Cardiovascular System: Heart Anatomy, Histology, and Function
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What are the main components of the cardiovascular system?
Blood, the heart (central pump), arterial and venous networks, and microcirculation.
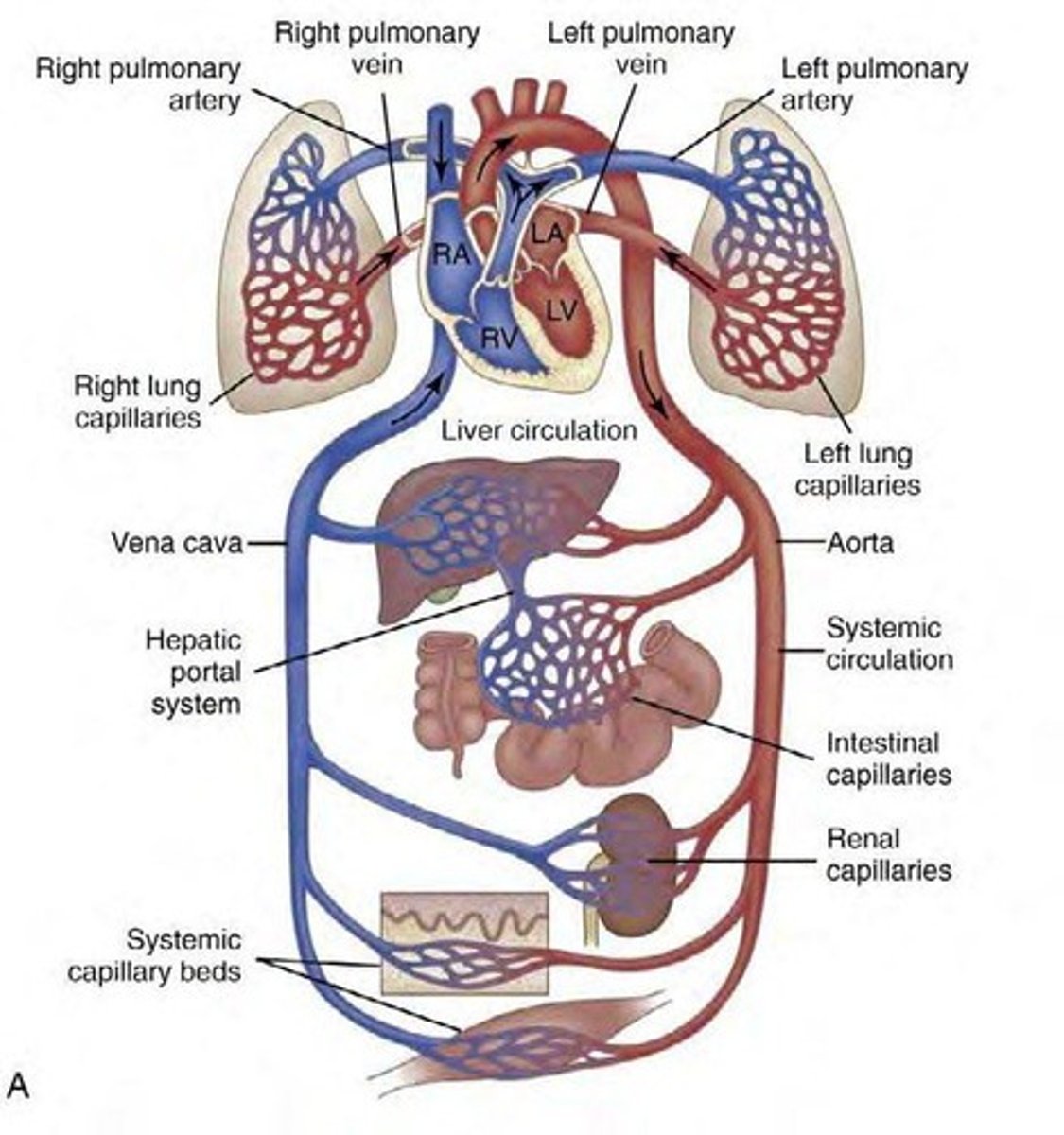
What is the primary function of the cardiovascular system?
