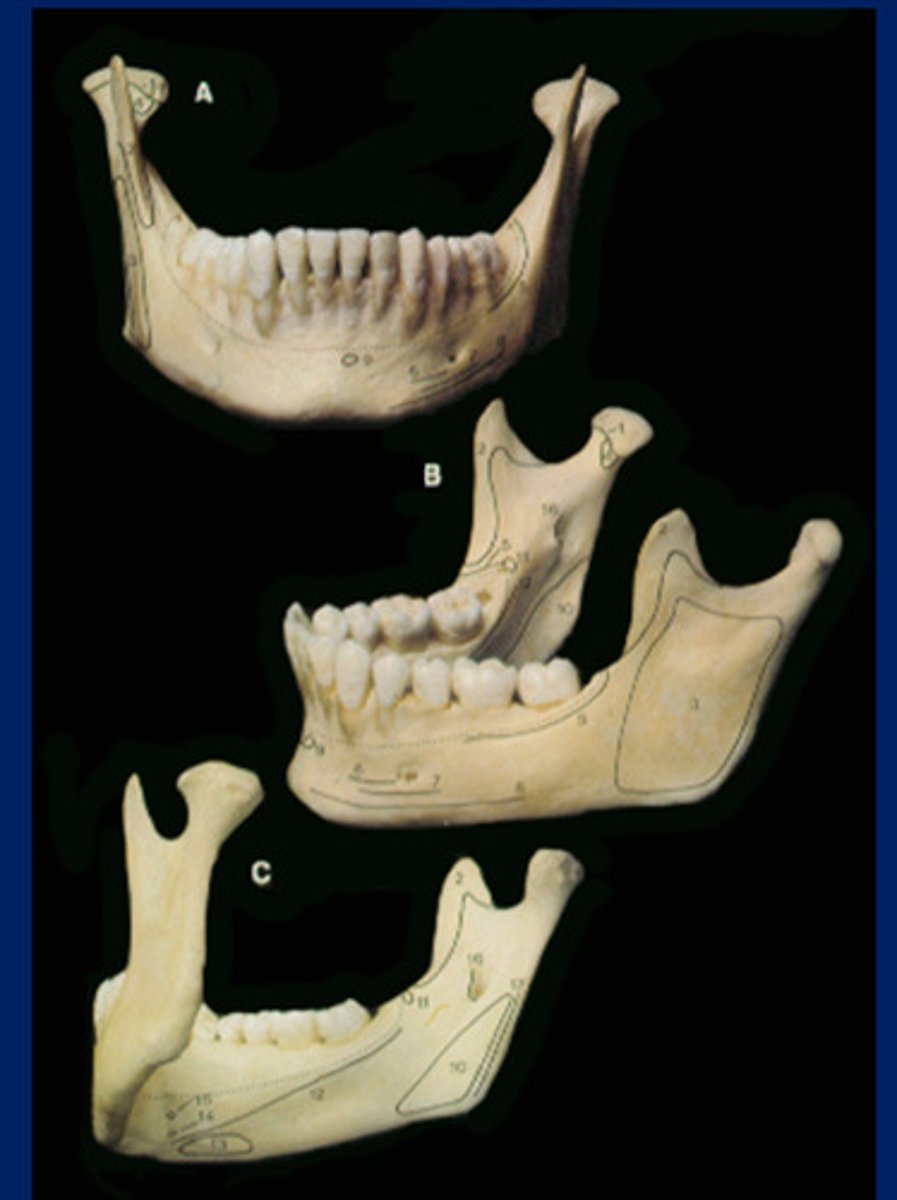
Skull
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Neurocranium
braincase (grey) contains chondrocranium and dermatocranium
Visceral arches
The neurocranium is not derived from
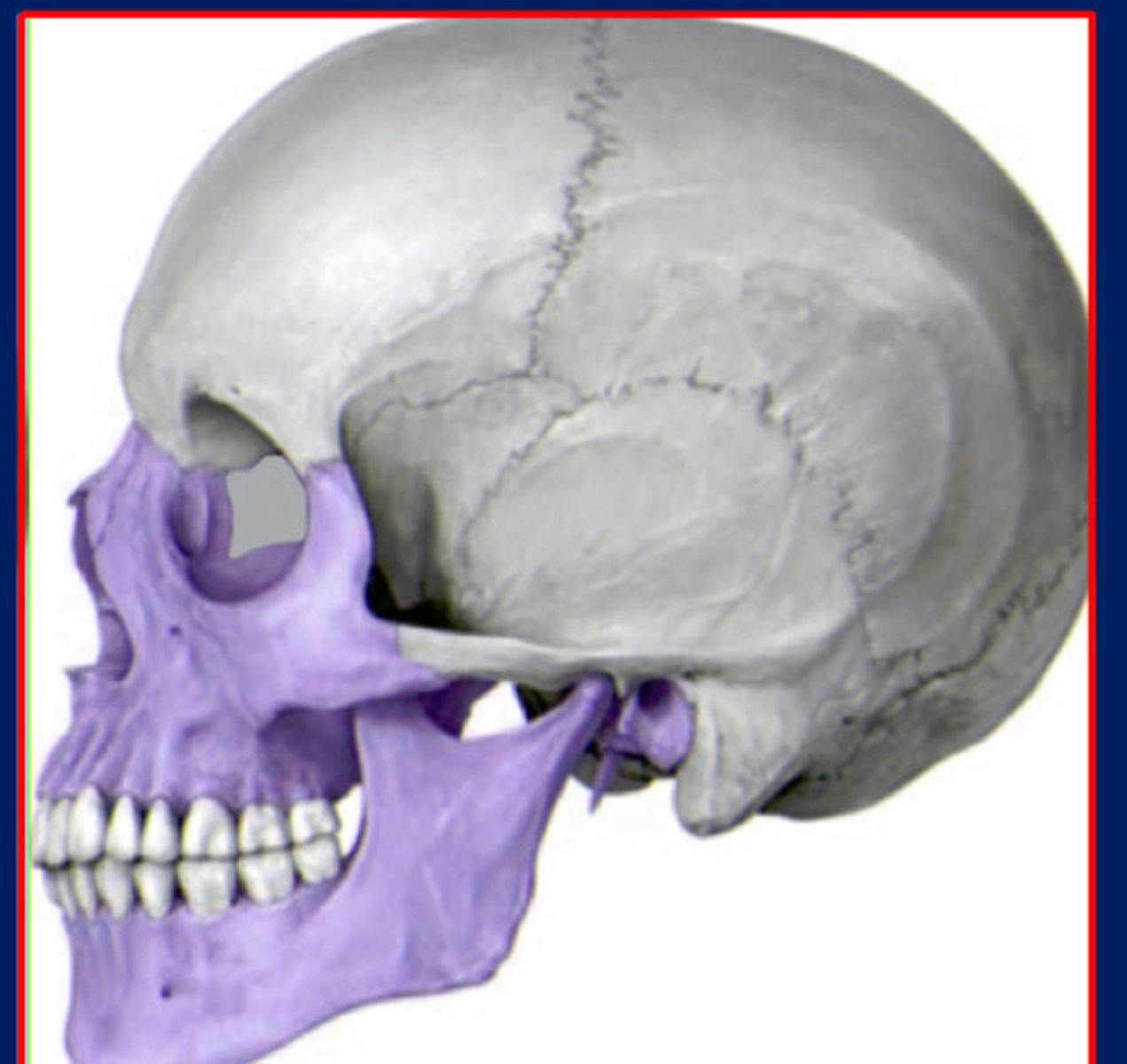
Splanchnocranium
facial skeleton or vsicerocranium (purple)
Visceral arches
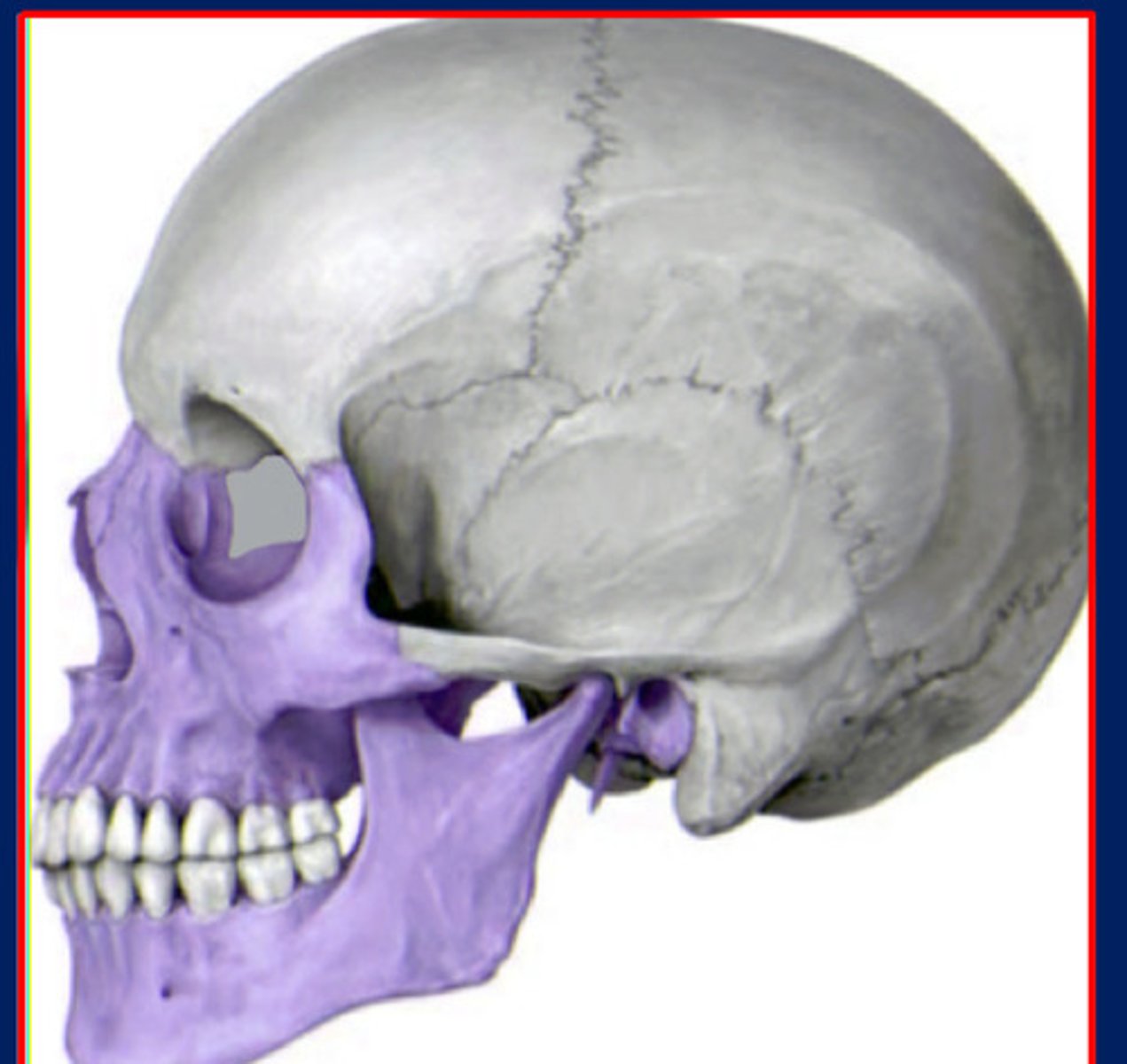
The splanchnocranium is derived from
Cranial base
floor of the cranial cavity, chondrocranium (purple)
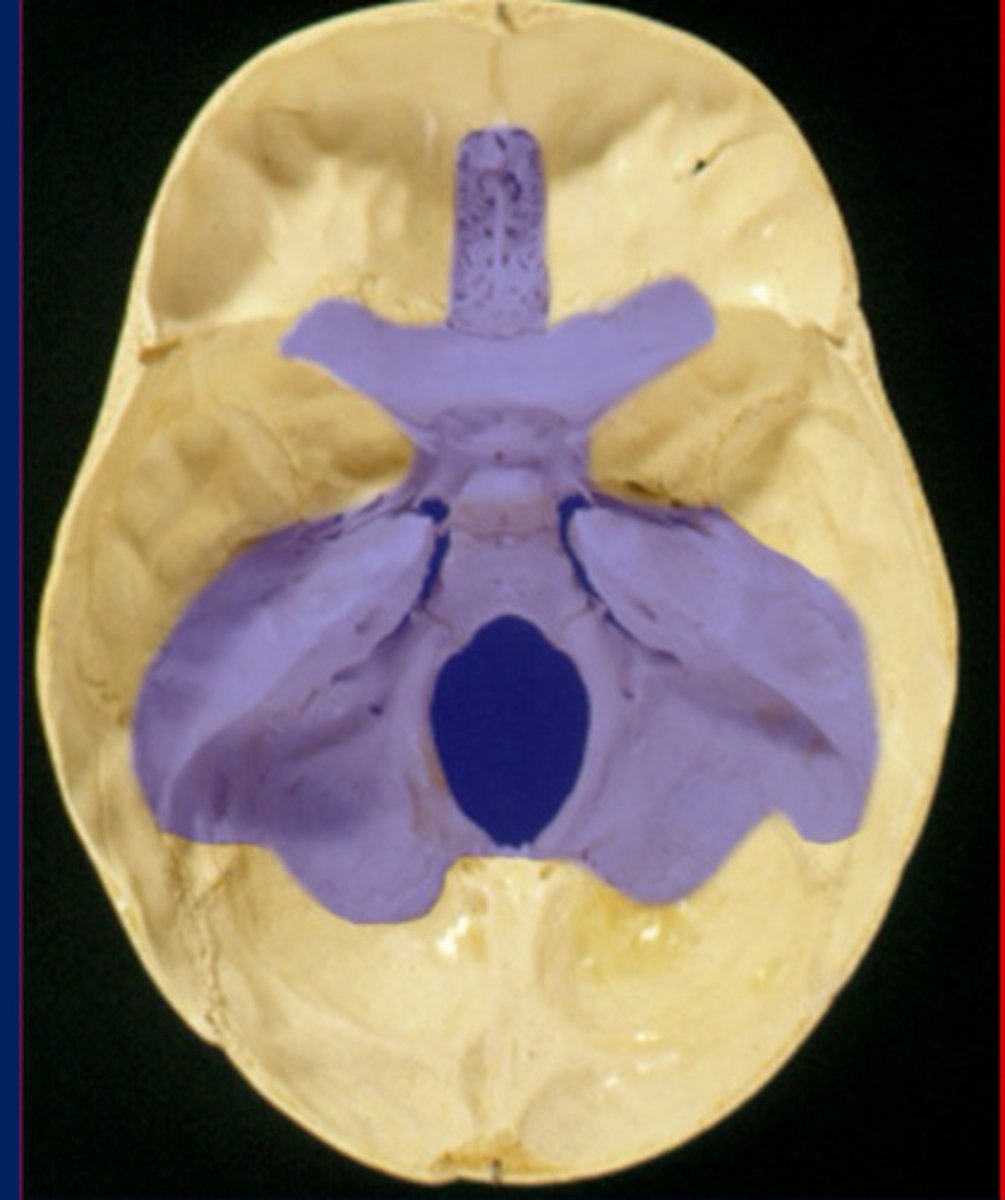
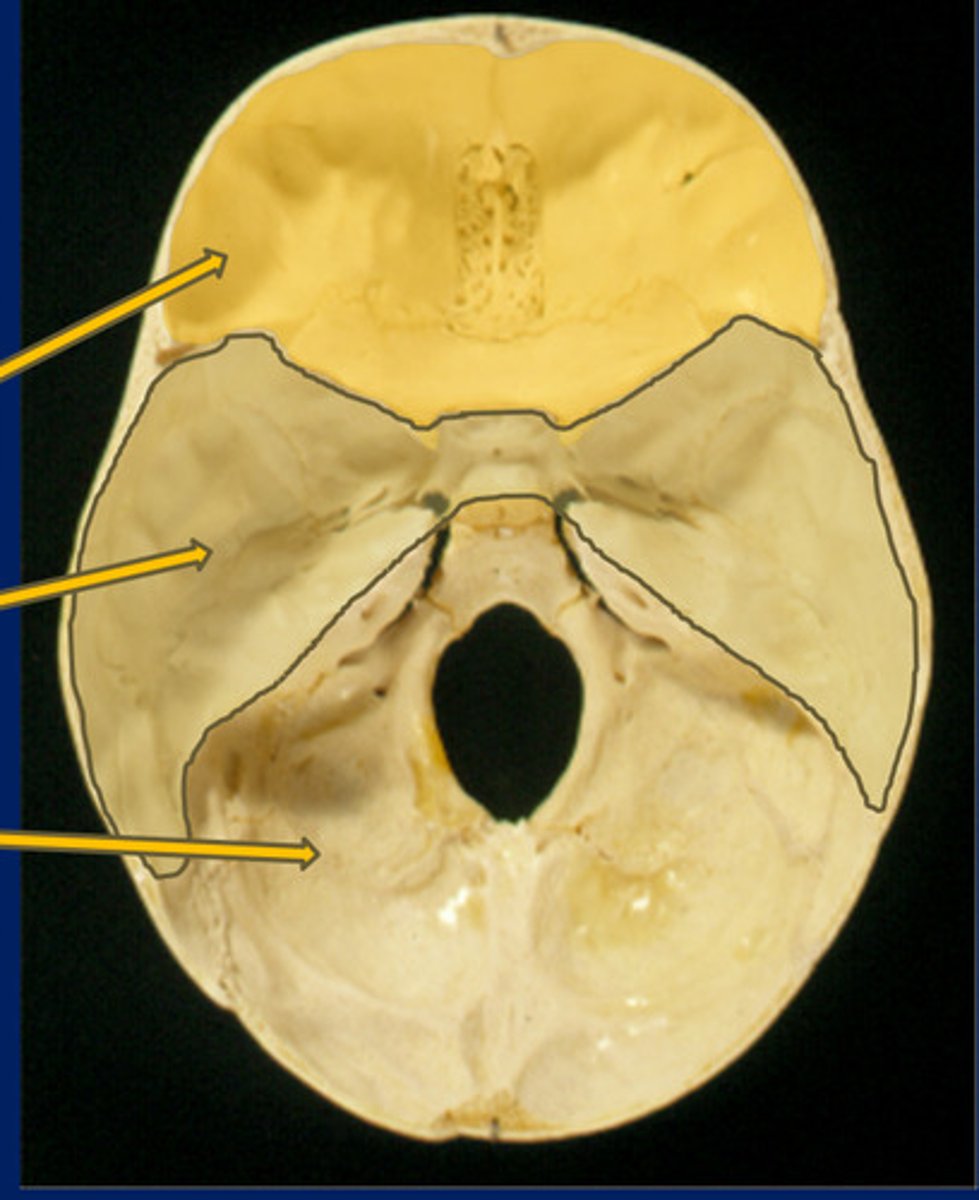
Anterior fossa
Top
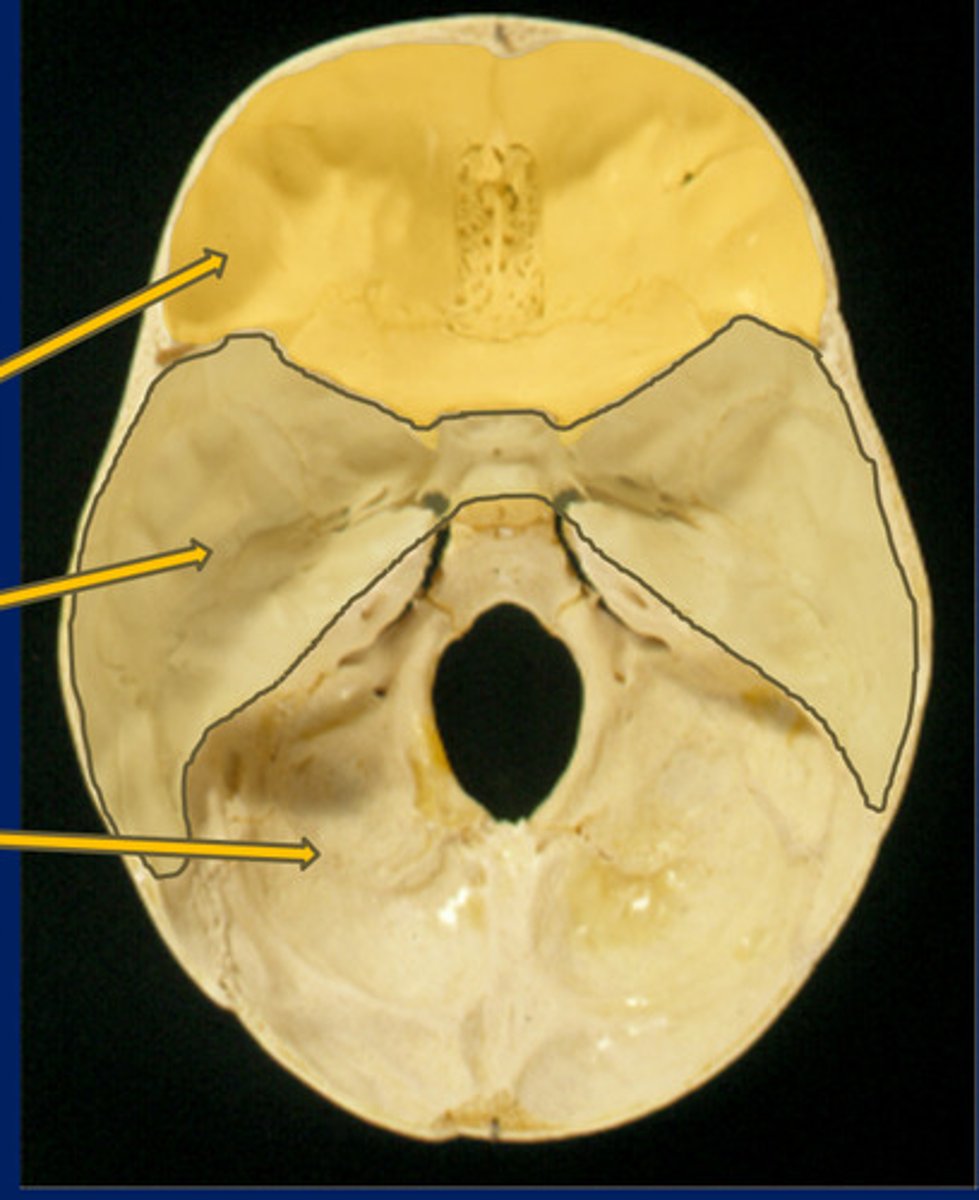
Middle fossa
Middle
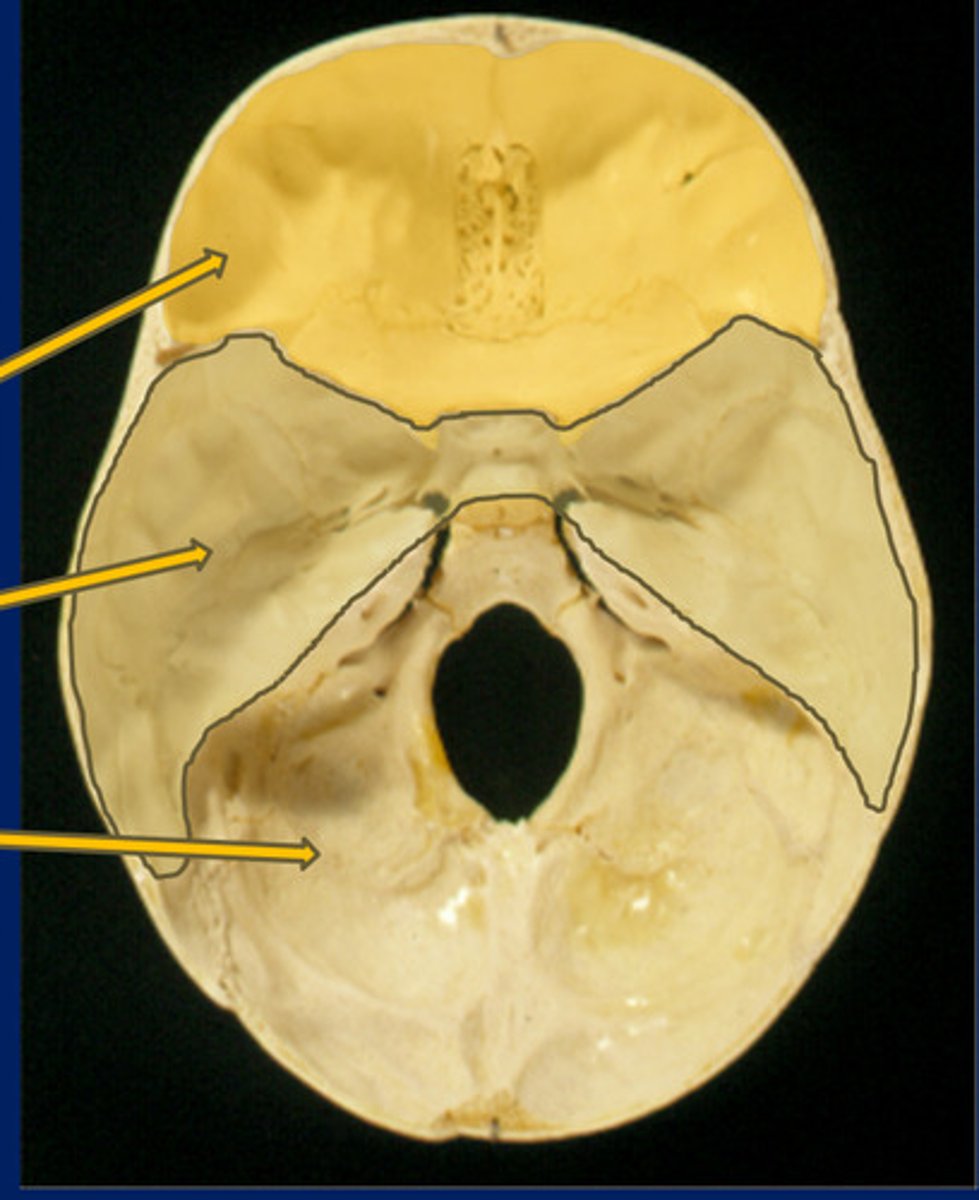
Posterior fossa
Bottom
Paraxial mesoderm
gives rise to somites (top two arrows)
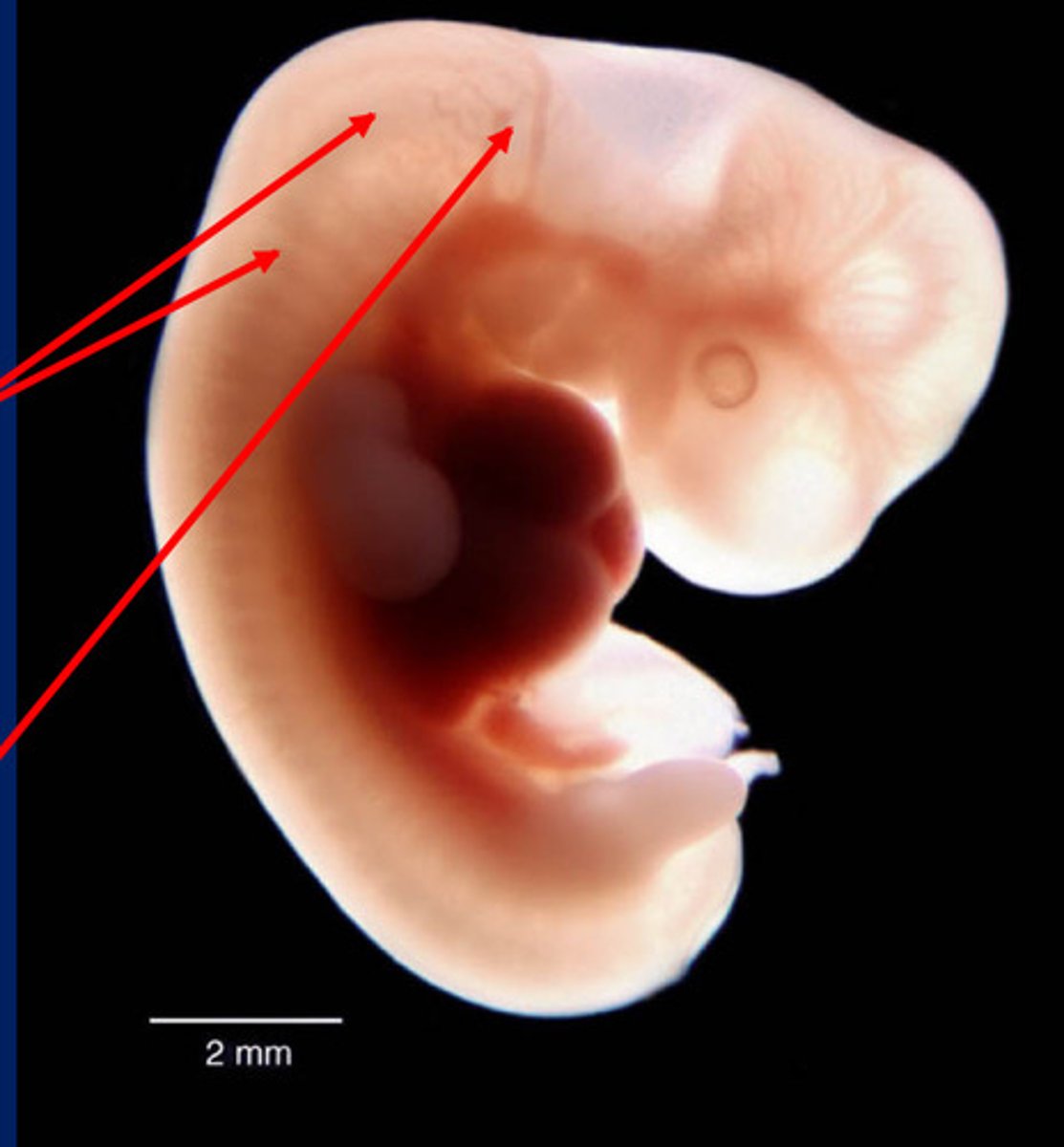
Somites
Paired blocks of mesoderm just lateral to the notochord of a vertebrate embryo. (Dermatome, myotome, sclerotome)
Mesenchyme
___ is of mesodermal origin in paraxial mesoderm
Neural crest
