7-8. drug elimination & ADME in special populations
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
how is drug elimination measured?
clearance = volume of plasma from which a drug is completely removed / time
what are the routes of drug elimination?
renal (major route)
hepatic (second most important route)
other body fluids (milk, sweat, expired air, tears; minor routes)
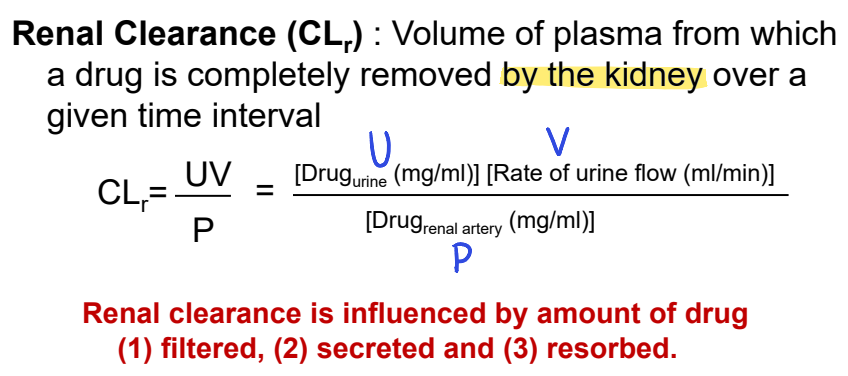
what is renal clearance? (CLr)
volume of plasma from which a drug is completely removed by the kidney over a given time interval
influenced by amount of drug filtered, secreted, and resorbed
what properties influence how easily drugs get through the filtration barrier?
size: solutes with MW < 50 kD are easily filtered
shape: flexibility & deformability ease filtration
charge: cationic solutes filter more easily anionic
Fx: fraction of a substance not bound to plasma proteins
i.e. low molecular weight, unbound drugs are filtered; the rest remain in blood
glomerular filtration of drugs
not transporter-mediated and is NOT saturable
dependent on glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
what types of drugs are actively secreted?
weak acids (organic anions)
weak bases (organic cations)
poorly filtered drugs (due to charge, size, or binding to plasma proteins)
tubular reabsorption of drugs
as water is reabsorbed from urine, lipophilic drugs passively diffuse through distal tubule & are resorbed back into blood
ionized drugs tend not to be reabsorbed (some exceptions & some drugs can use SLCs for resorption)
passive resorption is influenced by drug lipophilicity & urine pH (affects ionization)
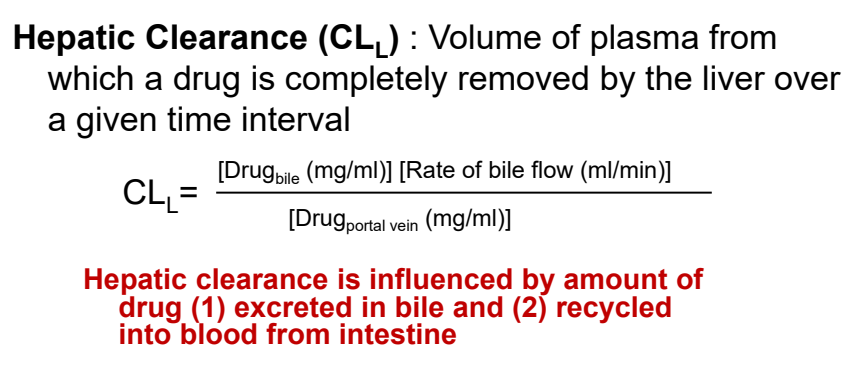
what is hepatic clearance? (CLL)
volume of plasma from which a drug is completely removed by the liver over a given time interval
influenced by amount of drug excreted in bile & recycled into blood from intestine
enterohepatic recirculation
drugs conjugated in liver
excreted in bile
microbes in intestine deconjugate drugs
drugs reabsorbed into portal vein & returned to liver

cholangiocyte uptake of drugs
lipophilic drugs: passively diffuse from blood into hepatocytes. not saturable
ionized drugs: actively transported into cholangiocytes by SLCs. saturable
cholangiocyte efflux of drugs into bile
lipophilic drugs: passively diffuse from cholangiocytes into bile
ionized drugs: actively transported by ABC transporters
efflux favors large molecules, especially glucuronide conjugates
saturable
metabolites can also move back into bloodstream
what does the milk-to-plasma drug-concentration ratio measure?
measures propensity for drug elimination in milk
pharmacogenetics
the study of genetic variation responsible for inter-individual variability in drug response and adverse drug reactions
genetic polymorphisms
heritable DNA sequence variations that occur in ≥ 1% of the population
different from mutations, which aren’t necessarily heritable & occur in <1% of the population
what are the effects of ABCB1-1Δ polymorphism?
4-base pair deletion mutation in dog p-glycoprotein
deletion reduces p-glycoprotein activity
increases sensitivity to many drugs, including ivermectins
dogs with 2 copies of the allele do not effectively efflux ivermectin from BBB, resulting in ivermectin neurotoxicity