Joints
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
articulations (joints)
a joint (articulation or arthrosis) is a point of contact between two or more bones, between cartilage and bones, or between teeth and bones
arthrology
the scientific study of joints
classification of joints
structural classification
functional classification
functional classification
based on the degree of movement permitted
synarthrosis
amphiarthrosis
diarthrosis
synarthrosis
completely immovable
e.g. suture of the skull
manubriosternal joint
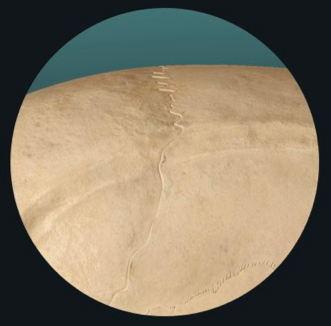
amphiarthrosis
slightly moveable
cartilaginous
e.g. intervertebral disc
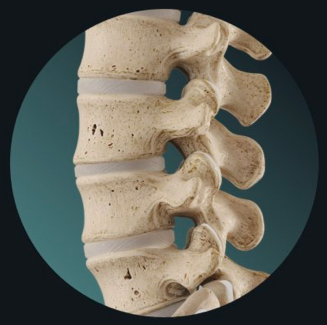
diarthrosis
freely moveable
synovial joints
also contains accessory ligaments and articular discs (menisci)—pads of fibrocartilage
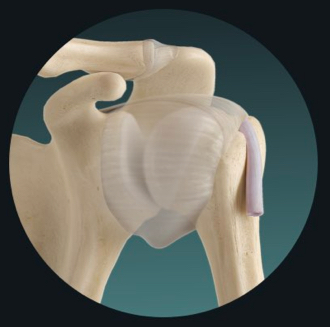
diarthrosis classification
uniaxial
biaxial
multiaxial
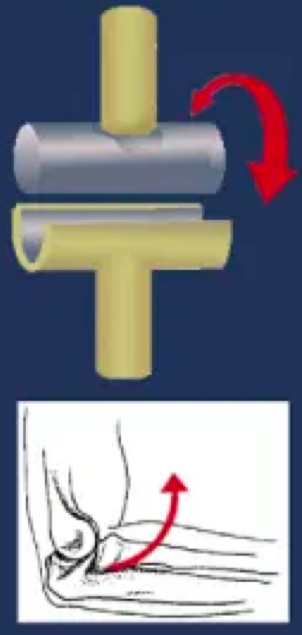
uniaxial diarthrosis
allows movement within a single anatomical plane or axis of motion
e.g. elbow joint
biaxial diarthrosis
allows for movement along two planes or axes
e.g. metacarpophalangeal joint
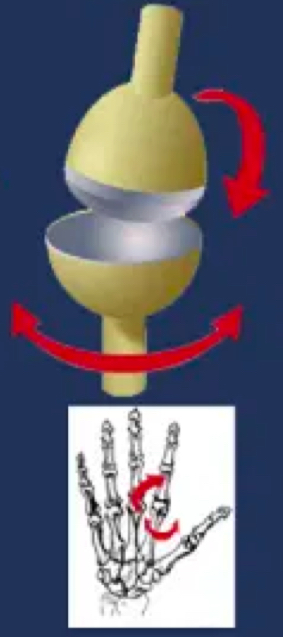
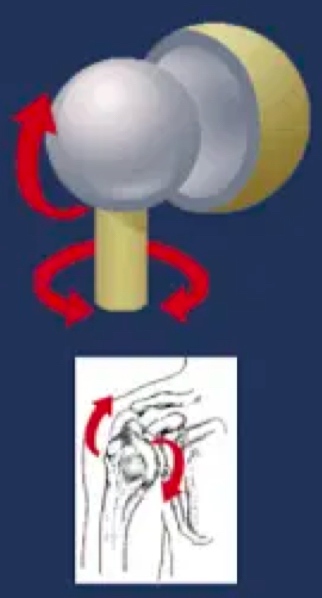
multiaxial diarthrosis
hip and shoulder joints
structural classification
based on the presence or absence of a synovial (joint) cavity and type of connecting tissue
classified as:
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
fibrous joint
dense irregular connective tissue
lacks a synovial cavity
have the articulating bones held together by fibrous connective tissue
permits little to no movement
types include:
sutures
syndesmosis
gomphosis
suture fibrous joint
composed of a thin layer of dense fibrous connective tissue that unites skull bones
synostosis
synostosis
a suture joint that has ossified
e.g. the frontal suture between the left and right sides of the frontal bone
functionally classified as a synarthrosis
syndesmosis fibrous joint
more connective tissue than in a suture
can form a wide fibrous joint where the shafts of two parallel bones are connected by a broad interosseous membrane
e.g. tibiofibular joint
gomphosis fibrous joint
dentoalveolar
a cone-shaped peg fits into a socket
dense irregular connective tissue—periodonatal ligament
degeneration of gums
periodontal ligament and bone = periodontal disease
e.g. the root of a tooth in its socket
cartilaginous joint
dense regular connective tissue
lacks a synovial cavity
has the articulating bones connected by either fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage
allows little or no movement
two types:
synchondroses
symphyses
synchondrosis cartilaginous joint
the connecting material is hyaline cartilage
symphysis cartilaginous joint
the connecting material is a disc of fibrocartilage
e.g. interverterbral discs and pubic symphysis
synovial joint
has a synovial (joint) cavity between the articulating bone and are freely moveable (diarthrotic)
types of synovial joints
plantar
hinge
pivot
condyloid
saddle
ball and socket
articular cartilage
covers the bones at synovial joints
reduces friction at the joint with movement and helps absorb shock
torn cartilage
occuring frequently in the knees of athletes
damage to the articular discs that lie between the ends of some bones
removal to prevent erosion and arthritis is accomplished by arthroscopy
techniques for cartilage replacement
alternative knee replacement
in cartilage transplantation chondrocytes are removed from the patient, grown in culture, and then placed in the damaged joint (autologous chondrocyte implantation)
articular capsule
surrounds a diarthrosis, encloses the synovial cavity, and unites the articulating bones