group of cells that develops from the embryo's ectoderm and contributes to the development of many vertebrate structures (bottom arrow)
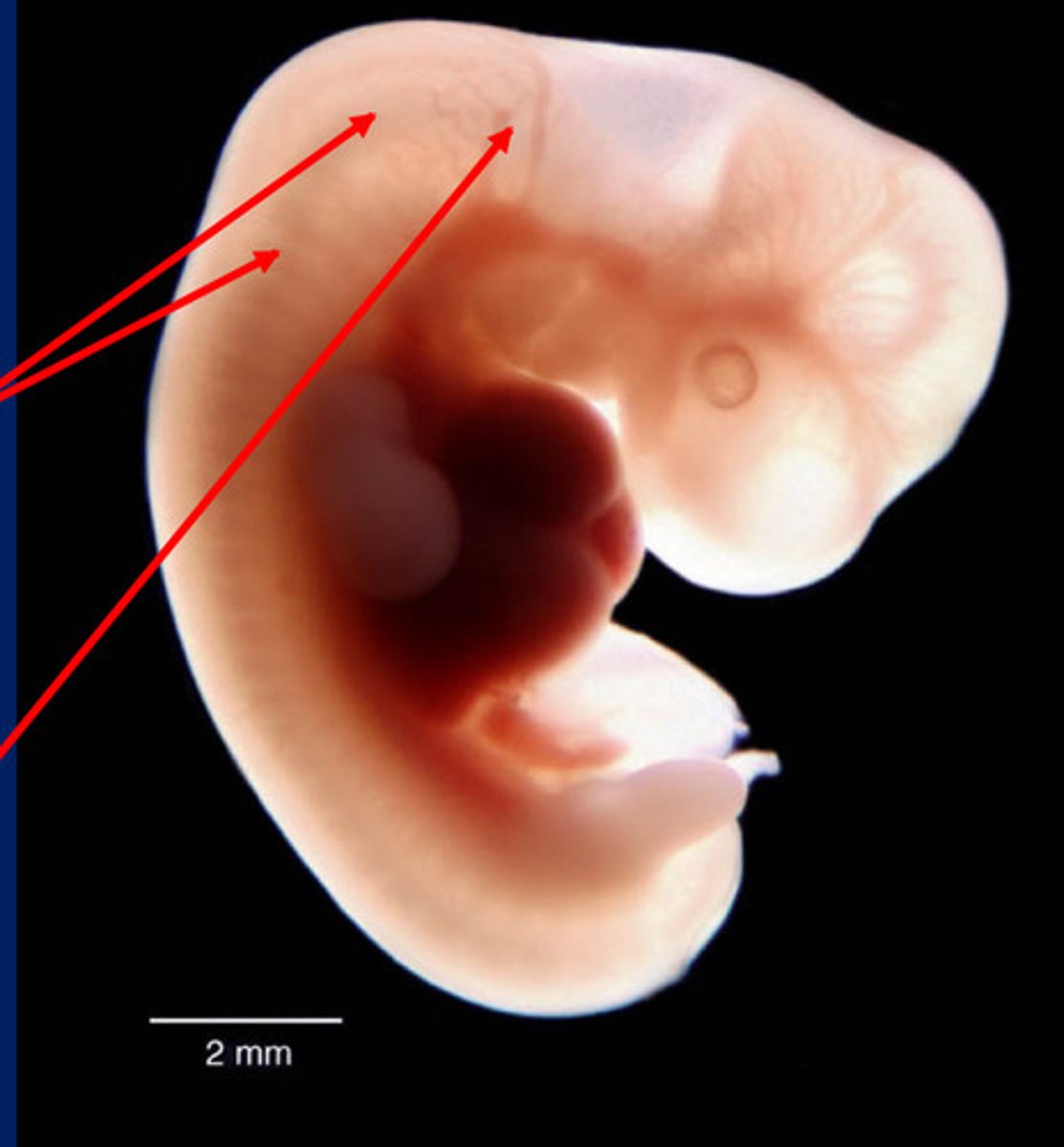
Mesenchyme
___ is of neural plate origin (ectomesenchyme) in neural crest
endochondral ossification
Replacement of a cartilage model via bone
deposition after calcified cartilage is removed
Intramembranous ossifcation
Ossification directly within a membrane (no
cartilaginous phase)
Neurocranium
The ___ has both a cartilaginous and a membranous portion.
Cartilaginous neurocranium
Consists of hyaline cartilage developed from mesenchyme at the base of the developing skull (chondrocranium)
Sphenoid, ethmoid, temporal, and occipital bones
The chondrocranium includes parts of the
membranous neurocranium
Comprises the flat bones that form around the brain (dermatocranium)
Cranial vault bones
Membranous neurocranium includes the ___ except temporal squama
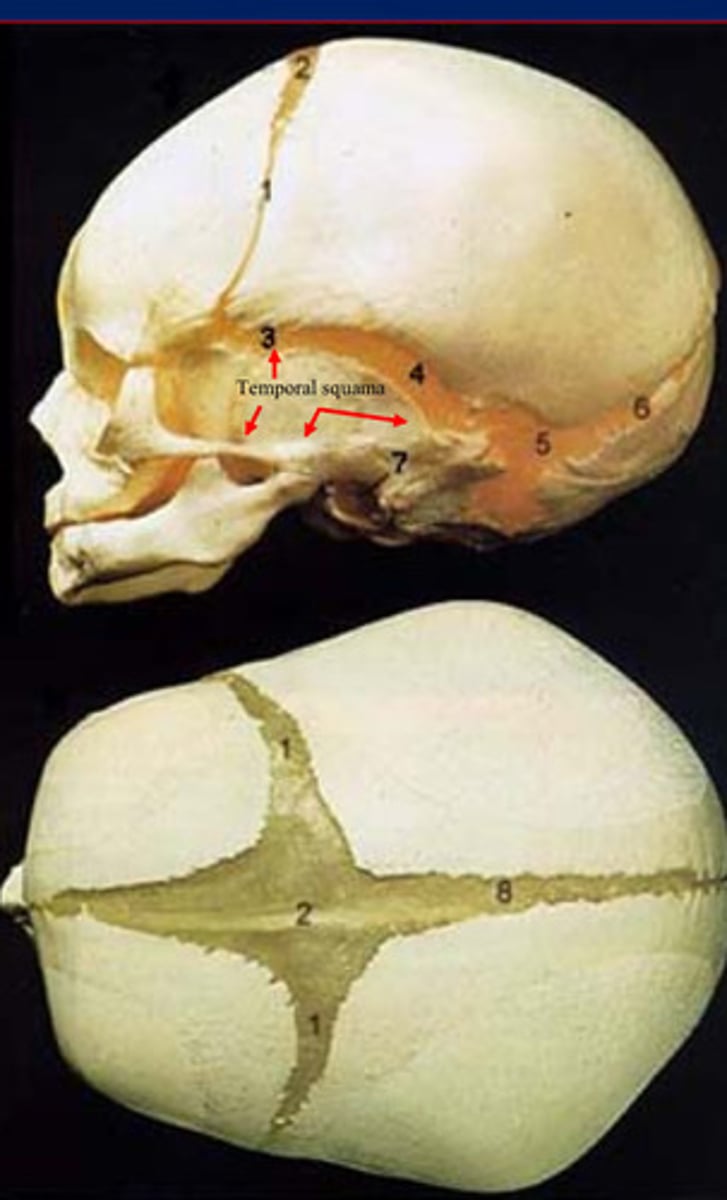
