FCM: practice questions (week 1)
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
intro to anesthesia, induction + maintenance pain mgmt, anesthesia equipment, airway devices, abdominal/thoracic radiographs, mechanical ventilation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What are the three essential components required to achieve a state of general anesthesia (triad of general anesthesia)?
Unconsciousness
Analgesia
Muscle relaxation
What is the proper order of the 6 anesthesia phases?
Pre-anesthetic assessment → Premedication → IV catheter placement → Induction/Intubation → Maintenance → Recovery
A vet practice is reviewing their anesthetic protocols to improve patient safety. The practice manager asks you to identify when most anesthetic-related deaths occur so they can allocate additional monitoring resources + staff training to that critical period. What phase of the anesthetic process should be prioritized for enhanced safety measures?
Recovery period
When recovering your patient from anesthesia, you should remove all devices immediately except which two?
SPO2 + CO2
A 4yo Lab is scheduled for an orthopedic surgery. After completing the PE & obtaining owner consent, the vet administers Acepromazine + Morphine IM. The dog is placed in a quiet kennel with a towel over the cage. What phase of anesthesia is being performed?
Preanesthetic medication
What are the typical preanesthetic diagnostics performed on young healthy patients?
Hematocrit, total protein, creatinine, BUN, glucose
What is the typical fasting time for small animal surgery patients?
4-6 hours
Which species are prone to laryngospasm during surgery?
Cats + Pigs
Which dog breed may be very sensitive to Acepromazine?
Boxers
A 7yo Lab presents for removal of a small benign lipoma on the shoulder. The dog has well-controlled DM managed with insulin therapy & regular monitoring, & the owner reports no recent complications. PE reveals normal cardiovascular + respiratory parameters. What is the most appropriate ASA status for this patient?
ASA II → mild systemic disease (DM)
A vet student observes that a healthy dog remains bradycardic 30 minutes after receiving dexmedetomidine premedication, despite the BP having normalized. What explains the persistent bradycardia at this timepoint?
Presynaptic effects of dexmedetomidine in the CNS
A vet administers ketamine to a 3yo dog as part of an anesthetic protocol. The dog remains in sternal recumbency with its eyes open & its limbs extended but does not respond to external stimuli. What term best describes the anesthetic state produced by ketamine?
Dissociative anesthesia
A vet is preparing to anesthetize a dog for an emergency exploratory laparotomy. The vet selects an inhalant anesthetic agent to achieve rapid induction + recovery times. What property of an inhalant anesthetic primarily determines how quickly induction & recovery occur?
Low blood-gas solubility coefficient
A 7yo Doberman is scheduled for dental extraction. The dog has been premedicated appropriately & an IV catheter has been placed. Before inducing anesthesia with propofol, the anesthetist administers 100% oxygen via face mask for 5 minutes. What is the primary reason for this pre-oxygenation step?
To increase the time before hypoxemia develops during the apneic period following induction
What are some of the indications for using TIVA (Total IV Anesthesia)?
Airway procedures, bronchoscopy, field procedures (horses, ruminants)
A 25kg dog requires general anesthesia induction using propofol-ketamine co-induction. The anesthetist administers 25% of the calculated propofol dose over 30 seconds, followed immediately by the full ketamine dose, then titrates additional propofol to effect after 60 seconds. What is the primary pharmacological reason for administering a partial propofol dose before the ketamine?
To reduce the risk of ketamine-induced emergence reactions + dysphoria during induction
At what MAC do we observe loss of cerebrovascular autoregulation?
1 MAC
What is the MAC of Isoflurane in dogs?
1.3-1.6 MAC
What is the MAC of Sevoflurane in dogs?
2.3 MAC
T/F: A low blood:gas solubility is desired in our patients as this means we will have a faster induction + recovery time.
True
A 4yo Lab is anesthetized with Isoflurane for a routine OVH. The anesthetist monitors the depth of anesthesia by adjusting the vaporizer setting to achieve an appropriate end-tidal concentration. What statistical concept does MAC (minimum alveolar concentration) represent in the anesthetized population?
The concentration at which 50% of patients will not move in response to a noxious stimulus
Which inhalant anesthetic is toxic to the kidneys of rats due to compound A?
Sevoflurane
At what point in the pain pathway do analgesics take effect?
Perception + Modulation
At what point in the pain pathway do NMDA receptor antagonists (ketamine) take effect?
Modulation
At what point in the pain pathway do local anesthetics take effect?
Transmission + Transduction
At what point in the pain pathway do NSAIDs take effect?
