Plate Tectonics
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Approximately how old is the Universe?
Approximately how old is the Earth?
The Universe is 13.7 billion years old
The Earth is 4.5 billion years old
The layers closer to the center of the Earth have a….
greater density & greater temperature
Crust + what is continental and ocean crust made of
The outermost layer of the Earth.
Composed of solid rock. Mainly (silicate) SiO2
Continental Crust made of mostly granite (high in silica)
Ocean Crust made of mostly basalt (low in silica)
Basalt is denser than granite because basalt (mafic rock) has a higher concentration of Fe & Mg than granite (felsic rock)
Mantle + upper and lower
mainly iron & magnesium silicates. contains most of the Earth’s volume & mass. Made of mostly semi solid rock.
Upper Mantle (10% of mantle) solid rock
Lower Mantle (90% of mantle) semi-solid rock
Range of density for the full mantle: 3.4 - 5.4 g/cm3
Outer Core
Molten (liquid) Metal.
Mainly iron & nickel alloy (Fe-Ni).
Responsible for Earth’s magnetic field.
Alloy = mixture of metals
Inner Core
Solid metal
Mainly iron & nickel alloy (Fe-Ni)
Same composition as the outer core
Center of gravity
What’s the difference between outer and inner core?
Same composition = iron and nickel alloy (Fe-Ni)
OUTER IS LIQUID METAL
INNER IS SOLID METAL
What is the composition of each layer
Crust
Mantle
Outer Core
Inner Core
Crust - Solid Rock (silicate, high in silica, low in Fe & Mg)
Mantle - Semi-Solid Rock (silicate, low in silica, high in Fe & Mg)
Outer Core - Molten Metal (iron-nickel alloy)
Inner Core - Solid Metal (iron-nickel alloy)
How come the inner core is hotter than the outer core yet the outer core is a liquid and the inner core is not? + where IS the inner core within the outer core
The inner core of the Earth has temperatures and pressures so great that the metals are squeezed together and are not able to move about like a liquid, but are forced to vibrate in place like a solid.
Inner core floats (suspended) within the molten outer core (like egg yolk in egg white)
Tectonic Plates
Large pieces of a crust & rigid upper mantle that fit together at their edges to cover Earth’s surface
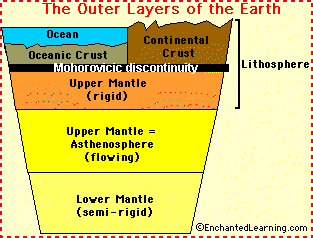
Lithosphere
The lithosphere consists of the entire Earth’s crust and the upper portion of the upper mantle
Made of solid rock
Lithosphere floats on top of the asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
layer of the upper mantle BENEATH the lithosphere
The lower portion of the upper mantle
It is made of molten rock and has the ability to flow.
It is thought to move the tectonic plates
Lithosphere vs Asthenosphere + lower mantle
The lithosphere consists of the entire crust, both continental and oceanic, and the upper portion of the upper mantle. (the orange in the diagram) The lithosphere is a solid rock layer.
The asthenosphere is made up of the lower portion of the upper mantle. (the neon yellow in the diagram) The asthenosphere flows like lava.
The lower mantle is semi-solid and is 90% of the entire mantle. (dull yellow on diagram)
Hypothesis of Continental Drift
The gradual movement of the continents across the earth’s surface through geological time.
In 1912 Alfred Wegener came up with the Hypothesis of Continental Drift. Wegener proposed that Earth’s continents had once been a single supercontinent called Pangaea.
His hypothesis was not accepted at the time because there was no explanation for why the continents moved.
Pangaea
A supercontinent that broke apart about 200 million years ago (mya) and sent the continents adrift. Pangaea is the Greek word meaning all lands.
Evidence for Continental Drift: Geographic Evidence
Continents fit together like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle
Evidence for Continental Drift: Fossil Evidence
The same fossils that were found on different continents are now separated by oceans
Evidence for Continental Drift: Rock Layer Evidence
Rock layers & mountain ranges found on different continents which are now separated by oceans.