Cranial vault bones
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid
Temporal squama
Membranous neurocranium Includes the cranial vault bones, with the exception of the
Viscerocranium
The facial bones also known as the ___ also has both a cartilaginous and a membranous portion
Paraxial mesoderm
The neurocranium is part of the
Neural crest cells
The viscerocranium is part of the
cartilaginous viscerocranium
comes from cartilage of the pharyngeal arches. This forms the ear bones and hyoid bone.
Meckels cartilage
1st arch: mandible precursor; degenerates to form the sphenomandibular ligament and the malleus and incus.
Reicherts cartilage
2nd arch: : forms the stapes, styloid process, and part of the hyoid.
Hyoid
3rd arch forms the
Laryngeal cartilage
4-6 arches form the
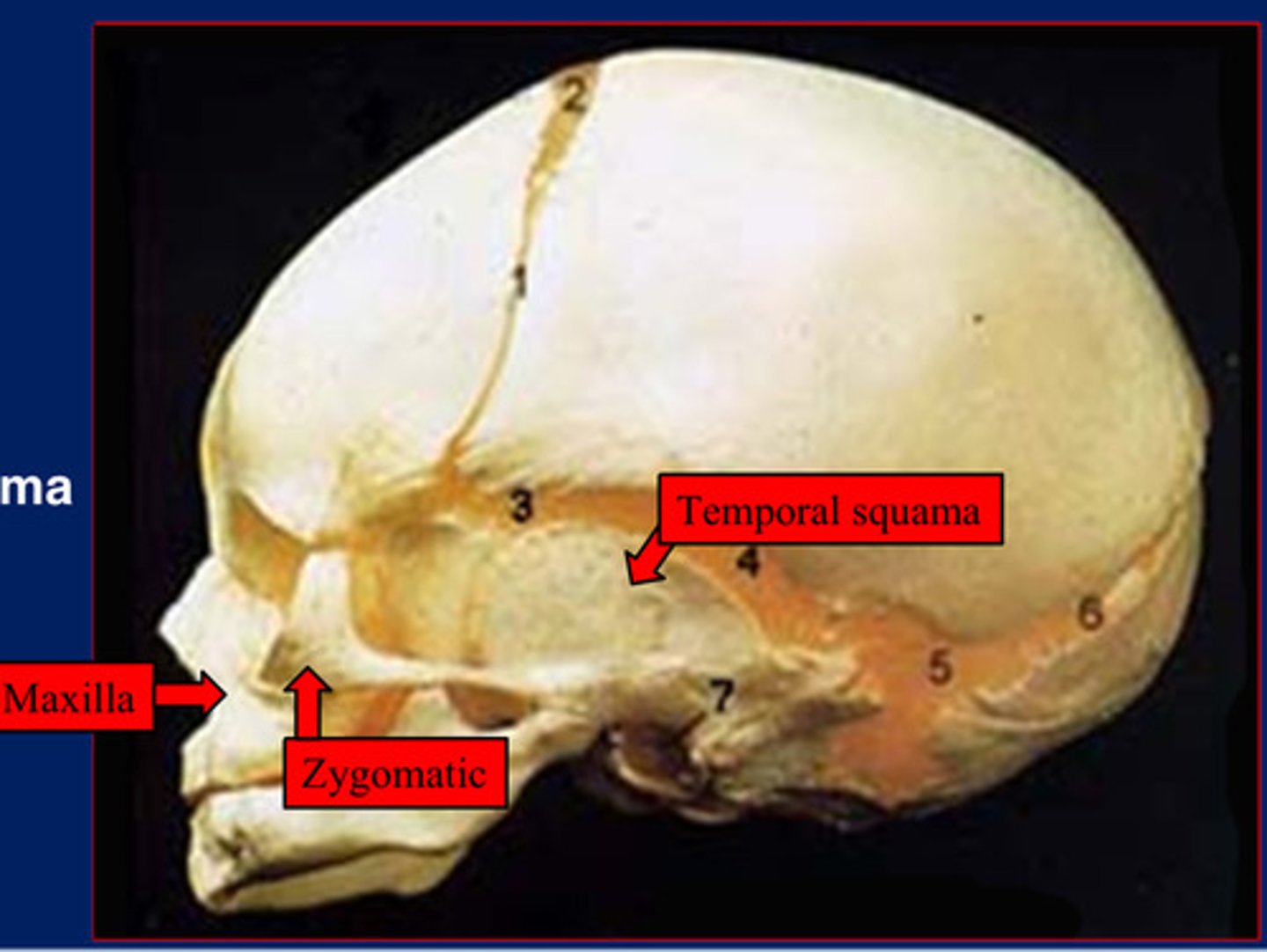
membranous viscerocranium
comes from mesenchyme of the first pharyngeal arch, undergoes intramembranous ossification and forms the facial bones.