composed of two layers:
outer fibrous capsule
inner synovial membrane
other capsule features include ligaments and articular fat pads
outer fibrous capsule
may contain ligaments
inner synovial membrane
secretes a lubricating and joint-nourishing synovial fluid
synovial fluid
secreted by the synovial membrane
lubricates and reduces friction in the joint and supplies nutrients to and removes metabolic wastes from the joint
when disease or injury leads to a buildup of synovial fluid, the fluid may be aspirated and medications may be injected into the cavity
ligaments
help hold bone to bone
extracapsular ligaments
intracapsular ligaments
extracapsular ligaments
collateral ligaments
intracapsular ligaments
ACL
PCL
sprain
forcible wrenching or twisting of a joint that stretches or tears its ligament but does not dislocate the bone
strain
a stretched or partially torn muscle
articular discs
modify the shape of the joint surfaces of the articulating bones
help maintain the stability of the joint, and direct the flow of synovial fluid to areas of greatest friction
nerves
nerves that supply a joint are the same as those that supply the skeletal muscles that move the joint
blood supply
numerous arteries and veins supply the joints and surrounding structures
bursae
synovial fluid filled sac-like structures that cushion the movement of one body part over another
found where one part of the body moves over another
tendon sheaths
tubelike bursae that wrap around tendons where there is considerable friction, such as the tendon of the biceps brachii at the shoulder joint
bursitis
chronic inflammation of a bursae
gliding movements
when relatively flat bone surfaces move back and forth from side to side with respect to one another
no significant alteration of the angle between the bones
occurs at plantar joints
angular movements
an increase or decrease in the angle between articulating bones
principal angular movements are:
flexion
extension
hyperextension
flexion
results in a decrease in the angle between articulating bones
extension
results in an increase in the angle between articulating bones
lateral flexion
the movement of the trunk sideways to the right or left at the waist
occurs in the frontal plane and involves the intervertebral joints
hyperextension
a continuation of extension beyond the anatomical position and is usually prevented by the arrangement of ligaments and the anatomical alignment of bones
abduction
the movement of a bone away from the midline
adduction
the movement of a bone toward the midline
circumduction
the movement of the distal end of a part of the body in a circle
occurs as a result of a continuous sequence of flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction
condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket joints
rotation
bone revolves around its own longitudinal axis
pivot and ball-and-socket joints
medial rotation
the anterior surface of a bone of the limb is turned toward the midline
lateral rotation
anterior surface of a bone of the limb is turned away from the midline
elevation
upward movement of a part of the body
depression
downward movement of a part of the body
protraction
movement of a part of the body anteriorly in the transverse plane
retraction
movement of a protracted part back to the anatomical position
inversion
movement of the soles medially at the intertarsal joints so that they face away from each other
eversion
movement of the soles laterally at the intertarsal joints so that they face away from each other
dorsiflexion
bending of the foot at the ankle in the direction of the superior surface
plantar flexion
bending of the foot at the ankle joint in the direction of the plantar surface
