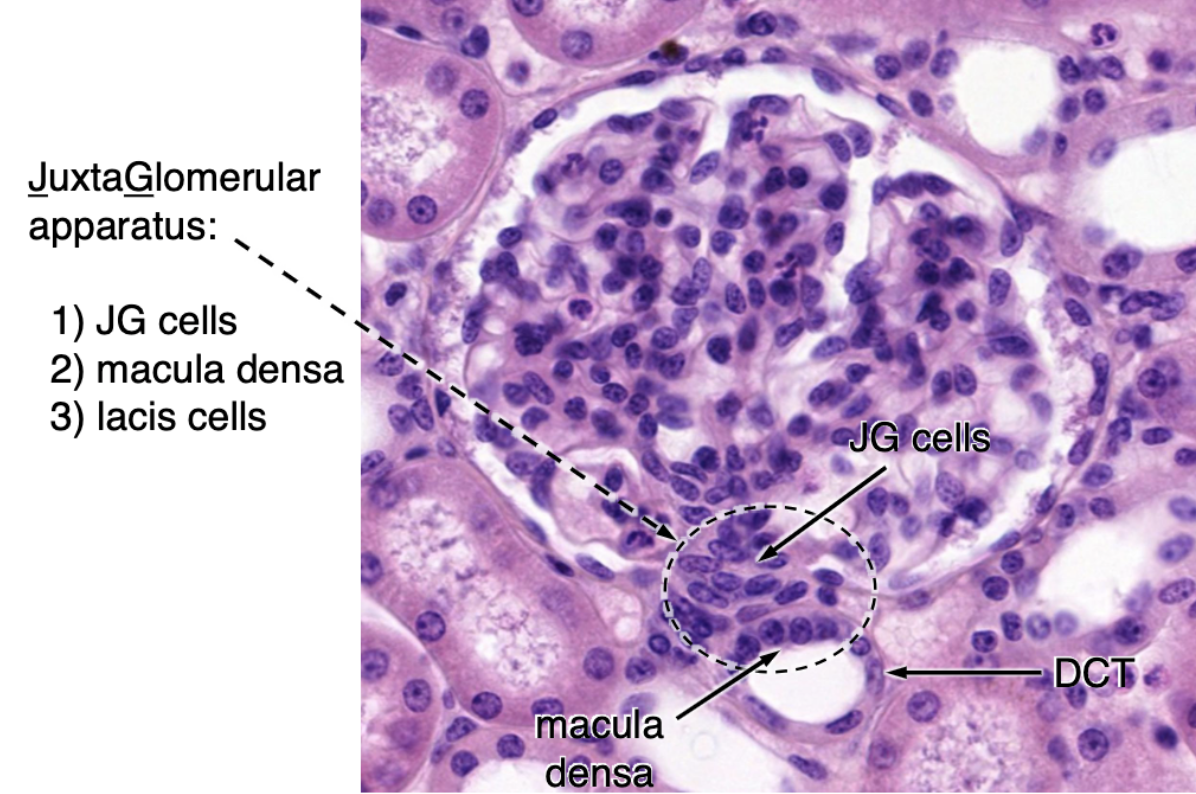
macula densa responds to…?
low salt concentration (chemoreceptors)
juxtaglomerular (JG) cells respond to…?
arterial pressure (baroreceptors)
when salt concentration is low, macula densa cells send a signal to ______ cells to release ______.