Evidence for Continental Drift: Climatic Evidence
Similar glaciers & coal deposits were found on different continents
Divergent Boundary
← →
Two tectonic plates move away (diverge) from each other.
Earthquakes are common.
Two Types of Divergent Boundaries (based on where the boundary occurs, water or land)
Divergent Boundary Occurring on the ocean floor AND Divergent Boundary occurring on Land
Divergent Boundary Occurring on the OCEAN floor
Creates an Oceanic Ridge which is a continuous chain of volcanoes on the ocean floor.
Intrusion of magma builds new oceanic crust.
Creates: Ocean ridge, chain of ocean floor volcanoes, new crust
Examples: Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Divergent Boundary occurring on LAND
Creates a Rift Valley which is a long narrow depression that forms when continental crust separates at divergent boundaries
Creates: Rift valley, new crust
Examples: East African Rift, Iceland
Convergent Boundary
→ ←
Two tectonic plates move toward (converge) each other
Subduction: is the term for when two plates collide, the denser plate descends below the less dense plate and into the mantle where the (denser) plate melts. (one plate goes underneath the other)
Earthquakes are common
Three Types (classified by types of crust involved)
Continental-Continental
Oceanic-Oceanic
Continental-Oceanic
Continental-Continental
two continental plates collide. Creates mountain ranges and earthquakes.
Examples: Himalayas, Rocky Mountains
Oceanic-Oceanic
two oceanic plates one subducting under the other
creates ocean trenches, island volcanoes & earthquakes
Ocean trench: an undersea valley on the ocean floor
Examples: Japan Trench, Mariana Trench
Continental-Oceanic
ocean plate subducts under the continental plate. Mountain ranges, continental chain volcanoes, ocean trenches, and earthquakes
Examples: Andes Mountains & Sierra Nevada Mountains
Ring of Fire: Runs along the Pacific Plate (largest in the world)
Along the ring of fire are where most of the Earth's volcanoes are located and where most of the world’s earthquakes occur.
Transform Boundary
↑↓
A place where two tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other at a fault zone.
Causes earthquakes, faults.
Fault: A crack in the Earth’s crust created when rocks on either side of the crack move.
Example: San Andreas Fault
All three BOUNDARIES
*all boundaries create earthquakes
Divergent Boundaries (moving away)
Ocean: ocean ridge, new crust, underwater chain volcanoes
Land: rift valleys, new crust
Convergent boundaries (coming together)
Continental-Continental: mountain ranges
Ocean-Oceanic: volcanoes, ocean trenches
Continental & Oceanic: volcanoes, ocean trenches, mountain ranges
Transform Boundary (sliding side by side)
Faults (don’t forget earthquakes)
Label if it is Convergent (Continental-continental, continental-oceanic, oceanic-oceanic), Transform Fault, Divergent (ocean or land)
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Himalayan Mountains
Andes Mountains
San Andreas Fault
East African Rift
Mariana Trench
Mid-Atlantic Ridge - Divergent ocean
Himalayan Mountains - Convergent continental-continental
Andes Mountains - convergent continental-oceanic
San Andreas Fault - by california, transform fault
East African Rift - Divergent land
Mariana Trench - convergent oceanic-oceanic
Identify the type of plate boundary associated with each term (convergent, divergent, or both)
Ocean trench
Continental mountains
Mid-oceanic ridge
Formation of new seafloor
Destruction of old seafloor
Volcano
Ocean trench - Convergent
Continental mountains - Convergent
Mid-oceanic ridge - Divergent
Formation of new seafloor - Divergent
Destruction of old seafloor - Convergent
Volcano - Both/Either
Seafloor Spreading Theory
The theory that explains how new ocean crust is formed at ocean ridges (found at divergent boundary) and destroyed at ocean trenches (found at convergent boundary)
Continental drift hypothesis explains HOW the tectonic plates move, the Seafloor Spreading theory explains WHY.
Evidence of Seafloor Spreading: Ages of Ocean Floor Rocks
The rock that makes up the ocean floor was dated and it was found that the FURTHER from the ocean ridge the rocks were, the OLDER the ocean floor. The rocks on the ocean floor CLOSER to the ocean ridge were found to be YOUNGER.
