
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What is study validity?
The validity of a research study refers to how well the results among the study participants represent true findings among similar individuals outside the study. Do the study results reflect the truth?
What are the two types of validity?
Internal
External
What is internal validity?
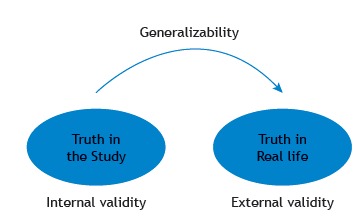
The extent to which the observed results represent the truth in the population we are studying and, thus, are not due to methodological errors.
Give 3 examples of threats to the internal validity of a study.
Chance
Bias
Confounding
Make two pairs out of these 4 words:
Validity
Reliability
Accuracy
Precision
Validity and accuracy
Reliability and precision
Which threat to internal validity affects the precision of the results?
Chance
Which threat to internal validity affects the accuracy of the results?
Bias
What is the alternative explanation or threat to internal validity that is neither chance nor bias?
Confounding
What is external validity?
The extent to which the results of a study are generalisable to patients in daily practice, especially for the population that the sample is thought to represent, or to other populations/settings.
What is the difference between internal and external validity?
What are the two types of error in epidemiological studies?
Random error
Systematic error
Describe the precision and accuracy of these results.
Low precision: scattered across different levels.
Low accuracy: not reflecting the truth.
Describe the precision and accuracy of these results.
High precision: data points close together, low variability
Low accuracy: not reflecting the truth
Describe the precision and accuracy of these results.
Low precision: data points scattered.
High accuracy: reflecting the truth.
Describe the precision and accuracy of these results.
High precision: data points close together
High accuracy: reflecting the truth
What are sources of random error?
Individual/subject
Observer
Machine
What are sources of systematic error?
Observer
Machine