Maxilla, zygomatic, temporal squama
The membranous viscerocranium is comprised of
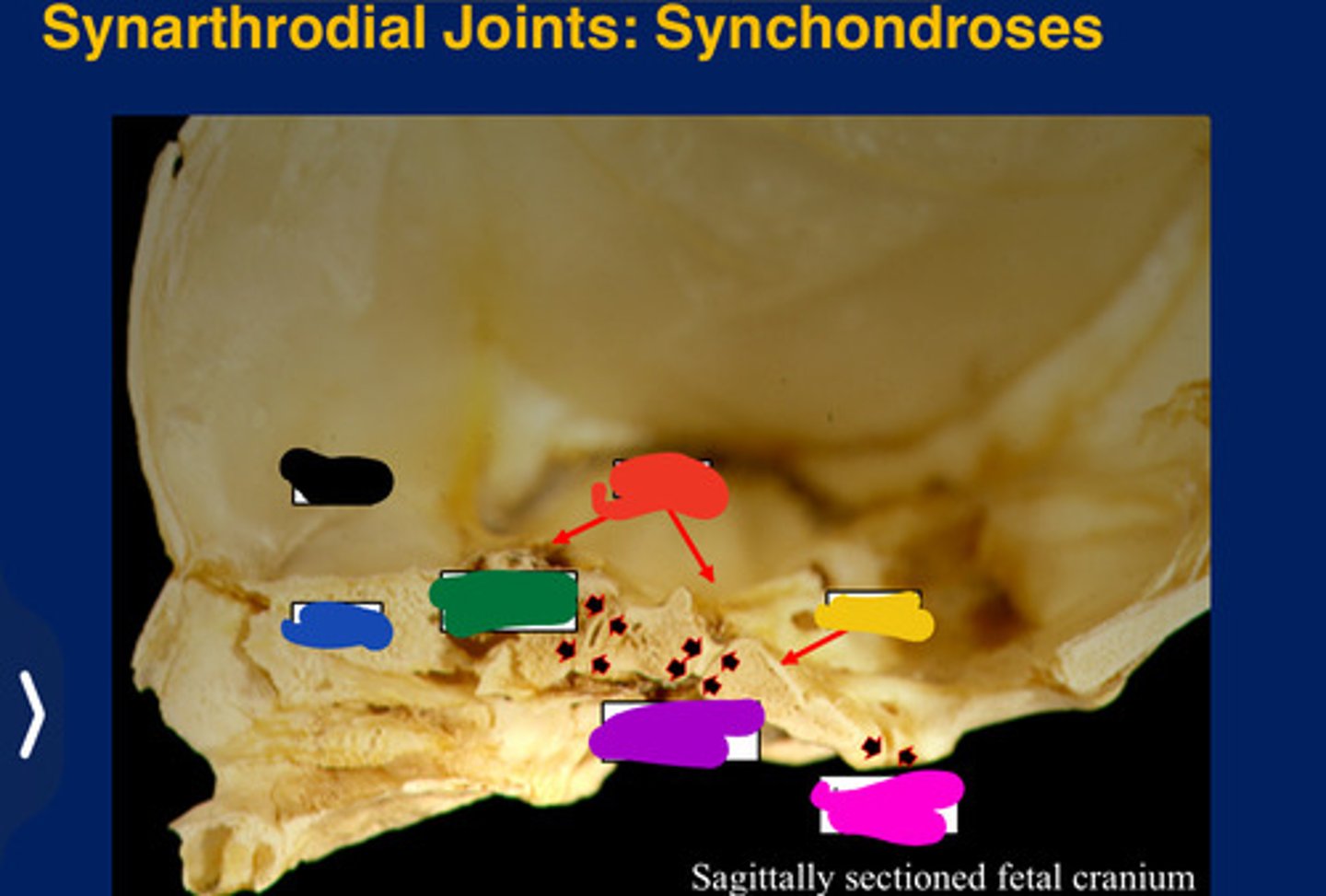
Synarthroses
Partially movable joints
Synchondrosis
Only occur between bones derived from
All form in the cranial base. (Synarthroses)
Sutures
Occur between cranial bone of either membranous or
cartilaginous origin.
(Synarthroses)
Diarthroses
