PATHFIT MIDTERM REVIEWER
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Physical Education
is an integral part of the education program purposely to promote optimum development of an individual
Physical Development
attainment of physical skills, maintain good health, high level of physical fitness, improved growth and development.
Social Development
provide opportunities for the development of enviable social traits.
Mental Development
develops mental capacities, obtains knowledge and understanding, enhances critical thinking how activities are done.
Emotional Development
offers opportunities for selfexpression and emotional mastery.
Article 1 and Article XIV
Legal Bases of Physical Education
skeletal system
provides support and protection for the body's internal organs while also serving as an attachment point for muscles.
Bones
provides structure and protection to bodies
300 bones
how many bones are in babies?
206
how many bones are in adult?
Ossification
process of bone formation
tendon
fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
ligaments
fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone
Cartilage
strong, flexible tissue that protects your joints and bones
long bones, short bones, flat bones and irregular bones
principal types of bones
axiel skeleton
central skeleton that protects and supports vital organs
skull
surrounds and shields the brain, brainstem, and eyes from external forces. It contains 22 bones, composing of cranial and facial bones.
hyoid
protects the esophagus
trunk
central part of body, consists of vertebral column, sternum and ribs
appendicular skeleton
facilitates movement and provides attachment joint
upper and lower extremities
two parts of appendicular skeleton
clavicle
collar bone
humerus, radius, ulna
parts of arm bones
arm bones
serves essential movements and roles in supporting the upper limb
scapula
shoulder blade
carpals
wrist bones
metacarpals
palm bones
phalanges
fingers bones
sternum
shield heart and stomach
chest bones
protect vital organ
spine
provides structural support for the entire body
pelvis
consists of three bones: ilium, ischium, and pubic bone
femur
strongest and longest bone in the body
patella
kneecap
tibia
which is longer and thicker, bears weight and articulates the femur
fibula
serves as an attachment point for leg muscles
foot
includes the tarsal, metatarsals and phalanges
650
The human body is composed of how many individual muscles
Muscular System
Give shape to the different parts of the body, Provide movement for the body
excitable, contractile, extensibility, elasticity
Characteristics of Muscles
Movement, Heat Production, Posture and Stability, Respiration, Digestion, Circulation
Functions of the Muscular System
excitement → action → movement → relaxation
How muscles work?
Involuntary muscles, Voluntary muscles
Types of Muscles
SMOOTH, CARDIAC, SKELETAL MUSCLES
Types of Muscle Tissue
SMOOTH MUSCLES
an involuntary muscle found in the internal organs and blood vessels.
CARDIAC MUSCLES
an involuntary muscle found only in the heart. They help your heart pump blood throughout your body.
SKELETAL MUSCLES
a voluntary muscle attached to the skeleton, comprise 30 to 40% of your total body mass.
Type I
red muscle which produces a small amount of force
Type IIa
pink muscle which produces a medium amount of force
Type IIx
white muscle which produces a large amount of force
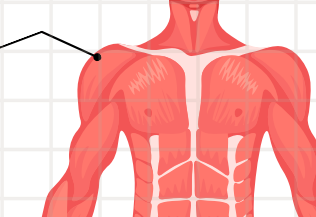
deltoid
is responsible for the abduction of the shoulder
FRONTALIS
a muscle which covers parts of the forehead of the skull and is also responsible for facial expressions.
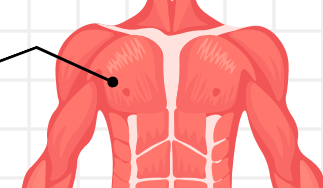
PECTORALIS MAJOR
responsible for the adduction of the shoulder (moving the arm towards the body) and the shoulder horizontal flexion (moving the arm forwards in front of the body).
BICEP
are responsible for flexing the elbow (bending the arm)
external obliques
are responsible for trunk rotation (twisting the body).
RECTUS ABDOMINIS
also known as the "abdominal muscle" a muscle in the front of the abdomen that helps with breathing, coughing, and crunches.
hip flexors
are responsible for hip flexion (moving the knee up to the chest).
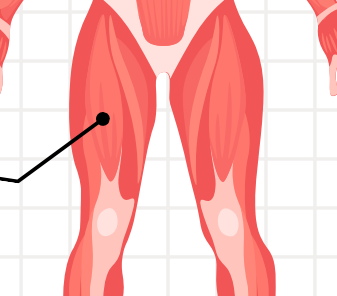
quadriceps
are responsible for extending the knee (straightening it).
tibialis anterior
is responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle (bringing the toes up in the direction of the shin).
