Genetics & Evolution
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Species (definition
Group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
What are the two types of variation?
Acquired. Inherited
What is acquired variation? Example?
Not inherited but developed during life e.g. Ability to ride a bike
What is inherited variation? Example?
Controlled by genes e.g. hair colour
Heredity (definition)
Passing on of features from parents to offspring by means of genes
What to things are chromosomes made of?
DNA. Protein
Function of protein in chromosomes
Holds DNA in tightly packed way inside the nucleus of the cell
What does DNA consist of?
Coding DNA. Non-coding DNA
What is non-coding DNA?
Has no genes and cannot code for the formation of proteins.
Function of non-coding DNA
Highly variable parts of it are used for DNA profiling
Draw a diagram of a chromosome
…
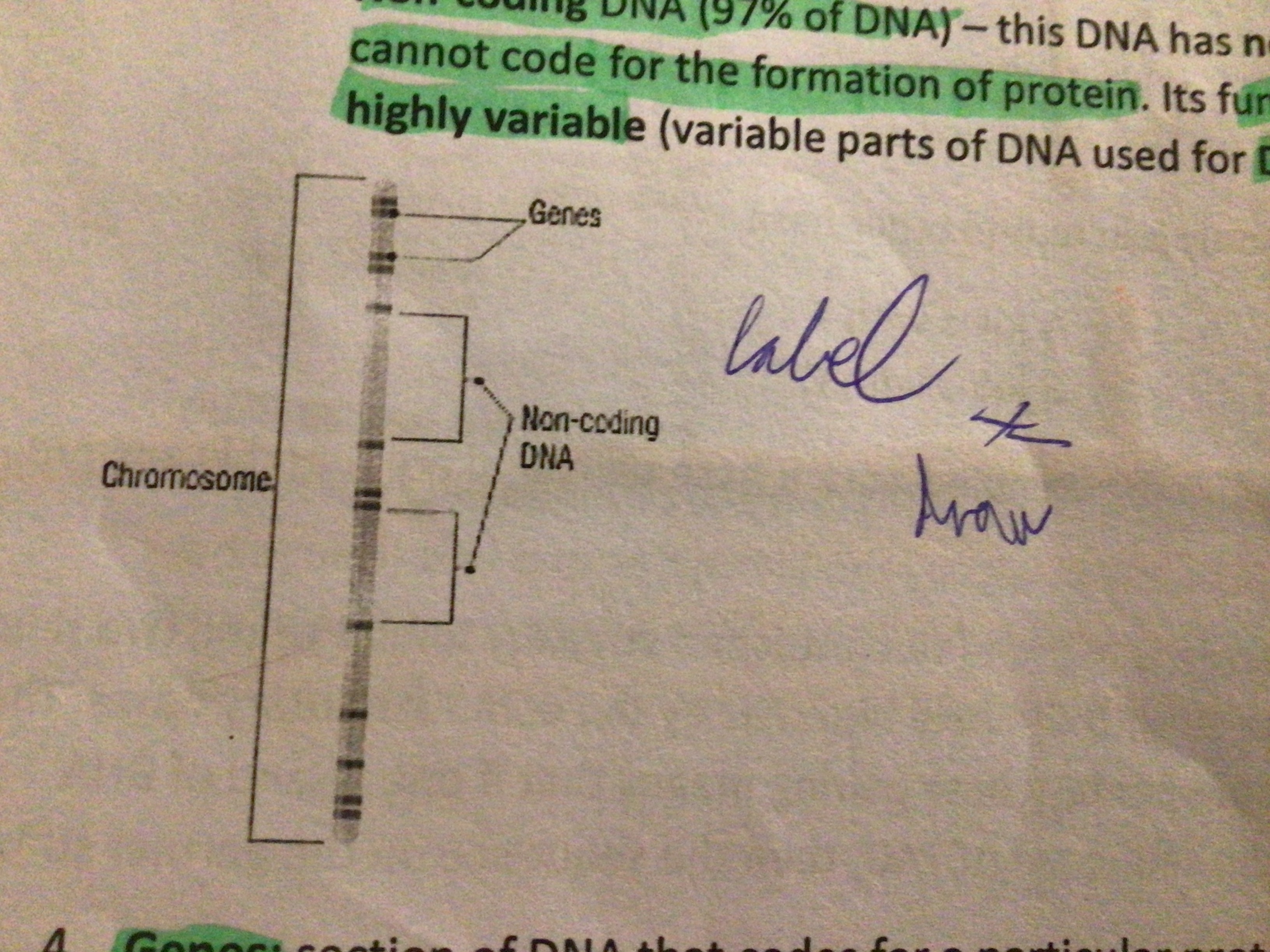
Genes (definition)
Section of DNA that codes for a particular protein.