juxtaglomerular (JG) cells (which are modified smooth muscle cells) to release renin
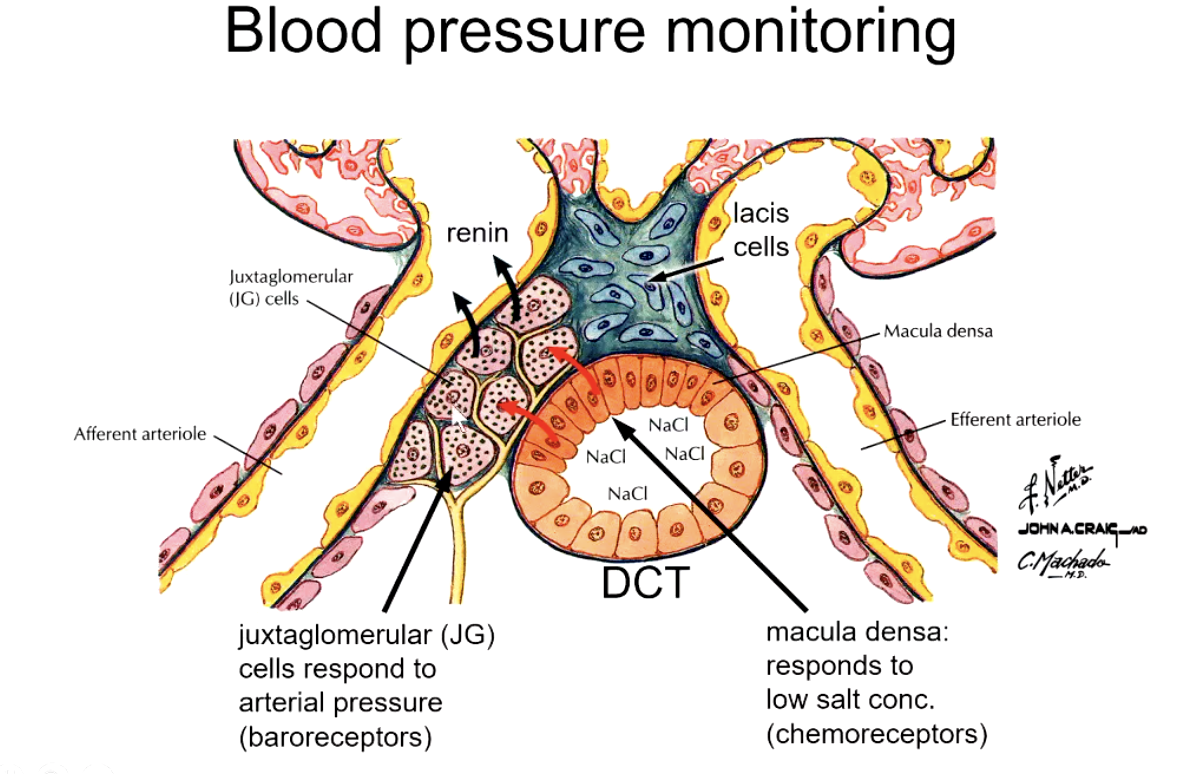
when arterial pressure is