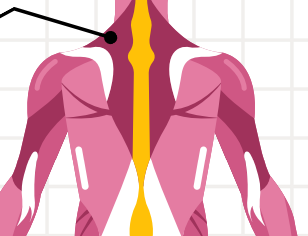
TRAPEZIUS
large, paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle, It moves the scapula and supports the arm.
Triceps
are responsible for extending the elbow (straightening it)
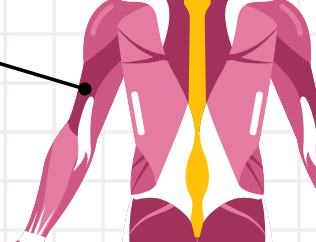
Latissimus dorsi
are responsible for shoulder adduction (moving the arm towards the body) .
gluteus maximus
is responsible for hip extension (moving the leg backwards)
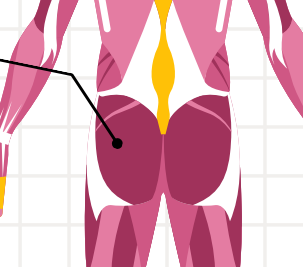
hamstrings
are responsible for flexing the knee (bending the leg).
gastrocnemius
is responsible for plantar flexion of the ankle (pointing the toes downwards).
circulatory system
transport blood, oxygen and nutrients to the body
heart, blood vessels and blood
three main part of circulatory system
5 liters
average person has how many liters of blood
red blood cells
carry oxygen and nutrients, represents 40-45% of your blood volume
white blood cells
fights diseases and protect body from infection, 1% of your blood
platelets
help the clotting process, controls bleeding
plasma
yellowish colored, lightest blood
blood vessels
tubes or channels that carry blood throughout our body
artery
thickest wall of all three blood vessels, supplies blood to all organs
capillary
thinnest wall that allow substances such as oxygen and sugars into or out of the blood
vein
less muscular and stretchy, carries oxygen poor blood and return it to the heart
sickle cell disease
is an inherited blood disorder. People with SCD have red blood cells that become hard and sticky, forming a C-shaped blood cell instead of the healthy disc- shaped one.
respiratory system
move air into the body and remove waste products. Body cells require oxygen for respiration.
Nose
Air makes its initial entrance to the body through the opening in the _______ called the nostrils.
Pharynx
carries air into the respiratory tract and foods and liquids into the digestive system.
Larynx
(voice box) is located between pharynx and trachea. It has a framework of cartilage that protrudes in the front of the neck and some tissues is referred to as the Adam’s apple.
Trachea
It’s often called the "windpipe," is like a special tube in your throat. Its job is to conduct air between the larynx and the lungs allowing you to breathe and talk.
Bronchi
They are like the branches of a tree inside your lungs. They let the air go inside your lungs.
Bronchioles
bronchus divides into smaller tubes called __________, which the air passes through.
Alveoli
are air sacs which facilitate gas exchange.
Lungs
They extract the oxygen your body needs when you breath in. When you breathe out, they take out the carbon dioxide.
Diaphragm
It is a dome-shaped muscle that helps you breathe. It helps your lungs expand and fill with air and contract when it exhales the air out.
Flexion
Decreasing the angle between two body parts (e.g., bending the elbow).
Extension
Increasing the angle between two body parts (e.g., straightening the elbow).
Adduction
Moving a body part toward the midline (e.g., lowering the arms back to the sides)
Medial Rotation
Rotating a body part toward the midline (e.g., turning the thigh inward).
Lateral Rotation
Rotating a body part away from the midline (e.g., turning the thigh outward).
Circumduction
A circular movement that combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction (e.g., moving the arm in a circular motion).
Pronation
Rotating the forearm so the palm faces down or backward
Supination
Rotating the forearm so the palm faces up or forward
Elevation
Moving a body part superiorly (e.g., shrugging the shoulders)
Depression
Moving a body part inferiorly (e.g., lowering the shoulders).
Dorsiflexion
Raising the foot upwards (toes toward the shin).
Plantarflexion
Pointing the toes downwards (away from the shin)
Opposition
Movement of the thumb across the palm to touch the fingertips.