To maintain adequate blood flow, deliver oxygen and nutrients, remove waste products, and regulate thermoregulation and glomerular filtration rate.
What type of blood does the right heart propel?
Unoxygenated blood through the pulmonary circulation.
What type of blood does the left heart propel?
Oxygenated blood through the systemic circulation.
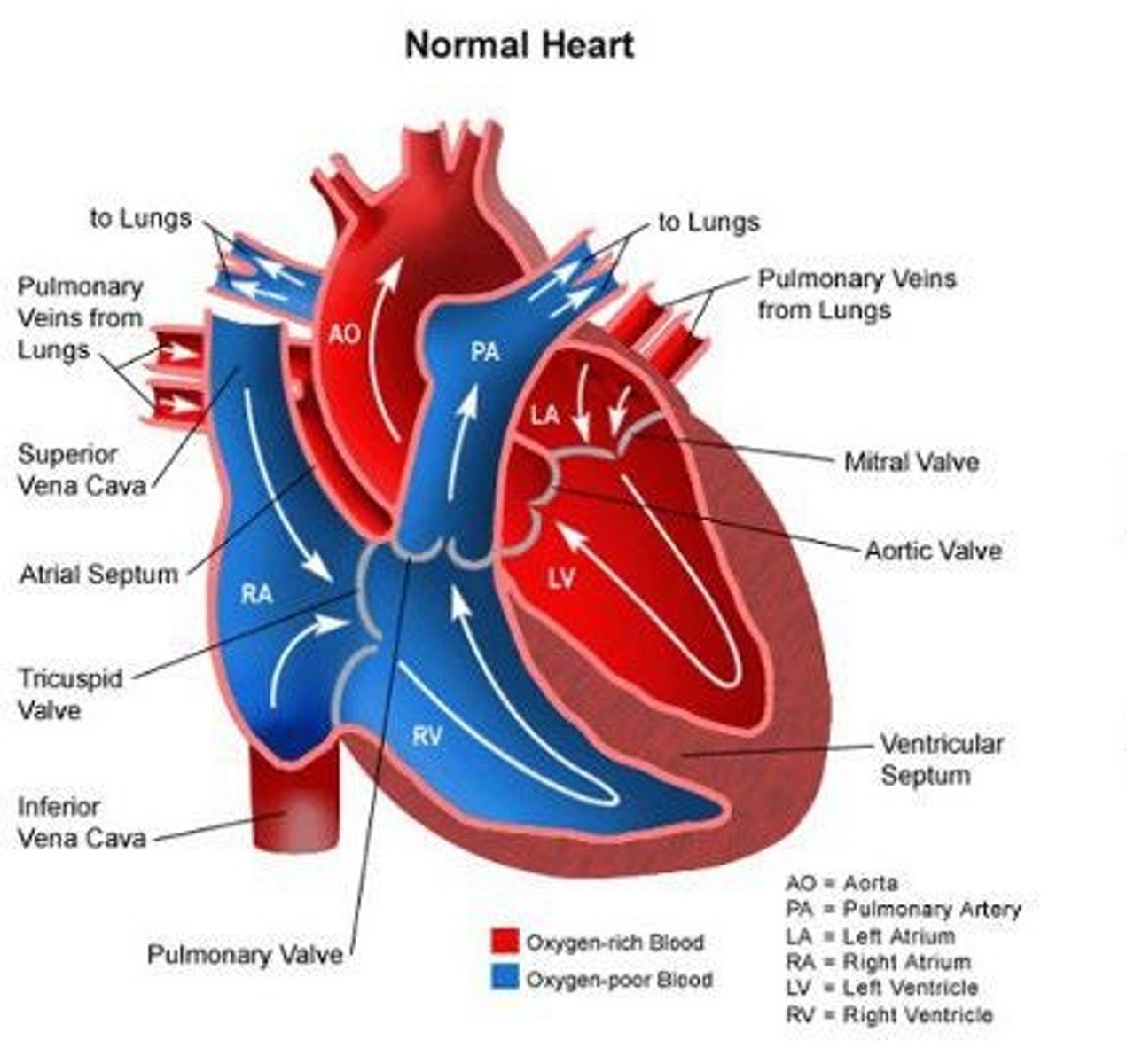
What are the four chambers of the mammalian heart?