low, juxtaglomerular cells release ________
renin
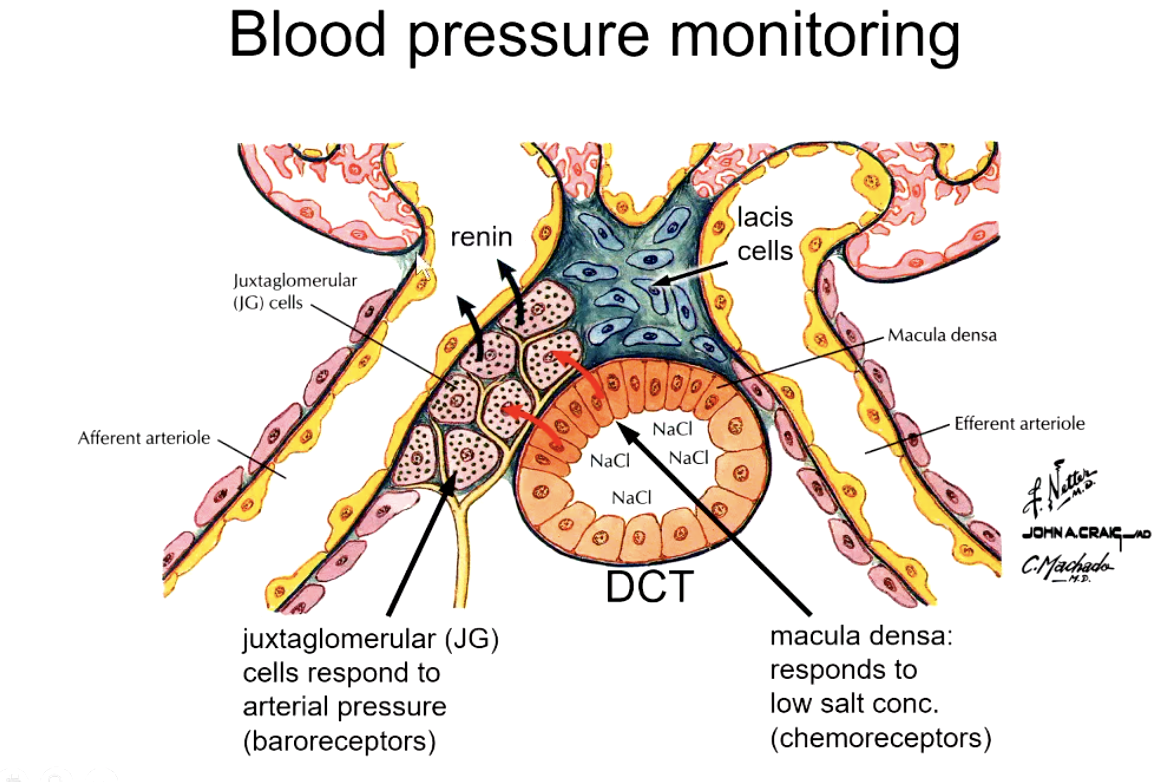
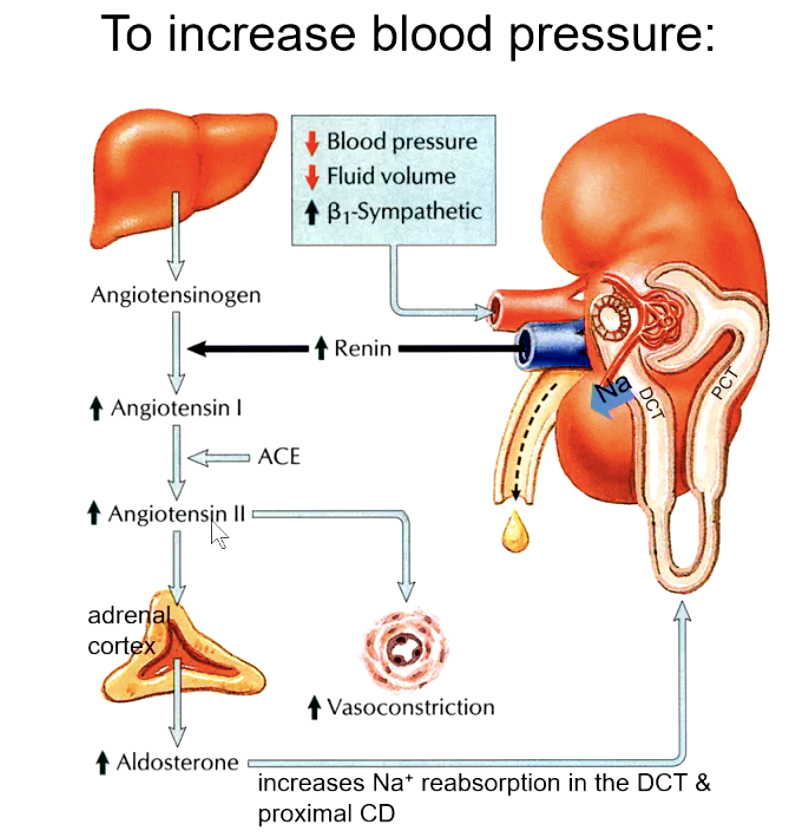
how does renin increase blood pressure?
