Physics AS/A level Paper 1
1/61
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Centre of Mass
“The point at which the total mass of the object is said to act”
Conservation of Energy
“The energy of the system before an event = the energy of the system after the event“
Conservation of Momentum
“Momentum of the system before an event = the momentum of the system after”
Drag
“The resistance against the motion of an object. Usually proportional to the speed of that object”
Efficiency

Elastic collision
“Kinetic energy of a system before an event = kinetic energy after”
Equilibrium
“Moments about a point are balanced and the resultant force on the object is zero”
Force
“The rate of change of momentum of an object”
Gravitational potential energy
“The energy gained by an object when it is raised by a height in a gravitational field”
Impulse
change in momentum
Equal to the area under a force-time graph
Force x change in time
newton-second(N s)
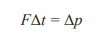
Kinetic energy
The energy an object has due to its motion
The amount of energy that would be transferred from the object when it decelerates to rest
Momentum
“The product of an objects mass and its velocity”
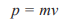
Moment
The product of a force and the perpendicular distance from the line of action to the pivot about which the force is acting
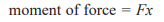
Newton’s First Law
“An object at a constant velocity will remain at a constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force”
Newton’s Second Law
“If an object is acted upon by a resultant force it will accelerate”
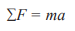
Newton’s Third Law
“Every action has an equal and opposite reaction”
Work Done
A force applied over a distance
Force x change in distance
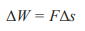
Current
“Rate of flow of charge”
Change in charge over the change in time
(Amps)
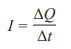
Potential Difference
Work done per coulomb
(Volts)
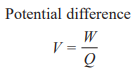
Resistance
“A measure of how difficult it is for current to flow in a circuit “
Directly proportional to the p.d.
Inversely proportional to the current flow
(Ohms)
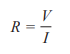
Ohmic Conductor
“A conductor which follows Ohm’s law, the current flowing through is directly proportional to the potential difference, when it is held at a constant temperature”
Resistivity
A measure of how easily it allows charge to flow through it
ρ- Resistivity
R- Resistance
l- lenght
(Ohm-metre)
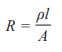
Current and Potential
n- number density(m^-3)
q- the charge of charge carriers (usually 1.6×10^-16C)
v- velocity of the charge carriers(ms^-1)
A- cross sectional area of the wire(m²), calculate using A=πr2
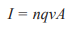
Superconductor
“Materials which have zero resistivity at and below a critical temperature”
Semiconductors
Components for which the resistance changes depending on external conditions:
LDRs- light sensitive
Thermistors- temperature sensitive
Power
“The rate of energy transfer”
(Watt)
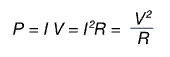
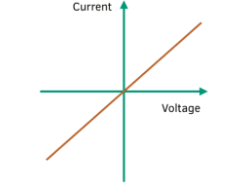
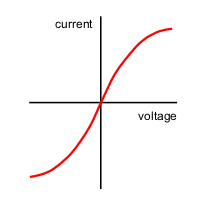
Filament Lamp
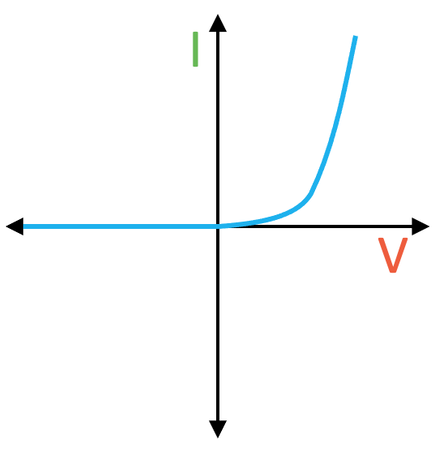
Diode
Series circuits
Total resistance:
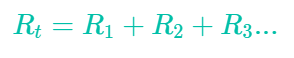
Parallel circuits
Total resistance:
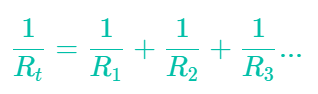
Kirchoff’s First Law
“The total current entering a junction is equal to the total current leaving it”
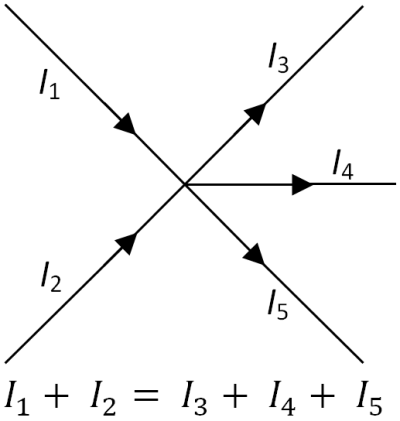
Kirchoff’s Second Law
“The sum of e.m.f in any loop of the circuit is equal to the sum of the p.d’s of each component”
E.M.F
“The amount of energy supplied by the source per unit charge”
(Volts)
Internal Resistance
“Opposition to the flow of charge within a cell”
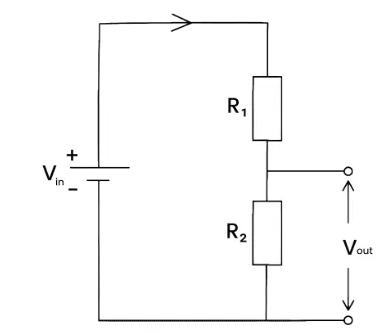
Potential Divider
A combination of two or more resistors in a series
The p.d in the circuit is split into a specific ratio
Angle in radians
s -arc length
r -radius
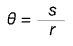
Angular speed -ω
v = ωr
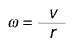
Connecting period and frequency to angular velocity
f = 1/T
T = 2π/ω
f = ω /2π
ω = f2π
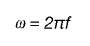
Centripetal force
“We know from Newton’s first law that to accelerate, an object must experience a resultant force, therefore an object moving in a circle must experience a force”
It always acts towards the centre of the circle
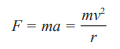
Centripetal acceleration
“The acceleration experienced while in uniform circular motion”
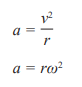
Simple Harmonic Motion
An object is experiencing SHM when its acceleration is directly proportional to displacement and is in the opposite direction”
x is the displacement from the equilibrium position

Electric Field
“A region of space in which an electric charge experiences a non-contact force. This force can be attractive or repulsive”
Coulomb’s Law
Determines the force acting between two charges.