Right atrium (RA), left atrium (LA), right ventricle (RV), and left ventricle (LV).
What are the three layers of the heart?
Endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium.
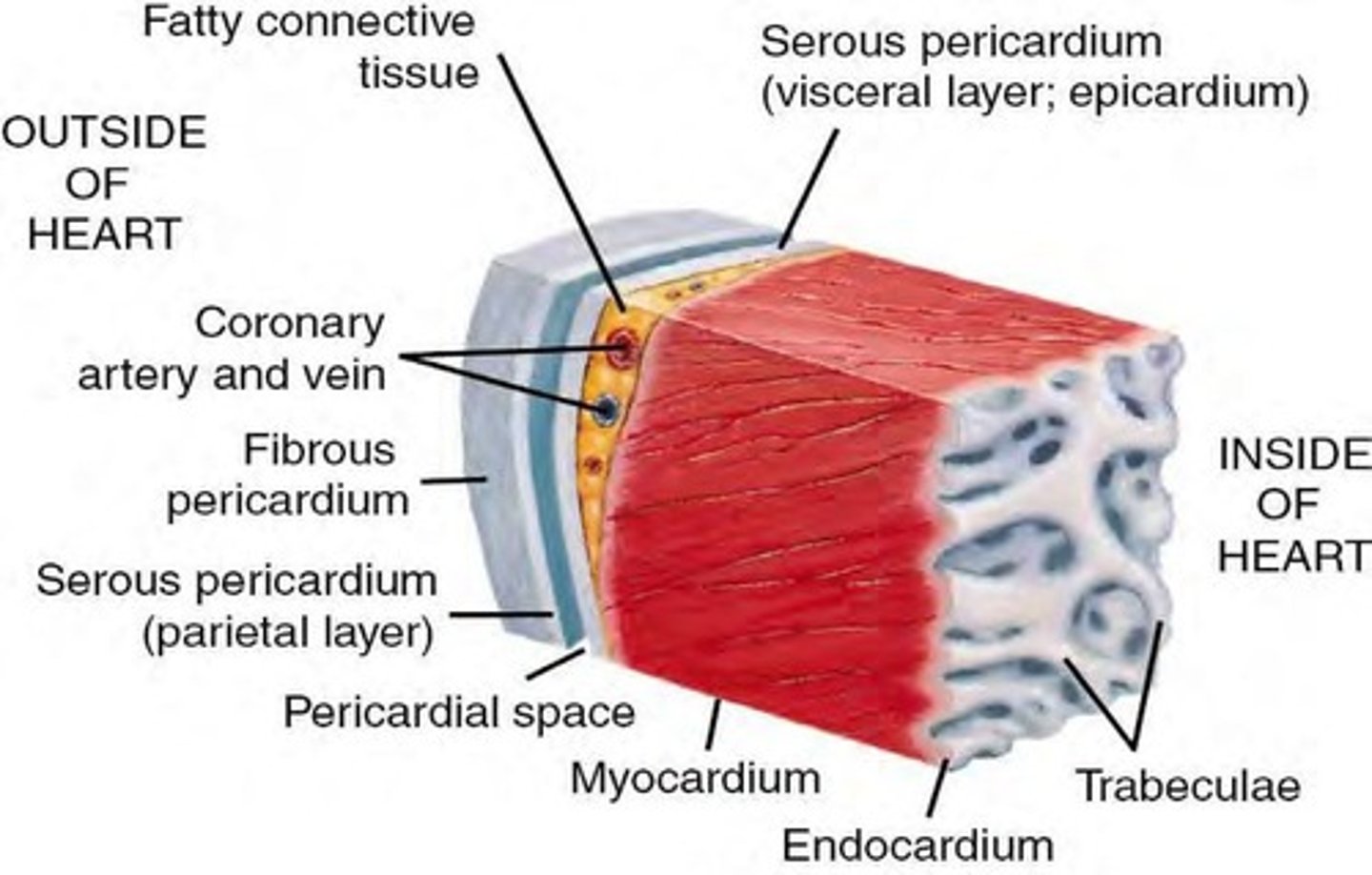
What is the role of the endocardium?