renin cleaves angiotensinogen into angiotensin I
ACE cleaves 2 AAs off of angiotensin I to turn into angiotensin II
angiotensin II increases vasoconstriction AND stimulates adrenal cortex to increase aldosterone levels
Na+ reabsorption in the DCT and proximal CD increases
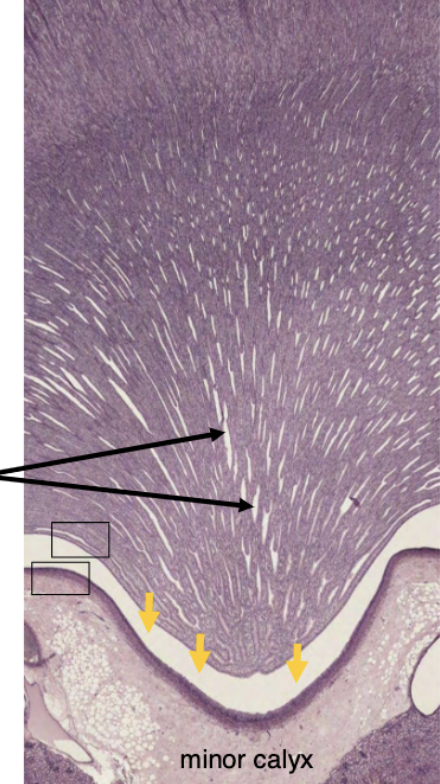
collecting ducts
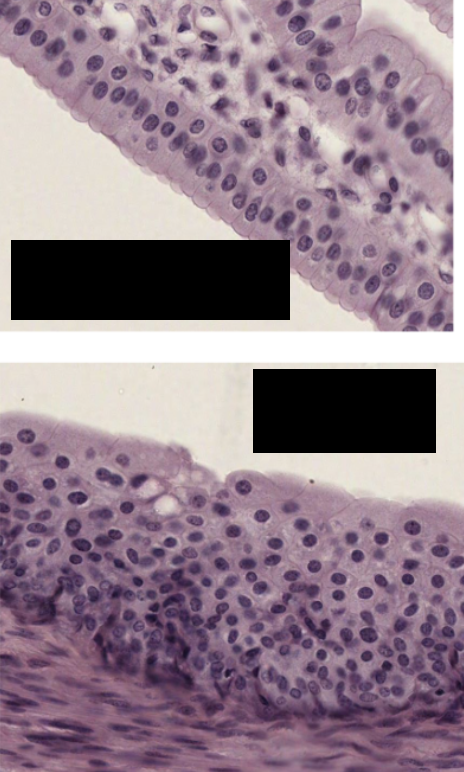
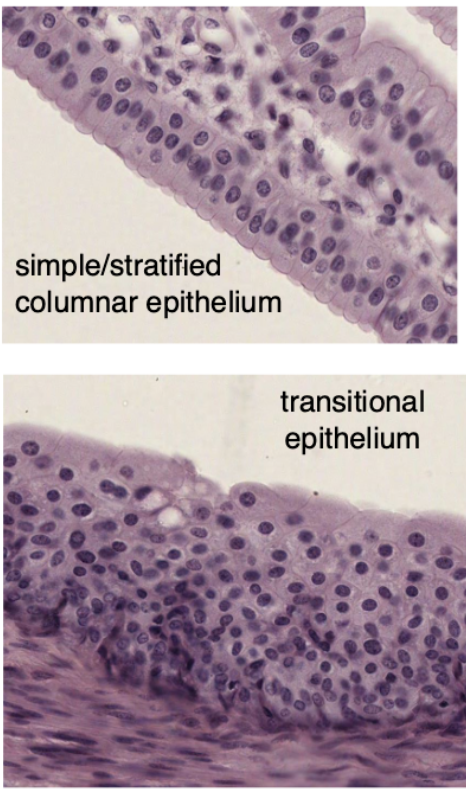
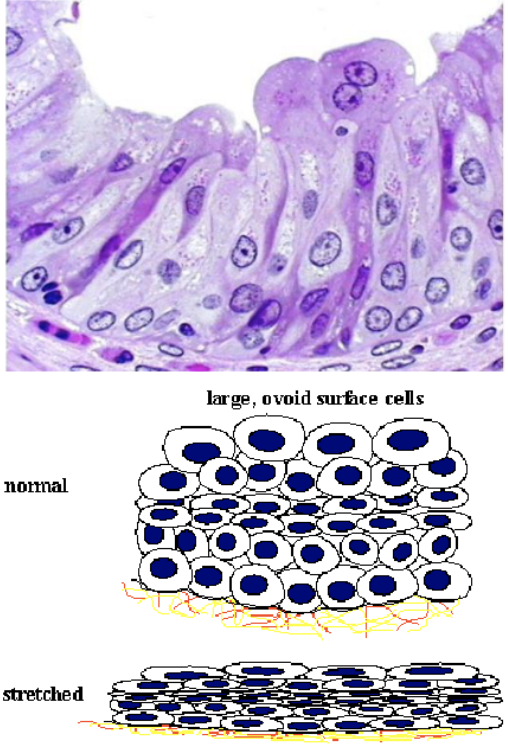
transitional epithelium (urothelium)
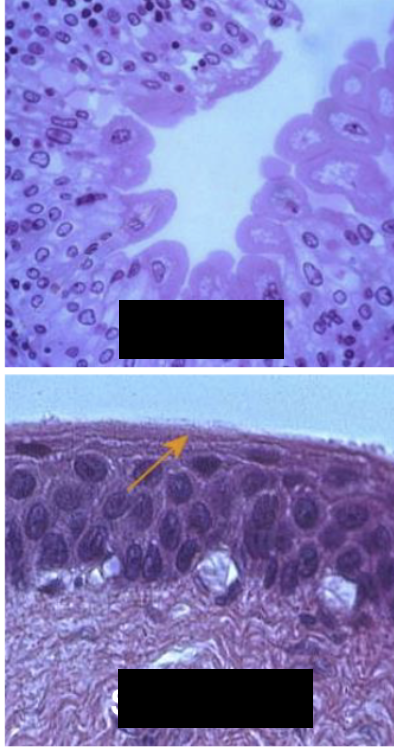
Transitional epithelium (urothelium)
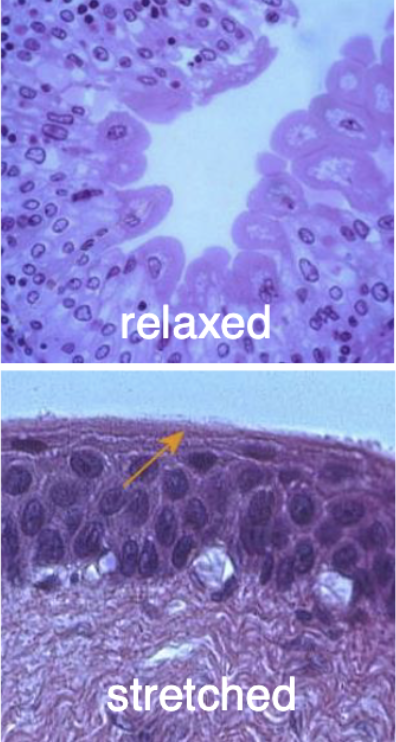
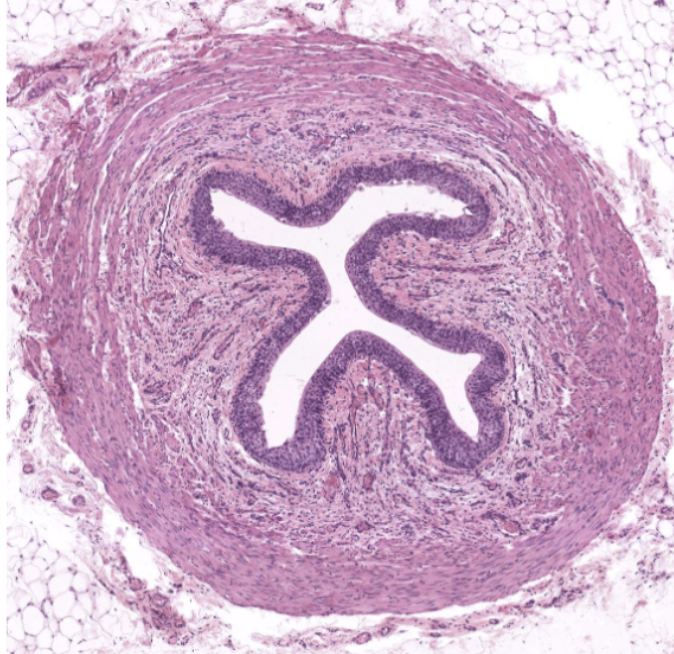
histological characteristics of ureter
transitional epithelium
no muscularis mucosae
3 layers in muscularis externa (distal portion only)
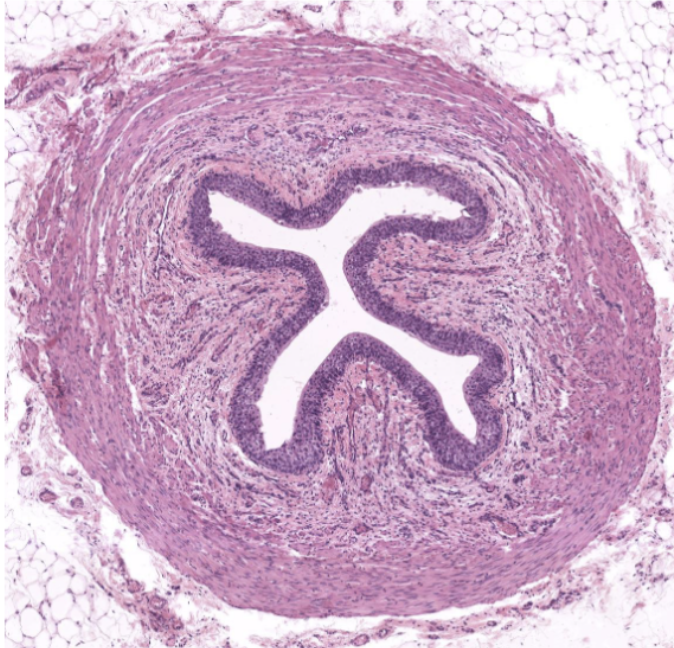
ureter
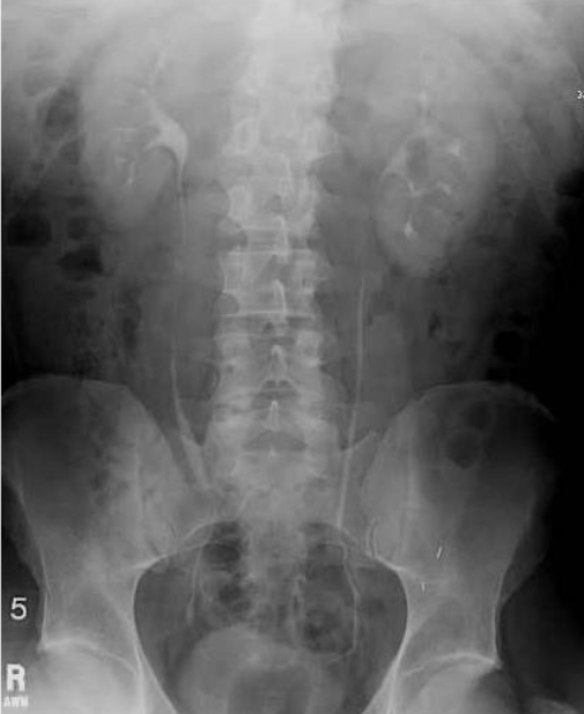
(where do kidney stones tend to get stuck most often?)