Allele (definition)
Alternative forms of the same gene. You get two genes for each trait
Gene expression (definition)
Process of changing the information in a gene into a protein. It is the expression of genes that produces the traits inherited.
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
What is DNA?
Hereditary material for all living organisms
Where is DNA found?
On chromosomes
Shape of DNA
Double helix
What are the two strands of DNA linked with?
Chemicals called bases
What does a pair of bases form in DNA?
A rung
Name the four bases of DNA?
Adenine. Thymine. Guanine. Cytosine
What base does Adenine join with?
Thymine
What base does Guanine join onto?
Cytosine
What A/T and G/C known as?
Complementary base pairs
What kind of bonding are base pairs held with?
Hydrogen bonding
Double-stranded DNA is …. to form it’s double helix shape?
Twisted
Draw a nucleotide
…
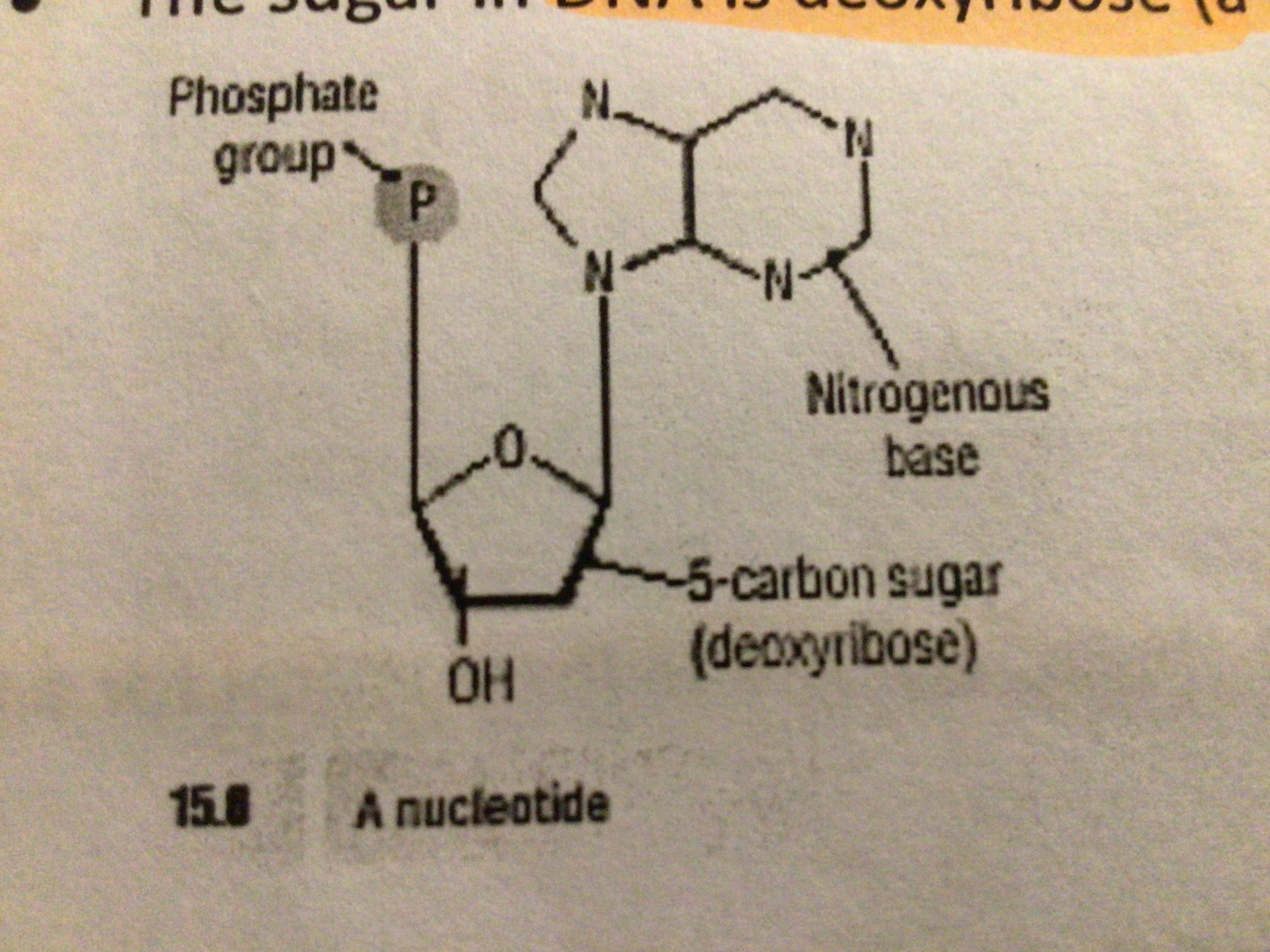
What two scientists worked out the structure of DNA?
James Watson & Francis Crick
Name the sugar found in DNA
Deoxyribose
Name the three parts in a nucleotide
Phosphate group. Deoxyribose. Nitrogen-containing base
What is the two types?
Purines. Pyrimidines
What is a purine base?
Double-ring molecule
What is a pyrimidine base?
Single-ring molecule
Which of the four bases are purine?
Adenine. Guanine
Which of the four bases are pyrimidines?
Thymine. Cytosine
Genetic code (definition)
The sequence of bases in DNA that provide the instructions for a cell to for, a protein
How many amino acids in one chain?
Over 200
Name of the three consecutive bases in DNA used to form an amino acid
Triplet or codon
Explain DNA replication