It forms the inner lining of the heart and includes the heart valves.
What is the myocardium?
The muscular layer of the heart responsible for contraction.
What is the epicardium?
The outer layer of the heart, also known as the visceral pericardium.
What are Purkinje fibers?
Modified cardiac muscle cells that are part of the heart's conduction system, specialized for impulse conduction.
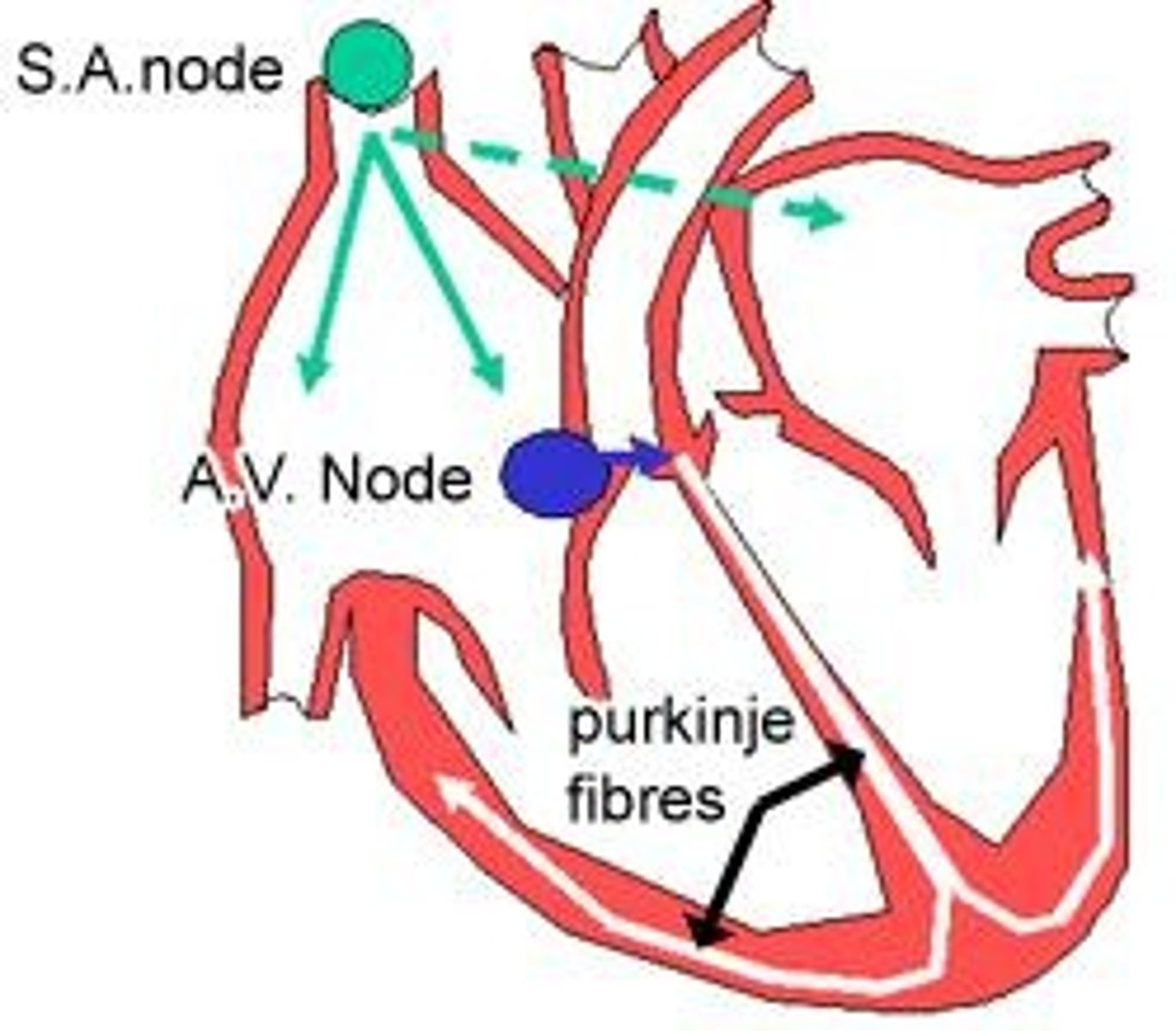
Where are Purkinje fibers located?