intravenous pyelogram (shows route of urine from kidneys through ureter into bladder)
bend as ureter enters pelvis!
What types of cells primarily make up the kidney, and what are the non-epithelial cells present?
mostly comprised of simple cuboidal epithelial cells for tubules and simple squamous cells for vasculature
Non-epithelial cells = smooth muscle cells, mesangial cells, and a few fibroblasts.
What type of connective tissue is found in the kidney?
Very little supporting connective tissue is present, but there is a dense connective tissue capsule surrounding the kidney.
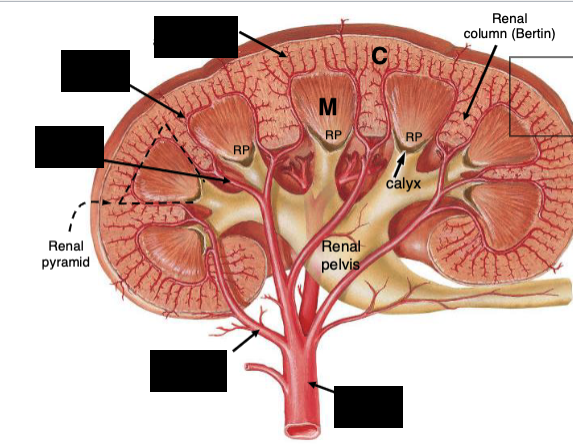
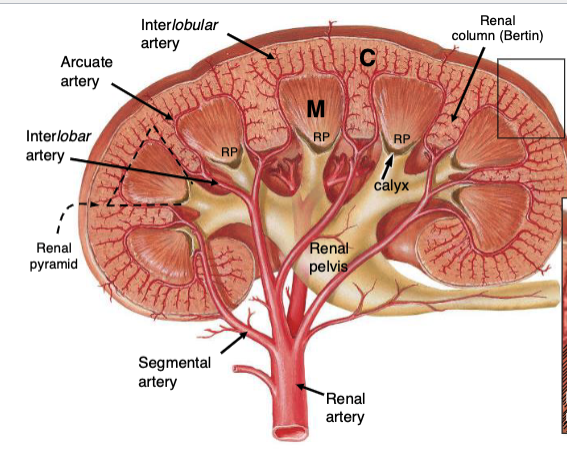
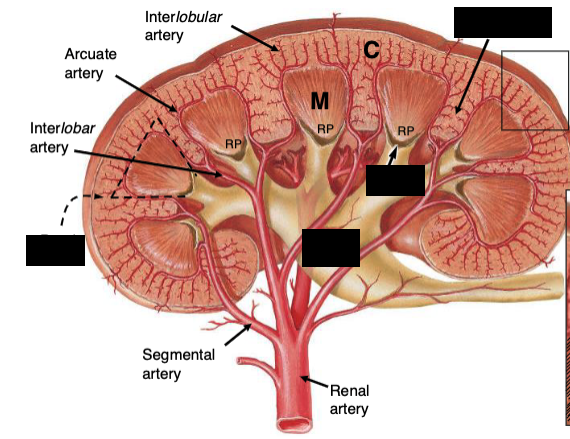
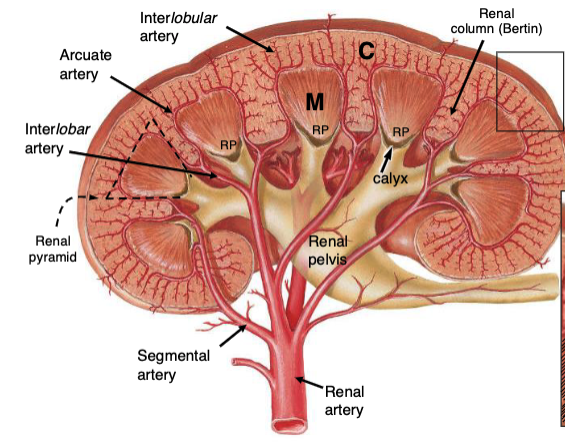
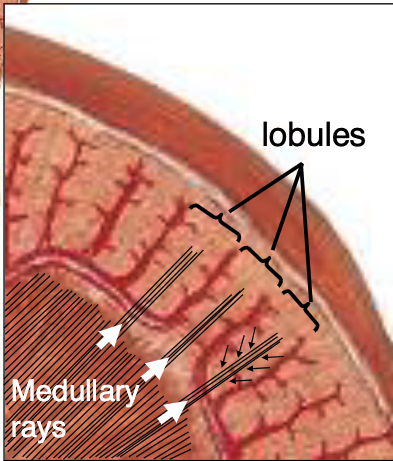
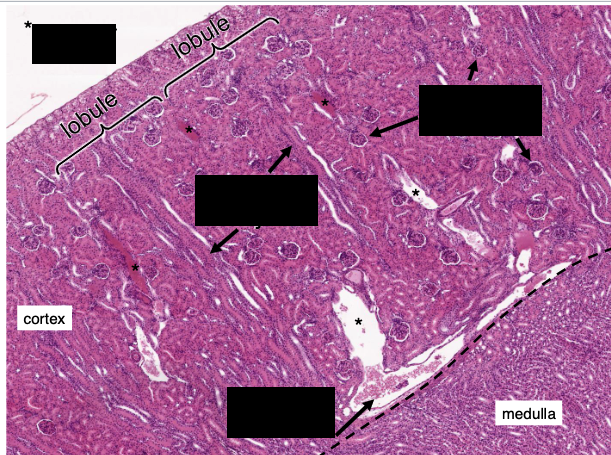
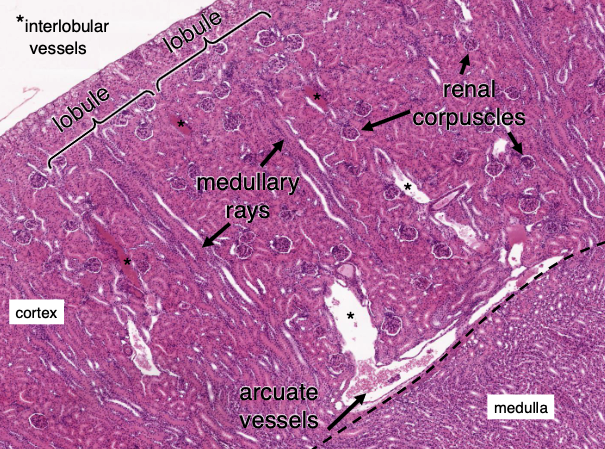
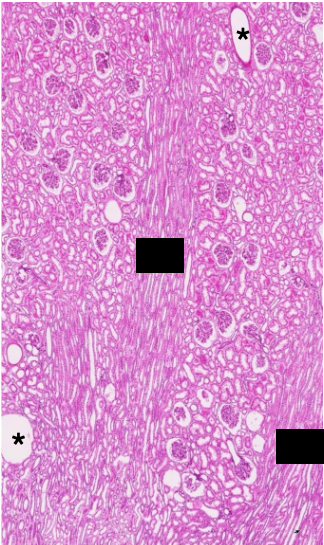
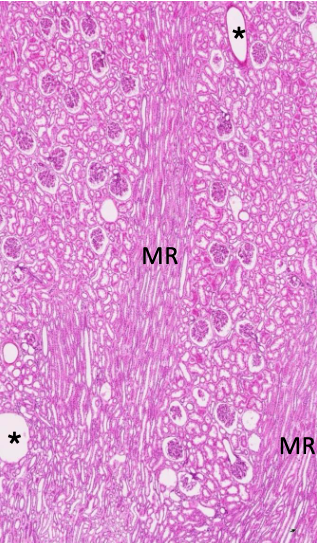