supination
movement of the forearm at the proximal and distal radioulnar joints in which the palm is turned anteriorly and superiorly
pronation
movement of the forearm at the proximal and distal radioulnar joints in whcih the distal end of the radius crosses over the distal end of the ulna and the palm is turned posteriorly or inferiorly
opposition
movement of the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint in which the thumb moves across the palm to touch the tips of the finger on the same hand
plantar joints
side-to-side and back-and-forth gliding movements
nonaxial
intercarpal
intertarsal
sternoclavicular
acromioclavicular
sternocostal
vertebrocostal
hinge joint
the convex surface of one bone fitting into a concave surface of another bone
movement is primarily flexion or extension in a single plane
elbow
knee
ankle
interphalangeal joints
pivot joint
round or pointed surface of one bone fits into a ring formed by another bone and a ligament
movement is rotational and monaxial
atlas rotating about the axis and turning the palms anterior and posterior
condyloid joint
oval-shaped condyle of one bone fits into an elliptical cavity of another bone
movements are flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, and circumduction
joint between the carpals and the radius
saddle joint
contains one bone whose articular surface is saddle-shaped another bone whose articular surface is shaped like a rider sitting in the saddle
movements are flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, circumduction
ball-and-socket joint
ball-shaped surface of one bone fits into the cuplike depression of another
movements are flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, rotation, and circumduction
shoulder joint
hip joint
factors affecting contact and range of motion at synovial joints
structure and shape of the articulating bone
strength and tautness of the joint ligaments
arrangement and tension of the muscles
contact of soft parts
hormones
disuse
range of motion effects of aging
various aging effects on joints include decreased production of synovial fluid
a thinning of the articular cartilage
loss of ligament length and flexibility
due to genetic factors as well as wear and tear on joints
arthroplasty
surgical replacement of a joint with an artificial joint
most commonly replaced joints:
hips
knees
shoulders
rheumatism
refers to any painful state of the supporting structures of the body
bones
ligaments
joints
tendons
muscles
arthritis
form of rheumatism in which the joints become inflamed
rheumatoid arthritis
an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks its own cartilage and joint linings resulting in loss of joint function
can lead to bony deformities, especially in the hands
osteoarthritis
a degenerative joint disease commonly known as “wear and tear” arthritis
characterized by deterioration of articular cartilage and bone spur formation
noninflammatory and primarily affects weight-bearing joints
ankylosing spondylitis
affects joints between the vertebrae and between the sacrum and hip bone
occurs often in men and in early adulthood
unknown cause
ankylosing spondylitis treatment
medication
physical therapy
rare cases surgery
gouty arthritis
a condition in which sodium urate crystals are deposited in soft tissues of joints, causing inflammation, swelling, and pain
if not treated, bones at affected joints will eventually fuse, rendering the joints immobile
most frequently injured major joint
the ankle
most common injury to the ankle
sprain
RICE
rest
ice
compression
elevation
pott’s fracture
fracture of the distal leg that involves both the medial and lateral malleoli