freely movable joints
Frontal
Black
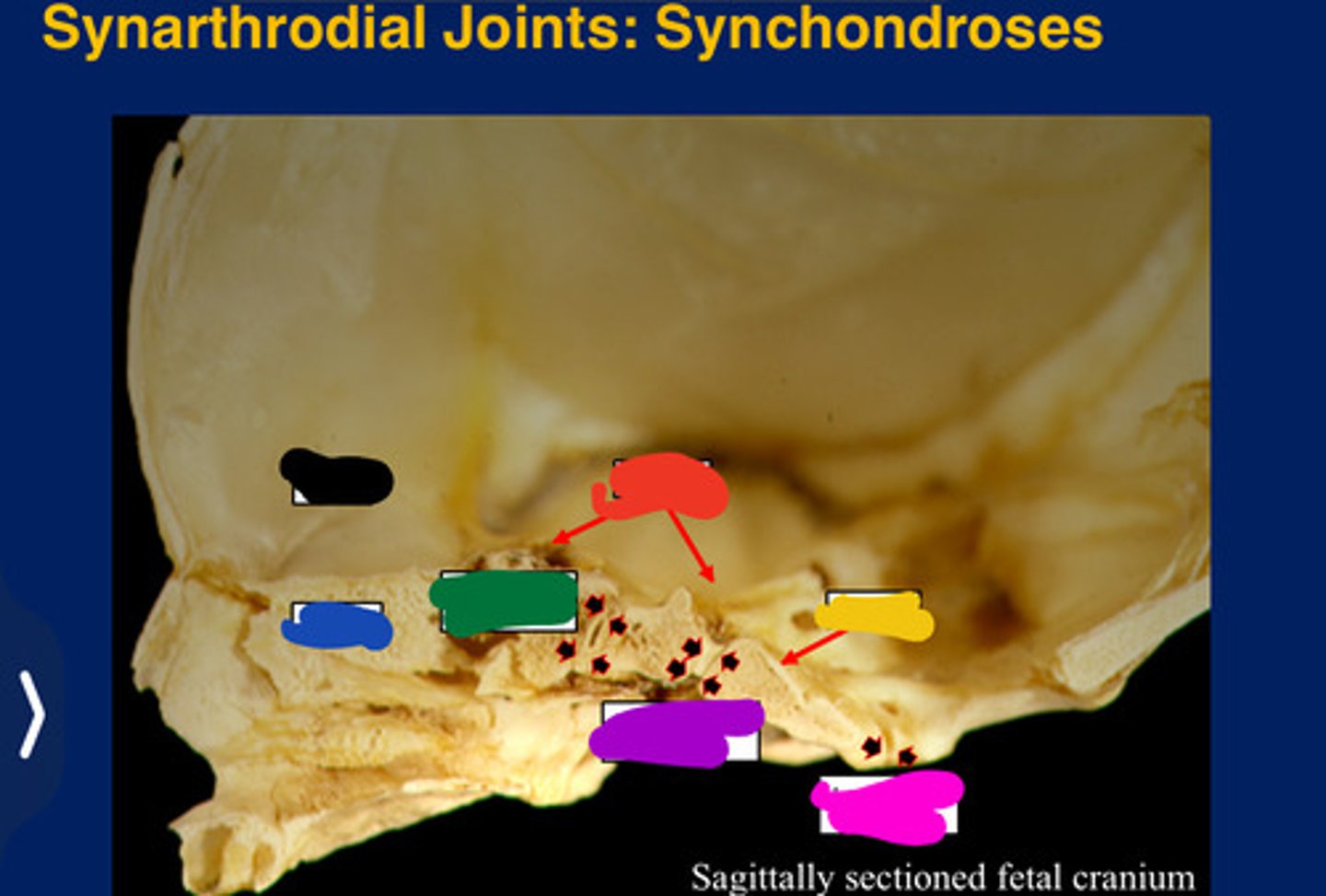
Ethmoid
Blue
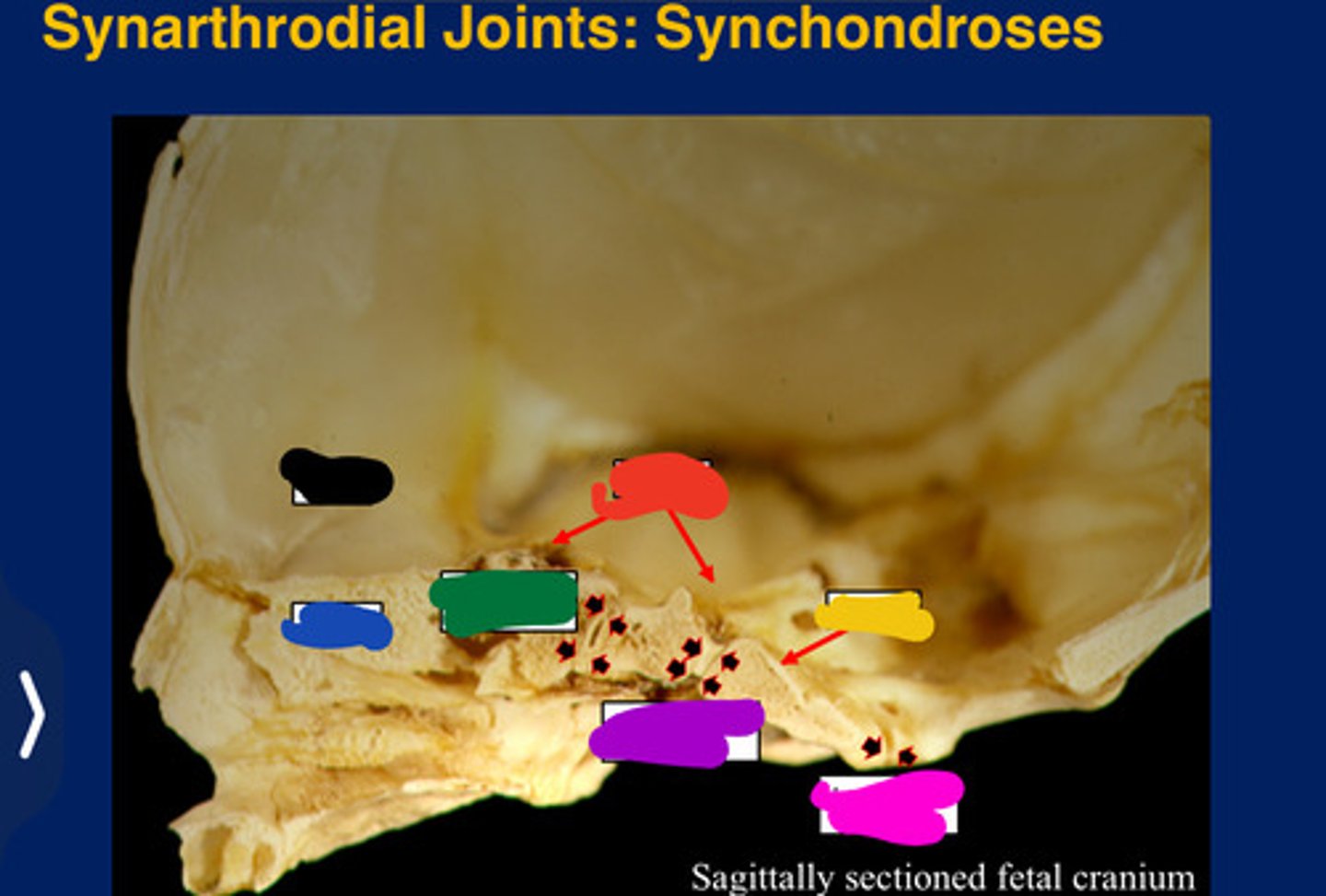
Sphenoid
Red
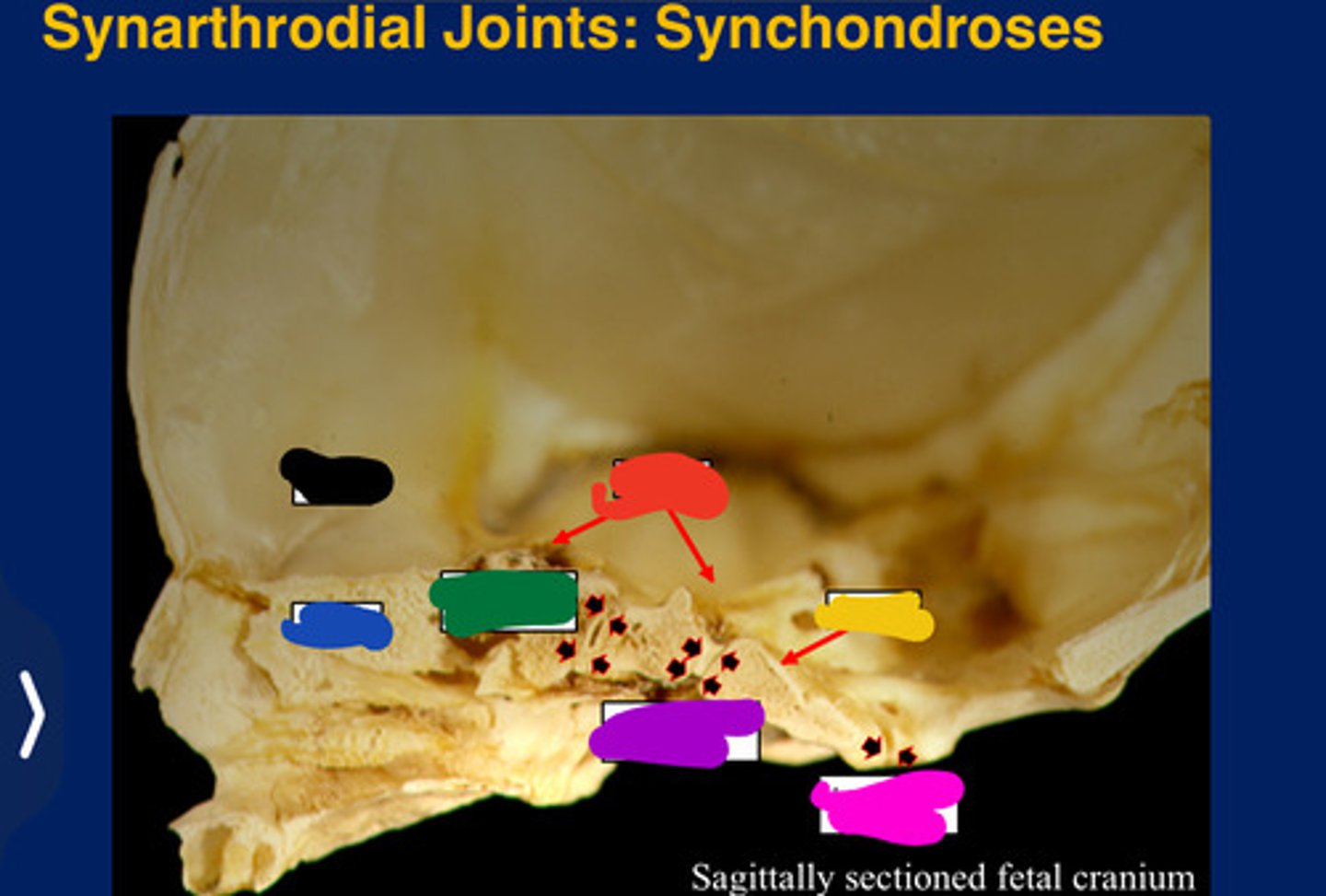
Occipital
Yellow
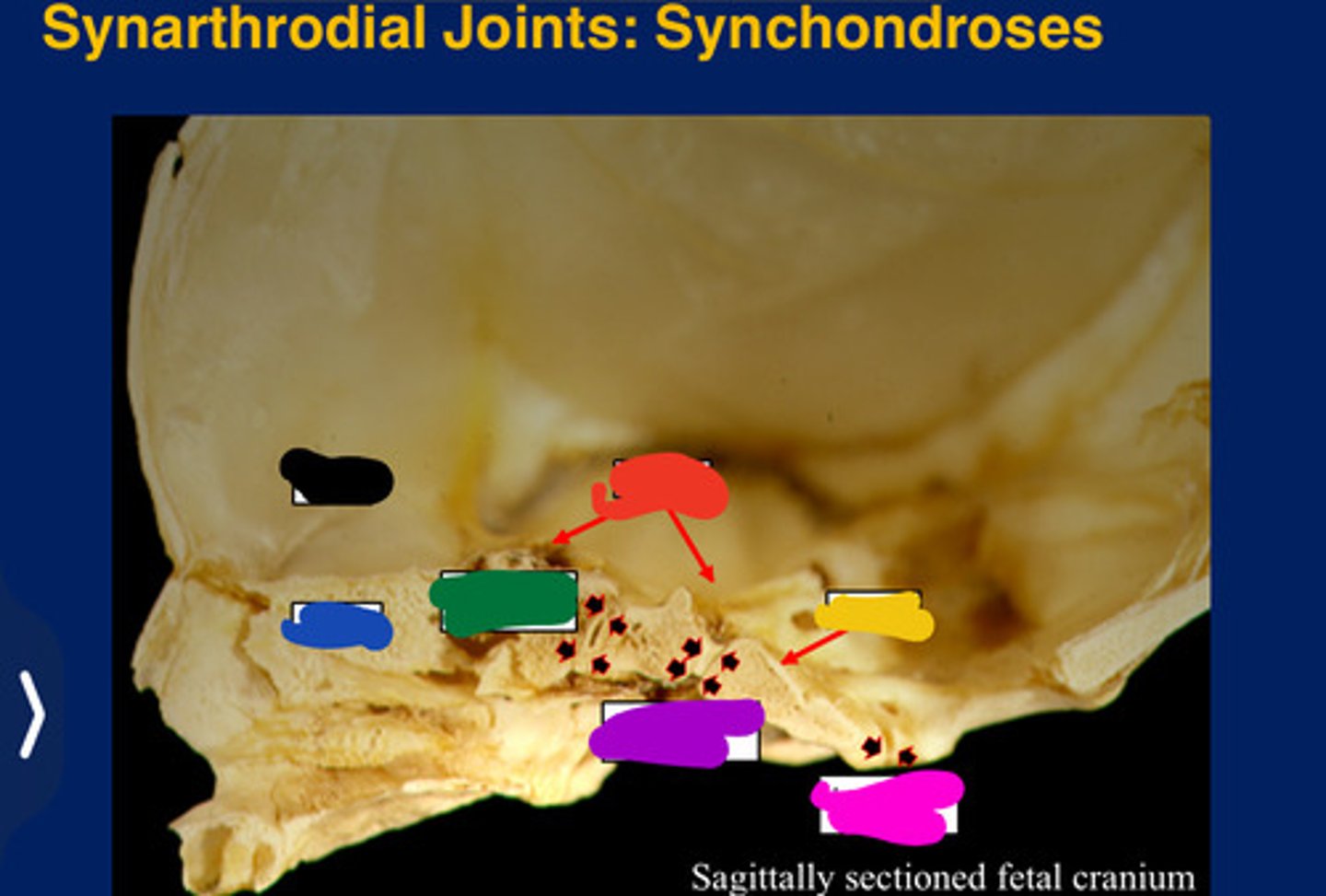
Presphenoidal synchondrosis
Green
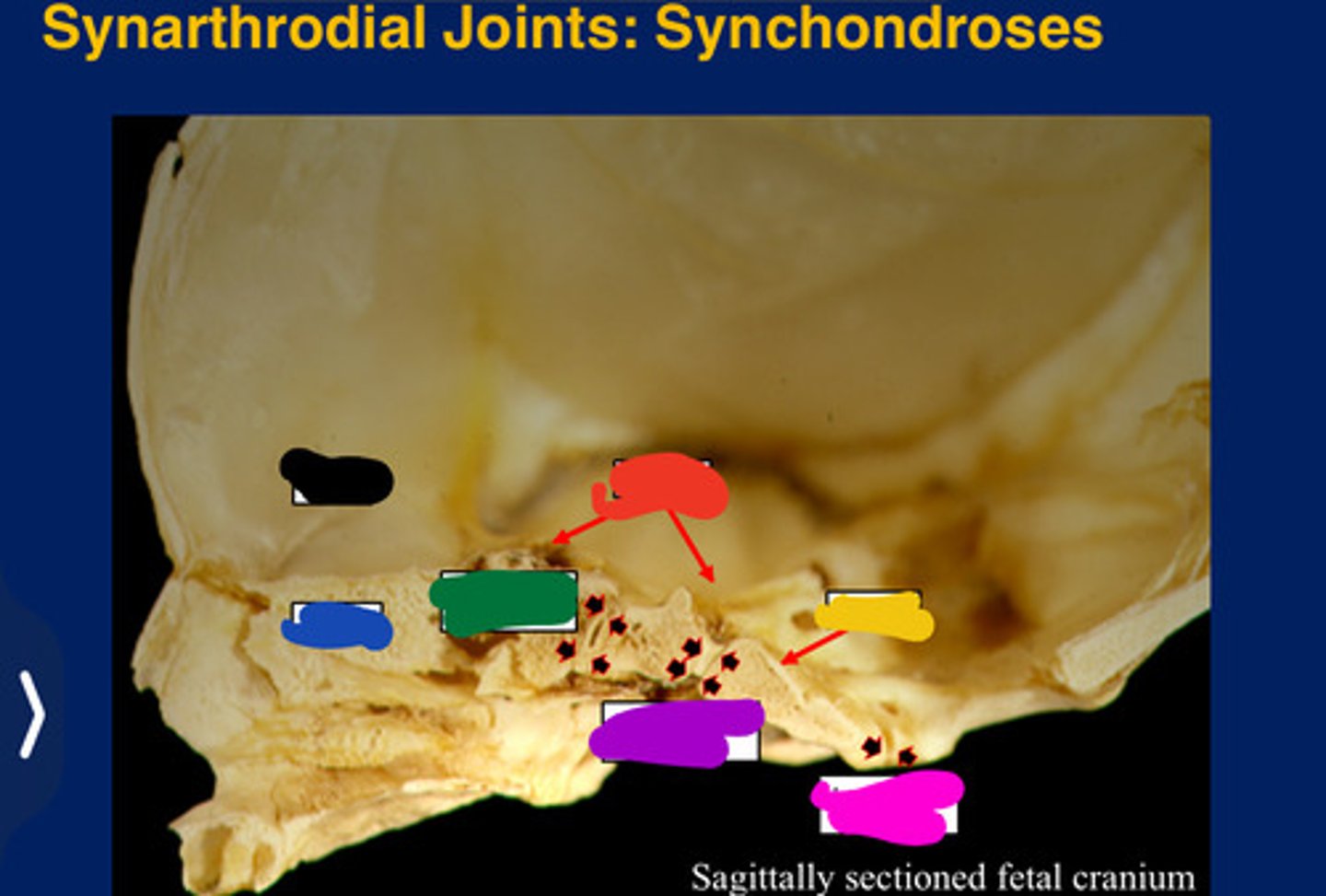
Sphenooccipital synchondrosis
Purple
