Cholesterol and lipoproteins
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Explain cholesterol structure in regards to plasma
esterified form with fatty acid attached at carbon 3
Explain cholesterol structure
4-ringed steroid nucleus, hydroxyl group attached to first ring, and short hydrocarbon side chain at the other end
what is cholesterol
structural component of all cell membranes, modulating their fluidity. and precursor of bile acids/steroid hormones/vit D
What is the role of NPC1L1 in regards to cholesterol
mediates uptake of cholesterol from intestine into enterocytes and hepatic reuptake of cholesterol from bile into hepatocytes
What is the role of ABCG5/8 in regards to cholesterol
regulate cholesterol levels via pumping cholesterol out of liver cells into bile and out of intestinal cells back into gut lumen
What inhibits NPC1L1 resulting in reduce absorption of dietary cholesterol
Ezetimibe
What is Sitosterolemia (aka phytosterolemia)
autosomal recessive disorder associated with defects in ABCG5/8 transporter
Where are cholesterol esters found
only at low levels in most cells
How is cholesterol and its esters transported
as a component of lipoprotein particle or solubilized by phospholipids and bile salts in bile
What tissues/organs synthesize the most cholesterol
liver, intestine, adrenal cortex, and reproductive tissue
Explain cholesterol biosynthesis
all carbon atoms in cholesterol are provided via acetyl CoA
NADPH provide reducing equivalents
pathway endergonic, driven by hydrolysis of higher energy thioester bond of acetyl CoA and terminal phosphate bond of ATP
requires enzymes in cytosol, sER membrane and peroxisome
responsive to changes in cholesterol concentration and regulatory mechanisms exist to balance rate of cholesterol synthesis against rate of cholesterol excretion
What can an imbalance of cholesterol regulation lead to
elevation in circulating levels of plasma cholesterol with potential for vascular disease
What is 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthesis
two acetyl CoA molecules condense = acetoacetyl CoA
third molecule of acetyl CoA is added via HMG CoA synthase = HMG CoA six carbon compound
liver parenchymal cells contain two isoenzymes of synthase
cytosolic enzyme participate in cholesterol synthesis
mitochondrial enzyme function in pathway for ketone body synthesis
What is mevalonate synthesis
HMG CoA reduce to mevalonate via HMG CoA reductase (rate limiting and key regulated step in cholesterol synthesis)
uses 2 NADPH molecules as reducing agent and release CoA making reaction irreversible
HMG CoA reductase is an integral membrane protein of sER with its catalytic domain projecting into cytosol
Where in the cell does mevalonate synthesis occur
cytosol
how many molecules of NADPH is used during mevalonate synthesis
2
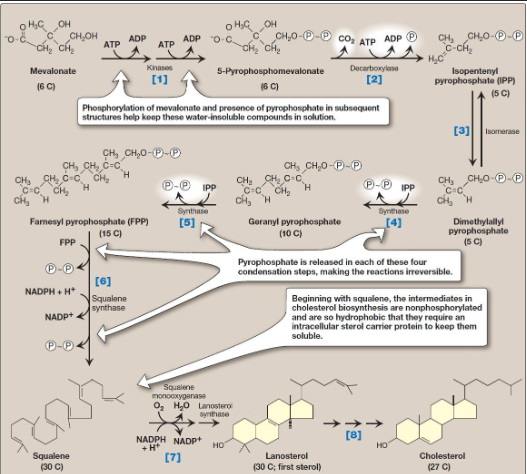
What type of synthesis is shown
cholesterol synthesis from mevalonate
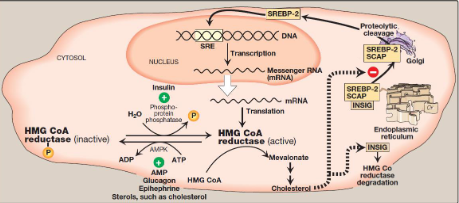
What does the image show
Cholesterol synthesis regulation
what are the 3 hormonal regulation components in cholesterol synthesis regulation
insulin
glucagon
epinephrine
what are the 2 sterol-independent phosphorylation/dephosphorylation components in cholesterol synthesis regulation
AMPK
phosphoprotein phosphatase
What is the sterol-dependent regulation of gene expression and sterol-accelerated enzyme degradation involved in cholesterol synthesis regulation
Sterol-dependent regulation of gene expression: sterol regulatory element binding protein-2 (SREBP-2)
sterol accelerated enzyme degradation: insulin-induced gene proteins (INSIGs)
What are statins
class of prescription drugs used to lower high cholesterol by blocking an enzyme in the liver that produces cholesterol
what is the benefit of statins in regards to LDL cholesterol