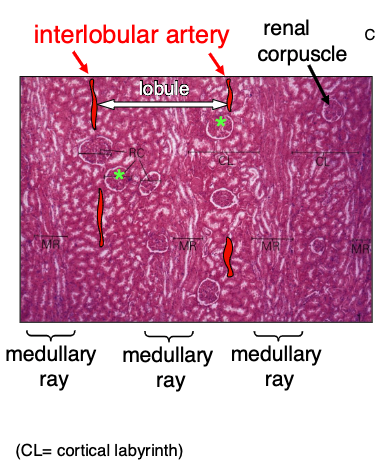
How is the renal cortex organized?
Lobules are defined by interlobular vessels (branches of arcuate vessels) and have a central medullary ray containing proximal collecting ducts and parts of the loop of Henle
The lobular arrangement in the renal cortex is analagous to…?
analogous to exocrine glands, with secretory cells (tubules) and a central duct (collecting system); the cortex produces provisional urine
What structures dominate the renal cortex and medulla by volume?
cortex contains mostly convoluted tubules (proximal:distal ratio of 3:1), renal corpuscles, and peritubular capillaries
medulla contains straight tubules (collecting ducts, loops of Henle, vasa recta)
What is the role of the glomerulus in filtration?
filters plasma into Bowman’s capsule through capillary loops supported by podocytes (with foot processes for filtration slits) and mesangial cells (which are supportive, contractile, and phagocytic).