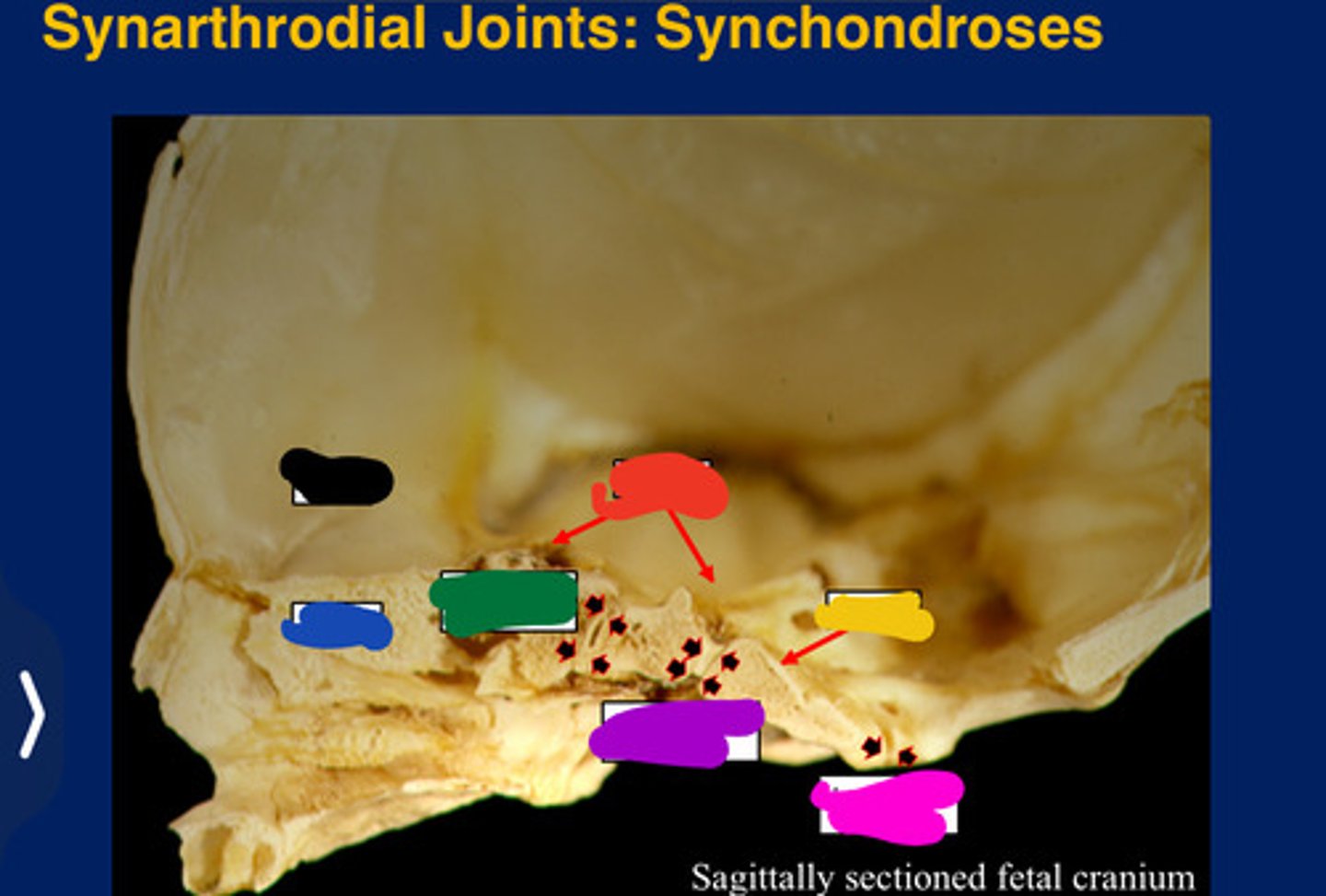
Interoccipita synchondrosis
Pink
temporomandibular joint
The joint formed where the mandible and cranium meet, just in front of the ear. (Diarthrodial)
Compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
trabeculated bone
Spongy bone that contains hemopoietic tissue
Frontal sinus
Black
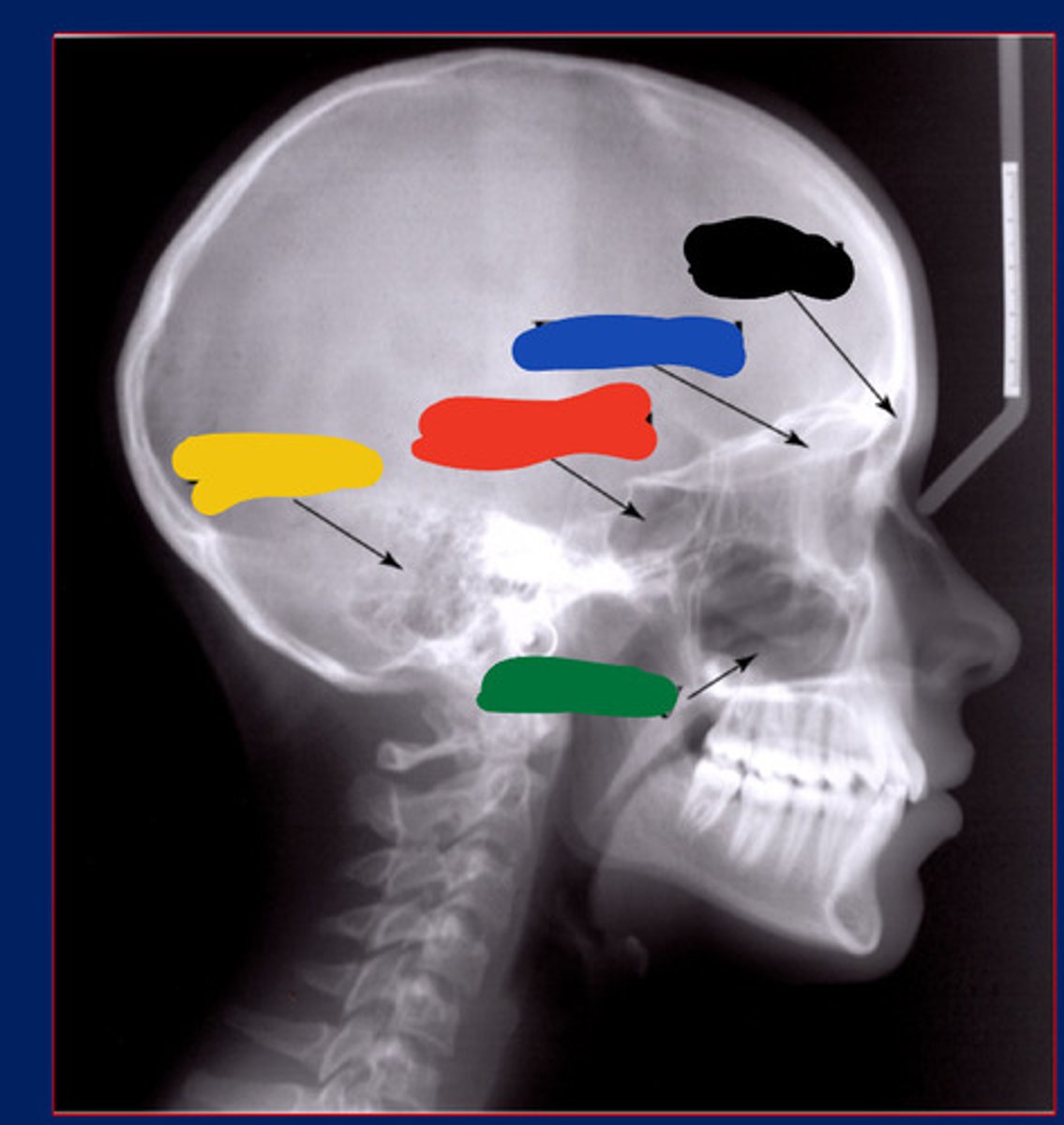
Maxillary sinus