In the subendocardium, between the endocardium and myocardium.
What is the function of the sinoatrial (SA) node?
It generates impulses for myocardial contraction, initiating the heartbeat.
What is the function of the atrioventricular (AV) node?
It receives impulses from the SA node and coordinates the contraction of the ventricles.
What is the significance of the cardiac output?
It reflects the volume of blood the heart pumps per minute, crucial for maintaining blood flow.
What is the role of the lymphatic system in circulation?
It drains fluid from extravascular spaces into the blood vascular system.
What is the relationship between blood pressure and vascular permeability?
Blood pressure influences the permeability of blood vessels, affecting fluid exchange.
What is the order of blood flow through the microcirculation?
Artery → Arteriole → Metarteriole → Capillaries → Venule → Vein.
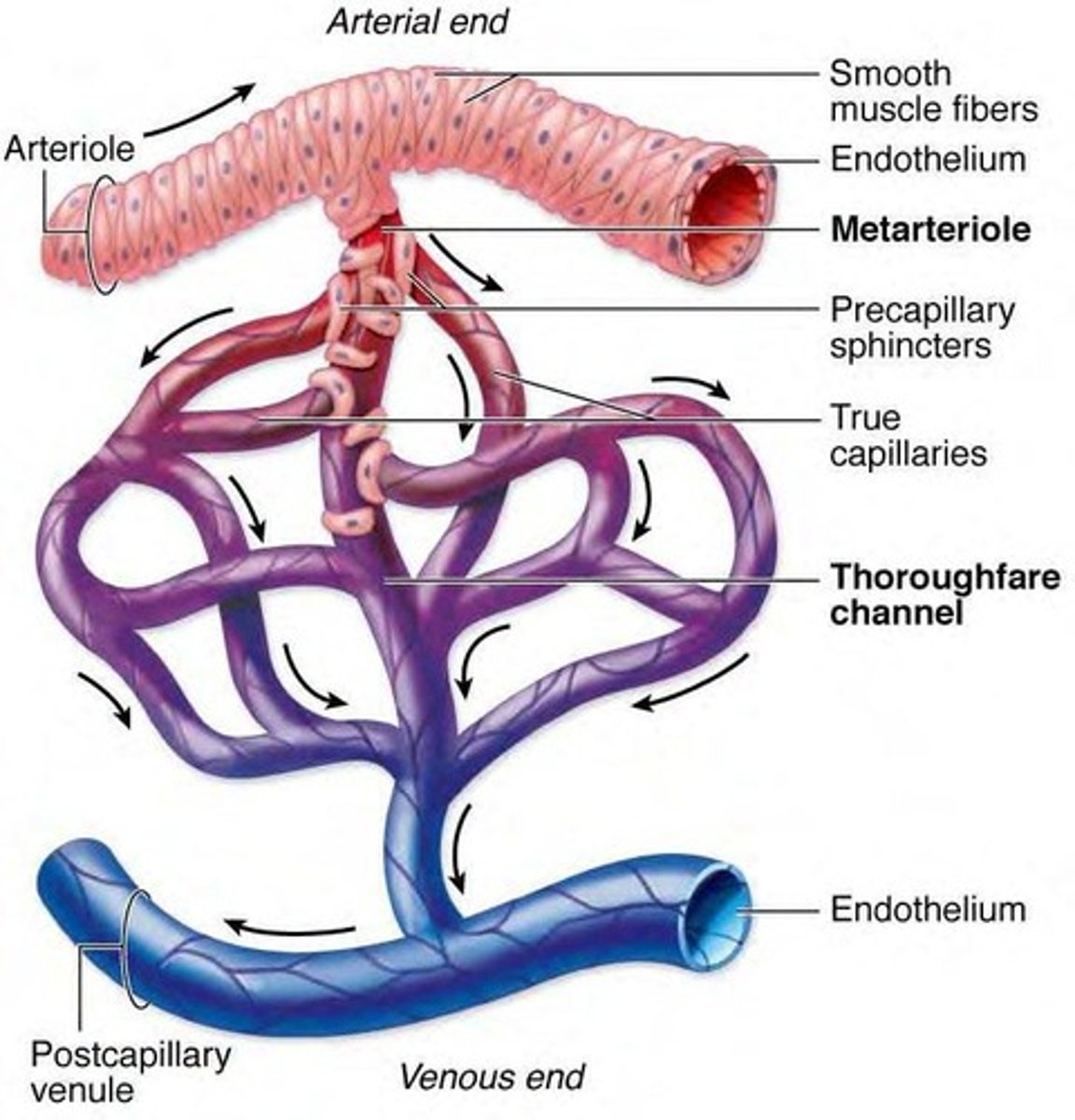
What is the importance of the basal lamina in the endocardium?