Transduction
For what types of procedures can we utilize topical local anesthetics?
Intubation, nasal cannulas, urinary catheter placement
What technique is described as the instillation of local anesthesia on open wounds/surgical sites before skin closure (or for abdominal analgesia)?
Intraperitoneal block (Splash block)
What are the indications for using infiltration local anesthesia in patients?
Small skin lesions + Next to skin incisions at the beginning or end of surgery (intratesticular block)
-Line block, Ring block
What are some of the areas of the body where we would use a peripheral nerve block (regional anesthesia)?
Head, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, intercostal, paravertebral
What is the regional anesthetic technique where we inject into a virtual space between fascias & spreads along the plane bathing multiple small nerve branches that traverse it?
Facial Plane Block (ex: TAP Block on abdominal wall or Serratus Block on thoracic wall)
What are two examples of Neuraxial anesthesia (regional anesthesia technique)?
Epidural (epidural space)
Spinal (subarachnoid space)
How would we evaluate pain in an unconscious animal?
Nociception → increased HR/BP/RR >25% for more than 2 mins
How would we evaluate pain in a conscious animal?
Pain scales (ex: VAS, DIVAS, NRS, SDS)
What is the most common pain scale used in dogs?
Glasgow Composite Measure Pain Scale-short form (CPMS-SF)
-need rescue analgesia if >=6/24 or >=5/20
Where is the high pressure zone within the anesthesia delivery system?
From the cylinder (2000psi) to pressure regulator (50psi)
Where is the intermediate pressure zone within the anesthesia delivery system?
From pressure regulator (50psi) to flowmeter (14psi)
Where is the low pressure zone within the anesthesia delivery system?
Downstream of flowmeter to common gas outlet
What size gas cylinder is most commonly used in the anesthesia machine for transport of anesthetized patients?
Size E
What size gas cylinder is most commonly used in the cylinder bank as the main oxygen source?
Size H
What is the color coding for oxygen, nitrous oxide, medical air, carbon dioxide, & entonox gas cylinders?
Oxygen → green
Nitrous oxide → blue
Medical air → white
Carbon dioxide → grey
Entonox → blue
What is the maximum achievable oxygen concentration in the gas supply of the anesthesia delivery system?
95%
Which part of the anesthesia machine reduces pressure & is located between high + intermediate systems?
Pressure regulator
Which part of the anesthesia machine indicates pressure in the cylinder & respiratory/breathing system to check the system for leaks + correct pressure during mechanical ventilation?
Pressure gauge
Which part of the anesthesia machine allows entrance of carrier gas into the machine & determines the fresh gas flow (FGF) in liters per minute (L/min)?
Flowmeter
When should you not use the oxygen flush valve on the anesthesia machine?
When a patient is connected to the breathing system
-only use for leak test really
Which part of the anesthesia machine lets out the mixture of carrier + anesthetic gas & allows for attachment of a breathing system?
Common gas outlet
Which part of the anesthesia machine allows excess gas to escape from the breathing system?
APL (adjustable pressure limiting) valve
What is the main purpose of the Pin Index Safety System (PISS)?
To prevent incorrect cylinder attachment
What correctly describes administering 3 L/min of 100% oxygen compared to 0.8L/min of 100% oxygen?
It delivers the same oxygen concentration, but at a higher flow rate
Where is the adjustable pressure limiting (APL) valve located on the anesthesia machine?
Expiratory part of the machine
What is the consequence of closing the APL valve during spontaneous ventilation?
Pressure builds up in the breathing system + lungs
What two components are found in rebreathing systems but not in non-rebreathing systems?
CO2 absorber + Unidirectional valves
What correctly describes a non-rebreathing system?
It requires high FGF to prevent rebreathing
What might be the consequences of rebreathing CO2 in a patient leading to hypercapnia?
Acidemia, hyperkalemia, reduced contractility, cardiac arrhythmias
What is the formula for calculating the FGF for non-rebreathing systems?
FGF = Minute Volume (Tidal Volume 10-15ml/kg x RR) x Circuit Factor
What device offers protection against anesthetic mortality in rabbits as compared to ET tubes or masks?
Supraglottic airway device
Which type of ET tube cuff covers a small contact area, so more pressure is exerted on that area when air is injected into the cuff?
Low-volume, high-pressure cuff (ex: Silicone, Red rubber)
Which type of ET tube covers a large contact area, so pressure is distributed across the area?
High-volume, low-pressure cuff (ex: Polyvinyl chloride - PVC)
How do you measure an ET tube for your patient?