Green
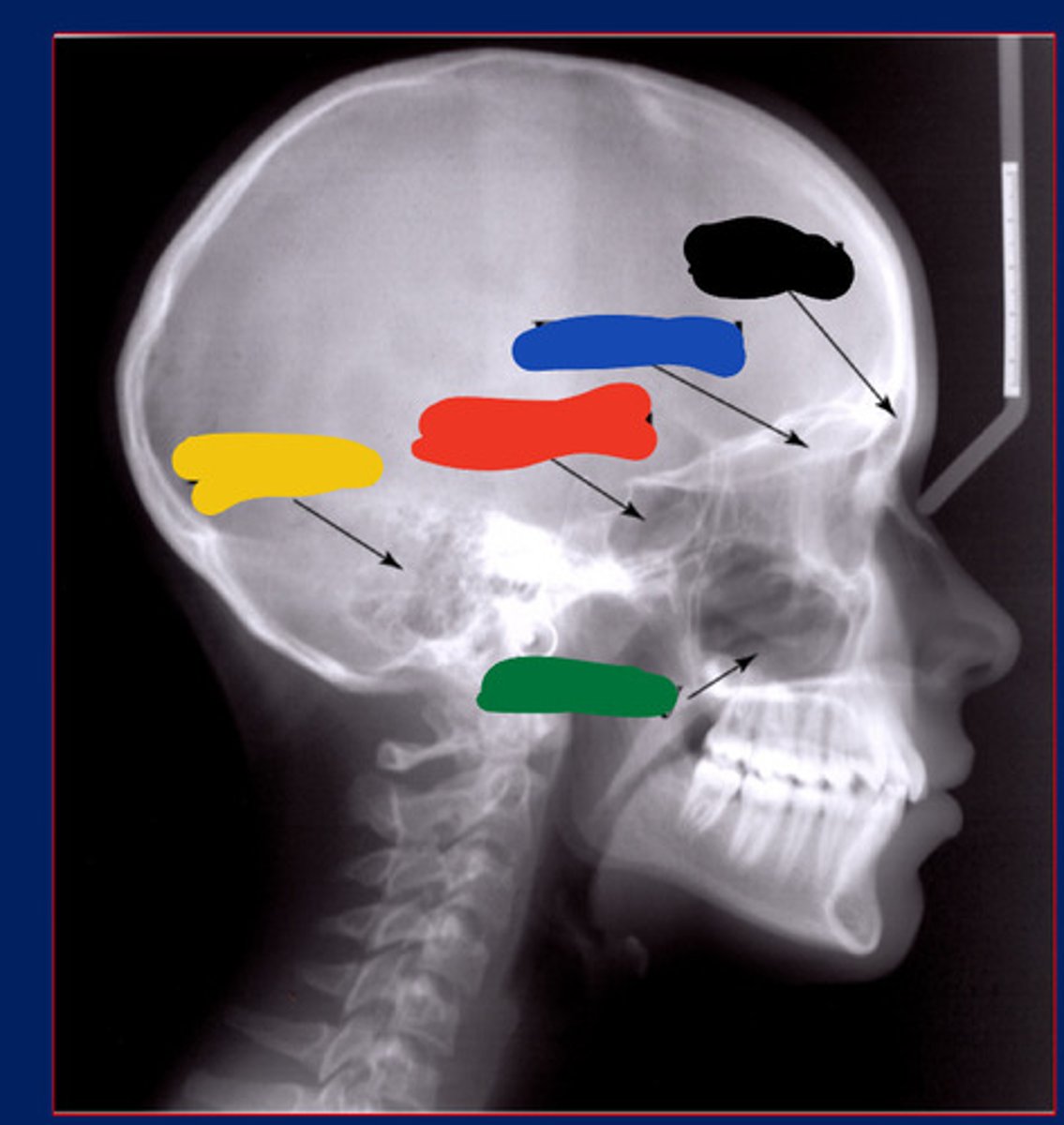
Ethmoidal sinus
Blue
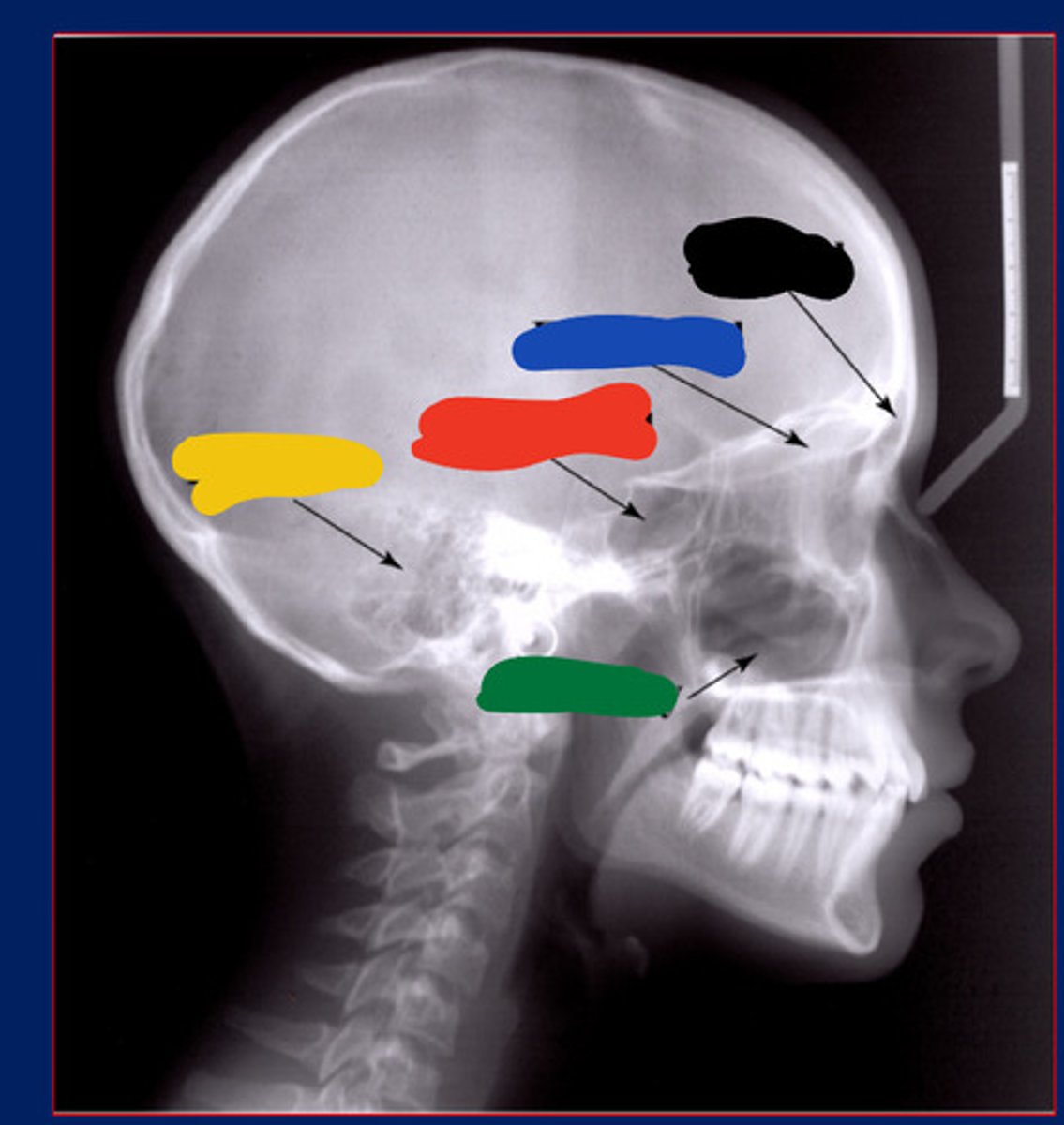
Ethmoidal sinus
Blue
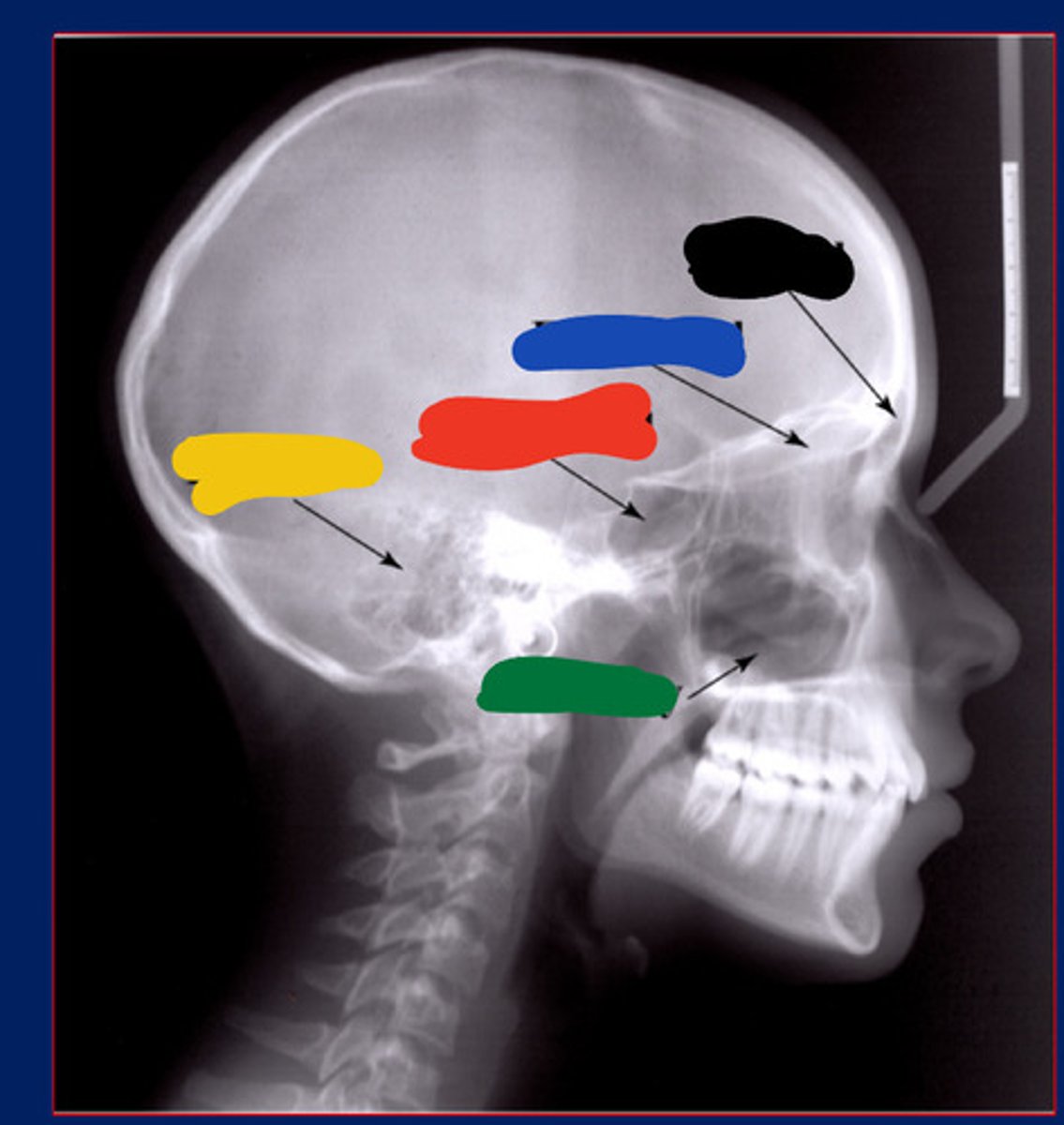
Temporal air cell
Yellow
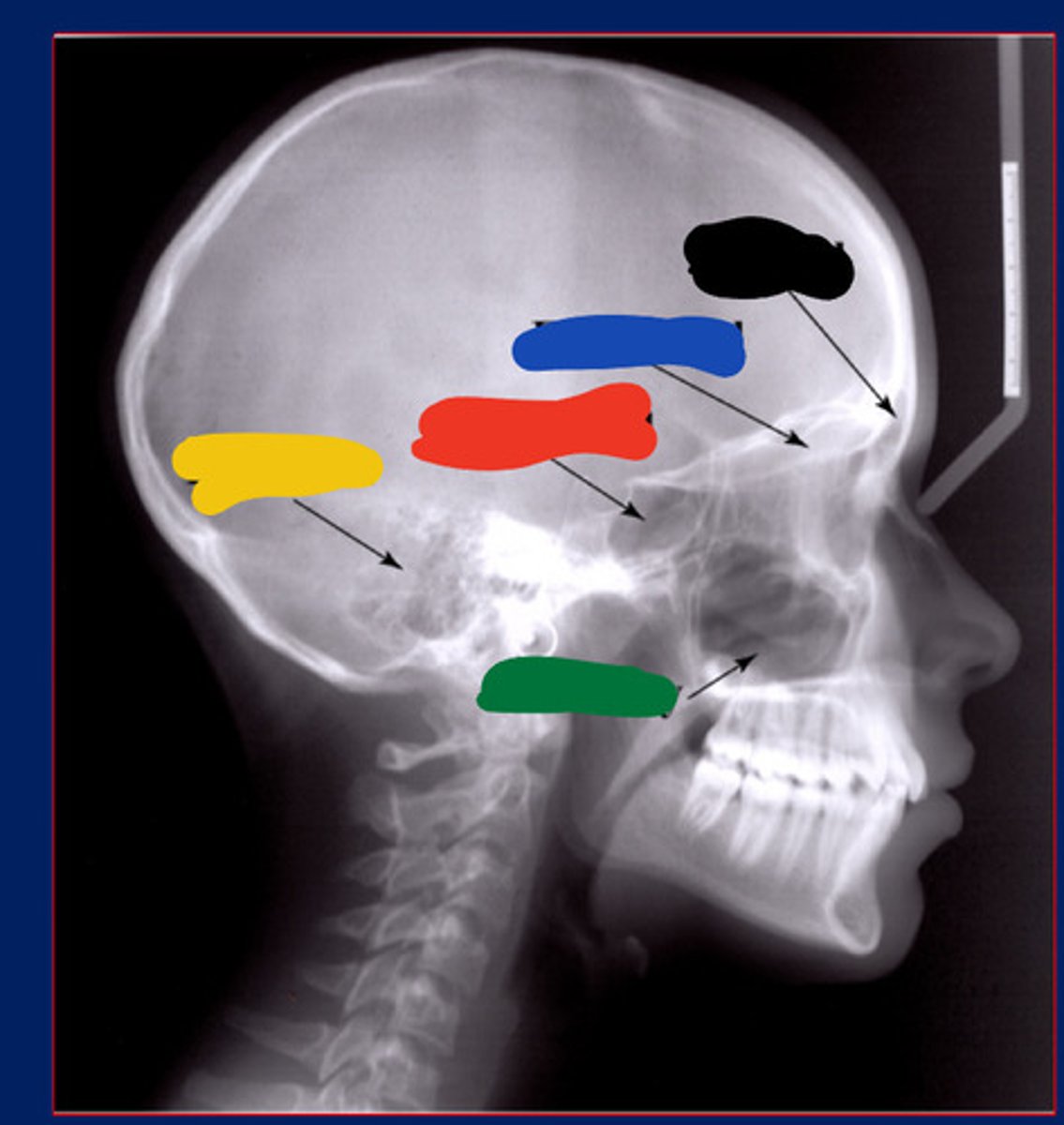
Sphenoidal sinus
Red
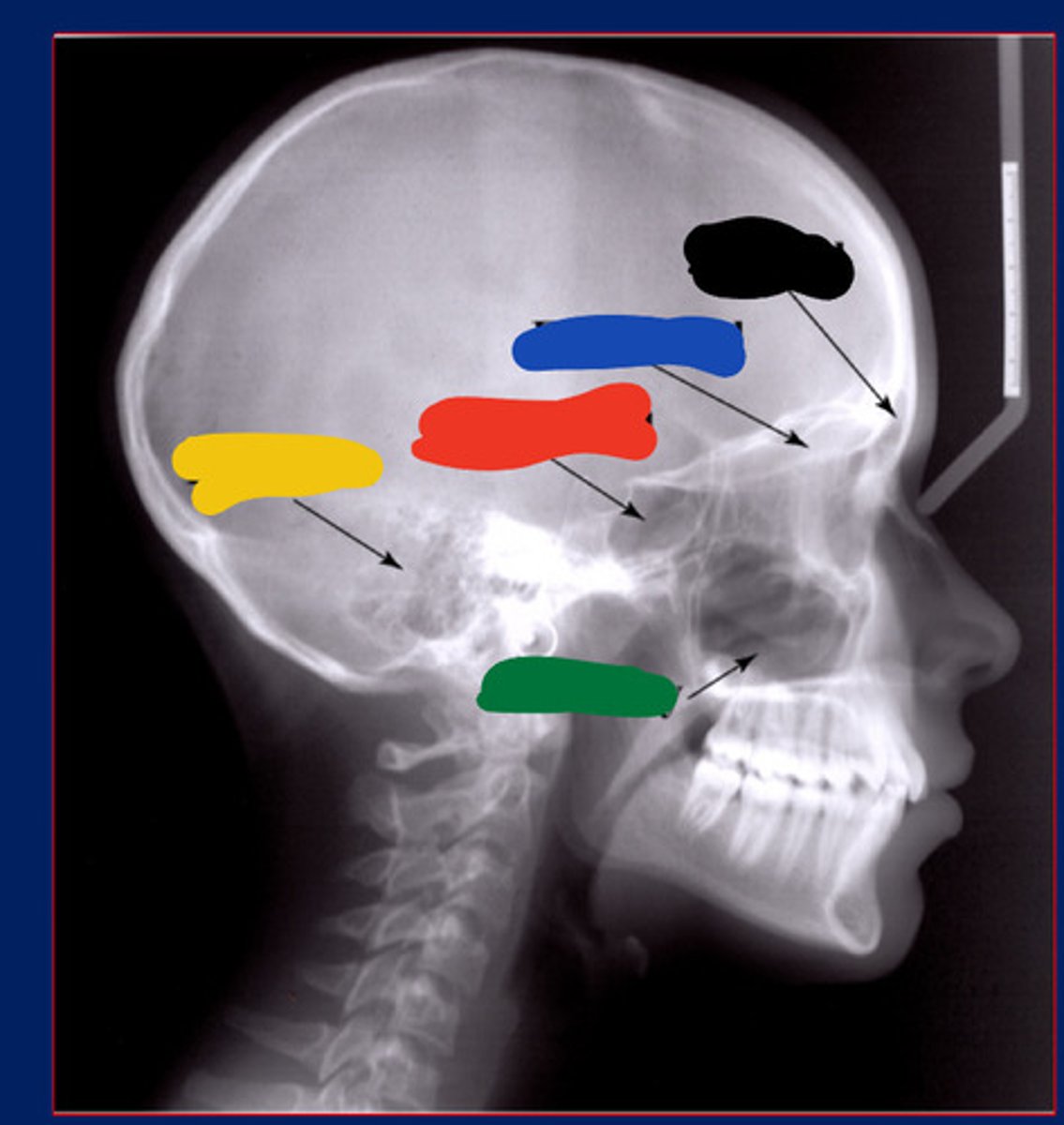
Sphenoidal sinus
Bottom
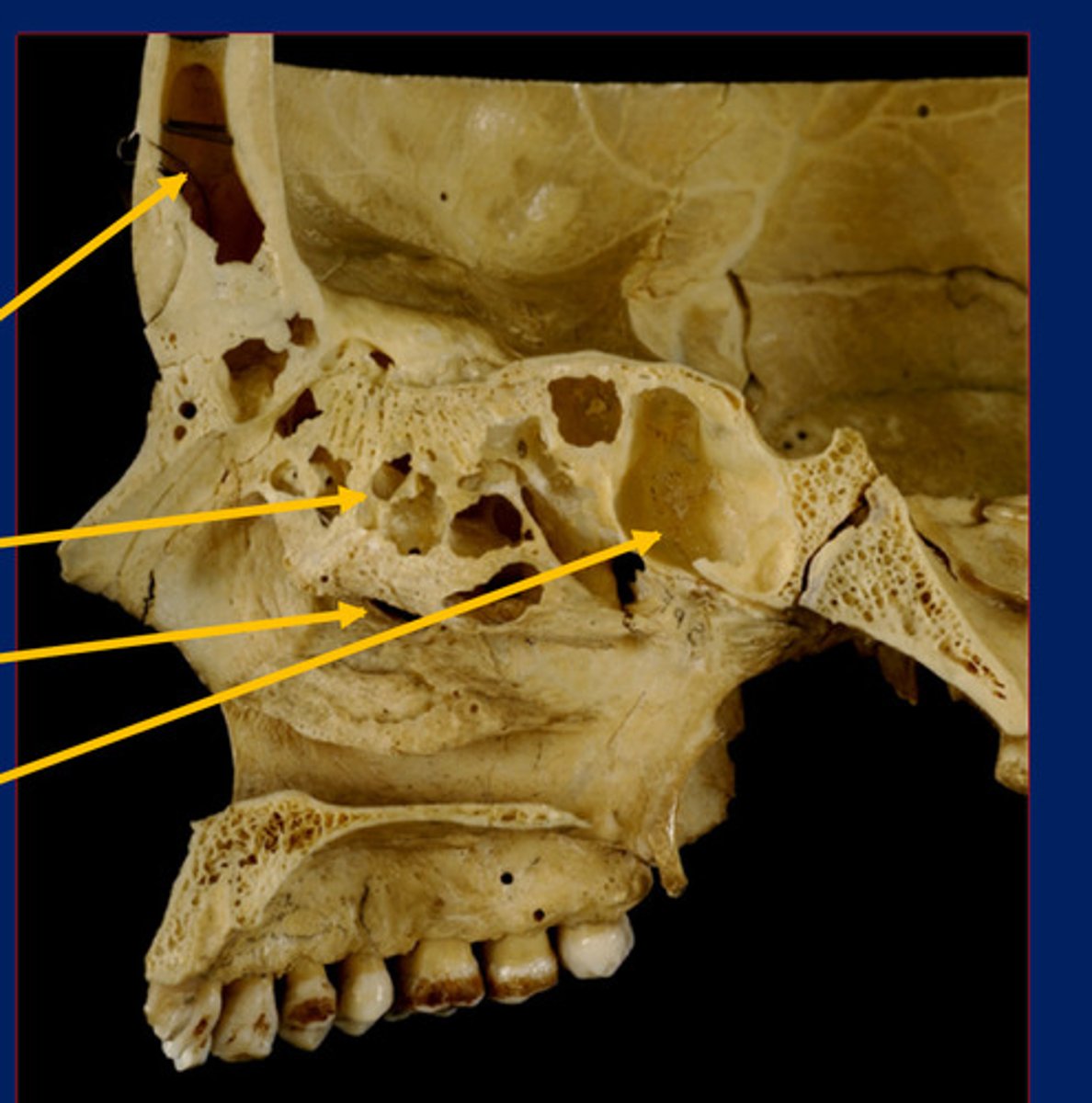