What cells contribute to the glomerular basement membrane and filtration slits?
Podocytes, through their interdigitating foot processes
What is the primary role of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Most reabsorption of filtered substances happens here, aided by abundant microvilli and glycocalyx on the apical surface, and basal transport to the extracellular matrix for uptake by peritubular capillaries
How does the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) differ from the PCT in structure and function?
DCT lacks microvilli and glycocalyx, focuses on ion reabsorption, and has fewer mitochondria than the PCT, giving it a clearer cytoplasm
What hormone influences the DCT and proximal collecting ducts, and what is its effect?
Aldosterone; it increases sodium reabsorption and water retention, raising blood pressure
What are the three cell types in collecting ducts, and what are their functions?
Dark (intercalated) cells:
α-cells secrete protons
β-cells secrete bicarbonate
Principal (light) cells: water permeability is regulated by ADH.
What are the components of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)?
Macula densa cells: salt chemosensors in the DCT
Juxtaglomerular (JG) cells: baroreceptors in the afferent arteriole releasing renin
Lacis cells: extraglomerular mesangial cells, likely smooth muscle, possibly producing renin
What triggers renin release from the JGA?
Low salt (detected by macula densa) or low blood pressure (detected by JG cells); also stimulated by sympathetic nerve fibers
What happens to urine after it leaves the renal papilla?
It enters the renal calyces and is no longer modified
What type of epithelium lines the renal calyces, pelvis, ureters, bladder, and proximal urethra?
Transitional epithelium, also known as urothelium