Double helix unwinds. Bonds between base pairs are broken. Strands of the double helix separate. DNA bases in the cytoplasm enter nucleus. Incoming bases attach to complementary bases. Each side acts as a template for the new DNA. Each rewinds, and a new helix is formed
What breaks the bonds between base pairs in DNA replication?
Enzyme
Why is DNA replication important?
Since DNA is able to produce exact copies of itself it lets the same DNA be passed on to new cells during mitosis
Genetics engineering (definition)
The artificial manipulation or alteration of genes
Name the five processes of genetic engineering
Isolation. Cutting. Insertion. Transformation. Expression
Explain isolation
Remove both DNA from the human (contains wanted gene) and cloning vector (plasmid from bacteria)
Explain cutting
Human DNA and plasmid DNA treated with the same restriction enzyme. Cut DNA only at certain sites
Why is the same restriction used for both samples of DNA?
In order for the cut ends to be complementary
What enzyme is used to combine DNA from the sources?
DNA ligase
What kind of enzyme is DNA ligase?
Anabolic enzyme
Explain insertion/ligation
Target gene placed into DNA of host. DNA ligase used to combine.
Explain transformation
Plasmid with human gene placed back into bacteria
Explain Expression
Getting bacteria to produce the wanted product
Applications of genetic engineering examples
Vitamin A in rice. Sheep produce clotting factor. Bacteria make insulin
Explain vitamin A in rice (genetic engineering)
Vitamin A deficiency in Asia. Rice is a staple of their diet doesn’t produce vitamin A. Vitamin A taken from daffodils and inserted into rice grains.
What does G.M stand for?