Frontal sinus
Top
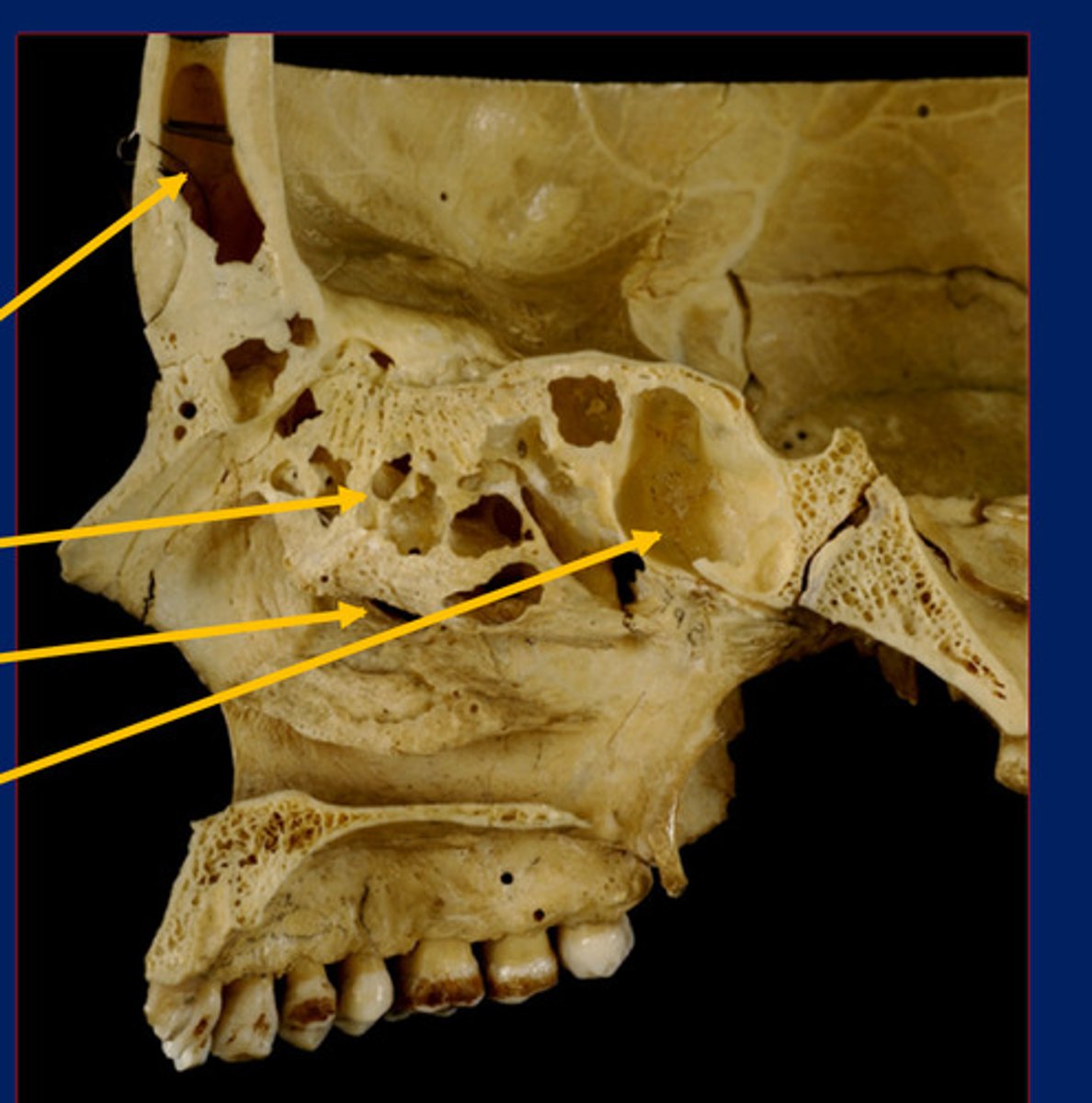
Maxillary sinus
2nd bottom
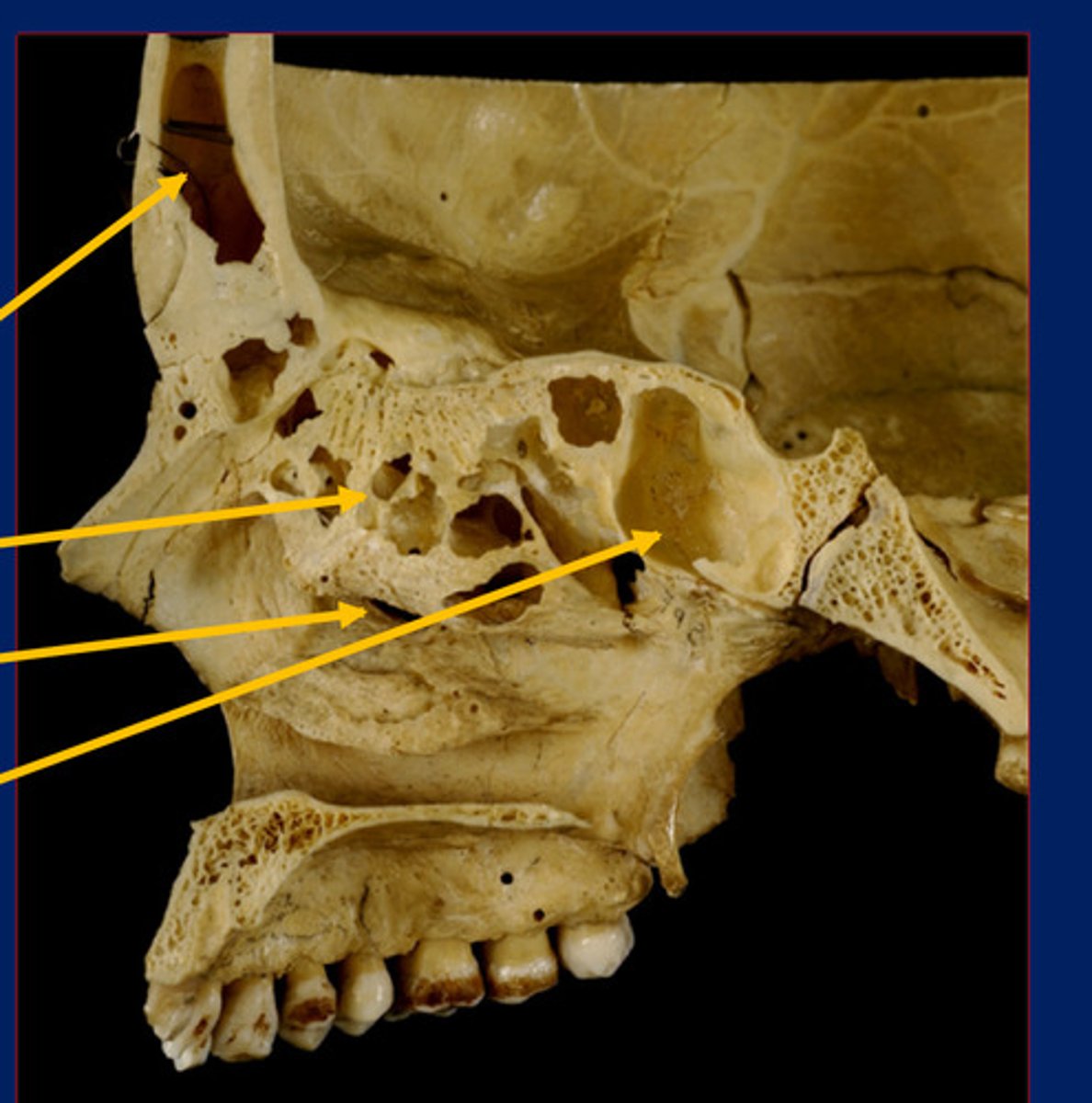
Ethmoidal sinus
2nd top
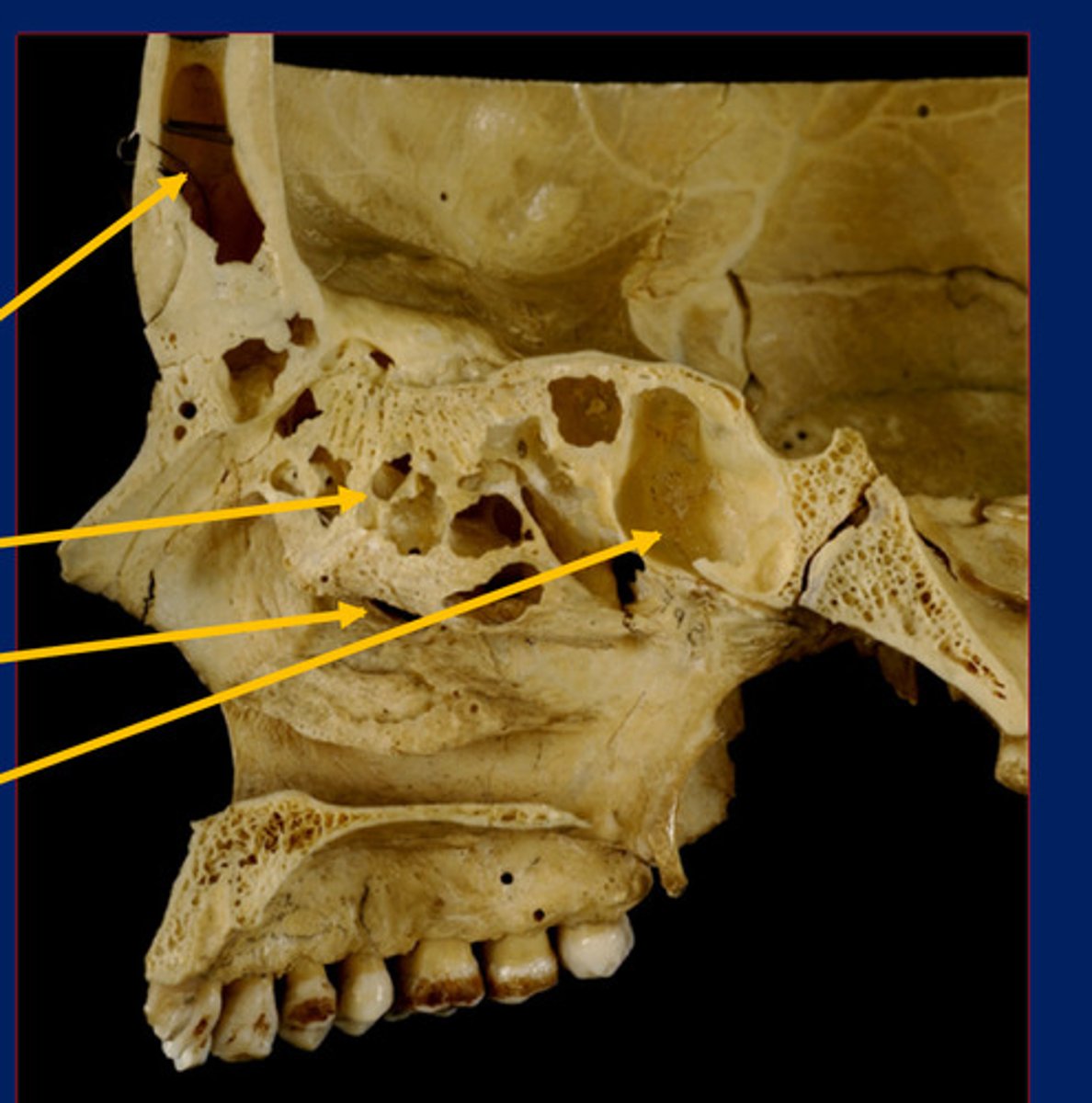
Arteriovenuous impressions
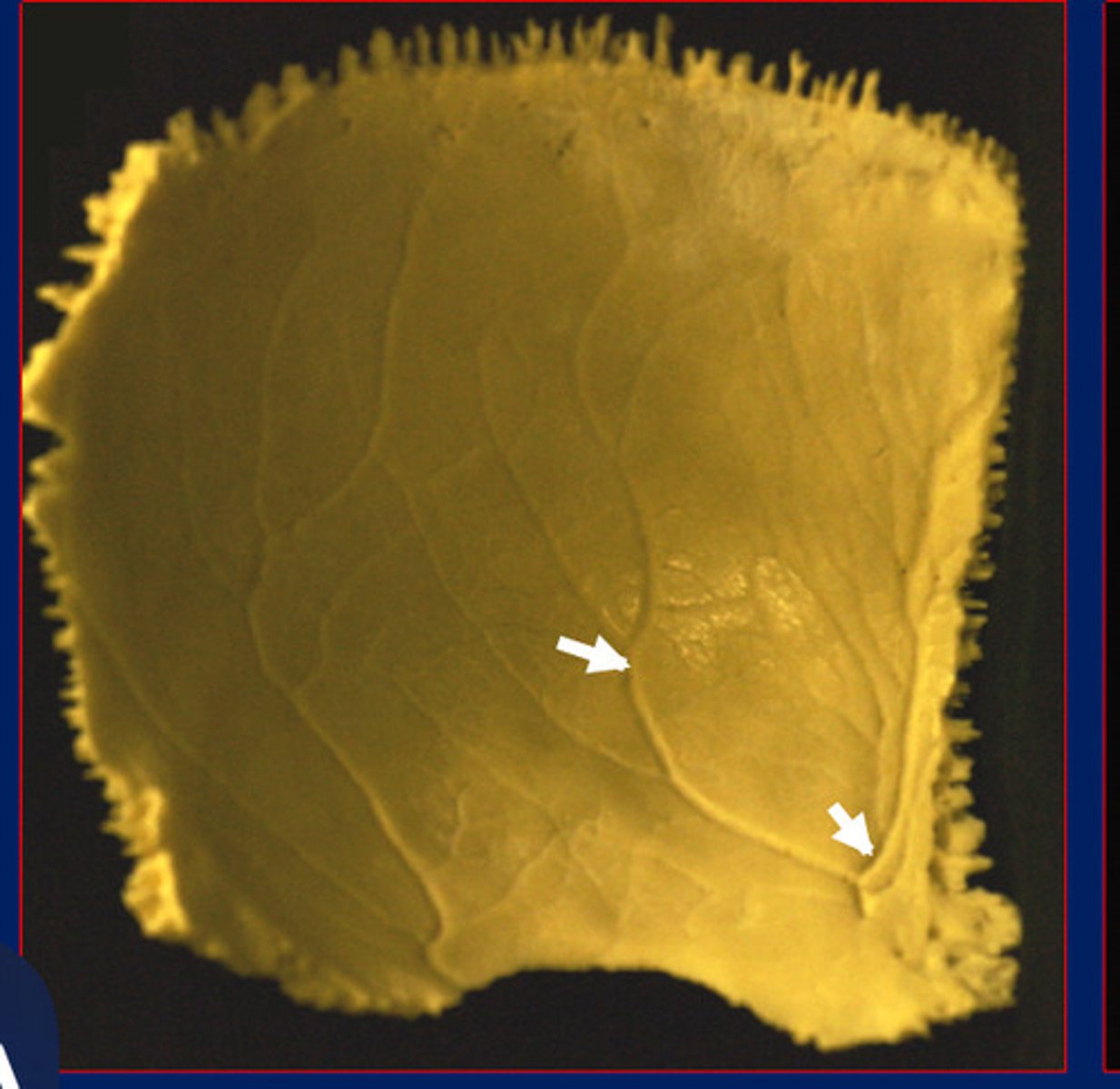
Venous sinus impressions
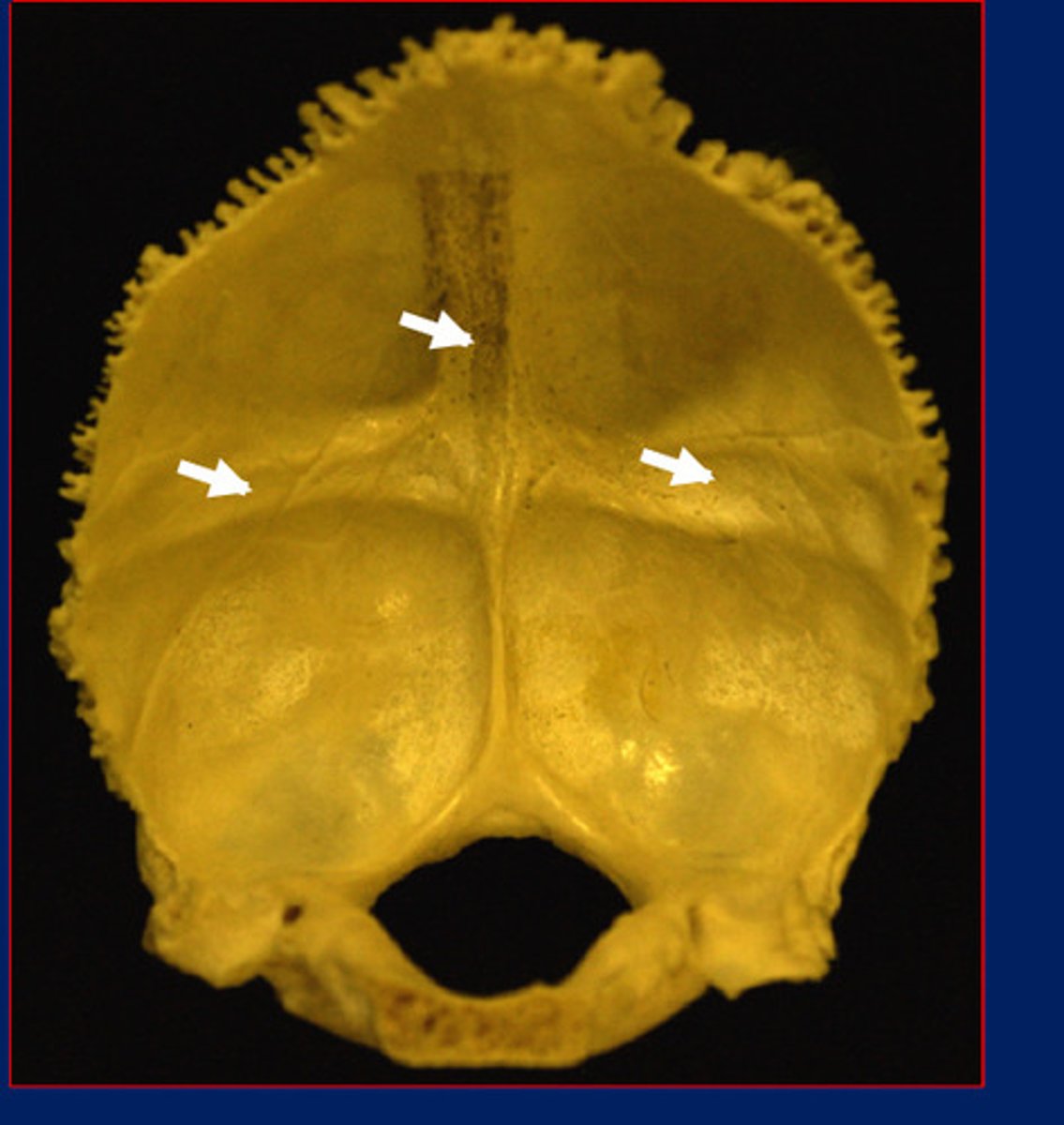
Musculotendinous/lingamentous attachments