Transport across membranes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what are the different types of transport membranes
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
active transport
co transport
simple diffusion
the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
kinetic energy of molecules in simple diffusion
molecules have kinetic energy that they possess which allows them to constantly move in fluids
facilitated diffusion
the passive movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane, from a high concentration to a low concentration, using specific transport proteins (carrier or channel proteins)
what type of substances does facilitated diffusion enable to diffuse across membranes
ions, polar molecules, large molecules
what do protein channels form
tubes filled with water which allows water soluble ions to pass through the membrane
are protein channels selective
yes as only open in presence of certain ions when they bind to a protein
carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion
molecule complementary in shape binds to protein
causing it to change shape
releasing the molecule to the other side of the membrane
what is osmosis
the movement of water from an area of high water potential to an area of lower water potential across a partially permeable membrane
hypotonic meaning
water potential of a solution more positive (closer to 0) than the cell
hypertonic meaning
water potential of a solution more negative than the cell
what is active transport
movement of molecules and ions from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration against the concentration gradient, using ATP and carrier proteins
how does active transport work
molecules bind to receptor sites on carrier proteins
ATP binds to inside of protein membrane
this causes it to be hydrolysed to ADP + Pi
this causes the protein molecule to change shape
releasing molecule to other side of the membrane
Pi released from the protein, causing it to revert back to its original shape
what is co-transport
the coupled movement of two substances across a membrane via a carrier protein
one moves down its concentration gradient, allowing the other to move against its gradient
why is co-transport and active transport used for glucose and sodium ions in the ileum
to absorb glucose from the lumen to the gut must have a higher concentration of glucose in the lumen compared to the epithelial cell (for facilitated diffusion)
however there is usually more glucose in the epithelial cells
needs active and co transport
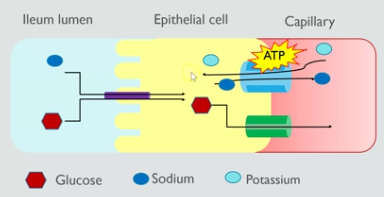
process of co transport of glucose and sodium ions in the ileum
sodium ions are actively transported out of the epithelial cell into the blood
this reduces the sodium ion concentration in the epithelial cell
sodium ions then diffuse from the lumen down their concentration gradient into the epithelial cell
sodium ions diffuse through a co-transporter protein, so either glucose or amino acids also attach and are transported into epithelial cells against their concentration gradient
glucose then moves by facilitated diffusion from the epithelial cell to the blood
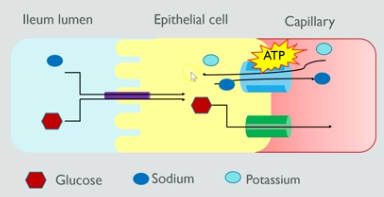
why doesn’t blood have a build up of glucose molecules as they are being absorbed
concentration of glucose in the blood is lower than the epithelial cells as blood flows and carries away absorbed glucose
function of microvilli on epithelial cell
increase surface area for co-transporter proteins giving maximum absorption of glucose
what is the sodium potassium pump
an active transport carrier protein that uses ATP to move ions across the cell membrane
what ions are moved per pump cycle
3 Na+ out of the cell
2 K+ into the cell
using 1 ATP
what is the role of the sodium potassium pump in neurons
maintains the resting potential by keeping the inside of the cell negatively charged