Concepts on Exam 1 and 2 MC
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
not the specific questions asked, but any concepts mentioned
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Unusual properties of water (7)
density (solid is less dense than liquid), water is most dense at 4 deg C, high boiling/freezing point, high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, universal solvent, greenhouse effect (absorbs infrared radiation as water vapor)
Adenovirus
waterborne viral pathogen
Giardia
protozoan pathogen, infected individuals spread the disease via dormant cysts, only 5-10% show symptoms, causes diarrhea and cramps, resistant to chlorine
Vibrio cholera
bacterial pathogen, from contaminated water and shellfish, causes extreme fluid loss and dehydration
Norovirus
easily transmitted through fecal-oral route involving surface contact, liquid out both ends
HBr is a strong acid. If NaBr is added to water at pH 7 and completely dissociates, what will happen to the pH and why?
pH will not change; anions of strong acids don’t attract protons (Br- doesn’t combine with H+); also, NaBr is a neutral salt (strong acid HBr with strong base NaOH)
Legionella pneumophila
bacterial pathogen, respiratory pneumonia, spreads through inhalation of aerosols, opportunistic pathogen
Schistosoma
animal pathogen, nematode (blood fluke), due to walking in water (burrows in skin), causes liver disease
If pH<pKa, which form is dominant? If pH>pKa?
protonated (nondissociated, protons stay); deprotonated (dissociated, protons leave)
Carbonate anion
CO3 2-
Bicarbonate anion
HCO3-
Hydroxide anion
OH-
Nitrate anion
NO3-
Sulfate anion
SO42-
Phosphate anion
PO43-
Ammonium cation
NH4+
Agriculture water pollutants
salts, phosphorus, nitrogen
Alkalinity
water’s ability to resist changes in pH, due to presence of buffering compounds
Turbidity
quantifies the amount of suspended solid particles in water, measure of cloudiness
different # of …protons → ___, electrons (same element) → ___, neutrons (same element) → ___
elements; ions; isotopes
Endocrine disruptors
interfere with hormone function, can have toxicological effects even at low concentration, categorized as “micropollutants” or PPCPs
What does the secondary drinking water standard regulate as part of the Safe Drinking Water Act?
taste and odor, color, corrosivity, hardness
Coagulation in drinking water treatment (solids removal)
neutralize surface charge of colloidal particles so they no longer repel each other
Flocculation in drinking water treatment (solids removal)
water is gently mixed so particles collide and aggregate into larger flocs; adhesion is due to van der Waals forces
Sedimentation in drinking water treatment (solids removal)
mixing is minimized and flocs are allowed to settle out onto the bottom of a clarifier
Granular media filtration in drinking water treatment (solids removal)
remaining particles are filtered out by passing through a bed of media; colloids collide with media particles and stick to them, thus removing colloidal particles from water
PFAS
large class of synthetic organic compounds; aka forever chemicals; all or most alkyl atoms are saturated with fluorine instead of hydrogen (fluorine-substituted carbon chains); carcinogenic; water repellant, grease repellant, surfactant/foam-forming, strong acids, flame retardant (strong chemical bonds → don’t burn)
Nonpoint source pollution
contamination as a result of contaminated rain, runoff (i.e agricultural runoff), snowmelt, or road salts; diffused discharge; not subject to permitting under CWA
Point source pollution
discharged from a discrete point (i.e pipe or smokestack); contained discharge; easier to regulate, treat, and control; CWA
Covalent bond
sharing of electrons among atoms
Ionic bond
electron transfer; atoms bound by electrostatic attraction between ions of opposite charge; very strong except when introduced to polar solution/solvent (i.e water)
Metallic bond
delocalized electron cloud; overall neutral
Hydrogen bond
electrostatic attraction between partially charged hydrogen atoms and an electronegative atom; weak; IMF
Salt (chemical contaminant)
issue for agriculture; sources include irrigation, road salt, reverse osmosis waste brines, oil/gas produced water
Nutrients (chemical contaminant)
mainly phosphorus and nitrogen; can cause eutrophication (nutrients → algal blooms → bacteria eat blooms and consume O2 → DO depletion)
Mercury (chemical contaminant)
heavy metal; bioaccumulates (accumulates in biological tissues and increases in concentration up the food chain)
Polyatomic ion
consists of two or more covalently bound atoms; dissolves but does not dissociate; non-zero charge
Organic molecule
contains one or more carbon (C) atom covalently bonded to other atoms (usually H and O)
Aromatic compound
organic compound containing a ring of 6 carbon atoms with alternating double and single bonds
Primary standards of the Safe Drinking Water Act come in which two forms?