decreases amount of LDL cholesterol in blood and increases the liver’s ability to remove it from bloodstream
slow the buildup of plaque in arteries, reducing risk of heart attack/stroke
What are structural analogs of HMG CoA
statins
What are reversible, competitive inhibitors of HMG CoA reductase
statin drugs like atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin and simvastatin
How is cholesterol degradation managed
via processes like reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) to the liver or releases of cholesterol within desquamating cells
How is cholesterol degraded within the body through RCT
intact steroid nucleus of cholesterol is eliminated from body via conversion to bile acids/salts, small percentage excreted in feces, and by secretion of free cholesterol into bile, which transports it to intestine for elimination
what are the primary compounds made when bacteria in the intestine modify some cholesterol before excretion,
reduced derivatives of cholesterol; coprostanol and cholestanol (isomers of each other)
What are the most important organic components of bile
PC, or lecithin and conjugated bile salts
Explain cholesterol transport
cholesterol transported via lipoproteins, both to tissues for use (via particles like LDL) and away from tissues to the liver via RCT that primarily involves HDL
inside cells cholesterol trafficked between organelles via vesicular transport and non-vesicular mechanisms that can involve sterol transfer proteins and membrane contact sites
What is Enterohepatic circulation
continuous cycle of bile salt secretion into the bile, pass through duodenum (some are deconjugated then dehydroxylated → secondary bile salts), uptake in ileum and subsequent return to the liver (mixture of primary/secondary forms)
What is the function of bile acid sequestrants (like cholestyramine) and its importance
bind to bile salts in gut, preventing reabsorption→ promoting excretion which relives inhibition of bile acid synthesis in liver therefore cholesterol is used in this pathway
importance: useful in treatment of hypercholesterolemia
What can lead to cholesterol gallstone disease or cholelithiasis
more cholesterol present than can be solubilized by the bile salts and PC present, cholesterol precipitate in gallbladder
what causes disorder of gallstone disease
decrease of bile acids in bile or also result from increased secretion of cholesterol into bile, seen with use of fibrates to reduce cholesterol and TAG in blood
what are the lipoprotein classes
Chylomicrons
chylomicron remnants
very low density lipoproteins= VLDL
intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL); which are VLDL remnants
low density lipoproteins (LDL)
high-density lipoproteins (HDL)
lipoprotein (Lp[a])
What is the composition of plasma lipoproteins
neutral lipid core (made of TAG + cholesteryl esters)
shell of amphipathic apolipoproteins, phospholipids and free cholesterol
what are apolipoproteins and their importance
proteins that bind to lipids to form lipoproteins
importance: provide recognition sites for cell-surface receptors or serve as activators/ coenzymes for enzymes involved in lipoprotein metabolism
What type of apolipoprotein functions as essential structural components of particles and cannot be removed (particles cannot be produced without them)
non-exchangeable apolipoproteins
What are some important non-exchangeable apolipoproteins
apoB-48 and apoB-100
What type of apolipoproteins are transferred freely between lipoproteins
exchangeable apolipoproteins
what are some important exchangeable apolipoproteins
apoAs
apoCs
apoEs
What is required for the assembly of apolipoprotein and lipid into chylomicrons
microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) → loads apo B-48 with lipid in ER
In Chylomicron assembly where are the particles moved from and to, and how are they packaged and transfered