It provides structural support and is part of the connective tissue layer.
What is the composition of the subendocardium?
It contains connective tissue and part of the heart's conductive system, including Purkinje fibers.
How do Purkinje fibers differ from regular cardiac muscle fibers?
They are larger, contain more glycogen, and are specialized for conduction rather than contraction.

What is the role of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
They connect cardiac muscle cells and facilitate synchronized contraction through desmosomes and gap junctions.
What is the significance of the heart being the first organ to form in the embryo?
It highlights the heart's critical role in establishing circulation early in development.
What is the function of the cardiovascular system in thermoregulation?
It helps maintain normal body temperature by regulating blood flow to the skin.
What structure sends impulses to the AV bundle?
The apex of the heart.
What is the sequence of contraction in the heart?
The apex contracts first, followed by the papillary muscles, then the wave of depolarization spreads up the walls of the ventricles.

What is the cardiac skeleton?
Four dense bands of fibrous connective tissue that encircle the base of the pulmonary trunk, aorta, and AV valves, providing structural support.
What is the fibrous trigon?
A triangular mass of fibrous connective tissue connecting the aortic ring and the left and right atrioventricular rings.
What is 'Os Cordis'?
An area that undergoes osseous differentiation, primarily seen in cattle.
Name the four cardiac valves.
1. Right atrio-ventricular (Tricuspid), 2. Pulmonary, 3. Left atrio-ventricular (Mitral), 4. Aortic.

What are the characteristics of cardiac valves?
They are thin, translucent, and shiny.
What are chordae tendineae?
Small strands of connective tissue that bind distal parts of valve leaflets.
What are cardiomyocytes?
Cardiac muscle cells that are involuntary, striated, and arranged in sarcomeres.
What is the thickness of the left ventricular myocardium compared to the right?
The left ventricular myocardium is approximately 2 to 4 times thicker than the right.
What is the function of intercalated discs?
They allow contraction signals to pass from cell to cell as a single wave.
What does the epicardium consist of?
A mesothelium layer, dense connective tissue, and a variable layer of adipose tissue.
What is the endocardium?
The endothelial lining of the heart chambers and covers the surface of the valves.
How does the epicardium relate to the pericardial sac?
The epicardium represents the visceral layer of the pericardial sac.
What is the role of mesothelial cells in the epicardium?
They secrete a small amount of serous fluid that lubricates the movement of the epicardium.
What is the primary function of the myocardium?
To facilitate the contraction of the heart.
What is the significance of gap junctions in cardiac muscle?
They form electrical synapses allowing for coordinated contraction.
What is the primary type of muscle found in the heart?
Involuntary striated muscle.
What is the regeneration capacity of cardiomyocytes?
They have a low regeneration capacity and do not undergo mitosis.
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
It anchors the valves and surrounds the atrioventricular canals, maintaining their shape.
What is the relationship between the endocardium and the myocardium?
The endocardium lines the heart chambers and covers the valves, while the myocardium is the muscle layer responsible for contraction.
What is the role of the pericardial sac?
To provide a protective layer around the heart and contain serous fluid for lubrication.
What is the appearance of cardiac muscle fibers?
They are branched and interdigitating, allowing for efficient contraction.