Evolution Mechanisms and Microevolution
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
sexual selection
certain traits make an individual more attractive to the opposite sex, and more likely to reproduce
what does sexual selection result in?
sexual dimorphism, members of the same species having different non-sexual characteristics due to which male the female picks
traits that handicap the individual, their reproductive chances are increased but it also decreases their ability to survive
Intrasexual Selection
individuals of one sex compete (before or after mating)
often results in increased aggressiveness and development of male secondary sex characteristics
increased characteristics in promiscuous species
Intrasexual precopulatory
competing over dominance or specific territories
intrasexual post-zygotic
after the egg was fertilized, induced abortion or infanticide
a new lion takes over a pride and the females have spontaneous abortion
Intersexual Selection
mate choice, generally the female chooses
male advertises qualities, female chooses best male
ex: specific bower bird species build their bowers how the female likes
natural selection works on _________ yet ________ evolve
individuals (same species, same place, same time), species (can breed & produce fertile offspring)
micro evolution
changes in a population’s gene pool from one generation to the next
gene pool
all the genes in the entire population
genetic equilibrium
no changes occur in gene frequency from generation to generation
what causes microevolution?
mutations resulting in new genetic variation
evolutionary mechanisms that alter the existing genetic variation
mutation
unpredictable change in DNA
source of new genetic variation
mutations _______ genetic variation
increase
mutations in ________ are inherited
germ cells
epigenetics
changes in organisms caused by modification of gene expression (what switch is turned on) rather than alteration of the genetic code
sequence is the same, but different genes are turned on/off
Genetic Drift
evolutionary mechanism
allele frequencies in small populations change by random chance events
this event is random, it is not related to reproductive success or better adaptability
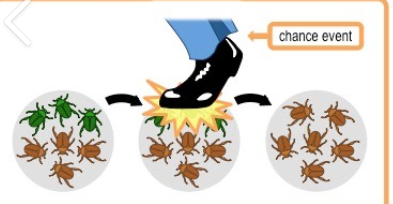
genetic drift
founders effect
small population establish in a new habitat; this new establishing population may not be the same as the ORIGINAL population of where they came from
random chance that the specific organism ended up in a new habitat
bottle neck effect
result of genetic drift
drastic population reduction where the original genetic frequencies do not reflect the original genetic frequencies of generations that came before
what could cause a bottle neck effect?
forest fire where the survivors do not reflect the original genetic frequencies of generations that came before
gene flow
migration of fertile individuals that become introduced to another population with a transfer of gametes from one population to another
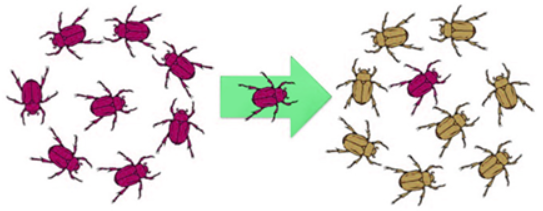
gene flow, introducing one population to another
Natural Selection
evolution mechanisms
a response to the environment- differential reproduction of individuals with different traits depending on how fit they are for the environment
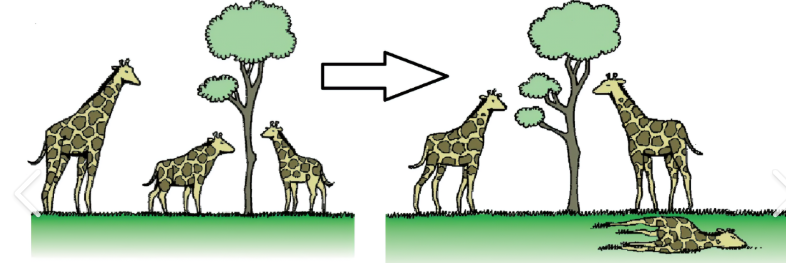
natural selection
for evolution to be natural selection it must be:
heritable variation
differential reproductive success
the Scarlett honeycreeper south gained a shorter bill after its favorite source of nectar began disappearing and they had to find it else where, what is this an example of?
natural selection - a response to the environment
natural selection: stabilizing
the “average” trait is selected
natural selection: disruptive
opposites or the extreme characteristics are selected
natural selection: directional
favors one extreme characteristic
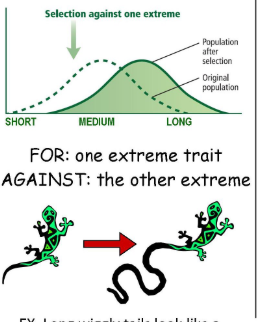
directional selection: directing toward one extreme trait
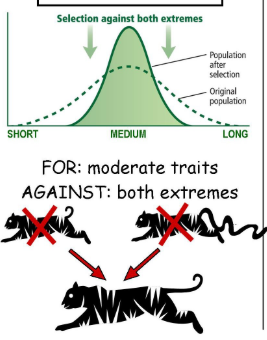
stabilizing selection: favoring an intermediate characteristic
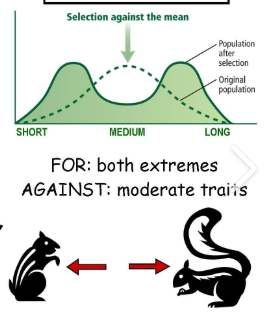
disruptive selection: favoring both extremes
balancing selection
maintains diversity in a population, doesn’t favor one form of a gene over another
opposite genes exist equally in a population