particles move from ER to Golgi
at Golgi particles are packaged in secretory vesicles which then fuse with plasma membrane releasing chylomicron particles which enter lymphatic system and ultimately blood
What is the particle released by intestinal mucosal cell and why
nascent chylomicron because its functionally incomplete
How is TAG degraded by LPL
LPL is activated by apo C-II on circulating chylomicrons, which hydrolyzes the TAG to fatty acid (stored in adipose or used as energy in muscles) and glycerol (taken up by liver, converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate for lipid synthesis or gluconeogenesis)
What is a deficiency of LPL and its effects
type I hyperlipoproteinemia/familial chylomicronemia
dramatic accumulation of chylomicron-TAG in plasma even in fasted state
Type IB hyperlipoproteinemia→ results from deficiency in apo C-II
what plays a role in TAG degradation
hepatic lipase on surface of endothelial cells of the liver
Where are VLDLs produced, their composition and their function
produced in liver
composed predominantly of endogenous TAGs
function: carry this lipid from liver (site of synthesis) to peripheral tissues
How is IDLs and LDLs converted
VLDL converted in plasma to LDL
IDLs can be taken up by liver cells through receptor mediated endocytosis that uses apo E as ligand
What are the 3 isoforms of Apo E and their effects
Least common: E-2, poorly binds to receptors and those who are homozygotic for it are deficient in the clearance of IDL and chylomicron remnants. Have familial type III hyperlipoproteinemia
Most common: E-3
E-4: confers increased susceptibility to an earlier age of onset to late-onset form of Alzheimer disease
How do statins reduce cholesterol synthesis in LDL receptor mediated endocytosis
via inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase
Resulting in increase production of LDLR
how does statins work in reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
two main biochemical mechanisms: inhibiting cholesterol synthesis and triggering pleiotropic (cholesterol independent) anti-inflammatory effects via blocking key enzyme in liver, statins decrease amount of “bad” cholesterol (LDL-C)
what is dyslipidemia
abnormal levels of cholesterol-carrying lipoproteins in blood caused by disruptions in body’s complex biochemical pathways for lipid metabolism
what are the dyslipidemia mechanisms and what they lead to
lead to overproduction or defective clearance of cholesterol and other lipids → imbalance of LDL and HDL cholesterol
mechanisms: involve in several stages of lipoprotein metabolism like; abnormal VLDL production, impaired processing of VLDL into LDL, defective LDL clearance, dysfunctional HDL, and genetic vs secondary causes
how does dyslipidemia mechanisms relate with ASCVD pathobiology and therapy
Dyslipidemia= central driver of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) through its role in formation and progression of arterial plaque. therapies target lipid abnormalities of ASCVD prevention and treatment
what is the structure of bile acids/salts and what are the most abundant bile acids in human bile
structure: 24 carbons with 2-3 hydroxyl groups and side chain that terminates in a carboxyl group
most abundant: cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid
What is the function of apoAs and their primary source
primary sources: intestine and liver
structural for HDL, activation of LCAT and HI, promotes LPL mediated TG-lipolysis
What is the function of apoCs and their primary source
primary source: Liver
activation of LCAT, cofactor for LPL, inhibits LPL and uptake of lipoproteins
What is the function of apoEs and its primary source
ligand for binding to LDLR
primary source: liver
Describe an overview of Chylomicron metabolism