Evidence of Seafloor Spreading: Polarity of Minerals in Seafloor Rocks
The polarity of the iron in the ocean floor changes over time due to earth’s magnetic pole reversals.
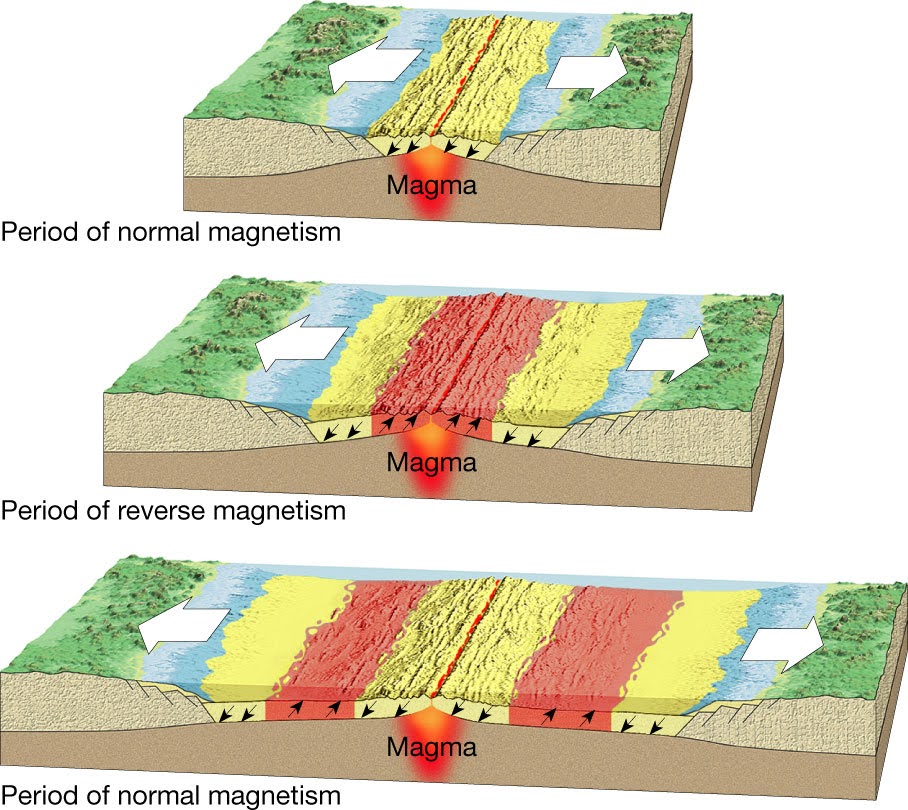
The diagram represents the Atlantic ocean getting bigger at a divergent boundary.
The top diagram is 200 mya (millions years ago)
The middle is 100 mya
The bottom is today.
*The rock closer to the line in the middle (the ridge) is NEWER, the rock farther away from that ridge is OLDER
Cause of Seafloor Spreading
The force of convection currents in the Earth’s mantle causes seafloor spreading and powers the movement of tectonic plates.
During seafloor spreading, magma, which is hotter and less dense than surrounding mantle material, is forced toward the surface of the crust along an ocean ridge.
As the two sides of the ridge spread apart, the rising magma fills the gap that is created. When the magma solidifies, a small amount of new ocean floor is added to Earth’s surface.
What does a divergent boundary make
*all boundaries create earthquakes
Divergent Boundaries (moving away)
Ocean: ocean ridge, new crust, underwater chain volcanoes
Land: rift valleys, new crust
What does a convergent boundary make
*all boundaries create earthquakes
Convergent boundaries (coming together)
Continental-Continental: mountain ranges
Ocean-Oceanic: volcanoes, ocean trenches
Continental & Oceanic: volcanoes, ocean trenches, mountain ranges
What does a transform boundary make
*all boundaries create earthquakes
Transform Boundary (sliding side by side)
Faults (don’t forget earthquakes)
Causes of Plate Boundaries: Convection Currents
The cyclical transfer of thermal energy (heat) to different areas of the Earth’s crust by the heating of a mantle by the Earth’s interior. Convection currents supply the energy for plate tectonic movement.
