density
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
MASS AND DENSITY DIRECTLY RELATED
VOLUME AND DENSITY ARE INVERSELY RELATED
heating causes object to expand, increasing volume, and thus decreasing mass
more dense objects will sink
when mass go up density go up
MD UP
when volume go up density go down
VD DOWN
what is chemistry?
science that seeks to understand what matter does by studying what atoms and molecules do
discover relationships between particle structure of matter and the properties of matter we observe
CENTRAL SCIENCE
what is matter
anything that takes up space (occupies volume) and has mass
TAKES UP SPACE/OCCUPIES VOLUME
HAS MASS
smooth and continous
made up of ATOMS - what make up elements and MOLECULES - what make up compounds (which are made up of 2+ atoms)
HOW MATTER IS CLASSIFIED:
Pure substrance: unfirom material of definite composition with characteristic properties
same physical and chemical properties
display constant composition; HOMOGENUS
separation by chemical properties
temperatures remain constant during phase changes
PURSE SUBSTANCE TWO SUBCATEGORIES
ELEMENTS (smallest pieces)
COMPOUNDS (2 or more diff elements)
MIXTURES: has variable compostion parts are separated by physical means
homogenous
heterogenous
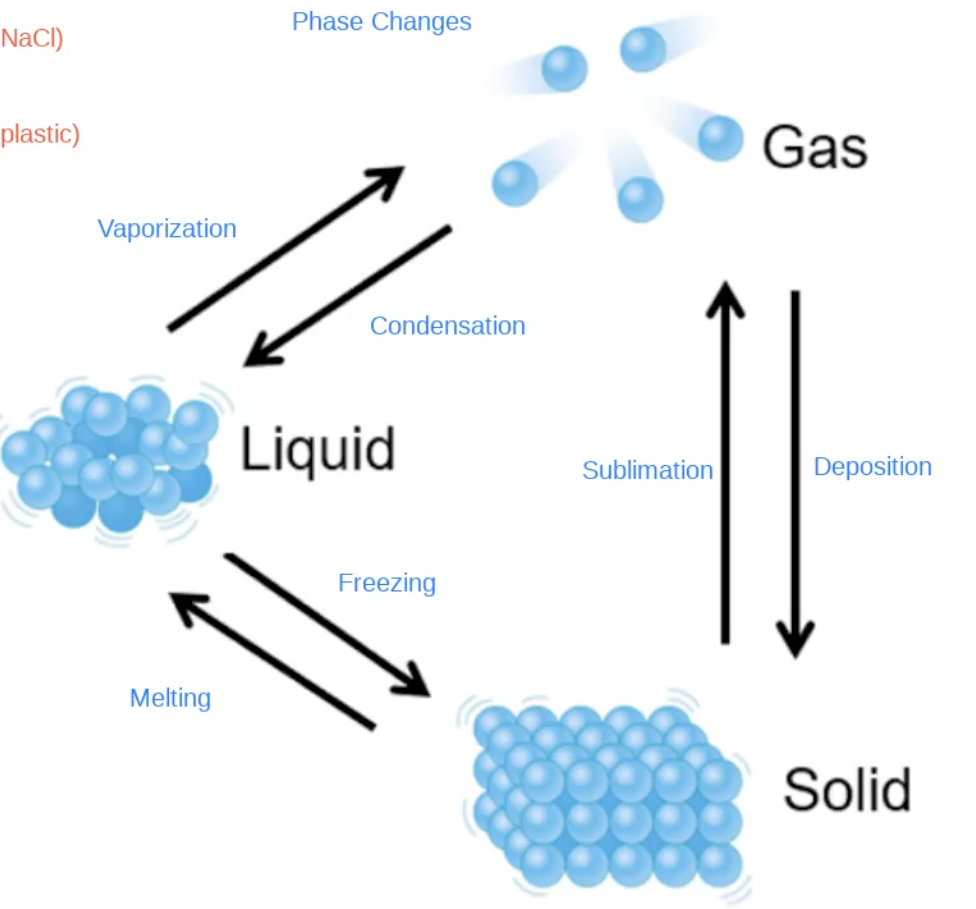
Phases of Matter
Solids
can be crystalline (longe range repeating order) or amorphouse (random)
FIXED SHAPE
DEFINITE VOLUME
NOTE COMPRESSIBLE
DO NOT FLOW
Liquids
definite volume but rates shape of containe
INDEFINITE SHAPE
DEFINITE VOLUME
NOT COMPRESSIBLE
CAN FLOW
Gas
INDEFINITE SHAPE
INDEFINITE VOLUME - TAKES SHAPE OF CONTAINER
COMPRESSIBLE - CAN BE PACKED INTO TIGHTER SPACE
CAN FLOW
sublimation solid to gas
gas to solid deposition
freezing, melting
vaporationz, condensation
Proprties and changes of matter
physical properties: can be changed without changing compostion, directly observable
Intensive properties (e.g., density, temperature, boiling point) are independent of the amount of substance present, often used to identify materials. Extensive properties (e.g., mass, volume, energy) depend on the total amount of matter, scaling with system size. Intensive properties are non-additive; extensive properties are additive
physical changes and separation techniques
alters the overall appearance but not the actual compostion of matter, not whats it made of
CHROMATOGRAPHY based on adherence to surface
EVAPORATION HOMOGENEOUS liquid removed from solid (water boil, salt)
DISTILLATION based on volatilty-boiling points of two liquids evenly mixed together a physical separation technique used to purify liquids or separate mixtures based on differences in their boiling points (volatilities)
FILTRATION - HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURES: insoluble solid is removed from a liquid (and vice versa)
chromatagraphy, evaporation, distillation, filtration
C E D F
cee diff…..
chromA AdherenCe
VAP FOR HOMOS liquid and solid
distillation boILIng poInts
FILL HETEROS insoluble solid and liquid
what is energy?
the ABILITY TO DO WORK
ABILITY TO CAUSE CHANGE
potential
kinetic
heat thermal energy: kinetic of particles
physical: energy is transfered as part of phase changes
chemical: added or released
endothermic: absorb heat energy as changes
exothermic: release heat energy as changes