TTU CHEM 1307 Exam 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Hurd Rule
electrons singly occupy, with parallel spins, all the degenerate orbitals within a subshell before spin-pairing electrons in an orbital
Pauli Exclusion Principle
no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers
subshells
number of orbitals
number of electrons
s (l=0), 1 orbital, 2 electrons
p (l=1), 3 orbitals, 6 electrons
d (l=2), 5 orbitals, 10 electrons
f (l=3), 7 orbitals, 14 electrons
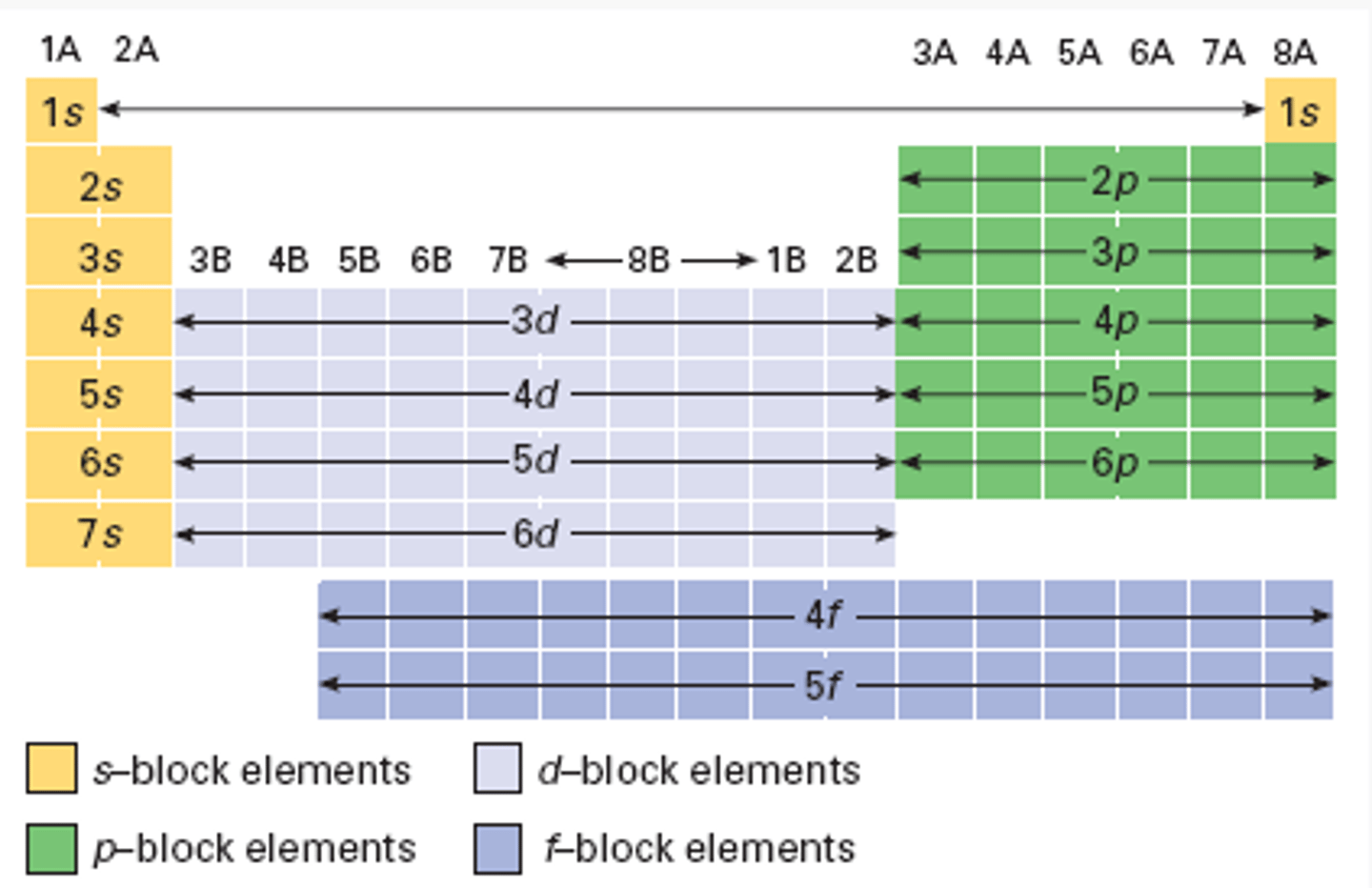
periodic table reference orbitals
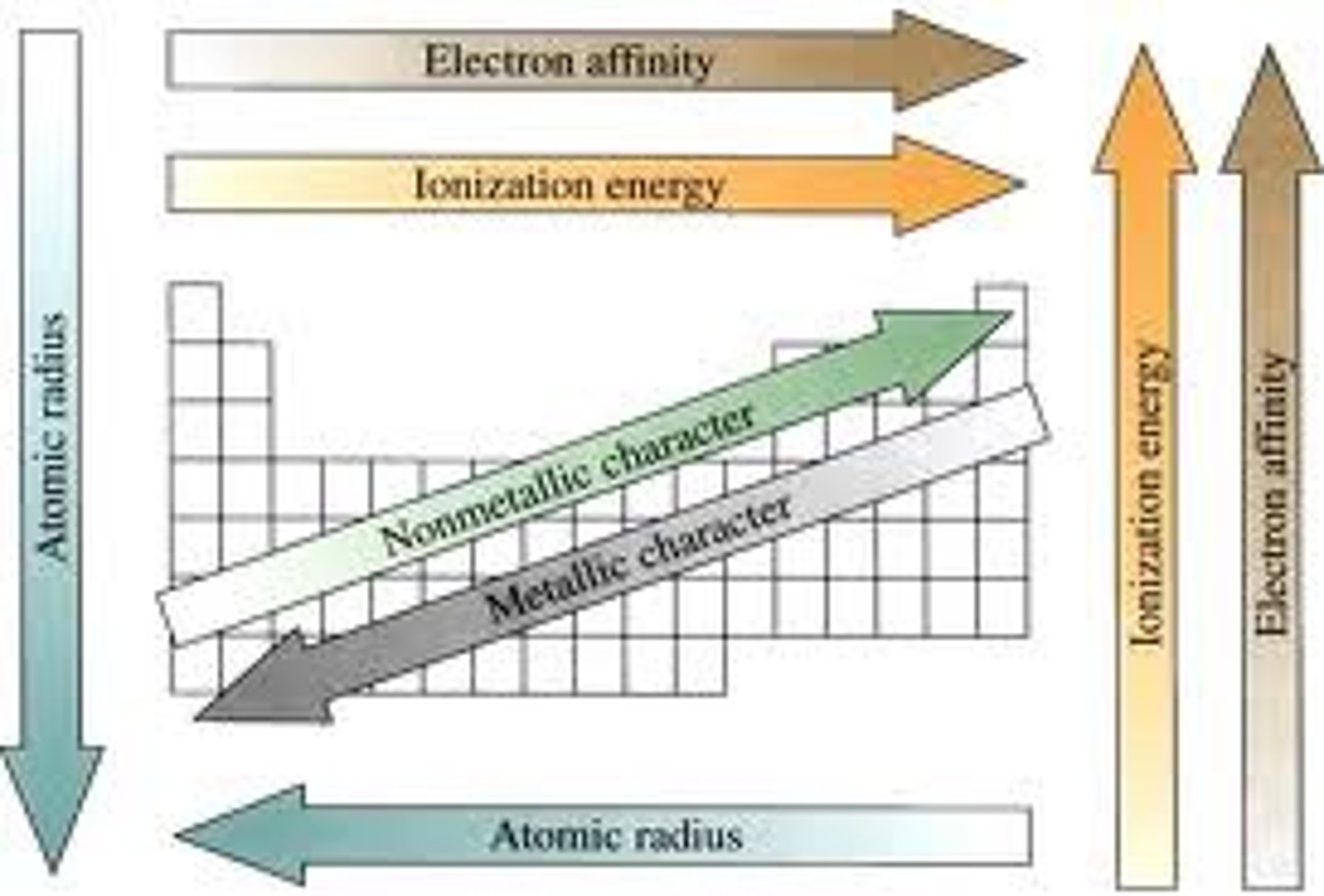
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
longer wavelength than 579 nm
lower energy and won't eject an electron
shorter wavelength than 579 nm
higher energy and will eject an electron
579 nm
the maximum of longest wavelength that can eject an electron
Enthalapy
The heat content of a system at constant pressure
H= E + PV
Constant pressure
Cp= △H
Calormetry
measurement of the amount of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction
Endothermic Reaction
rxn absorbs energy as heat making the surroundings colder because of lost heat
△Hrxn is positive
Exothermic Reaction
rxn releases energy as heat making the surroundings hotter as they absorb the heat
△Hrxn is negative
energy
The ability to do work or produce heat
Kinetic Energy
the energy an object has due to its motion, depends on mass and velocity
Potential Energy
energy due to position or composition
Joule (J)
SI unit of energy, 1 atm = 101.325 J
Heat (q)
the transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference
Work (w)
force over a distance
state function
function of a property at its present state
system
part of universe we focus on
surroundings
everything else in the universe we are not focusing on
law of conservation of energy