assembled in intestinal mucosal cells and carry dietary (exogenous) TAGs, cholesterol, fat-soluble vitamins, and cholesteryl esters to peripheral tissues
What is the 5 overall steps in chylomicron metabolism
intestinal mucosal cells secrete nascent TAG-rich chylomicrons
ApoC-II and apo E are transferred from HDL to nascent chylomicron
Extracellular lipoprotein lipase, activated by apoC-II, degrades TAG in chylomicrons
ApoC-II is returned to HDL
CE-rich chylomicron remnants bind through apo E to specific receptors on the liver and are endocytosed
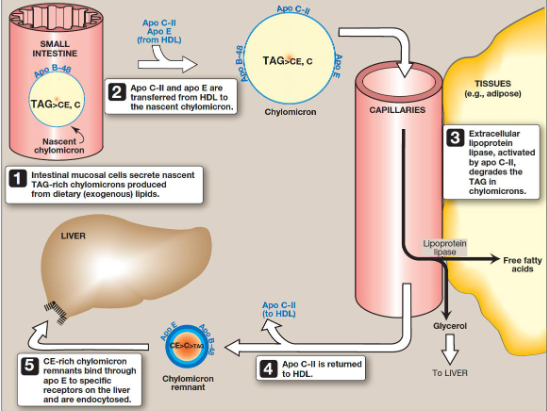
What is the process shown in the image
Chylomicron metabolism
What is Apo48
form of apolipoprotein B
synthesized in intestine, specific to chylomicrons; dietary fat absorption
What is ApoB100
form of apolipoprotein B
produced by liver, found in VLDL, IDL, and LDL particles
transport cholesterol and triglycerides throughout the body
What apolipoprotein B is the result of post-transcriptional RNA editing; C→U, creating a stop codon in apoB mRNA
ApoB48
what reduces LDLR recycling
proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9)
What is autosomal dominant familial hypercholesterolemia 3 associated with
gain of function in PCSK9, which promotes lysosomal degradation of LDLR
How is synthesis of new LDLR protein reduced
via decreasing expression of LDLR gene, limiting further entry of LDL-C
What is the result if cholesterol is not required immediately for structural or synthetic purpose
its esterified by acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) which transfers a fatty acid from fatty acyl CoA to cholesterol→ producing cholesteryl ester that can be stored in the cell
How is activity of ACAT enhanced when cholesterol is not required immediately for structural/synthetic purpose
enhanced in presence of increased intracellular cholesterol
What is the importance of scavenger receptors (SRs) specifically SR-A and what other cellular component possess high levels of it
Macrophage possess high levels of SRs
SR-A can bind a broad range of ligands and mediate endocytosis of chemically modified LDL, especially oxidized LDL (oxLDL)
How is SRA different from LDLR
SRA is not downregulated in response to increased intracellular cholesterol
cholesteryl esters accumulate in macrophages causing their transformation into “foam” cells that participate in formation of atherosclerotic plaque
Where are high density lipoproteins (HDLs) formed and how are they formed
formed in blood by addition of lipid to apoA-1 (made/secreted by liver and intestine as lipid poor protein)
what type of particle serves as circulating reservoir of apo C-II and apo E
HDL particles
In HDL metabolism how is free cholesterol uptake
nascent HDLs containing primarily phospholipid and apo A/C/E, take up free cholesterol from non-hepatic peripheral tissues and return it to liver as cholesteryl esters
ABCA1 & ABCG1 mediate free cholesterol uptake from peripheral cells to lipid poor apoAI and HDL particles
In HDL metabolism how does cholesterol esterification happen
cholesterol taken up by HDL→ immediately esterified by plasma enzyme lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) which transfers fatty acid from carbon 2 of PC to cholesterol
esterification maintains cholesterol concentration gradient→ allows continued efflux of cholesterol to HDL
discoidal nascent HDL accumulates cholesteryl esters it becomes spherical cholesteryl ester poor HDL3→ cholesteryl ester rich HDL2 particle
what is the function of CETP in HDL metabolism cholesterol esterification
transfers some cholesteryl esters from HDL to VLDL in exchange for TAG
why is reverse cholesterol transport important
key component of cholesterol homeostasis and essence of HDL metabolism so cholesterol from peripheral cells to apoAI/HDL and from HDL to liver for bile acid synthesis/disposal