MCL (max contaminant levels) and TT (treatment techniques)
Activated sludge process
biosolids recycling; RAS and WAS flow ratio affects BOD conversion to CO2 vs biomass, F/M ratio, and cell retention time
Nitrogen fixation
the conversion of N2 gas to nitrogen-containing nutrients such as nitrate and ammonia
Combined chlorine disinfection (3)
involves both addition of free chlorine and ammonia, leads to fewer byproducts than free chlorine, provides relatively long-lasting residual in the distribution system
Denitrification
anaerobic stage in wastewater treatment to remove N2; microbes use NO3- as an electron acceptor and reduce it to inert N2
Secondary sedimentation
stage in activated sludge process (wastewater treatment) where sludge is removed (WAS) or recycled (RAS)
Membrane bioreactor
alternative process to activated sludge for BOD removal; water is pulled through fiber membranes, leaving bacteria behind
Resistance to inactivation by chemical oxidants (i.e chlorine):
Cryptosporidium parvum cysts, viruses, bacteria (i.e Legionella)
cysts are most resistant, then bacteria, then viruses
Activated sludge process with high BOD removal ratio, high aeration requirements, and poor settleability of solids is characteristic of what type of cell retention time?
high (>6 days)
Activated sludge process with good BOD removal ratio, mid aeration requirements, and good settleability of solids is characteristic of what type of cell retention time?
moderate (3-4 days)
Activated sludge process with low BOD removal ratio and low aeration requirements is characteristic of what type of cell retention time?
low (< .5 days)
Anaerobic digestors in wastewater treatment
convert BOD to CO2 and CH4 (methane) gases → fuel; digested sludge has less mass, nutrients/BOD, and pathogens; removal of CO2 and methane
How is phosphorus removed from wastewater?
precipitated (using alum or lime) to a solid, then removed via sedimentation during secondary clarification
PFR
water enters from one end and flows steadily out of the other; think of a pipe
CSTR
one inflow and outflow, constantly mixed, outflow conc. = conc. in tank
Batch reactor
chemical reaction/biological process contained in a vessel, no inflow or outflow; can be used to determine the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction because it’s a closed system
Fermentation
heterotroph; type of metabolism microbes use to obtain energy; only organic compounds present with no external electron acceptors like O2 or SO4 2-; anaerobic
Chemolithotroph/chemoautotroph
obtains carbon from CO2 and energy for metabolism from inorganic redox pair
Aerobic respiration
heterotroph; get energy from carbon-based electron donor and O2 as electron acceptor
Heterotrophs (3)
require preexisting organic compounds (reduced carbon), obtain energy from thermodynamically favorable redox reactions, contribute to oxygen depletion in waters with high BOD
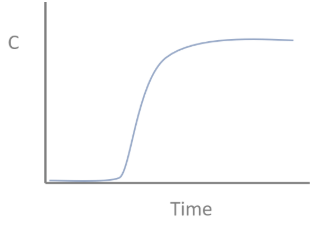
Graph if the influent concentration of a CSTR suddenly changes
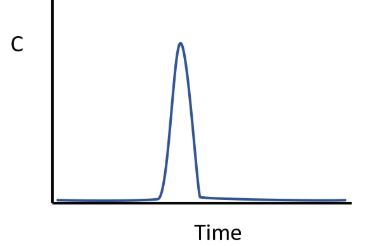
Graph if an unreactive compound is briefly injected into the influent of an ideal PFR
Zero-order rate expression for a chemical degradation reaction
dC/dt = -k
First-order rate expression for a chemical degradation reaction
dC/dt = -kC
Second-order rate expression for a chemical degradation reaction
dC/dt = -k[A][B]
When an acid is added to water with high alkalinity, what happens to the pH?
pH decreases slightly at first, then doesn’t change (until buffer is depleted)
When an acid is added to water with high alkalinity, what happens to the concentration of CO32- and why?
concentration decreases; it accepts H+ to form HCO3-
How are nitrogen compounds removed in wastewater treatment?
aeration/aerobic conditions (nitrification, NH4+ + 2O2 → NO3- + 2H+ + H2O) followed by anaerobic conditions (denitrification, 2NO3- + organic matter → N2 + CO2 + H2O)
Autotroph
obtains carbon for synthesis from CO2
Photoheterotroph
obtains energy for metabolism from sunlight and carbon from organic compounds
Chemoheterotroph
obtains both carbon and energy from organic compounds
Photoautotroph
obtains carbon from CO2 and energy from sunlight
Free chlorine
water disinfectant; ruptures cell membranes and degrades enzymes/cellular components; produces DBPs; primary and secondary; example = trihalomethanes
Ozone
water disinfectant; very strong oxidant, soluble gas; stronger than chlorine; unstable (must be produced on site); doesn’t leave residual for secondary; produces few DBPs; primary only
Ultraviolet radiation
water disinfectant; inactivates microorganisms by directly causing DNA mutations (renders bacteria and viruses incapable of replicating); virtually no byproducts; primary only