If the force has a positive value, it is a repulsive force
If the force has a negative value, it is an attractive force
F - electric force
Q1 and Q2 - charges
r - distance of separation
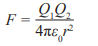
Electric Field Strength (E)
“The electrostatic force that a unit positive charge would experience, at a given point in the field”
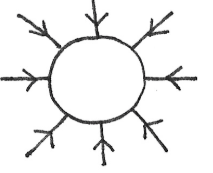
Radial Field
The field is stronger nearer the surface of the object, and weakens as you move further away
For a positive charge, the arrows point outwards
For a negative, the arrows point inwards
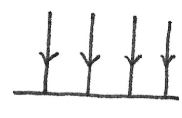
Uniform Field
Exerts that same electric force everywhere in the field
Electric Field Strength Equations
The first equation is for a radial field
Second is for a field formed by parallel plates
V- voltage
d- distance between the plates
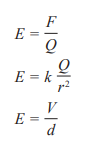
Electric Potential
“The amount of work done in moving a unit positive charge from infinity to that point”
k- Coulomb constant
Q- charge
r- distance of separation
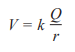
Electric potential difference
The work done moving a positive charge from one point to another
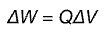
Capacitance (C)
The amount of charge a capacitor can store per unit of p.d
(Farads)
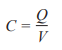
Energy stored by a capacitor
The second and third equations are derived by substituting the capacitance equation into the first
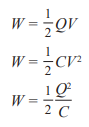
Energy stored by a capacitor- graph
Area under a charge-voltage graph gives the energy stored
The gradient of the graph is the capacitance
Charging graph for a capacitor
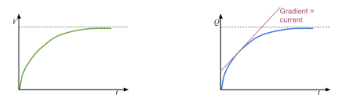
Discharging graph for a capacitor
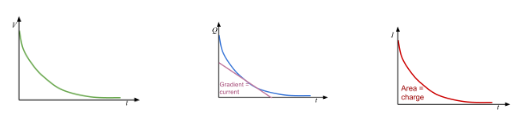
Capacitor discharging
Q0 is the initial charge…
To simplify the first three equations, take natural logs of both sides
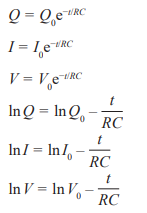
Time Constant
The product of the resistance in the circuit and the capacitance of the capacitor
The time taken to charge the capacitor to 1-1/e of its final value
The time taken to discharge the capacitor to 1/e of its initial value
Magnetic Flux Density
A measure of the strength of a field
(Tesla)
Motor Effect
Is when a current-carrying wire experiences a force in a field
Motor Effect- magnitude of the force
B- Magnetic Flux Density (T)
I- current (A)
L- length of wire (m)
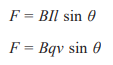
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
Direction of the force experienced by a current-carrying wire
Forefinger: point in the direction of the magnetic filed
Middle finger: the direction of the current
Thumb will be pointing in the direction of the force
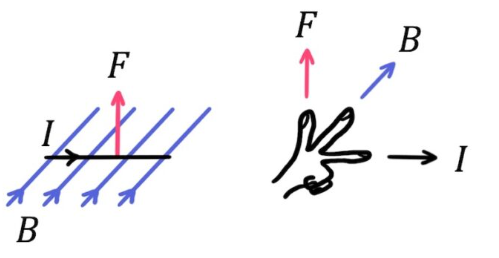
Magnetic Flux
“A measure of the magnetic field that passes through a given area”
Magnetic Flux (Wb) = Magnetic Flux Density (T) x Area (m2)
This applies if the magnetic field lines are perpendicular to the area
Magnetic Flux Linkage
more useful if using a coil
N Φ = B A N cos θ
N- number of turns