Length: From incisors to thoracic inlet
Size: Palpate trachea or nasal septal width
A 4kg dog is intubated with a 4mm internal diameter ET tube. The tube is 19cm long, but the distance from the thoracic inlet to the incisors is 12cm. What are the consequences if the ET tube is inserted completely into the lungs? What about if it is left protruding outside the mouth?
Into one lung (endobronchial intubation): hypoxemia due to decreased SPO2
Outside mouth: increased mechanical dead space
A vet intubates a 10kg dog & performs an ET tube leak test. By mistake, he injects 5ml of air into the pilot balloon, inflating the cuff to a pressure of 40 cmH20. Can this cuff pressure be safely maintained? If not, what complications may occur?
No, normal is 20-30 cmH20 → may cause ischemia + have to resect trachea due to damage if left at 40
A vet is inducing anesthesia in a 3kg cat but forgets to administer lidocaine before intubation. What is the major risk associated with this omission?
Laryngospasm
What parameter can tell us if we accidentally inserted the ET tube into the esophagus rather than the trachea?
Capnograph (will see flatline in CO2 if in esophagus)
What type of ET tubes are useful in pediatric patients, small dogs, or small cats due to having less risk of tracheal damage?
Uncuffed ETTs
Which type of ET tubes are typically used in exotics due to being narrower at the tip of the tube below the larynx?
Cole ETTs
Which type of ET tubes have a helical wire within the wall to prevent occlusion during extreme patient neck positioning?
Armored or re-enforced ETTs
A 2yo healthy cat, an 8yo dog with chronic kidney disease, a 15yo horse with colic requiring emergency surgery, & a 6yo rabbit with a dental abscess all require general anesthesia. What factor most significantly increases anesthetic mortality risk across all these species?
Poor physical health status (ASA class >3)
What is the typical surgical plane of anesthesia?
1.3x MAC (Minimum Alveolar Concentration)
What are the mechanisms of action of inhalant anesthetic agents?
Enhance inhibitory receptors (GABA + Glycine)
Reduce excitatory pathways (Nicotinic + Glutamate)
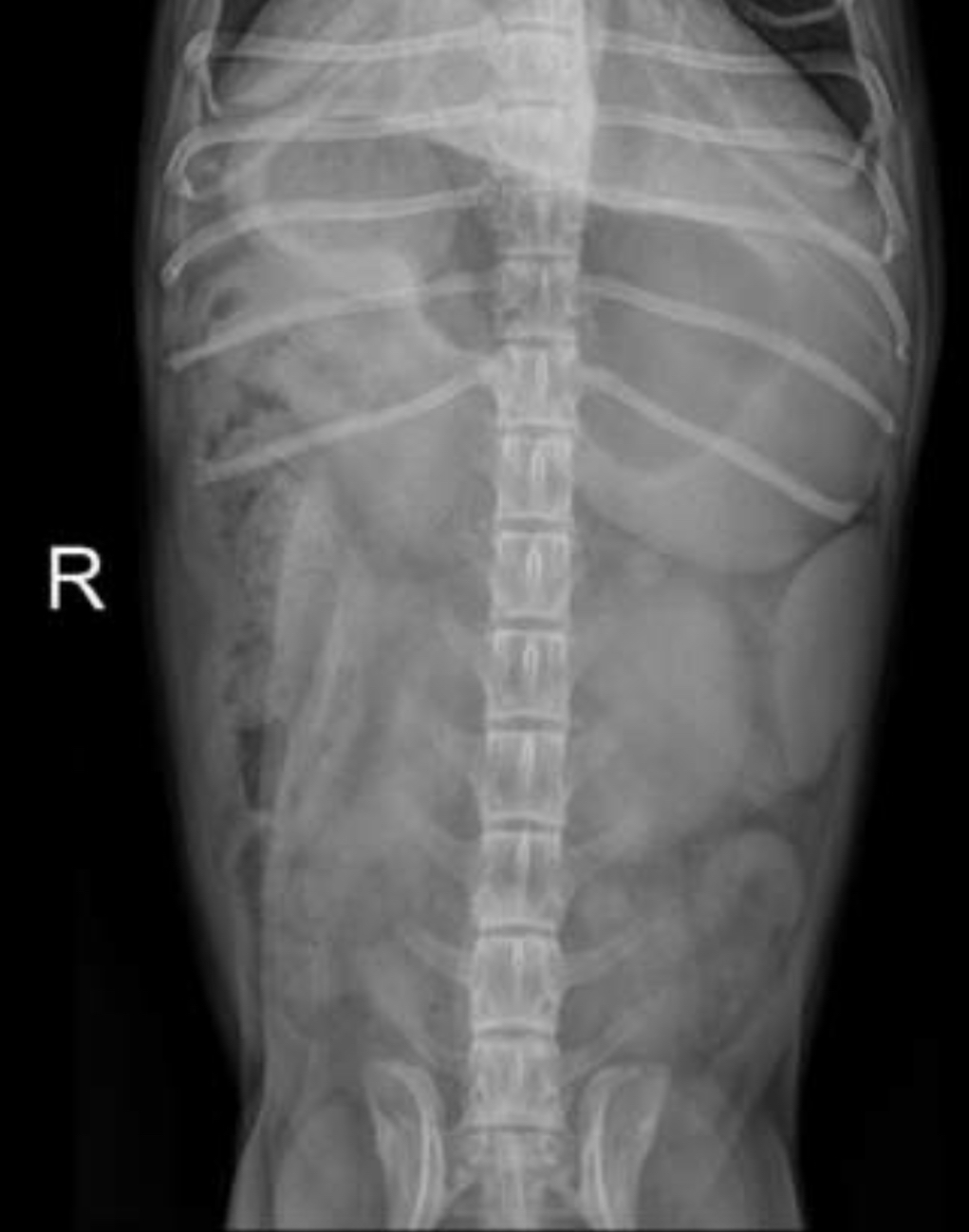
This is a ventro-dorsal radiograph of a canine patient presenting with vomiting & lethargy. What makes this view of poor quality for interpretation?
Beam collimation
-view is cut off too cranially (does not show caudal thorax, diaphragm, or liver)
-view is also cut off too caudally (does not show caudal abdomen to coxofemoral joint)
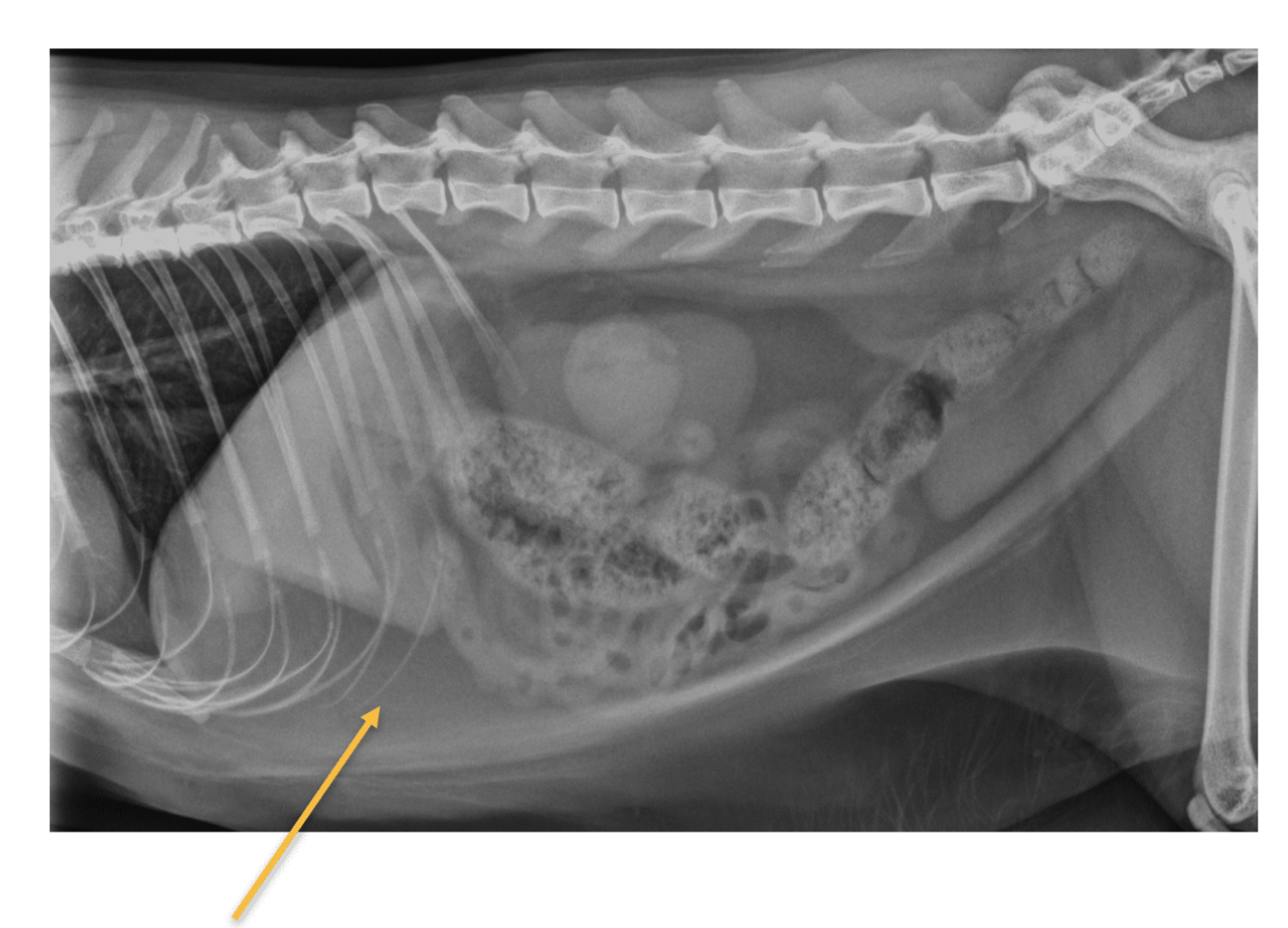
This is a right lateral view of feline patient presented with fever, lethargy, & vomiting. What is the structure noted by the yellow arrow?