Cooled matter contracts causing an increase in density. The cooled matter then sinks as a result of gravity.
Warmed matter spreads out causing a decrease in density. The warmed matter then rises.
This up-and-down (rising and sinking) flow produced a pattern of motion called a convection current
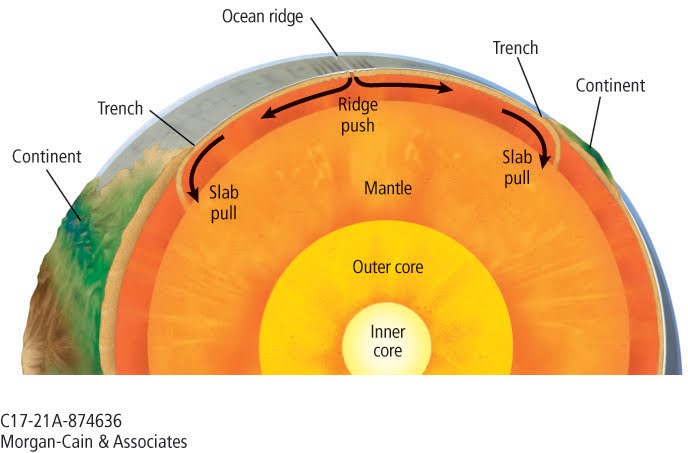
Ridge Push
The rising material in convection currents spread and reach the upper mantle causing both upward and sideways forces. The force lifts and splits the lithosphere at divergent boundaries.
Ridge push: occurs at divergent boundary, creates an ocean ridge
Crust created
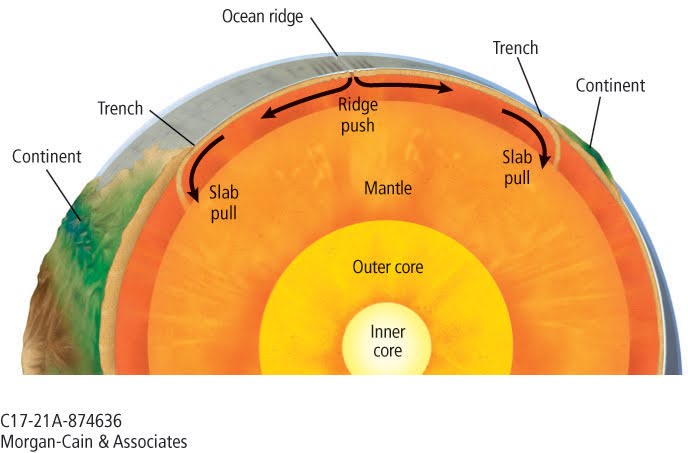
Slab Pull
The downward pull of the convection current occurs when a sinking force pulls tectonic plates downward at convergent boundaries.
Slab pull: occurs at convergent boundary, creates an ocean trench.
Crust destroyed
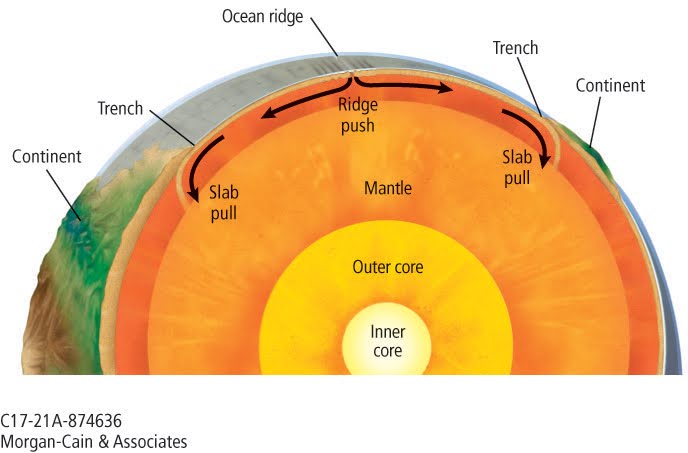
Ridge push vs Slab pull
Ridge push: occurs at divergent boundary, creates an ocean ridge
Crust created
Slab pull: occurs at convergent boundary, creates an ocean trench.