Genetically Modified
Explain sheep producing human clotting factor
Haemophiliacs can’t produce a clotting factor (their blood fails to clot). Human gen inserted into DNA of sheep. Clotting factor produced in their milk
Explain how bacteria make insulin (genetic engineering)
Human gene for insulin inserted into bacterium. Bacterium produces large quality of insulin. People with diabetes can inject themselves
Ethical issues of genetic engineering
Release of GMOs into the environment. GMOs as a good source. Animal welfare
Example the release of GMOs into the environment
If gene for weed killer resistance transferred to weed plants, result in uncontrolled growth of weeds
Example of GMOs as a food source
Eating animal genes contained in food plants would concern vegetarians
Example of animal welfare
Use of growth hormones in animals may cause limb deformation and arthritis
Genetic Screening (definition)
Testing DNA for the presence or absence of a particular gene or an altered gene
Explain adult screening
Screening carried out on adults who may carry a defective gene in each of their cells. People get information on the chances of having a child with a disorder or prépa for a disease that might affect them
Embryonic or foetal screening
Cells removed from the embryo, placenta, or fluid around foetus. Cells tested to detect any genetic disorder
Name genetic disorders (4)
Albinism. Haemochromatosis. Cystic fibrosis. Cancer
Explain albinism
Pigment melanin not be made
Explain haemochromatosis
Too much iron accumulates in the body and has to be removed by regular bleeding
Explain cystic fibrosis
Build up of mucus in the lungs and intestine
Differences between DNA and RNA (DNA)
Bases are ATCG. Double-stranded. Found in nucleus
Differences between DNA and RNA (RNA)
The bases are AUGC. Single-stranded. Found in nucleus and cytoplasm
What is the U base in RNA?
Uracil
How many different types of amino acids are there in the cytoplasm
20
What are the two processes of protein synthesis?
Transcription. Translation
Transcription (definition)
Rewriting the code from DNA to RNA
Where does transcription occur?
Nucleus
The bases in DNA work in groups of …
Three
What do the enzymes in the nucleus do in transcription?
Unwind DNA double helix
What happens when strands are separated in the nucleus?
RNA bases enter nucleus and bond with one of the exposed DNA strands. RNA bases join together to form mRNA
What enzyme joins RNA bases together?
RNA polymerase
What kind of enzyme is RNA polymerase?
Anabolic
Why is the genetic code to make a protein copied from DNA to mRNA?
DNA can’t leave the nucleus
What does each mRNA strand carry?
Start codon. Series of codons for particular amino acids. Stop codon
What is a stop codon?
Where the protein chain ends
Translation (definition)
Production of a protein according to the RNA code
Where is ribosomal RNA found (rRNA)?
Ribosomes of the cell
Function of rRNA
Bind mRNA to the ribosome
Where does the mRNA move from to?
Nucleus to cytoplasm
What attaches to the mRNA?
Ribosomes
Where is the site of protein synthesis?
Ribosomes
What are ribosomes?
Special decoding device ensuring that the amino acids are assembled in the correct sequence as instructed by the genetic code on the mRNA.
What does the cytoplasm supply the ribosome with?
tRNA (Transfer RNA)
What does each tRNA molecule have attached to them?
Anticodon and a specific amino acid on the other end
What is an anticodon?
Special triplet of bases
Where will the first tRNA molecule attach on the mRNA?
Just after the start codon
How do the tRNA molecules attach to the mRNA?
Two at a time, bringing their particular amino acid with them
Each amino acid type has its own particular …
Anticodon
What happens to the amino acids connected to the tRNA after the tRNA attaches to the mRNA?
Detached from tRNA and bonded together by ribosome to form part of the protein chains
tRNA molecules will continue to bind until a … is reached.
Stop codon
What happens to the chain of amino acids after it's made?
Protein is folded
What is the result at the end of translation in protein synthesis?
New protein is formed
DNA Profiling (definition)
Method of making a unique pattern of bands from the DNA of a person. Which can then be used to compare with the DNA profile of another person.