Falciform fat

This is a close up VD radiograph of a canine patient focusing on the right cranial + mid-abdomen. What does the following radiograph indicates?
Positive contrast study of the Pseudo-ulcers in the duodenum
Which organs can we NOT normally see on abdominal radiographs?
Pancreas, Adrenals, Lymph nodes, Ureters, Ovaries/Uterus
What does it mean if you have reduced serosal detail on a radiograph due to excessive fat, fluid, masses, etc.?
Difficulty seeing contours of individual organs
-adjacent soft tissue structures will no longer be seen as separate
A large amount of _____ ______ can cause an overall increase in opacity on abdominal radiographs.
Free fluid
What does pneumoperitoneum most commonly occur secondary to, leading to increased contrast of serosal definition on abdominal radiographs?
Surgery
What are the common radiographic signs of pneumoperitoneum?
-Highlighted serosal surfaces
-Geometric-shaped gas opacities near diaphragm, liver, & cranial to bladder
-Focal loss of serosal detail
What is the incidental findings on an abdominal radiograph in cats that appears as intrabdominal mineralization?
Bates body
What are some of the main causes of generalized hepatomegaly?
CHF, EMH, Hypothyroidism, Hyperadrenocorticism, DM, Neoplasia, Lipidosis
What are some of the main causes of focal hepatomegaly?
Normal aging, Hepatocellular + Bile duct carcinoma (dogs), Biliary cystadenoma/adenocarcinoma (cats)
What are some of the main causes of microhepatica?
Normal, PSS, Microvascular dysplasia, Cirrhosis
What are the radiographic signs of pancreatitis?
-Loss of serosal definition
-Lateral displacement of descending duodenum
-Caudal displacement of transverse colon
-Cranial displacement of stomach
-Persistent gas dilation of small intestine
-Thickening, corrugation, or spasticity of the duodenum
What is the only radiographic view where we can see the head of the spleen on cats?
V/D
-if see spleen on lateral = splenomegaly
If you can see a large C-shaped soft tissue opacity on both V/D & lateral radiographic abdominal views of a dog, what is likely occurring?
Splenomegaly/torsion
What are the most common causes of splenomegaly in dogs? In cats?
Dogs: Neoplasia, EMH, Hematoma
Cats: Diffuse splenomegaly, Lymphoma
If volvulus is suspected in a patient with gastric dilation, what radiographic changes would we see on an abdominal radiograph?
-Pylorus moves dorsal + cranial with air on RL
-Fundus/greater curvature moves ventral + to the right
-Splenic displacement
What are the major radiographic signs of a pyloric outflow onstruction?
-Gastric dilation
-”Gravel sign” → mineral granular material in pyloric antrum region
What are the major radiographic signs of gastritis?
-Gastric wall thickening
-Thickening &/or increase in # of rugal folds near pyloric antrum
-Mineralization with uremic gastritis
What are the main radiographic changes of mechanical ileus?
-Mainly gaseous, some fluid
-SI loops may stack + curve abnormally (hairpin-like appearance)
-”Gravel sign'“ in chronic partial obstruction
A ratio of maximum colon diameter to length of vertebral body L5 ________ suggests constipation, while a ratio of _______ is suggestive of megacolon.