1st law of thermodynamics
energy can be converted from one form to another but never created or destroyed, energy of universe is constant
Thermodynamics
the study of energy and its interconversions
Internal Energy (E)
the sum of kinetic and potential energy, E= q+w
How do you calculate work done on or by a system?
w= -P(external) x V(system)
how do you calculate the change in internal energy for a closed system
E(closed)= q+w
calculating heat from heat capacity
q = C(capacity) x T(temp)
calculating heat from specific heat capacity
q= m C(specific) x T
calculating heat from molar heat capacity
q= n(moles) C(molar) x T
Amplitude
the height of a wave's crest
wavelength (λ)
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
speed (c)
The distance an object travels per unit of time
Frequency (v / hz)
period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
interference
the combination of two or more waves that results in a single wave
wave-particle duality
electrons and light can behave as both a wave and a particle
de Broglie wavelength
λ=h/mv
the wavelength associated with a moving particle
Bohr's theory of a hydrogen atom
Electron can exist in any one set of discrete states (energy levels) and can move from one to another by emitting or absorbing energy
difference of electron ground state and electron excited state
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle
Describe the quantum mechanical model of the atom
The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. The electron cloud is a visual model of the probable locations of electrons in an probability of finding an electron is higher in the denser regions of the cloud.
Aufbau Principle
states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available
periodic trends in atomic radius and ionization energy