Crust destroyed
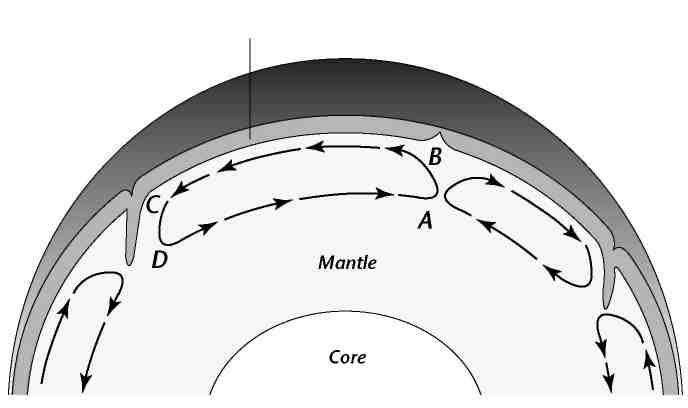
Hottest: A
Coldest: C
At point A the magma now has a lower density than surrounding magma and rises. From A to B the temperature of the magma is decreasing because it is getting further from the hot core. This decrease in temperature causes the density of magma to increase. At point B the density is about the same as the surrounding magma and no longer rises. From B to C the magma continues to decrease in temperature (and increase in density because of its distance from the core (it continues to cool off)
What percentage makes up the upper mantle & what percentage makes up the lower mantle?
Upper Mantle (10% of mantle) solid rock
Lower Mantle (90% of mantle) semi-solid rock
Which layer contains most of the Earth’s mass & volume?
Mantle
Which layer is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field?
Outer Core
Which layer contains the center of gravity?
Inner Core
The 2 parts of the upper mantle
the upper mantle is split up into 2 parts as well: upper portion (lithosphere), lower portion (asthenosphere)
The lithosphere floats over the asthenosphere like graham crackers floating on honey
Lithosphere floats over which layer?
Asthenosphere
What is the Hypothesis of Continental Drift and who came up with it?
The gradual movement of the continents across the earth’s surface through geological time.
In 1912 Alfred Wegener came up with the Hypothesis of Continental Drift. Wegener proposed that Earth’s continents had once been a single supercontinent called Pangaea.
What is happening to the tectonic plates at an ocean ridge
new ocean crust is formed at ocean ridges (found at divergent boundary)
What is happening to the tectonic plates at an ocean trench?
new ocean crust is destroyed at ocean trenches (found at convergent boundary)
What is the force that drives seafloor spreading?
Mantle Convection currents
What is subduction?
The term for when two plates collide, the denser plate descends below the less dense plate and into the mantle where the (denser) plate melts. (one plate goes underneath the other)
What is a fault?
A crack in the Earth’s crust created when rocks on either side of the crack move.
31. Rift valley (where does in occur)
32. Ocean Ridge (where does it occur)
33. Mountain range (be specific)
34. Ocean trench (be specific)
35. Island volcanoes (be specific)
36. Continental chain volcanoes (be specific)
37. Continuous chain of underwater volcanoes on the ocean floor
38. Earthquakes
31. Rift valley (where does in occur)
Divergent boundaries on Land
32. Ocean Ridge (where does it occur)
Divergent boundaries on Ocean floor
33. Mountain range (be specific)
Convergent boundaries Continental-Continental and Continental-Oceanic
34. Ocean trench (be specific)
Convergent boundaries Oceanic-Oceanic
35. Island volcanoes (be specific)
Convergent boundaries Oceanic-ocean
36. Continental chain volcanoes (be specific)
Convergent boundaries Continental-oceanic
37. Continuous chain of underwater volcanoes on the ocean floor
Divergent Boundaries on Ocean floor
38. Earthquakes
ALL plate boundaries
What are convection currents?
Currents that flow in the mantle of the Earth, they supply the energy for plate tectonic movement. Convection currents transfer heat from the core to the crust through the mantle.