1.28-1.48, 1.48
You have a feline patient presenting with a history of ingesting a FB. Plain X-rays shows evidence for GI obstruction with no visible FB & possible perforation. What is the preferable contrast study to be conducted for this patient?
Positive contrast study / Iodinated contrast medium via oral route
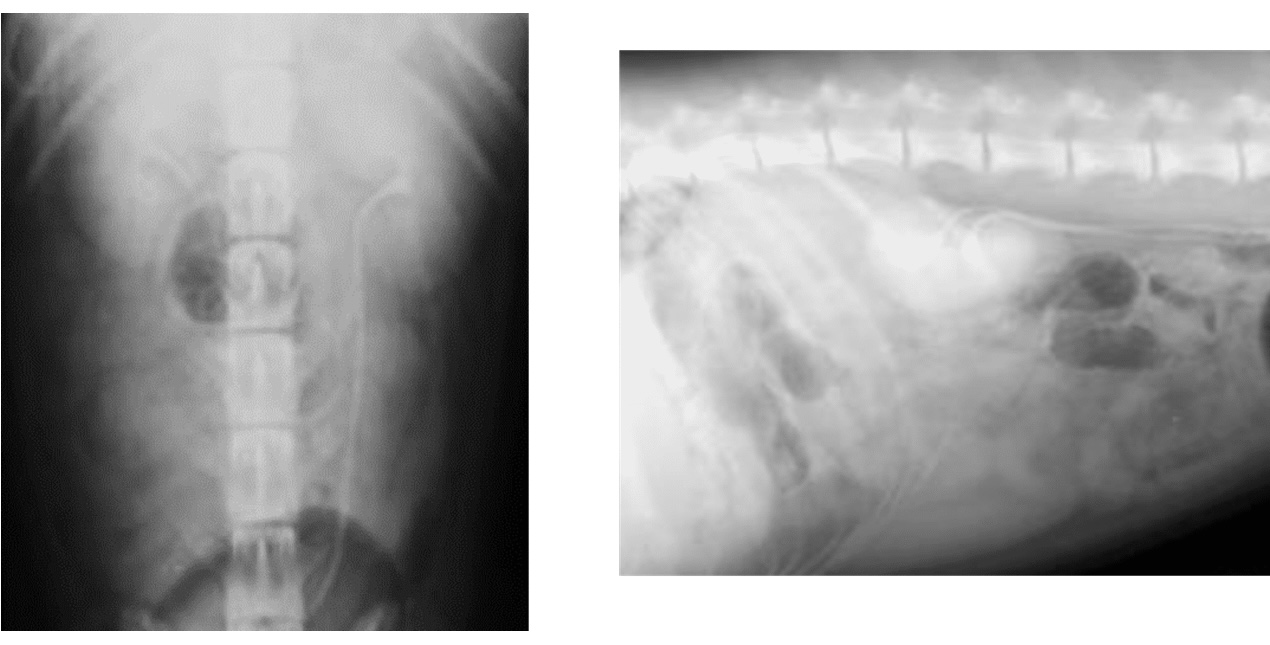
This patient has been admitted for EU/IVP study. These VD + lateral views were taken after 20 minutes from IV administration of the contrast media. What do they indicate?
The presence of contrast medium in the renal pelvis + ureters (pyelogram phase)
What happens to intrapulmonary (alveolar) pressure during spontaneous ventilation (inspiration)?
It decreases below atmospheric pressure → negative intrapulmonary pressure
During spontaneous expiration, what happens to intrapulmonary (alveolar) pressure?
It increases above atmospheric pressure → positive intrapulmonary pressure
What method maintains airway pressure above atmospheric pressure during inspiration & then falls to atmospheric pressure, allowing for passive expiration?
Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (IPPV) → utilizes manual (reservoir bags) + mechanical (machine) ventilation
What parameter describes the positive pressure that the ventilator maintains within the breathing system after the end of each expiratory phase (between breaths) in order to keep the alveoli open so they do not collapse completely after expiration?
Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP)
If high PEEP values are maintained on a mechanical ventilator for a patient, what may occur?
Collapse of capillaries in the lung → exacerbate reduction preload + hypotension
What are the basic settings on mechanical ventilators for small animals?
PIP: 10-12 cmH20
RR: 10-20 bpm
VT: 10-15 ml/kg
I:E Ratio: 1:2
PEEP: 0-4 cmH20
In an ascending (standing) bellow, in which direction does the bellow move upon expiration?
Upward